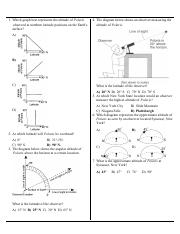
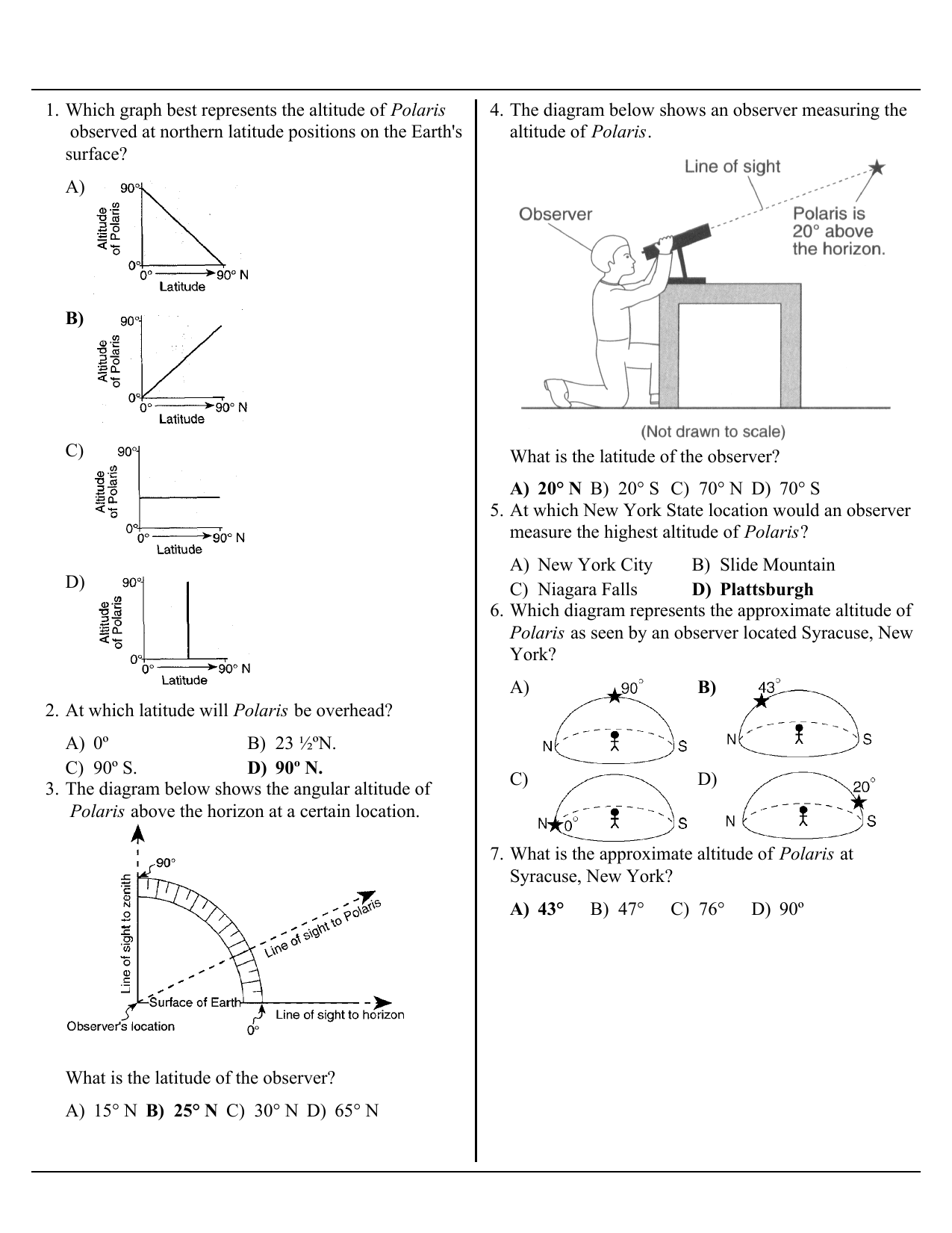
37 in the following diagram what is the latitude of the observer
Jul 15, 2021 · In The Following Diagram What Is The Latitude Of The Observer. What is the observer’s latitude?, Since the observer’s latitude is 40° N, the noon sun must be 16.5° south of his zenith. Equally well, we could say the sun has an altitude of 73.5° above the observer’s southern horizon. Notice also that the north celestial pole is 40° above the observer’s northern horizon, exactly the ...
