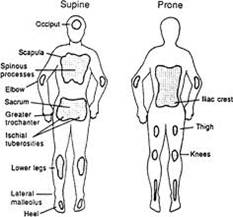
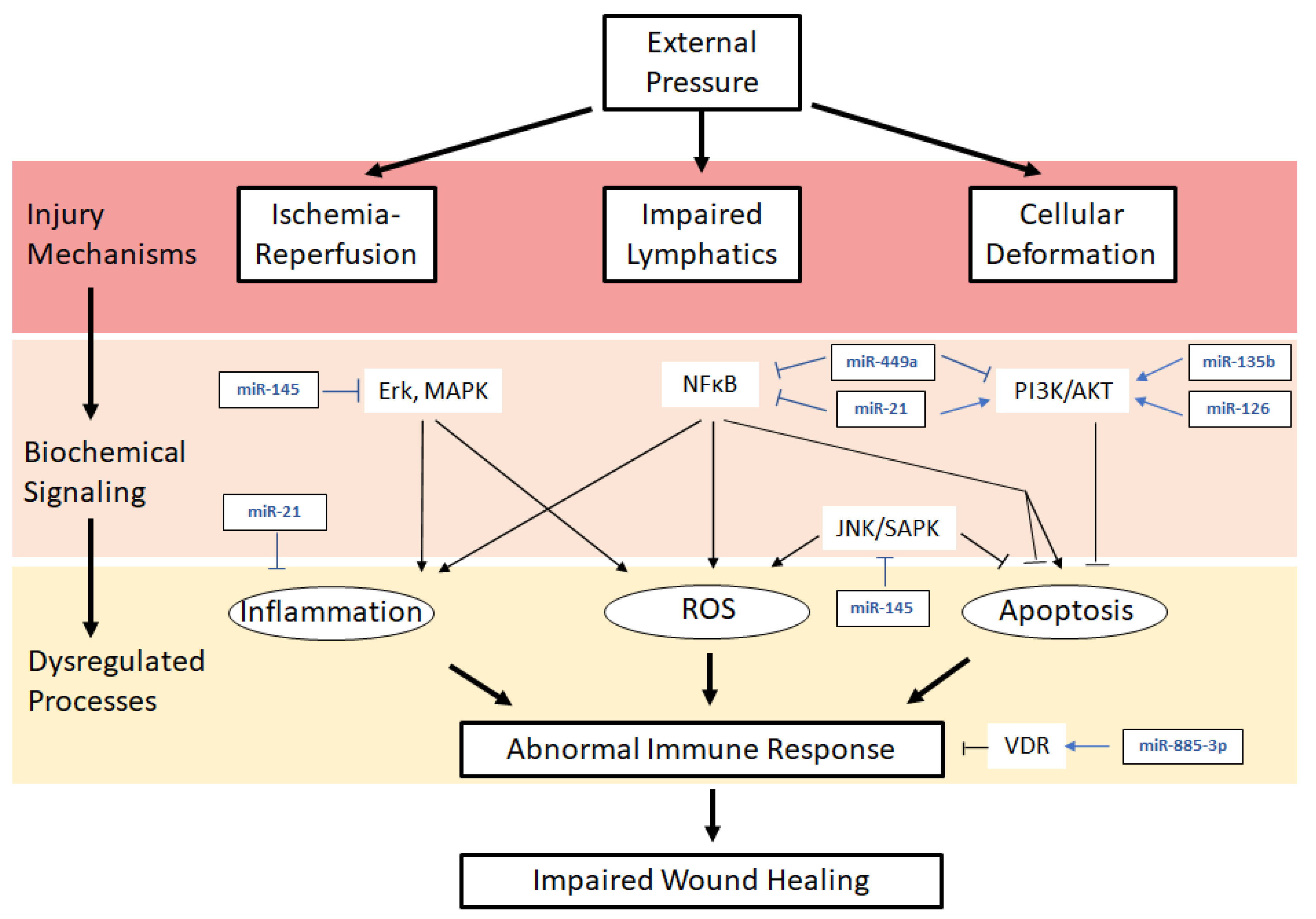
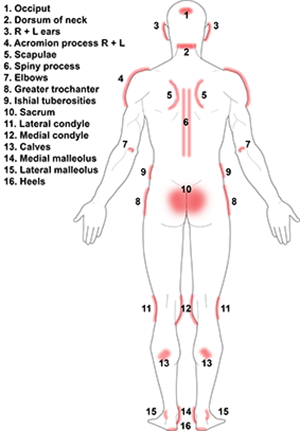
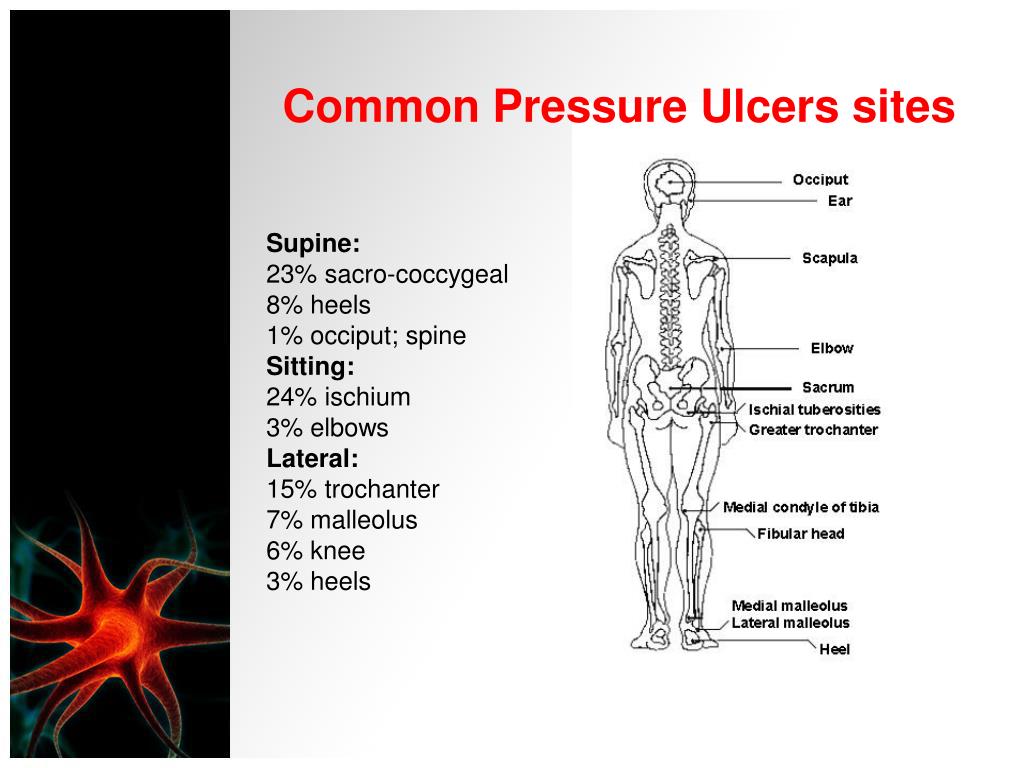
36 pressure ulcer sites diagram
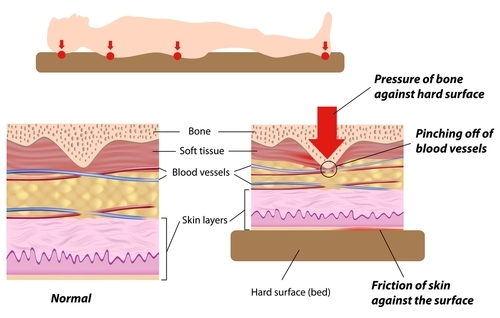
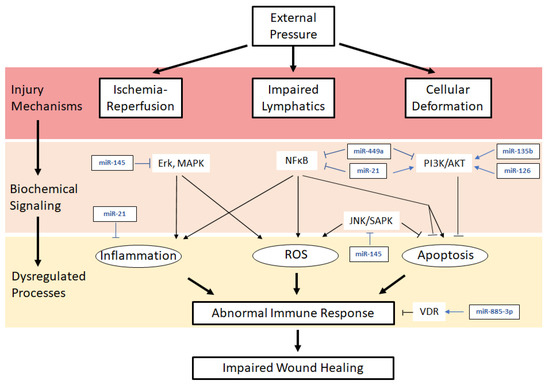
A pressure ulcer is an ulcer related to some form of pressure and should not be confused with ulcers relating to disease (like cancer), vascular flow (venous or arterial) or neuropathy (like in persons with diabetes) You should be able to see a “cause and effect” relating to pressure with the ulcer. Prosper: Pressure Ulcer– Driver Diagram. Outcome/Aim ... Introduce Staff pressure ulcer prevention workbook ... Inspect skin/pressure areas with a frequency.
