38 pressure specific volume diagram
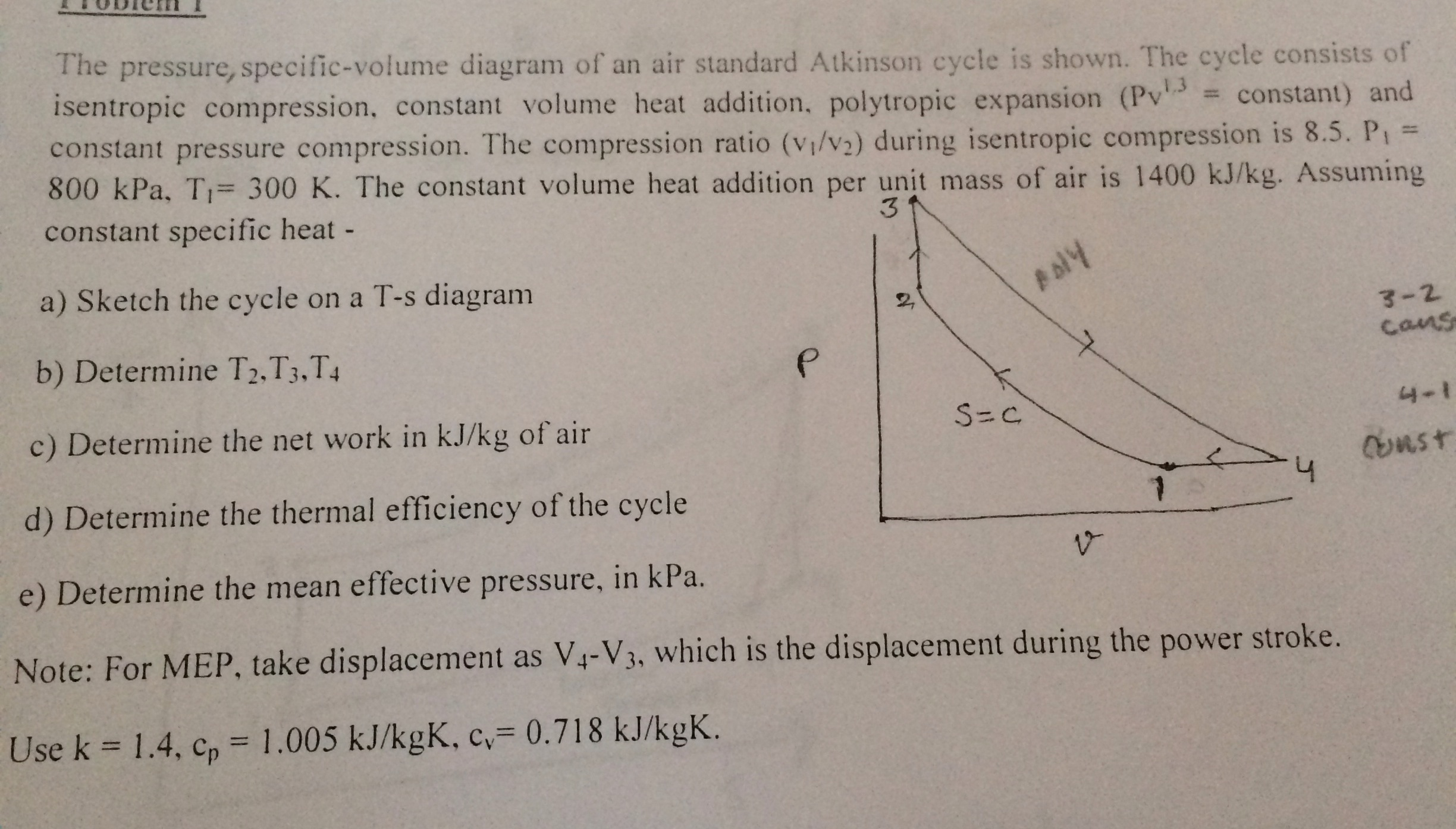
In thermodynamics, the specific volume of a substance (symbol: ν or ) is an intrinsic property of the substance, defined as the ratio of the substance's volume (V) to its mass (m).It is the reciprocal of density and it is related to the molar volume and molar mass: = = = ~ The standard unit of specific volume is cubic meters per kilogram (m 3 /kg), but other units include ft 3 /lb, ft 3 /slug ... The pressure-specific volume diagram of the air-standard Atkinson cycle is shown in the figure. The cycle consists of isentropic compression, constant volume heat addition, isentropic expansion ...
