40 nerves of the foot and ankle diagram
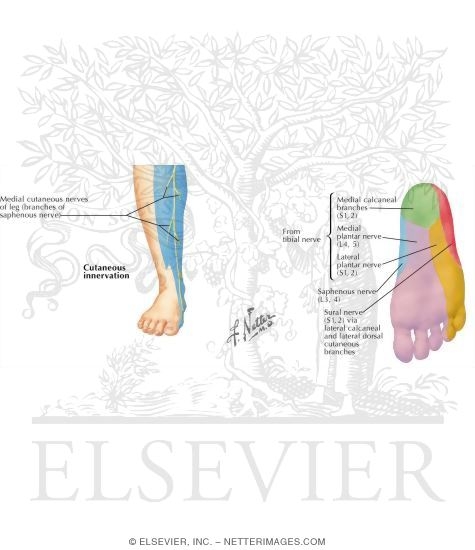
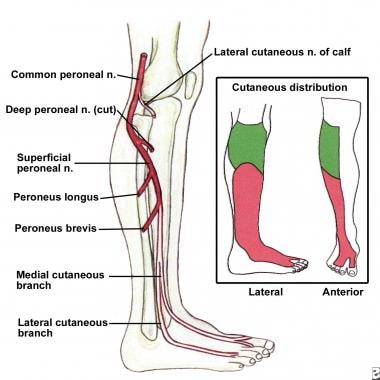
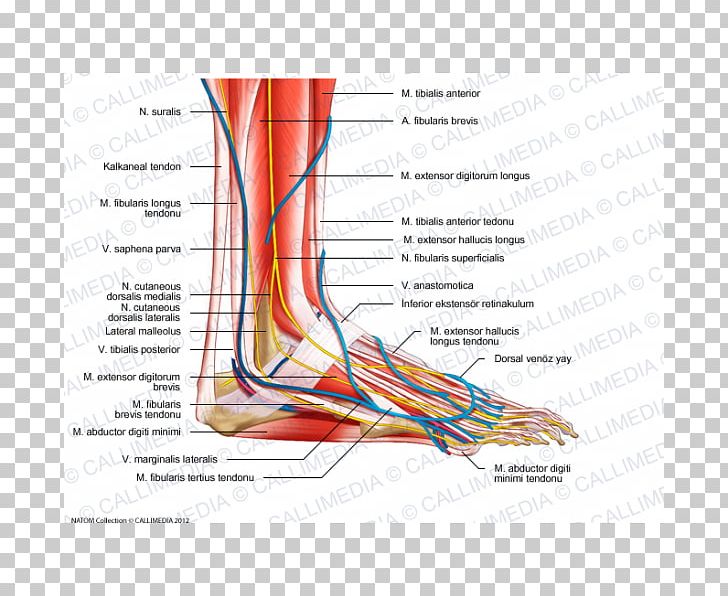
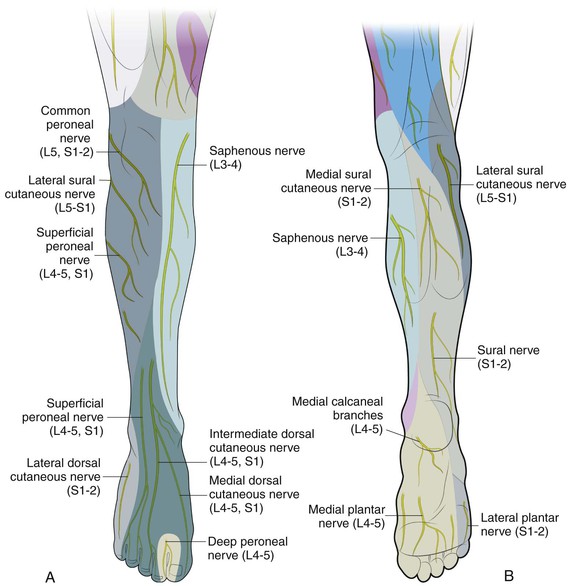
Sural Nerve. The fourth nerve of the foot is another branch of the tibial nerve, known as the sural nerve (Figure 17). This nerve runs from slightly below the knee to the lateral aspect of the foot. It becomes a very superficial nerve at the level of the posterolateral ankle and continues distally to provide sensation to the outside of the foot. Nerves In Foot Diagram. nerves of the leg and foot along its route through the legs the sciatic nerve splits into the tibial and mon fibular peroneal nerves which in turn split into many smaller nerves in the legs and feet the nerves of the foot help move the body and keep balance both while it’s moving and at rest a plete guide to the nerves in your feet foot vitals tingling feet the ...