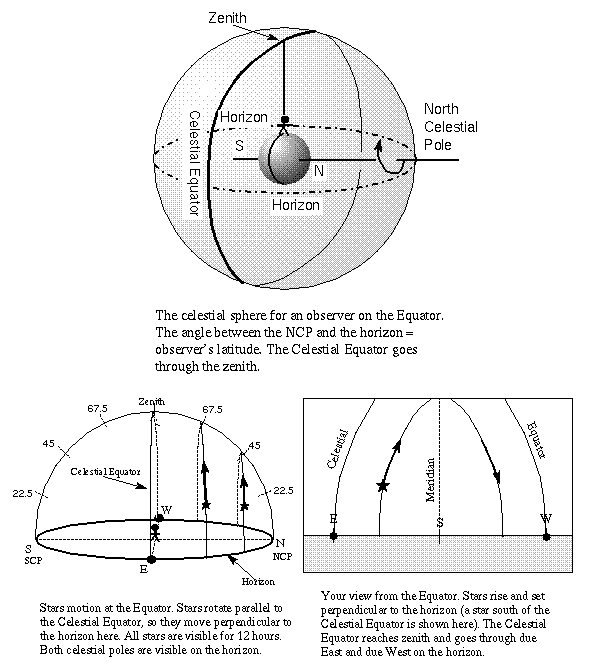
In the following diagram what is the latitude of the observerThe diagram is a model of the sky (celestial sphere) for an observer at 50° N latitude. The Sun's apparent path on June 21 is shown. Point A is a position along the Sun's apparent path.

through a refer to the following: The diagram below represents the Sun's apparent paths as viewed by an observer located at 50N latitude on June 21 and March 21. The data table shows the sun's maximum altitude for the same two dates of the year. The sun's maximum altitude for December 21 has been left blank Sun's noon position BO 0 90 Sun's 7 ... What is the approximate latitude of the observer in the diagram below? asked Jun 6, 2017 in Physics & Space Science by Janessa. a. 90° N b. 90° S c. 50° N d. Join The Discussion. Answer: Option C . 5. 1. The diagram below shows an observer on Earth viewing the star Polaris. Which element is represented by the What is this observer's latitude? (1) 38° N (3) 52° N (2) 38° S (4) 52° S 3. The pie graph below shows the elements comprising Earth's crust in percent by mass. 6.18 - Be able to find the latitude of an observer using Polaris . For an ...
In the following diagram what is the latitude of the observer. The diagram below shows an observer on Earth measuring the altitude of Polaris. What is the latitude of this observer? 110. Base your answer to the following ... Observer a is on earth looking at the moon, and observer b is on the moon looking at earth. 0° of latitude is found at the _____ and the 90° of latitude is found at the _____. What is the latitude of point a in the diagram; An observer on the ground hears a sonic boom that is created by an airplane flying at a speed the latitude of the observer Diagram: Observer's altitude = 66.5 degrees North. 4. The Earth rotates. West to east 15 degrees per hour in 24 hours or one day. 5. Latitude lines run Longitude lines run. east-west, but measure north or south of the equator The diagram below shows the positions of the Earth, Moon and Sun. What is the date? June 21. On August 14, what season is it in Sydney, Australia (Latitude 35° South)? winter. Fill in the blank: In the Northern Hemisphere, June 21 has _____ than December 21. ... In which of the images below is the observer experiencing the highest tide?