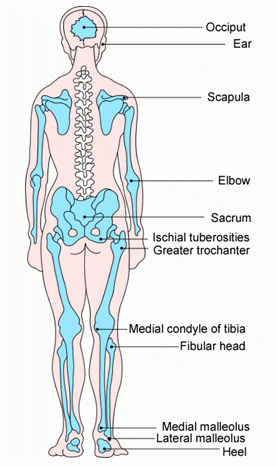
The bridge of the nose, ear, occiput and malleolus do not have (adipose) subcutaneous tissue and Category/Stage III ulcers can be shallow. In contrast, areas of ...
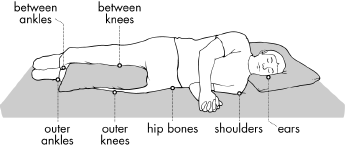
Pressure ulcer sites diagram
The SSKIN bundle can be applied across all areas of care and can be instigated where a service user is deemed at risk of pressure ulcer development as. Secondary hypertension is hypertension due to an identifiable cause, and may result in certain specific additional signs and symptoms. For example, as well as causing high blood pressure, Cushing's syndrome frequently causes truncal obesity, glucose intolerance, moon face, a hump of fat behind the neck and shoulders (referred to as a buffalo hump), and purple abdominal stretch marks. Pressure ulcer risk assessment is a standardized and ongoing process with the goal of identifying patients at risk for the development of a pressure ulcer so that plans for targeted preventive care to address the identified risk can be implemented. This process is multifaceted and includes many components, one of which is a validated risk ...
Pressure ulcer sites diagram. by K Agrawal · 2012 · Cited by 213 — Pressure ulcer in an otherwise sick patient is a matter of concern for the care ... the contribution of Ms. Shrreya Agrawal for preparing the line diagram. –Pressure ulcer –Rash –Infection, cellulitis •Deficiencies can also affect skin: –Vitamin C deficiency causes purplish blotches on lightly traumatized areas. –Zinc deficiency causes redness of the nasolabial fold and eyebrows. 17 Skeleton presentation–Common sites of pressure ulcers. The most common sites are the sacrum, greater trochanters, ischial tuberosities, medical and lateral ... Jan 31, 2019 · Pressure ulcer risk assessment using clinical judgement alone: Braden pressure ulcer risk assessment and training: Pressure ulcer incidence Visual skin assessment Follow‐up: 8 weeks: Study population: RR 1.43 (0.77 to 2.68) 65 more per 1000 (from 35 fewer to 254 more) 180 (1 study) ⊕⊝⊝⊝ Very low 1