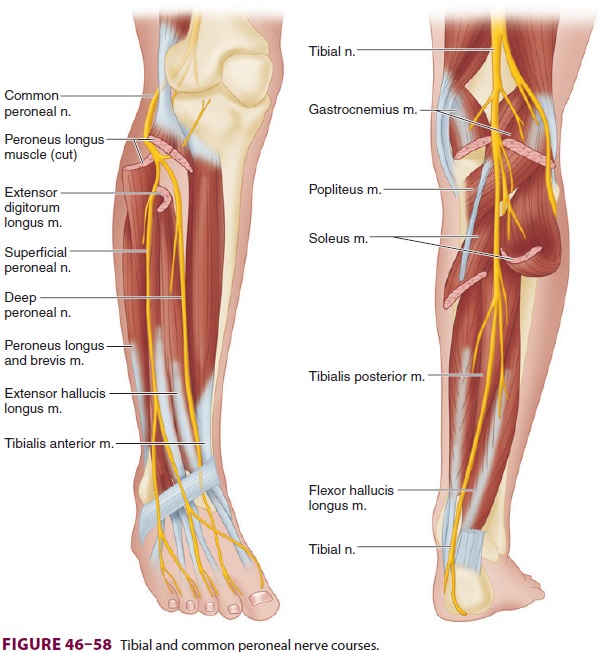
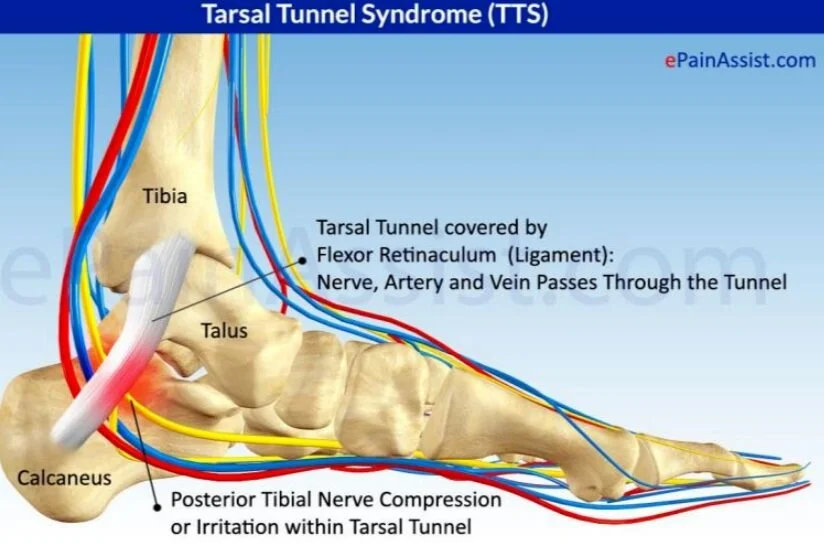
Tibial nerve: This nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. It runs down the leg, between the heads of the gastrocnemius, and passes under the soleus. It curves under the medial malleolus and continues into the foot. It innervates all the muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg. Common fibular (peroneal) nerve: This nerve branches off ...