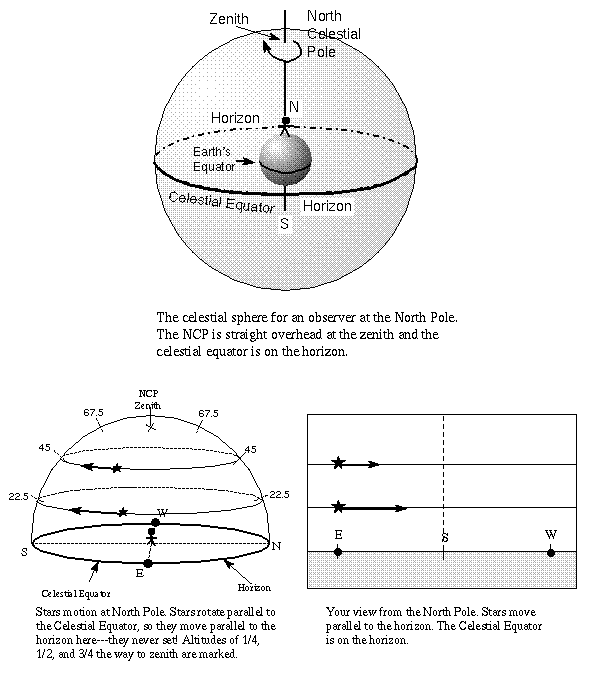
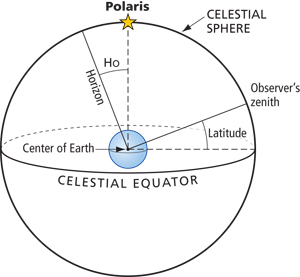
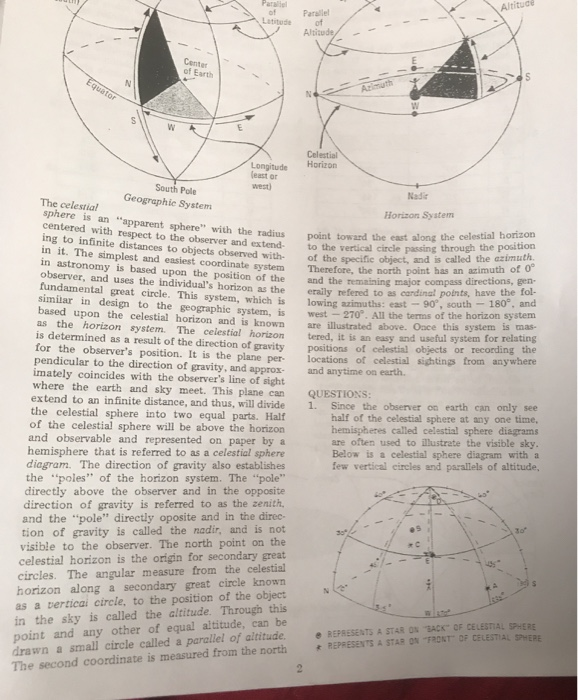
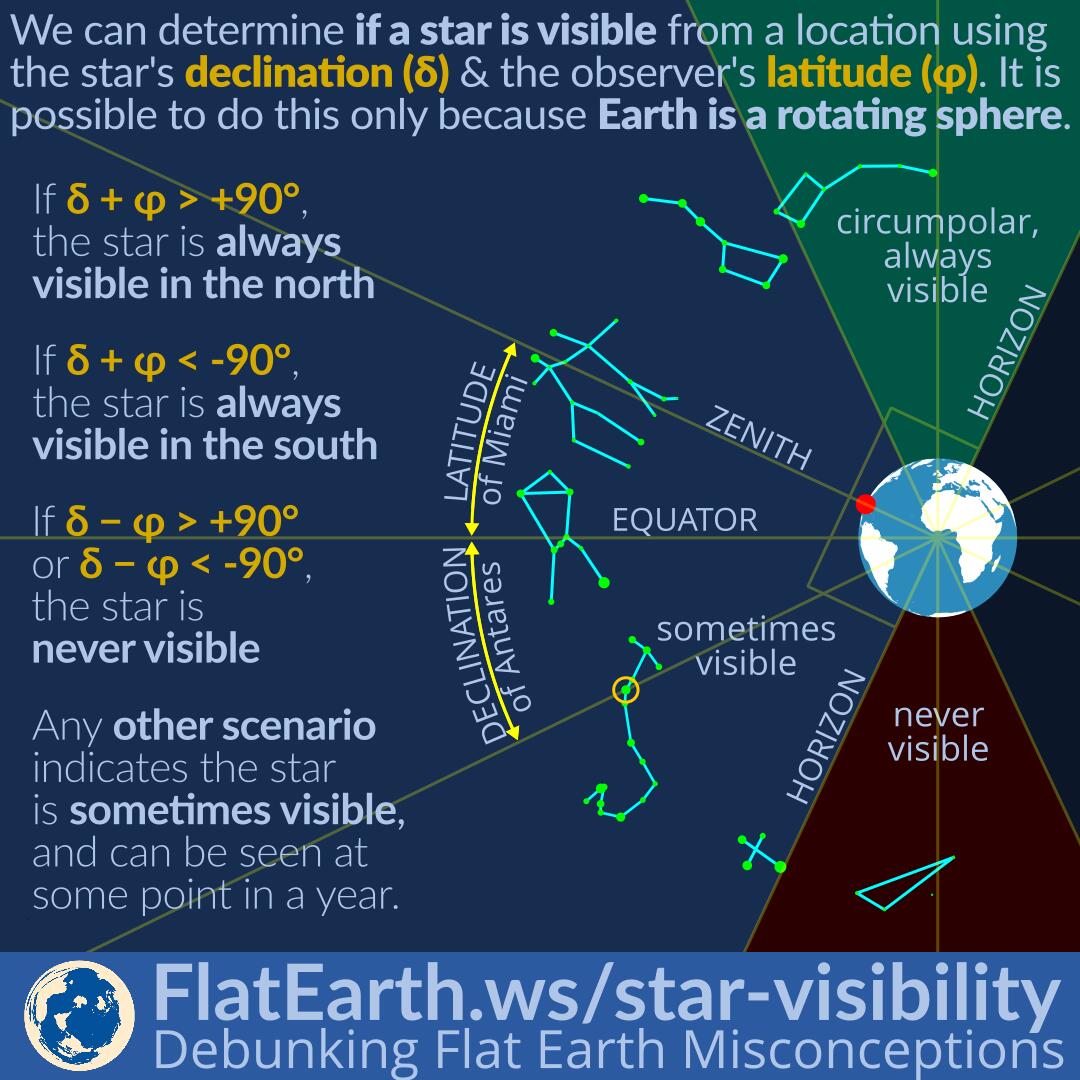
The following diagrams will help to explain how the latitude can be calculated from the Sun's midday altitude and its declination. In the following diagram , NOS represents the horizon and O represents the position of the observer, The diagram represents the Sun's apparent paths as viewed by an observer located at 500 N latitude on June 21 and March 21 The data table shows the Sun's maximum altitude for the same two dates of the year. The Sun's maximum altitude for December 21 has been left blank. The latitude is the angle from the zenith to the Earth's equator. "Up" point to the circle on the celestial sphere with declination +40 degrees Notice that the south pole is below the horizon and invisible for an observer located at 40 degrees N latitude Rotating the diagram so the zenith is up make it easier to visualize the local sky. For an observer in New York State (NYS), the altitude of Polaris is 43 o above the northern horizon. This observer's latitude is closest to the latitude of
15.The diagram below represents positions of Earth in its orbit around the Sun and twelve constellations that can be seen in the midnight sky by an observer in New York State at different times of the year. The approximate locations of the constellations in relation to Earth's orbit are shown. What is the approximate latitude of the observer in the diagram below? asked Jun 6, 2017 in Physics & Space Science by Rapunzel. a. 20° N b. 20° S c. 70° N d. In The following diagram what is the latitude of the observer? 30 N. ... 75 55 W. Which diagram best shows the latitude of Polaris observe near Buffalo New York? 2. Which reference line passes through both the geographic north pole in the geographic south pole? 0 longitude. The following diagram represents a portion of earths latitude and ... Answer: The altitude of the celestial equator is 90 − the observer's latitude. At the poles, the latitude is 90 N or 90 S. So, 90 −90 = 0 . See also what does altiplano mean What is declination diagram? A declination diagram is '…a diagram that shows the angular relationship, represented by prongs, among grid, magnetic, and true norths… …
1) Which of the stars (#1-#5) in the diagram is closest to the zenith? ... of Polaris off of the horizon is equivalent to the latitude of the observer.
