40 gibbs free energy diagram
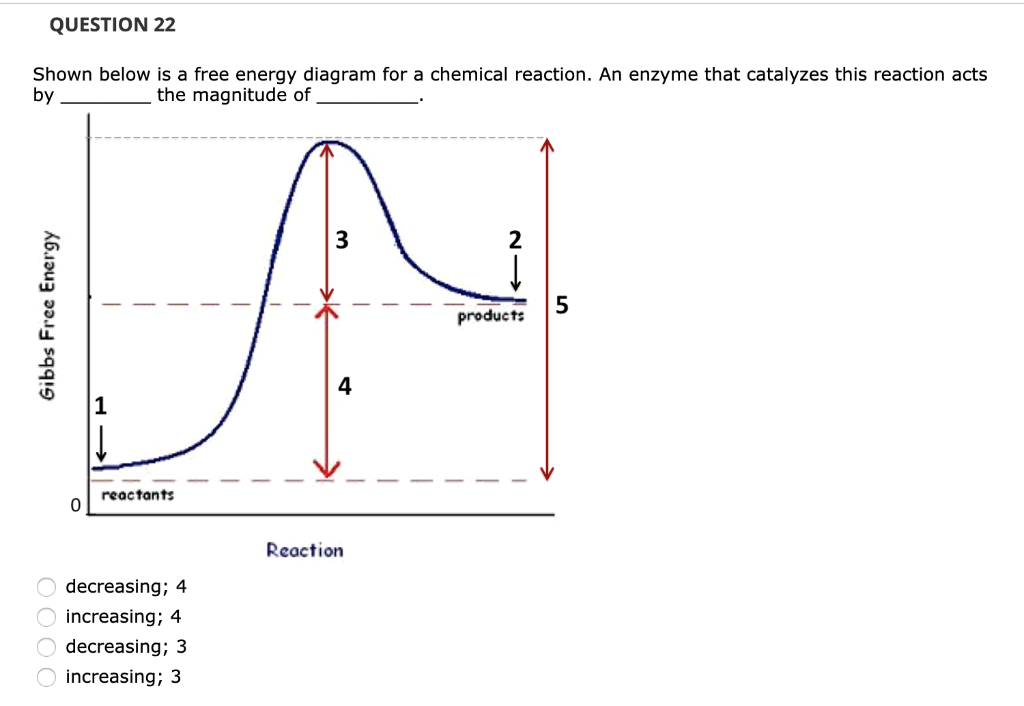
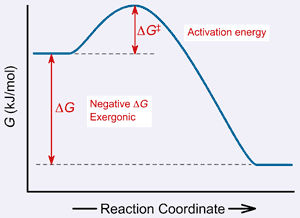
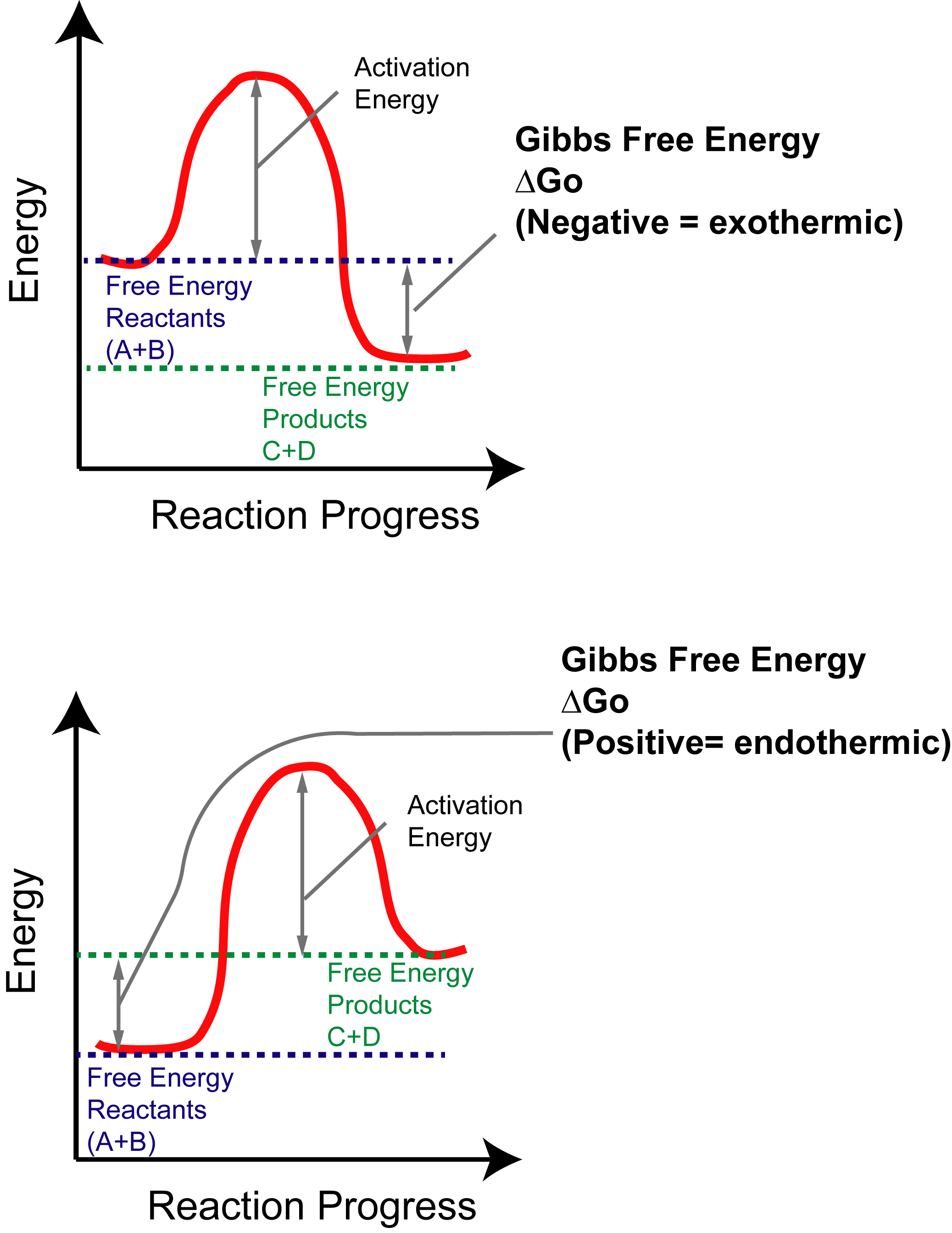
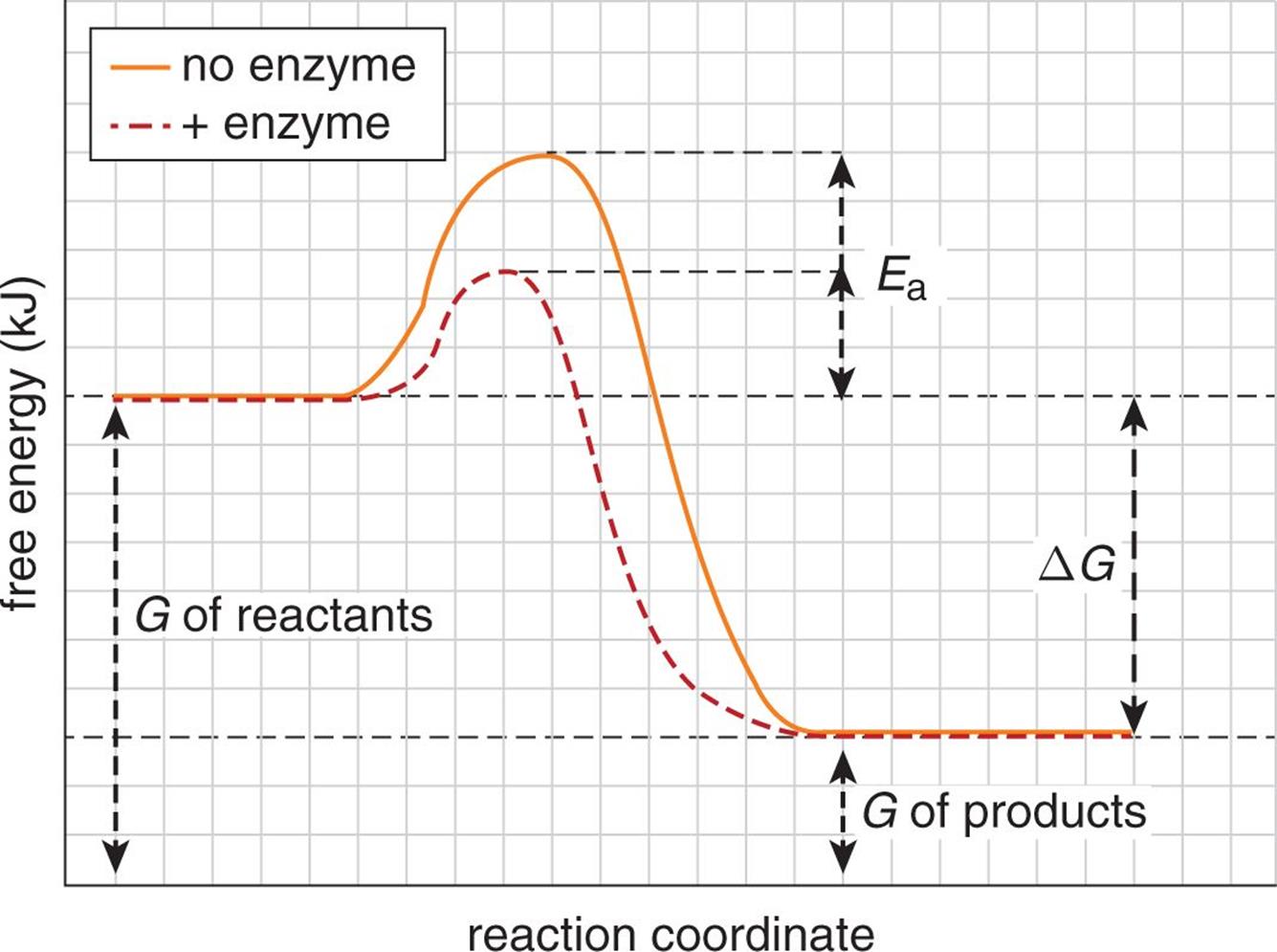
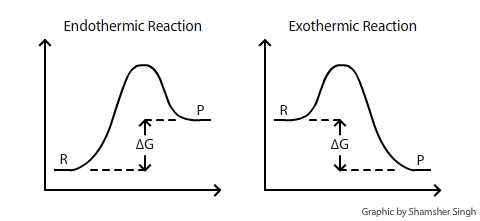
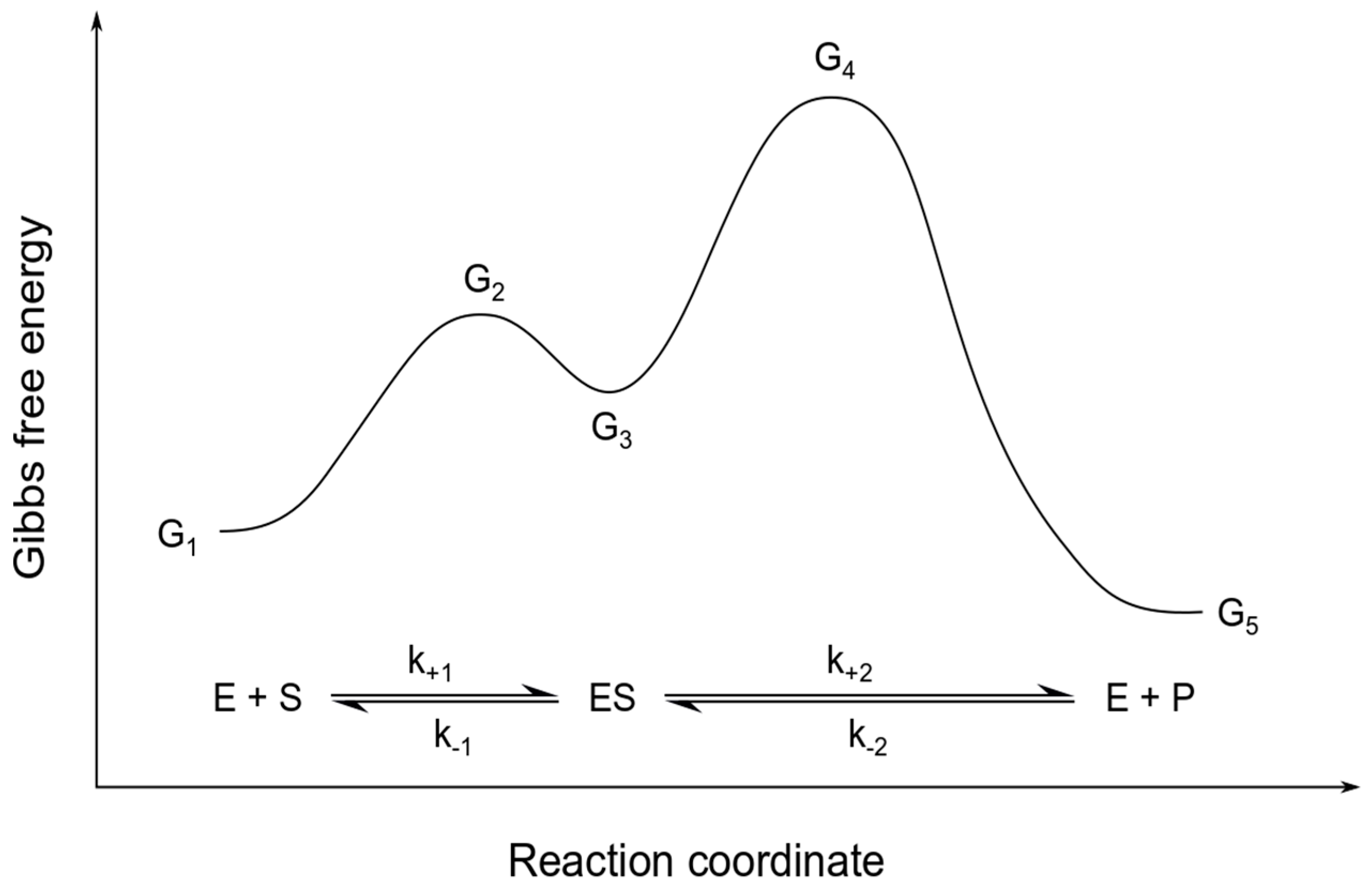
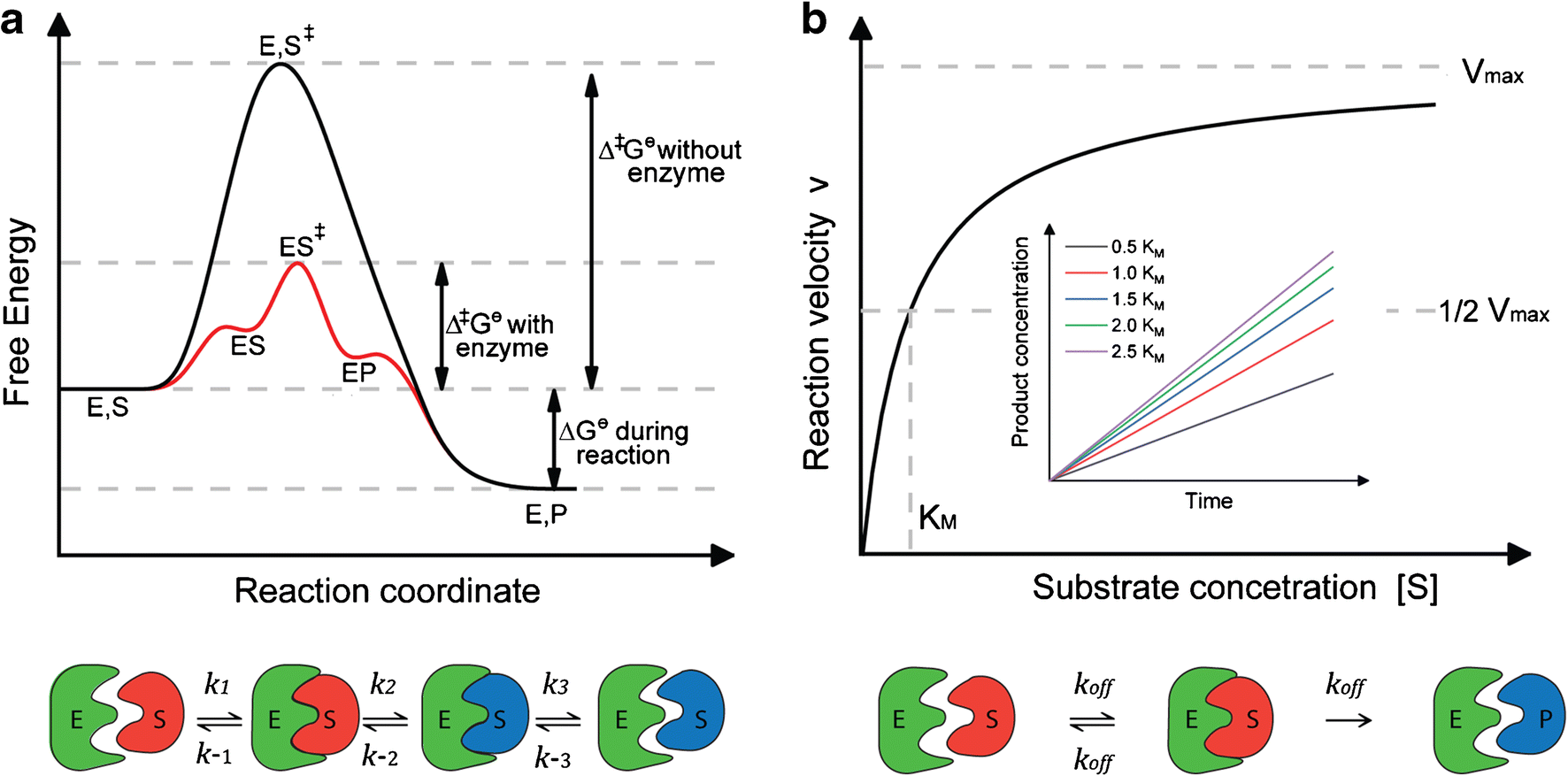
Energy Energy Diagrams 6 • Transition state ‡: - An unstable species of maximum energy formed during the course of a reaction. - A maximum on an energy diagram. • Activation Energy, ∆G‡: The difference in Gibbs free energy between reactants and a transition state. - If ∆G‡ is large, few collisions occur with sufficient Gibbs Free Energy Diagram. Here are a number of highest rated Gibbs Free Energy Diagram pictures on internet. We identified it from honorable source. Its submitted by government in the best field. We say you will this nice of Gibbs Free Energy Diagram graphic could possibly be the most trending topic when we allowance it in google lead or facebook.
An open source python library for equilibrium calculation based on global minimization of Gibbs free energy. What you will find here? Simply put, a library for calculating equilibrium and related properties, like phase diagrams, by means of formulating the equilibrium as a optimization problem instead of non-linear flash calculations systems.