The net work done in a thermodynamic cycle would be the area enclosed by the PV cycle, and so forth. Insofar as using specific volume v or total volume V is concerned, you can use either. However, for a closed system the mass is constant (e.g., ideal gas in cylinder/piston). Since the mass is fixed (and can be obtained by ideal gas law), you ...
Pressure specific volume diagram
Classify items a through g shown on the pressure-specific volume diagram in Fig. P1.23C as a property,a state,or a process. A. When a system is isolated,(a) its mass remains constant.(b) its temperature may change.(c) its pressure may change.(d) all of the above. Buoyancy force. The pressure-volume diagram (abbreviated as the P-V diagram) is a graphical representation of the changes in pressure with respect to volume in a closed system. P-V diagrams are useful for determining the efficiency of a system and/or the work done by or to a system. The classic example given is of a cylinder and a piston with some type of gas ... How to Read a Pressure-Enthalpy Diagram In chemical engineering, it is often necessary to know how properties like pressure, enthalpy, volume, and entropy relate to each other at a certain temperature. A Pressure-Enthalpy Diagram provides this information but can be cryptic to decipher. What you need to know: Liquid/vapor dome region
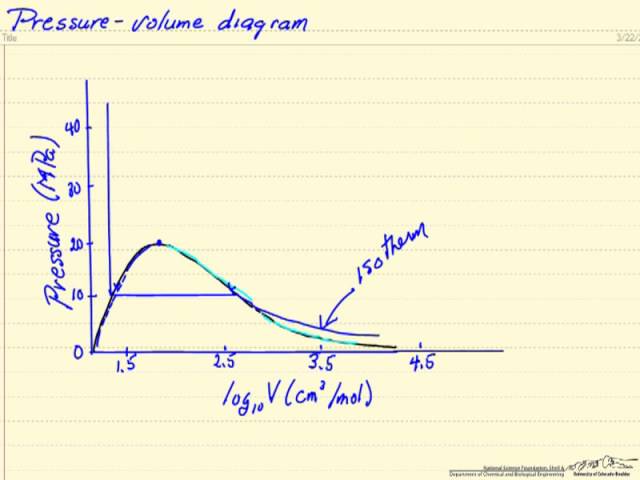
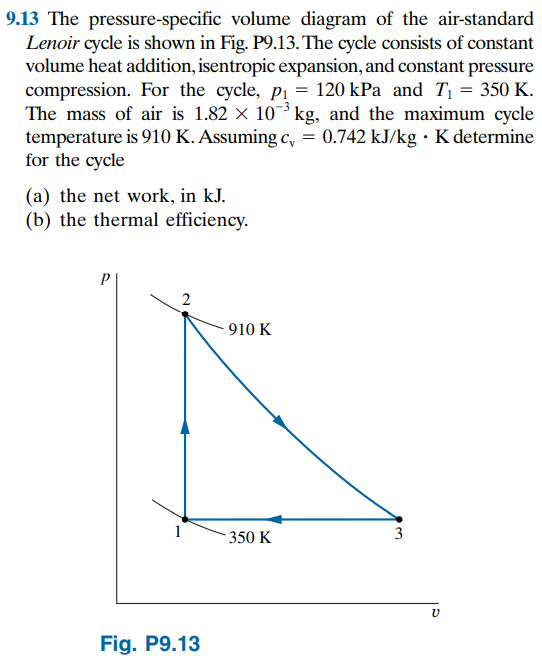
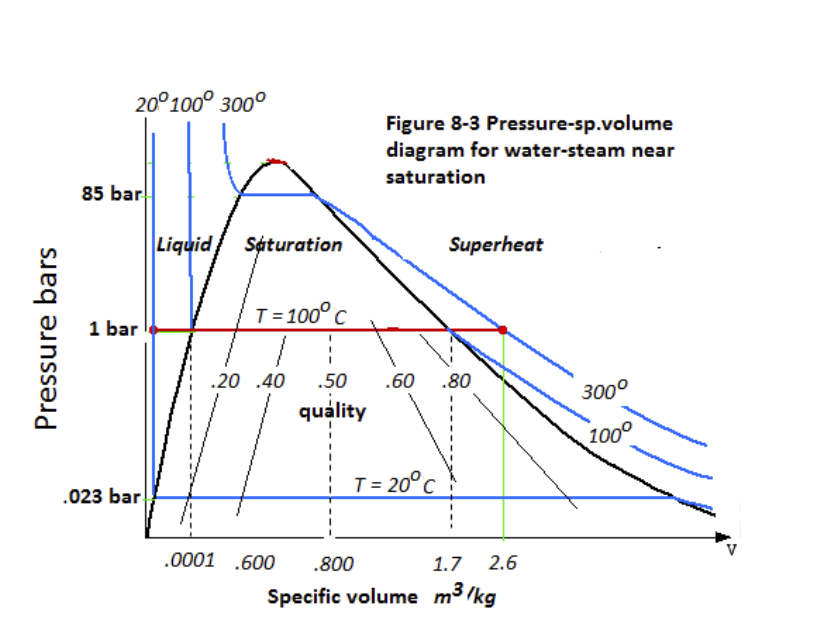
Pressure specific volume diagram. Heat is added to the cylinder while the pressure is maintained constant until the temperature reaches 300°C, as shown in the following T-v diagram (temperature vs specific volume): From State (1) to State (2) the water maintains its liquid phase and the specific volume increases very slightly until the temperature reaches close to 100°C ... The pressure-specific volume diagram of the air-standard Lenoir cycle is shown in Fig. P9.17. The cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, isentropic expansion, and constant pressure compression. For the cycle, p1 = 14.7ibf/in.