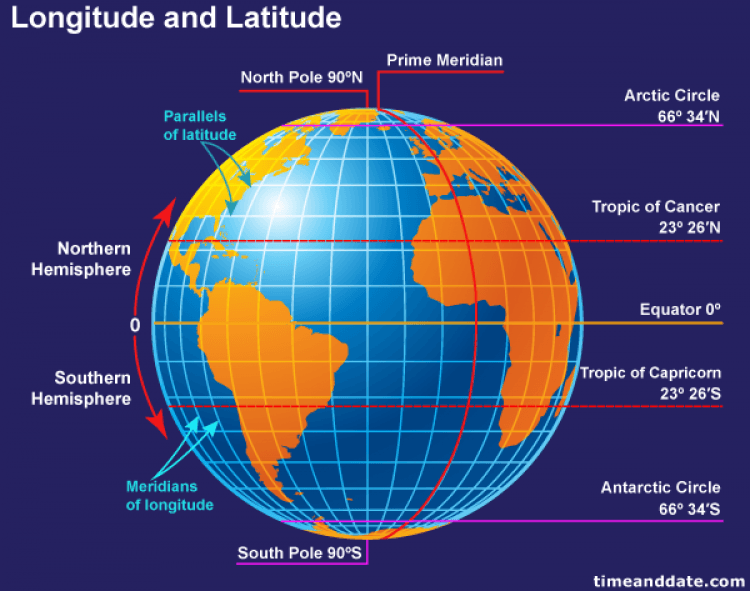
In the following diagram what is the latitude of the observer The uneven distribution of insolation by latitude is primarily a result of The climate zones lying between 23.5° and 66.5° north and south latitude are called the
Lab 3 - The Rotating Sky Quiz. At any one instance, the percentage of the celestial sphere that is visible for an observer at 0° S is ___________ %. Nice work! You just studied 20 terms! Now up your study game with Learn mode.
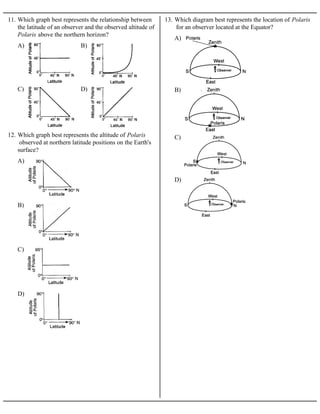
Which diagram represents the approximate altitude of Polaris as seen by an observer located Syracuse, New York? A) 5° E 30° N B) 5° W 30° S C) 5° N 30° E D) 5° S 30° W 14. The diagram below represents part of Earth's latitude-longitude system. What is the latitude and longitude of point L?
Dec 02, 2016 · 22.The diagram below shows an observer on Earth measuring the altitude of Polaris. What is the latitude of this observer? A)60° south latitude and 0° longitude B)60° north latitude and 0° longitude C)0° latitude and 60° east longitude D)0° latitude and 60° west longitude 23.As a ship crosses the Prime Meridian, an observer on
Transcribed image text: The above diagram is for an observer at 45° latitude depicting possible Sun paths at various times a year Use the diagram to answer the following questions. summer solstice? i) Which path corresponds to the Sun's path on the fall equinox?