Nerves of the foot and ankle diagram
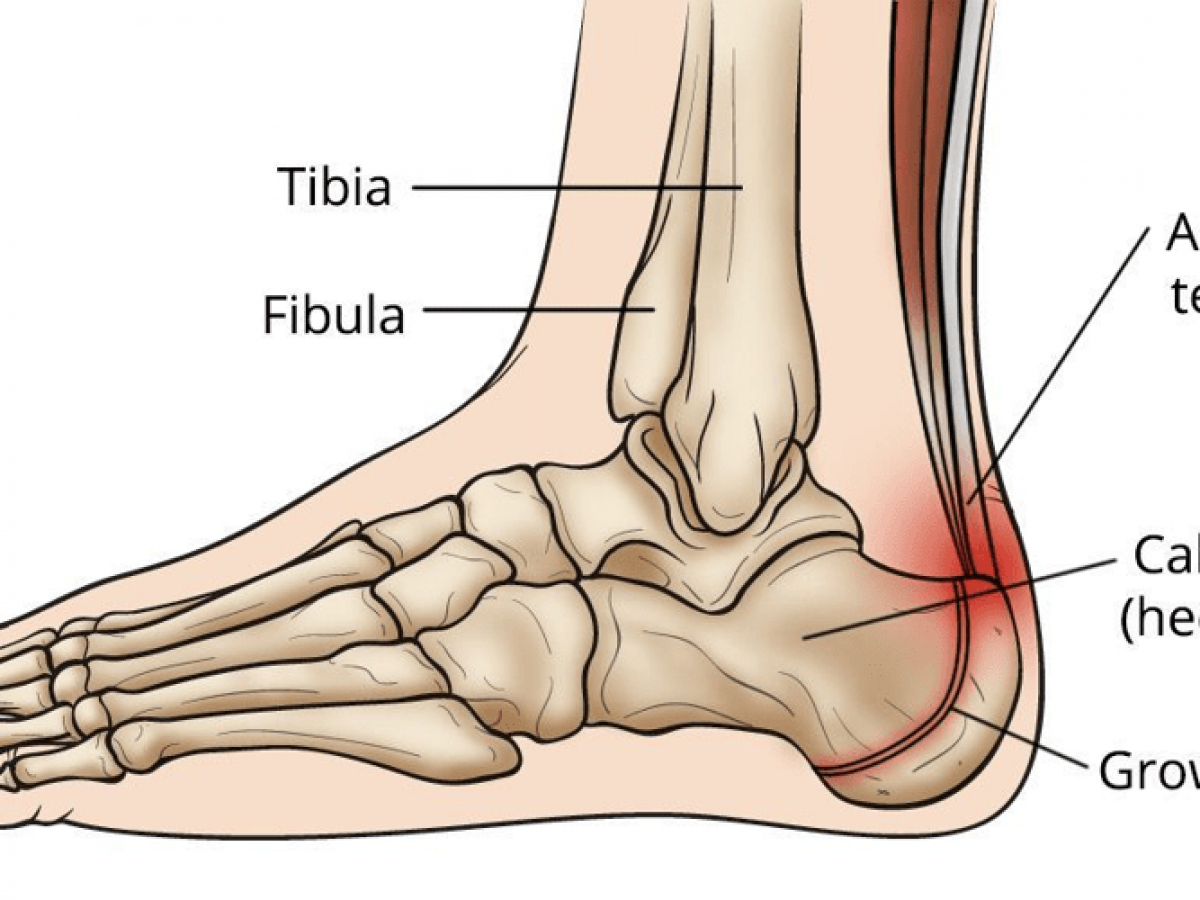
Foot Pain Diagram. Written By: Chloe Wilson BSc(Hons) Physiotherapy Reviewed By: FPE Medical Review Board A foot pain diagram is a great tool to help you work out what is causing your ankle and foot pain. There are a whole range of structures e.g. bones, muscles, tendons and nerves which will each give slightly different foot pain symptoms. The nerves of the ankle are derived from the deep and superficial peroneal nerves, the tibial nerves, and the sural and saphenous nerves. The Foot Bones of the foot as seen from the medial (arch) side. The foot is a firm platform that support the weight of the body. The nerves of the foot help move the body and keep balance both while it’s moving and at rest. All of these nerves extend as branches of nerves in the leg that pass through the ankle and into the foot. The sural nerve branches from the tibial and common fibular nerves and is responsible for feeling on the outside of the foot and the small toe.