Gibbs free energy diagram
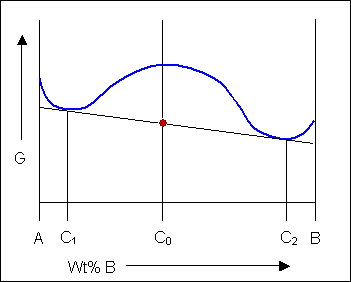
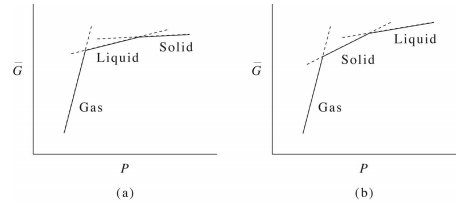
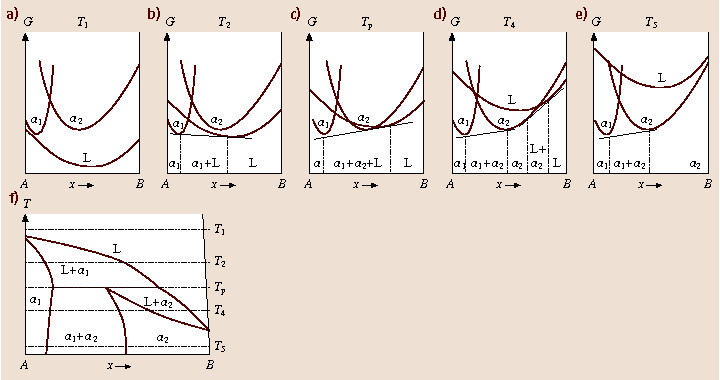
Free Energy Diagram to Phase Diagram Example THE GIBBS FREE ENERGY BEHIND THE PHASE DIAGRAM OF A BINARY, ISOMORPHOUS SYSTEM G = H - TS (1) H = enthalpy T = temperature S = entropy Define molar quantities: g = G/mole h = H/mole s = S/mole X i = mole fraction of i = N i / ΣN i temperature, T liquid sol + liq solid . A composition, X B B Therefore, we choose the Gibbs free energy as a model function in the calculation of the phase diagram.For a system with a certain material but energy exchange with the outside world (closed system), the constant temperature and pressure process is always in the direction of Gibbs free energy reduction, and the total Gibbs free energy of the ... Figure 5 shows the Gibbs free energy of \(\ce{Fe_2O_3}\), as a scatter plot, superimposed over the Pourbaix diagram of Fe. For a material with more than one non H and O elements, the ratio of these elements is fixed to the ratio of elements of the material but the concentration of ions can be varied similar to the single- and multi-element ...
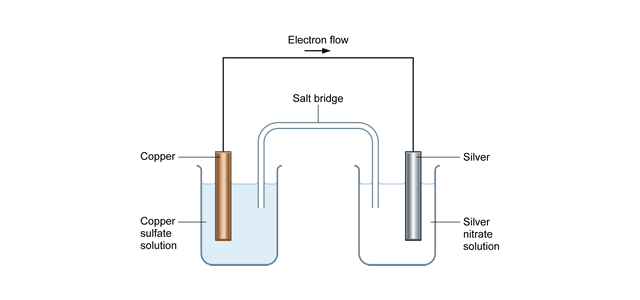
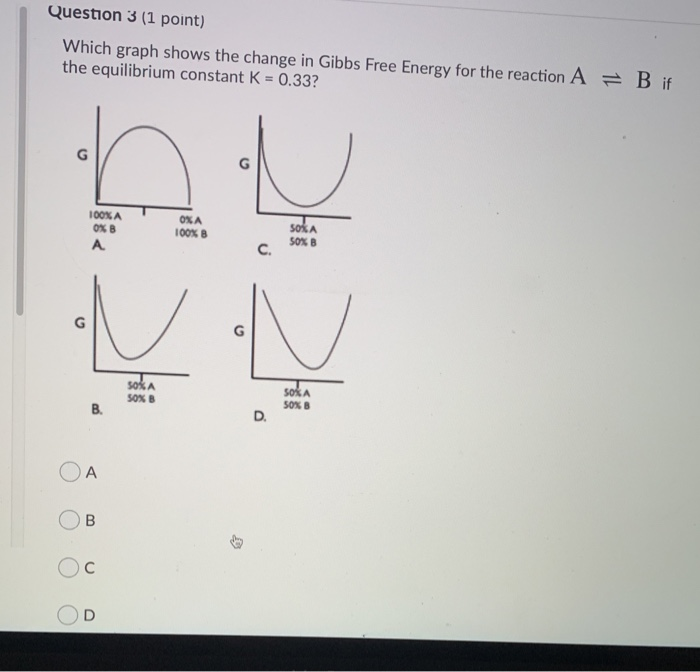
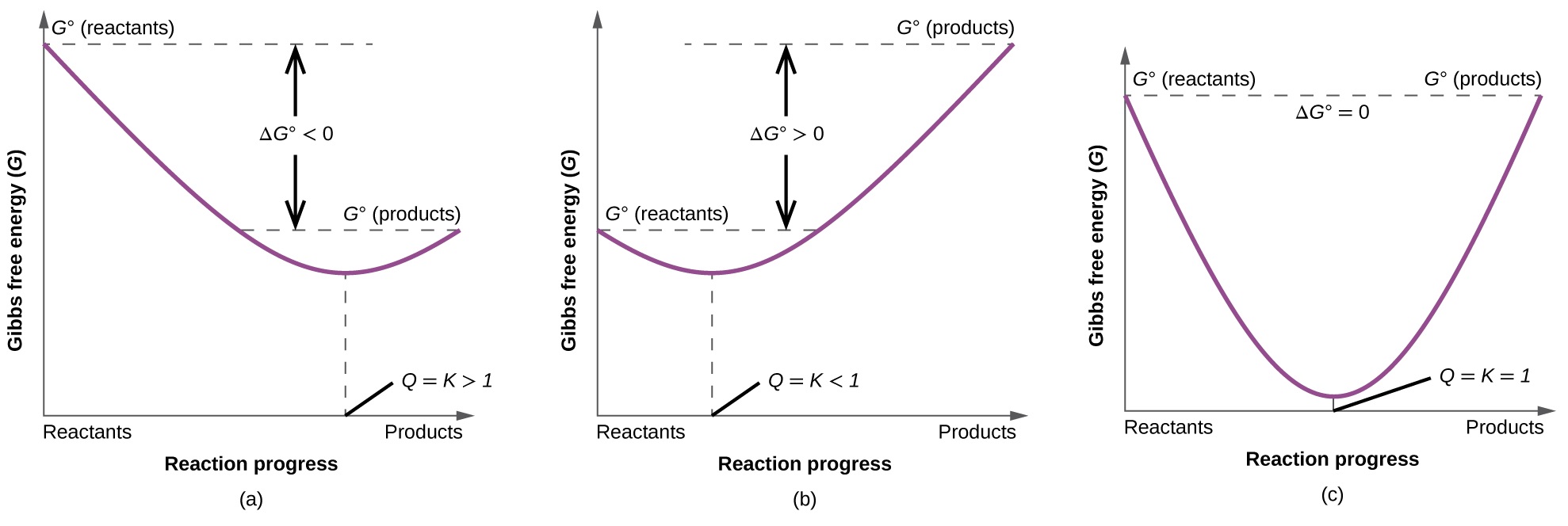
Gibbs free energy diagram. Gibbs Free Energy Concepts and Calculations Van't Hoff Equation Environment, Fossil Fuels, Alternative Fuels Biological Examples (*DNA Structural Transitions, etc.) Electrochemistry Balancing Redox Reactions Galvanic/Voltaic Cells, Calculating Standard Cell Potentials, Cell Diagrams Work, Gibbs Free Energy, Cell (Redox) Potentials Construct a phase diagram given free energy vs. composition curves at different temperatures. Draw the schematic free energy vs. composition curves at different temperatures given the phase diagrams. State and interpret the Gibbs Phase Rule. Author: Kartikay