At which location could an observer not see Polaris in the night sky at any time during the year? A)90° N B)66.5° N C)43° N D)23.5° N 23.The diagram below shows an observer on Earth measuring the altitude of Polaris. What is the latitude of this observer? A)Jamestown B)Plattsburgh C)Oswego D)New York City
Read more at … 1. The diagram below shows an observer on Earth viewing the star Polaris. Which element is represented by the What is this observer's latitude? (1) 38° N (3) 52° N (2) 38° S (4) 52° S 3. The pie graph below shows the elements comprising Earth's crust in percent by mass. Solstice, the tilt of the Earth's axis, and the Observer's Latitude. It's the values you get ...
22.The diagram below shows an observer on Earth measuring the altitude of Polaris. What is the latitude of this observer? A)60° south latitude and 0° longitude B)60° north latitude and 0° longitude C)0° latitude and 60° east longitude D)0° latitude and 60° west longitude 23.As a ship crosses the Prime Meridian, an observer on
Base your answers to questions 10 through 13 on the diagram below. The diagram represents the Earth at a position in orbit around the Sun, the Sun's rays at solar noon, and the direction to Polaris. Letters A through D represent positions on the Earth's surface. 10. What is the latitude of position A? 1) 23¡º N 3) 66¡º N 2) 47º N 4) 90º N 11.
20.Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which represents Earth in its orbit around the Sun. The position of Earth on the first day of each season is labeled A, B, C, and D. A)A B)B C)C D)D ... occurs for an observer at 50° N latitude.
Meridian Passage occurs when a celestial body crosses the observer's meridian of longitude and at that instant, it will reach its greatest altitude above the observer's horizon. The following diagrams will help to explain how the latitude can be calculated from the Sun's declination and altitude at Mer. Pas. Consider the following diagram: NOS represents the horizon.…
The diagram represents the Sun's apparent paths as viewed by an observer located at 50° N latitude on June 21 and March 21. The data table shows the Sun's maximum altitude for the same two dates of the year. The Sun's maximum altitude for December 21 has been left blank. A)The intensity and angle of insolation are greatest on March 21.
The apparent visual magnitude of a star is 7.3. This tells us that the star is. not visible with the unaided eye. Precession of the rotation axis of Earth is caused by. the force of gravity from the sun and moon on Earth's equatorial bulge. The apparent visual magnitude of a star is a measure of the star's. intensity.
diagram and data table below. The diagram represents the Sun's apparent paths as viewed by an observer located at 50° N latitude on June 21 and March 21. The data table shows the Sun's maximum altitude for the same two dates of the year. The Sun's maximum altitude for December 21 has been left blank.
32. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram and data table below. The diagram represents the Sun's apparent paths as viewed by an observer located at 50 N latitude on June 21 and March 21. The data table shows the Sun's maximum altitude for the same two dates of the year. The Sun's maximum altitude for
D) Latitude lines are parallel and longitude lines meet at the Equator. 2) The diagram below illustrates the position of the Earth in relation to the Sun on one particular day. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on the Earth's surface. In which direction would an observer at point D look to find Polaris? A) north B) west C) south D) east
Join The Discussion. Answer: Option C . 5. 1. The diagram below shows an observer on Earth viewing the star Polaris. Which element is represented by the What is this observer's latitude? (1) 38° N (3) 52° N (2) 38° S (4) 52° S 3. The pie graph below shows the elements comprising Earth's crust in percent by mass. 6.18 - Be able to find the latitude of an observer using Polaris . For an ...
What is the approximate latitude of the observer in the diagram below? asked Jun 6, 2017 in Physics & Space Science by Janessa. a. 90° N b. 90° S c. 50° N d.
through a refer to the following: The diagram below represents the Sun's apparent paths as viewed by an observer located at 50N latitude on June 21 and March 21. The data table shows the sun's maximum altitude for the same two dates of the year. The sun's maximum altitude for December 21 has been left blank Sun's noon position BO 0 90 Sun's 7 ...







0 Response to "37 in the following diagram what is the latitude of the observer"
Post a Comment