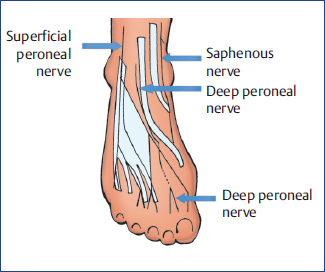
Nerves of the foot and ankle diagram. 1. It is the terminal branch of the saphenous nerve; injury leads to first MTP joint abduction weakness. 6%. (164/2722) 2. It is the terminal branch of the superficial peroneal nerve; injury leads to first interphylangeal joint extension weakness. 3%. A Complete Guide To The Nerves In Your Feet. Problems with nerves in the feet are very common. Many times, an injured nerve will cause intense pain and heat felt within the foot. Nerves act as a network, communicating important information from the foot to the brain. Learn more about the various conditions and problems that can affect the ... Another of the nerves of the foot situated on the side of the big toe is the medial dorsal cutaneous nerve, with cutaneous referring to the fact that this nerve innervates the skin. Also splitting into two branches after crossing the ankle, this dorsal digital nerve innervates the first two toes and the medial side of the third toe. 4:44Dr. Ebraheim's educational animated video describes the nerves of the lower leg in a very easy and simple ...4 Mar 2013 · Uploaded by nabil ebraheim