Agarwal Shrey Singh The Gibbs free energy (∆G) of a reaction is a measure of the thermodynamic driving force that makes a reaction occur. A negative value for ∆G indicates that a reaction can proceed spontaneously without external inputs, while a positive value indicates that it will not. The equation for Gibbs free energy is: • Gibbs Free Energy (and co-energy) 4. Equilibrium Phase diagrams 5. Critical Fields October 30, 2003. Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.763 2003 Lecture 17 Fluxoid Quantization and Type II Superconductors. Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.763 2003 Lecture 17 The Vortex State
Gibbs Free Energy Gibbs free energy is a measure of the amount of work that is potentially obtainable. Instead of absolute quantities, what is usually measured is the change in free energy: ΔG = ΔH - TΔS -6-dG = VdP - SdT dG = VdP - SdT + Σµ i dn i Gibbs free energy 1.2. Thermodynamic study of phase diagrams. Minimisation of the Gibbs free energy XFirst law of thermodynamics: conservation of the energy in any process Introduction of the internal energy E Introduction of the enthalpy function H = E + PV and dH = dE + PdV + VdP oSecond law of thermodynamics ... In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy (or Gibbs energy) is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum reversible work that may be performed by a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure.The Gibbs free energy (=, measured in joules in SI) is the maximum amount of non-expansion work that can be extracted from a thermodynamically closed system (one ... The Gibbs free energy of a system at any moment in time is defined as the enthalpy of the system minus the product of the temperature times the entropy of the system. G = H - TS The Gibbs free energy of the system is a state function because it is defined in terms of thermodynamic properties that are state functions.