^2 and T1=540R. The mass of air is 4.24 x 10^-3 lb, and the c1=0.171 Btu/lb. R, determine for the cycle (a) the ... Figure 3.1-2 is a T-v diagram for water. For pressure greater than or equal to the critical pressure, temperature increases continously at fixed pressure as the specific volume increases and there is no passage across the two-phase liquid-vapor region. The isobaric curve marked 50 MPa in Figure 3.1-2 shows this behavior. Describes the regions of a pressure-temperature projection and the behavior across phase boundaries. Made by faculty at the University of Colorado Boulder, ...
a. Specific volume b. Density c. Specific gravity d. Humidity 1.2 DESCRIBE the following classifications of thermodynamic properties: a. Intensive properties b. Extensive properties 1.3 DEFINE the thermodynamic properties temperature and pressure. 1.4 DESCRIBE the Fahrenheit, Celsius, Kelvin, and Rankine temperature scales including: a ... The given PV diagram is for a gas which undergoes compression… View the full answer Transcribed image text : Classify items a through f shown on the pressure-specific volume diagram in the following figure as a property, a state, or a process. Carbon dioxide - Density and Specific Weight vs. Temperature and Pressure - Online calculator, figures and tables showing density and specific weight of carbon dioxide, CO 2, at temperatures ranging from -50 to 775 °C (-50 to 1400 °F) at atmospheric and higher pressure - Imperial and SI Units. A system can be described by three thermodynamic variables — pressure, volume, and temperature. Well, maybe it's only two variables. With everything tied together by the ideal gas law, one variable can always be described as dependent on the other two.