The superficial peroneal nerve runs down in front of the lateral side of the ankle, and breaks up into several branches. These fan out to provide sensation to ... by M De Maeseneer · 2015 · Cited by 69 — It divides into several thin branches known as dorsal interosseous nerves (1). The lateral branch also provides sensory innervation to the ankle ...Skip main navigation · Abstract · Introduction · Normal Anatomy and Nerve... by A Tang · 2021 · Cited by 1 — The foot receives its nerve supply from the superficial peroneal (fibular) nerve, deep fibular nerve, tibial nerve (and its branches), ... 6 Jul 2020 — The main nerve to the foot, the posterior tibial nerve, enters the sole of the foot by running behind the inside bump on the ankle (medial ...
The peroneal tendons run down together behind the outer side of the ankle and then split before attaching to different parts of the foot. Peroneus Longus: Originates from the upper part of the fibula, passes underneath the foot and attaches by the medial foot arch Peroneus Brevis: Originates from the lower part of the fibula and attaches to the outer side of the midfoot The nerves of the foot help move the body and keep balance both while it’s moving and at rest. All of these nerves extend as branches of nerves in the leg that pass through the ankle and into the foot. The sural nerve branches from the tibial and common fibular nerves and is responsible for feeling on the outside of the foot and the small toe. The nerves of the ankle are derived from the deep and superficial peroneal nerves, the tibial nerves, and the sural and saphenous nerves. The Foot Bones of the foot as seen from the medial (arch) side. The foot is a firm platform that support the weight of the body. Foot Pain Diagram. Written By: Chloe Wilson BSc(Hons) Physiotherapy Reviewed By: FPE Medical Review Board A foot pain diagram is a great tool to help you work out what is causing your ankle and foot pain. There are a whole range of structures e.g. bones, muscles, tendons and nerves which will each give slightly different foot pain symptoms.
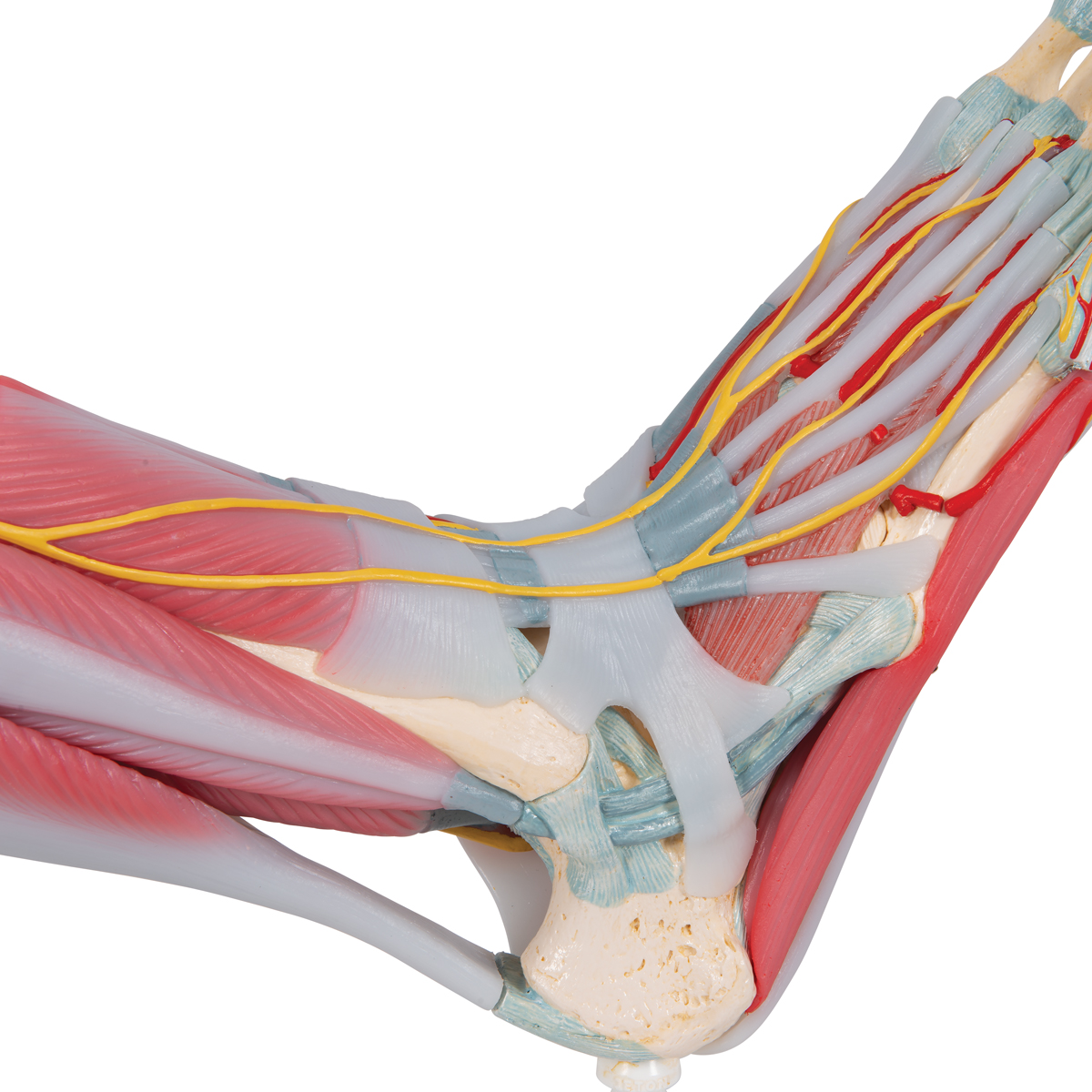