Gibbs Free Energy Doodle Diagram Notes. SKU 0061303. $6.00. In stock. Quantity: 1. Add to Bag. Product Details. This set of guided notes with chemistry doodles can be little anchor charts for your student to keep in their notebook! Gibbs Free Energy Four quantities called "thermodynamic potentials" are useful in the chemical thermodynamics of reactions and non-cyclic processes.They are internal energy, the enthalpy, the Helmholtz free energy and the Gibbs free energy. The Gibbs free energy G is defined by. The internal energy U might be thought of as the energy required to create a system in the absence of changes in ... Energy Diagram Module Series- Part Two: Gibbs Free Energy and Spontaneity. This is part 2 of a four part series in the Energy Diagram Module. Stay tuned for the other parts! To see part 1 click here. In order to talk about energy of the reaction, a few key concepts are needed. If the products have less potential energy than the reactants, the ... an introduction to gibbs free energy This page introduces Gibbs free energy (often just called free energy), and shows how it can be used to predict the feasibility of reactions. If you have already read the page about how to do this with total entropy changes, you will find a little bit of repetition on this page.
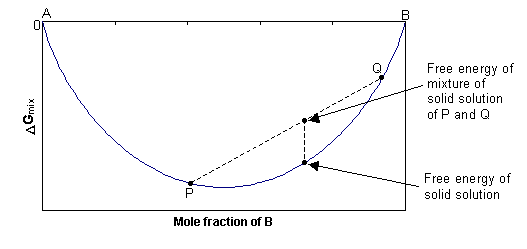
Chapter10 Gibbs Free Energy-Composition Curves and Binary Phase Diagrams §10-1. Introduction §10-2. Gibbs Free Energy Curve, ∆ ( ) B GM X §10-3. ∆ ( ) B GM X of a Regular Solution §10-4. Criteria For Phase Stability in Regular Solutions §10-5. Standard States and Two-Phase Equilibrium §10-6. Binary Phase Diagrams with Liquid and Solid ...
FIGURE 3.9 Gibbs free energy diagram for ammonia synthesison the stepped Ru(OOOl) surface at 1,10, and 100 har. The numbers correspond to the six different reaction steps(see also Figs. 2.6 and 3.9) as defined in the preceding text. Data was obtained from the CatApp and corrected for ZPE and entropy contrihutions.
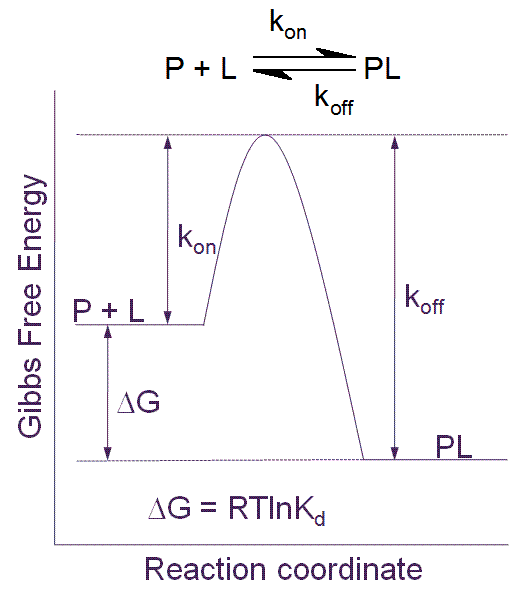
The Gibbs [free] energy (also known as the Gibbs function) is defined as. G = H - T S (4-1). in which S refers to the entropy of the system.Since H, T and S are all state functions, so is G.Thus for any change in state, we can write the extremely important relation . ΔG = ΔH - T ΔS (4-2) Must know this!. How does this simple equation encompass the entropy change of the world ΔS total ...