Specific Volume Formulas. There are three common formulas used to calculate specific volume (ν): ν = V / m where V is volume and m is mass. ν = 1 /ρ = ρ-1 where ρ is density. ν = RT / PM = RT / P where R is the ideal gas constant, T is temperature, P is pressure, and M is the molarity. The second equation usually is applied to liquids ... A pressure-volume diagram (or PV diagram, or volume-pressure loop) is used to describe corresponding changes in volume and pressure in a system. They are commonly used in thermodynamics, cardiovascular physiology, and respiratory physiology.. PV diagrams, originally called indicator diagrams, were developed in the 18th century as tools for understanding the efficiency of steam engines and has constant specific heat evaluated at room temperature (25oC or 77oF). Chapter 8-4 ... The compression ratio r of an engine is the ratio of the maximum volume to the minimum volume formed in the cylinder. ... and the mean effective pressure. Process Diagrams: Review the P-v and T-s diagrams given above for the The PV diagram models the relationship between pressure (P) and volume (V) for an ideal gas.An ideal gas is one that never condenses regardless of the various changes its state variables (pressure, volume, temperature) undergo. In addition, the processes plotted on PV diagrams only work for a closed system (in this case the ideal gas), so there is no exchange of matter, but still an exchange ...
Pressure and Volume. Pressure is force (in newtons, N) divided by the area ( in square meters, m 2) over which it acts (P = F/A). Volume is the amount of space is taken up by an object or, in our ...
How to use equation 1 to calculate gas volume or pressure. At constant temperature of 35 ºC, a sample of gas occupies a volume of 5.0 L and has a pressure of 2 atm. If the volume of the gas decreased to 2.0 L, calculate its new pressure. Answer. Let's use the following models to make sense of the problem. As volume decrease, pressure increase
Pressure vs. Volume Phase Diagram...You will be able to see this "bell-shape" in which the liquid of mixture is visible.This is a very useful diagram for mix...
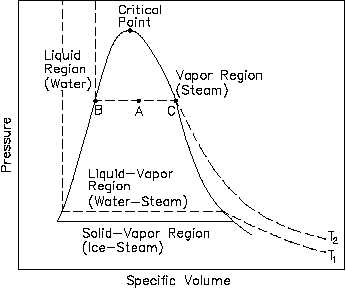
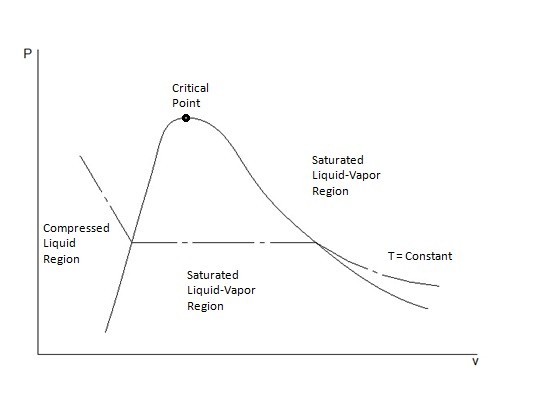
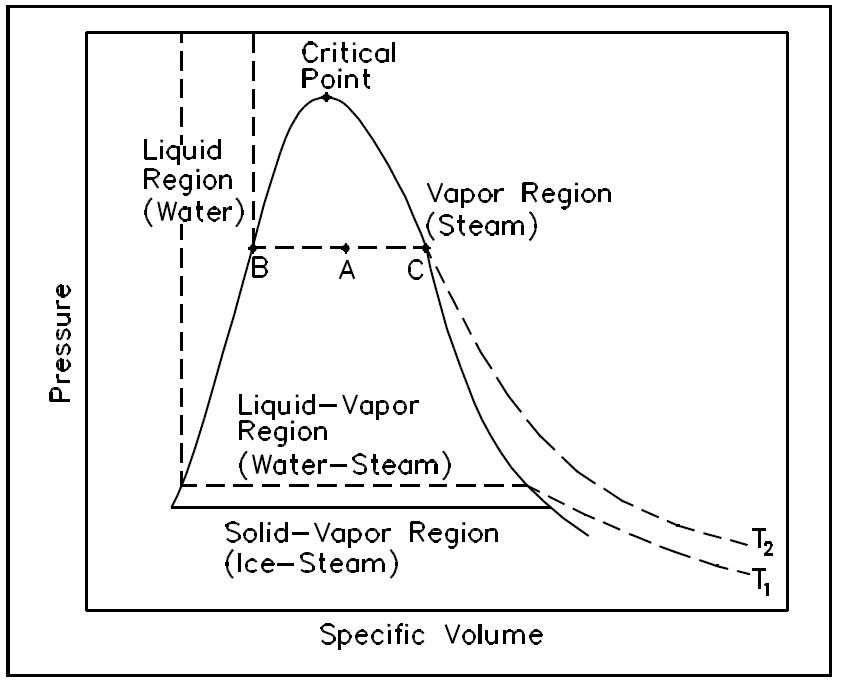
There are regions on a P-n diagram in which two phases exist together. In the liquid-vapor region in Figure 10, water and steam exist together. For example, at point A, water with a specific volume (nf ), given by point B, exists together with steam with a specific volume (ng ), given by point C.