10 Dec 2020 — How to use this tool well. The chart contains diagrams of the body and the location of a pressure ulcer is recorded by numbering the location of ... Also check for pressure injuries on the skin over implanted medical devices, such as pacemakers. Pressure points to remember. Common sites of pressure ulcers ... Implementation of the prevention and management of pressure ulcer standards ... Inspect skin / pressure areas regularly to identify pressure damage. A professional is providing skin care (treatment) for a client who has a pressure ulcer. The HCS/AAA/DDD Social Worker/Nurse or other contracted nursing resource must: Verify . with [Health Care Provider Name (HCP)] by ( ) that a treatment plan is in place for the client’s pressure ulcer(s).
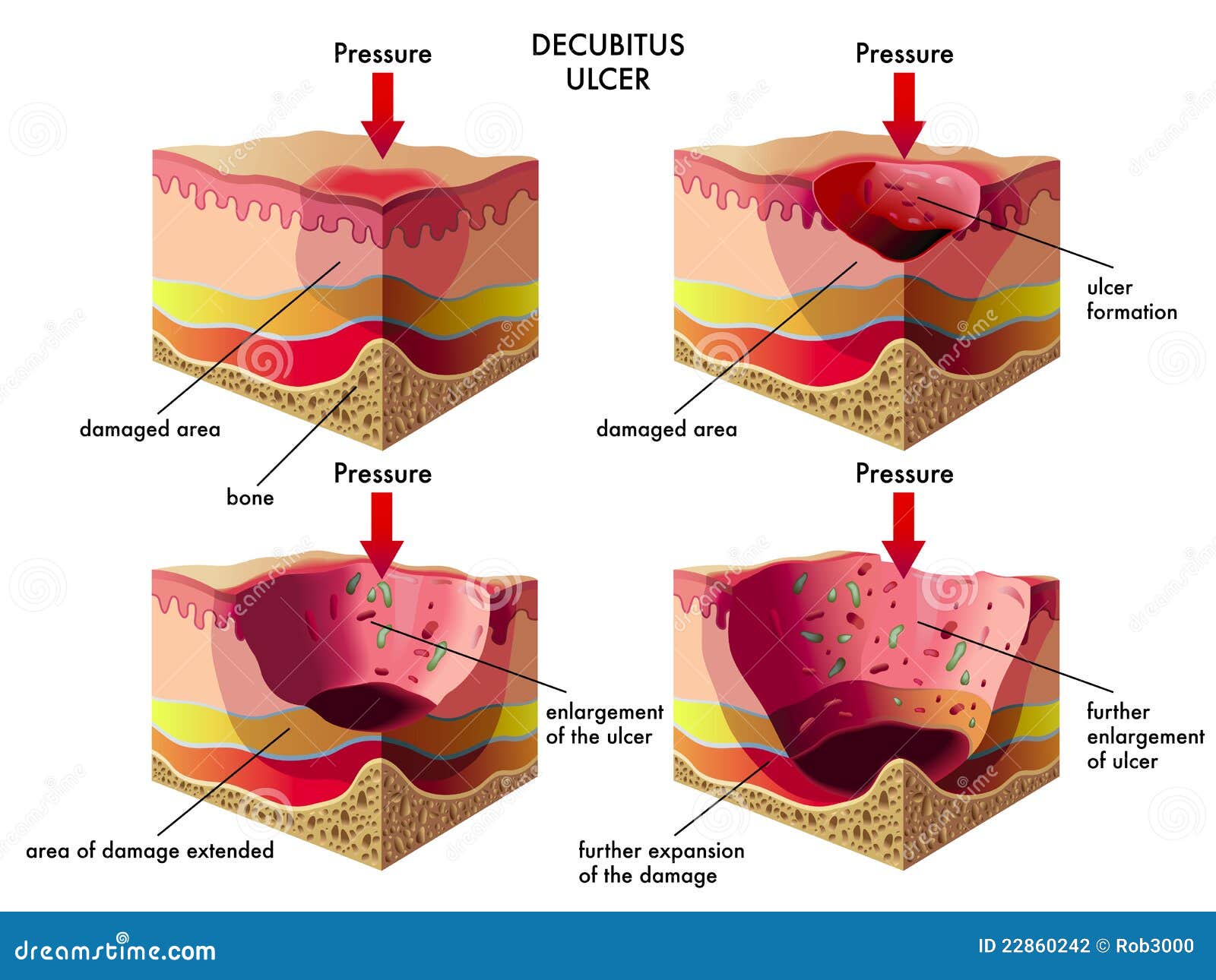
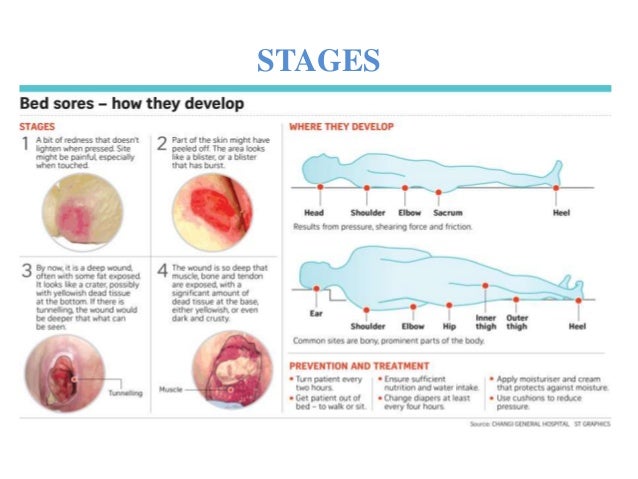
... prominences") and areas that are under the most pressure are at greatest risk for developing pressure sores. diagram of woman sitting in wheelchair. Feb 01, 2018 · Top diagram showing pressure ulcers Stage I: skin intact. Stage II: partial skin loss. Stage III: full-thickness skin loss, subcutaneous tissue exposed. Stage IV: muscle, tendon, bone or organs exposed. Bottom diagram showing unstageable pressure ulcer with tissue damage hidden from observer by eschar over entire wound. Deep tissue injury ... Pressure ulcer risk assessment is a standardized and ongoing process with the goal of identifying patients at risk for the development of a pressure ulcer so that plans for targeted preventive care to address the identified risk can be implemented. This process is multifaceted and includes many components, one of which is a validated risk ... Secondary hypertension is hypertension due to an identifiable cause, and may result in certain specific additional signs and symptoms. For example, as well as causing high blood pressure, Cushing's syndrome frequently causes truncal obesity, glucose intolerance, moon face, a hump of fat behind the neck and shoulders (referred to as a buffalo hump), and purple abdominal stretch marks.
The SSKIN bundle can be applied across all areas of care and can be instigated where a service user is deemed at risk of pressure ulcer development as.





















0 Response to "36 pressure ulcer sites diagram"
Post a Comment