Anatomical Teaching Models Plastic Human Joint Models Foot Skeleton Model With Ligaments And Muscles
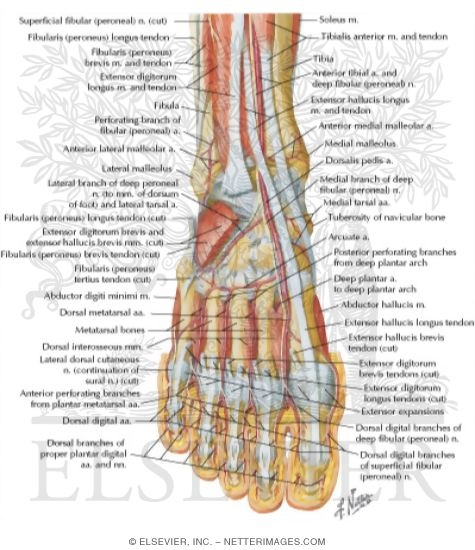
Muscles Arteries And Nerves Of Front Of Ankle And Dorsum Of Foot Deeper Dissection Dorsum Of Foot Deep Dissection

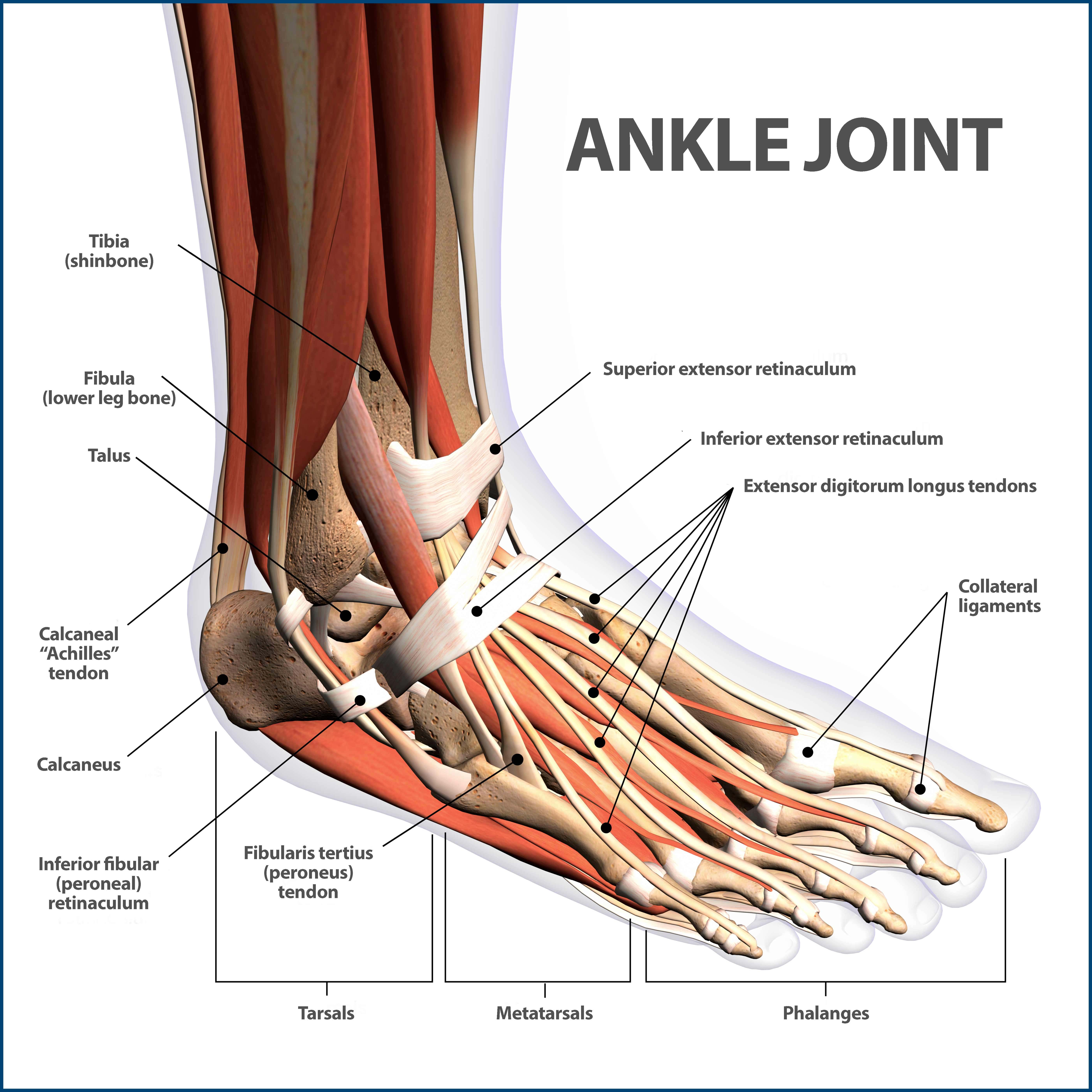
Anatomy Of Ankle And Foot Overview Bones Of Ankle And Foot Functions Blood Vessels And Nerves Parts Of The Foot Arches Of The Foot Joints Tendons And Ppt Download
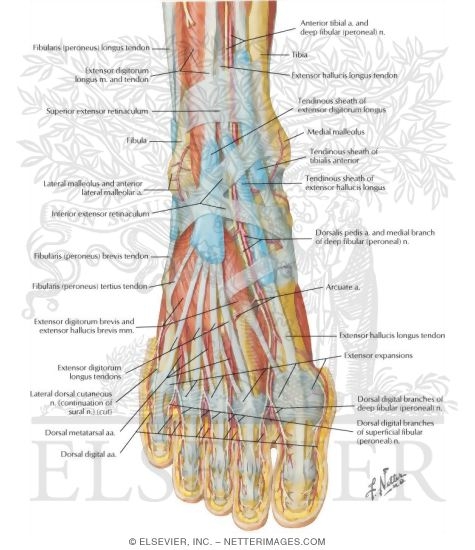
Muscles Arteries And Nerves Of Front Of Ankle And Dorsum Of Foot Superficial Dissection Muscles Of Dorsum Of Foot Superficial Dissection

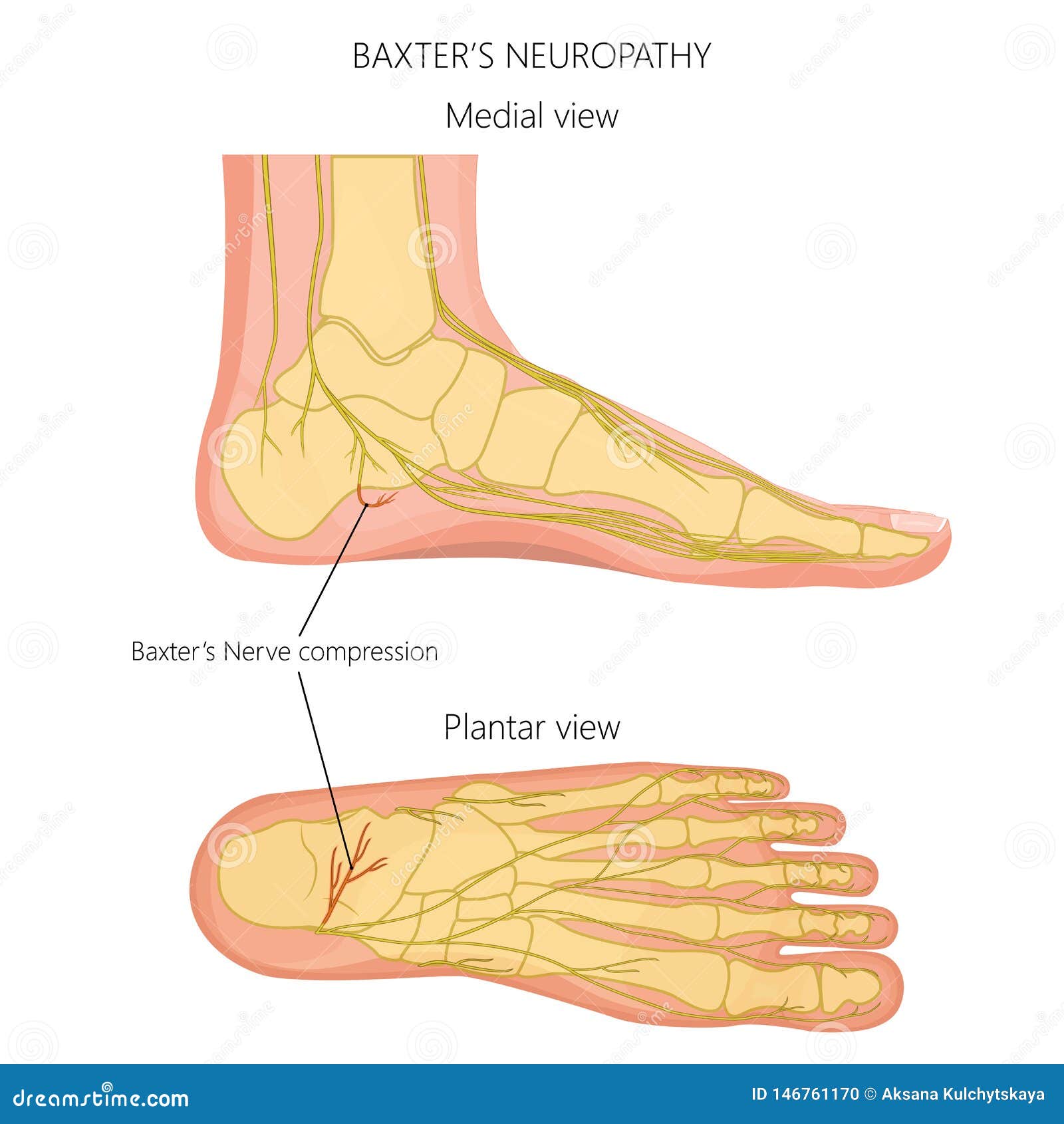
Normal Anatomy And Compression Areas Of Nerves Of The Foot And Ankle Us And Mr Imaging With Anatomic Correlation Radiographics

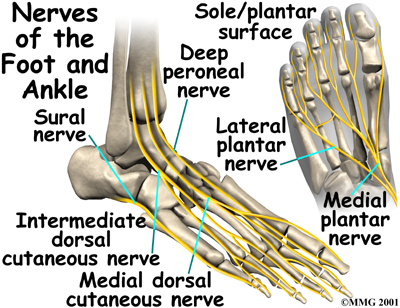

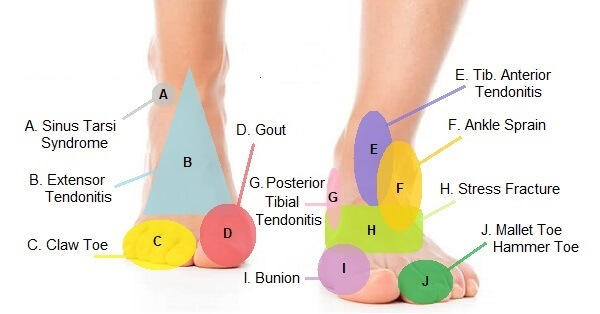













:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/footpainfinal-01-d507e82b3e844d068c0089cbb7004d76.png)

0 Response to "40 nerves of the foot and ankle diagram"
Post a Comment