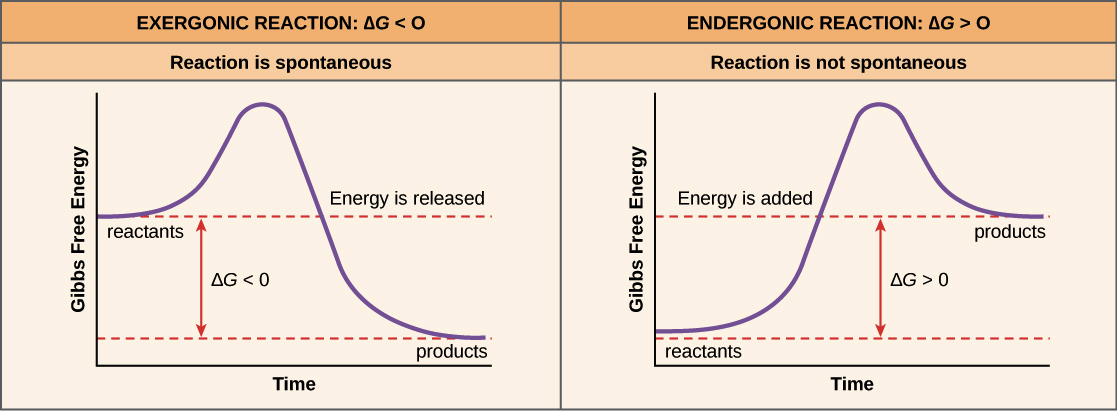
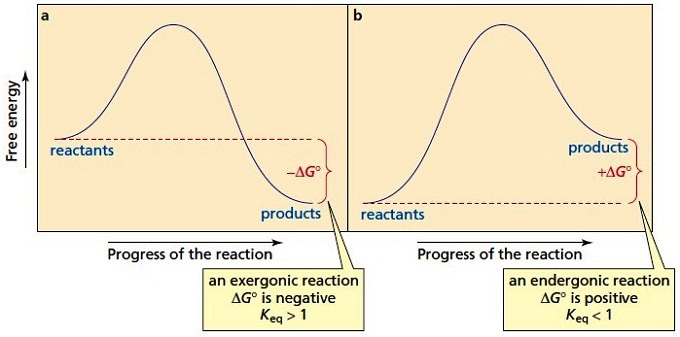
Gibbs free energy and spontaneity. When a process occurs at constant temperature and pressure , we can rearrange the second law of thermodynamics and define a new quantity known as Gibbs free energy: where is enthalpy, is temperature (in kelvin, ), and is the entropy. Gibbs free energy is represented using the symbol and typically has units of .
The Gibbs free energy ( G) of a system is a measure of the amount of usable energy (energy that can do work) in that system. The change in Gibbs free energy during a reaction provides useful information about the reaction's energetics and spontaneity (whether it can happen without added energy).
Phase Diagrams Last Time Common Tangent Construction Construction of Phase Diagrams from Gibbs Free Energy Curves If the temperature in Figure 28-5 is decreased a little further: G Tm (pure A) < T2 < T1 P =constant XB solid liquid XL XS Figure 30-1: Figure 28-5 drawn at an even lower temperature than Figure 28-3.
pg. 402, Part2 of Ref.[1], Gibbs original free energy diagram exists in the energy-entropy plane, which Gibbs actually labeled as "available energy". Maxwell developed a very clear explanation of thermodynamic processes associated with the triple point mixed state, pp. 195-208, together with
10. 6 Phase Diagrams, Gibbs Free Energy, and Thermodynamic Activity The Gibbs free energy of formation of the liquid solutions in the system A-B at the temperature T is shown in Fig. 10.15b. The "double tangent" to the a solid solution and liquid solution curves is reduced to a tangent drawn from the point on the X A =1 axis
3.2 Gibbs Free Energy Josiah Willard Gibbs (1839-1903) was an American theoretical physi-cist, chemist, and mathematician. he devised much of the theoretical foundation for chemical thermodynamics and physical chemistry. yale University awarded Gibbs the first American Ph.D. in engineering in 1863, and he spent his entire career at Yale.
Gibbs Free Energy, Spontaneity and Entropy. According to the 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics, the entropy of the universe always increases for a spontaneous process. This is illustrated by the equation: Second Law of Thermodynamics. Gibbs Free Energy is a thermodynamic property that can be used in determining the direction of a spontaneous process at either constant temperature (isothermal) or ...
Ellingham Diagram for Selected Bromides: Part-1 ... Data from Thomas B. Reed, Free Energy of Formation of Binary Compounds, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1971. m B M AlBr 3 m M B BeBr 3 B BBr 3 HBr B M FeBr 2 B M m PbBr 2 b M m LiBr B b M m MgBr 2 B b M HgBr 2 PBr 3 B b M m KBr B M m NaBr B M TiBr 4 WBr 6 B B ZrBr 4 -1-2-4-6-8-10-15-20-25-30-35-40 ...
Figure 5 shows the Gibbs free energy of \(\ce{Fe_2O_3}\), as a scatter plot, superimposed over the Pourbaix diagram of Fe. For a material with more than one non H and O elements, the ratio of these elements is fixed to the ratio of elements of the material but the concentration of ions can be varied similar to the single- and multi-element ...
Therefore, we choose the Gibbs free energy as a model function in the calculation of the phase diagram.For a system with a certain material but energy exchange with the outside world (closed system), the constant temperature and pressure process is always in the direction of Gibbs free energy reduction, and the total Gibbs free energy of the ...
Free Energy Diagram to Phase Diagram Example THE GIBBS FREE ENERGY BEHIND THE PHASE DIAGRAM OF A BINARY, ISOMORPHOUS SYSTEM G = H - TS (1) H = enthalpy T = temperature S = entropy Define molar quantities: g = G/mole h = H/mole s = S/mole X i = mole fraction of i = N i / ΣN i temperature, T liquid sol + liq solid . A composition, X B B
















0 Response to "40 gibbs free energy diagram"
Post a Comment