Neatly sketch the pressure-volume [P-v] diagram for this cycle, and using the specific heat values for air at a typical average cycle temperaure of 900K determine: a) the temperature and pressure of the air at the end of each process. b) the net work output/cycle [kj/kg], and. c) the thermal efficiency [η th] of this engine cycle. Solution ...
Specific Volume (ft 3 /lb, m 3 /kg) 194, 12.1: Density of liquid at atmospheric pressure ... The hydrogen phase diagram shows the phase behavior with changes in temperature and pressure. ... Ratios of Specific Heat - Ratios of specific heat for gases with constant pressure and volume processes. Gases - Specific Gravities - Specific gravity of ...
Z is the ratio of the ACTUAL specific volume to the IDEAL specific volume of the gas. Z = (v ACTUAL)/(v IDEAL) Z is found in the charts in Figure 2-40 and Appendix A-13, using the quantities: P R (Reduced Pressure) = P/P CRITICAL. T R (Reduced Temperature) = T/T CRITICAL. v R ("Reduced" Specific Vol.) = v ACTUAL P CR / (R T CR)
Thermodynamics PROPERTY DIAGRAMS AND STEAM TABLES Pressure-Specific Volume (P-n) Diagram A P-n diagram is another common Figure 10 P-v Diagram for Water type of property diagram. Figure 10 is the P-n diagram for pure water. A P-n diagram can be constructed for any pure substance.
Pressure-Specific Volume Diagram Assignment Help. The P-ν diagram is another general kind of property diagram. Figure below is the P-ν diagram for pure water. The P-ν diagram can be built for any pure substance. A P-ν diagram is dissimilar from a P-T diagram in one specifically significant way. There are areas on a P-ν diagram in which two ...
Read the value of enthalpy (h) and specific volume (v) from Mollier diagram corresponding to point '1'. (i) Specific enthalpy of wet steam, h = 2508 KJ/kg (ii) Specific volume of wet steam, v = 0.0935 m 3 /kg (iii) Specific Internal energy of wet steam, u u = h - pv
In T-V diagram, process is carried out by increasing pressure. As we increases pressure, specific volume of saturated liquid is larger and specific volume of saturated vapor smaller.
How to Read a Pressure-Enthalpy Diagram In chemical engineering, it is often necessary to know how properties like pressure, enthalpy, volume, and entropy relate to each other at a certain temperature. A Pressure-Enthalpy Diagram provides this information but can be cryptic to decipher. What you need to know: Liquid/vapor dome region
The pressure-volume diagram (abbreviated as the P-V diagram) is a graphical representation of the changes in pressure with respect to volume in a closed system. P-V diagrams are useful for determining the efficiency of a system and/or the work done by or to a system. The classic example given is of a cylinder and a piston with some type of gas ...
Classify items a through g shown on the pressure-specific volume diagram in Fig. P1.23C as a property,a state,or a process. A. When a system is isolated,(a) its mass remains constant.(b) its temperature may change.(c) its pressure may change.(d) all of the above. Buoyancy force.




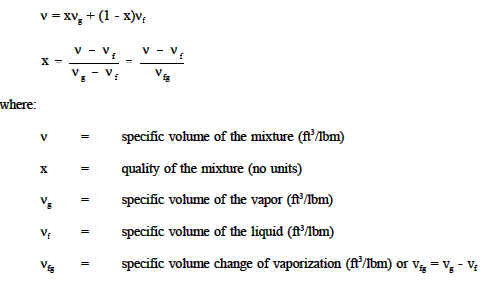

















0 Response to "38 pressure specific volume diagram"
Post a Comment