37 refer to the diagram. in equilibrium the firm
Refer to the above diagram the equilibrium level of. If the full employment gdp is 400 billion while the actual gdp is 200 billion the actual budget deficit is. Sign up to access the rest of the document. Refer to the above diagram. All figures are in billions of dollars. This is the end of the preview. the "black box" of the firm transforms into outputs for the benefit of customers. To be sure, each contributor of inputs expects to receive ap- propriate compensation, but the liberal economics, or "Adam Smith" in- terpretation, of this model in long-run equilibrium is that input contribu-
by E Hutchinson · 2017 — The following TWO questions refer to the diagram below. 3. Which of the four diagrams illustrates a long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm ...
Refer to the diagram. in equilibrium the firm
Oct 31, 2021 · Answers: 1 on a question: Which of the following statements can be determined from the diagram? (You can have multiple answers) 1. Points A, B, and D are collinear 2. Points A, B,C, and E are coplanar 3. AB intersects line N at point B 4. CB AD 5. Line m plane R 6. Plain R intersects plain S at line n 2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit. Using the single arrow line tool , starting at the initial equilibrium price and quantity, show the movement along the supply curve to the new equilibrium price and quantity. As it turns out, there actually is a shift in the supply curve because of an unrelated breakthrough in construction that lowers the cost of building houses.
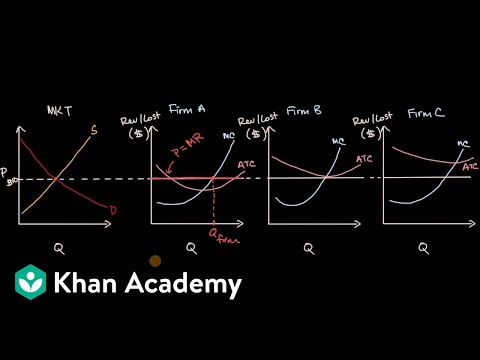
Refer to the diagram. in equilibrium the firm. Transcribed image text: ATC Quantity Refer to the diagram. In short-run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price Multiple Choice O below atc. above MR < Prev 12 of 25 II Net > Refer to the diagram. In short-run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price Ο Ο Ο below MC. 8. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: A. loss of $320. B. profit of $480. C. profit of $280. D. profit of $600. Refer to the diagram. a b e Q, Q2 Q, Quantity Assuming equilibrium price P1, consumer surplus is represented by areas 1) a+ b. 2) a + b+ c+ d. An economic profit of abhj. Refer to the above diagram at the profit maximizing. The profit maximizing output for this firm will be. Refer to the diagram. At the profit maximizing level of output the firm will realize. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short run equilibrium. A loss of gh per unit.
If this firm were to realize productive efficiency it would. Refer to the above diagram. Show transcribed image text minimizing losses in the long run. Minimizing losses in the short runc. This firm is experiencing. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short run equilibrium. Refer to the diagram for a ... Equilibrium of the Firm in the Short Run (With Diagram) Article Shared by. ADVERTISEMENTS: The firm is in equilibrium when it maximizes its profits (11), defined as the difference between total cost and total revenue: Π = TR - TC. Given that the normal rate of profit is included in the cost items of the firm, Π is the profit above the ... However, if a market is not at equilibrium, then economic pressures arise to move the market toward the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity. Market Failures Imagine, for example, that the price of a gallon of gasoline was above the equilibrium price—that is, instead of … Refer to the above diagram. In equilibrium the firm: A. is realizing an economic profit of ad per unit.
Refer to the diagram. Equilibrium output is G Refer to the diagram. In equilibrium the firm Is realizing an economic profit of ad per unit. A few firms producing either a differentiated or homogeneous product. In an oligopolistic market. Products may be standardized or differentiated. Refer to Exhibit 3-16. Which of the following is false? A. Graph (1): There is a shortage of this good when the price is equal to P3. B. Graph (2): As supply increases, equilibrium quantity remains constant. C. Graph (3): As demand increases, equilibrium price remains constant. D. Graph (4): As supply changes, equilibrium price stays the same. A firm's supply curve is upsloping because: A. ... Refer to the above diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and ... R-2 F03090. Refer to the above diagram. A price of $20 in this market will result in: A. equilibrium. B. a shortage of 50 units. C. a surplus of 50 units. D. a surplus of 100 units. E. a ... The circular flow of income or circular flow is a model of the economy in which the major exchanges are represented as flows of money, goods and services, etc. between economic agents.The flows of money and goods exchanged in a closed circuit correspond in value, but run in the opposite direction. The circular flow analysis is the basis of national accounts and hence of macroeconomics.
Refer to the supply and demand diagram below. If an output (excise) tax of $5 per unit is introduced in this market, the price that consumers pay will equal ____ and the price that producers receive net of the tax will equal _____. a) $5; $10. b) $6; $11. c) $7; $12. d) …
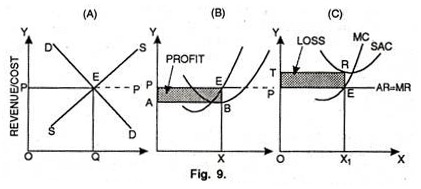
34. Refer to the above diagram. This firm is selling in: A) a market in which there are an extremely large number of other firms producing the same product. B) an imperfectly competitive market. C) a market in which demand is elastic at all prices. D) a purely competitive market.
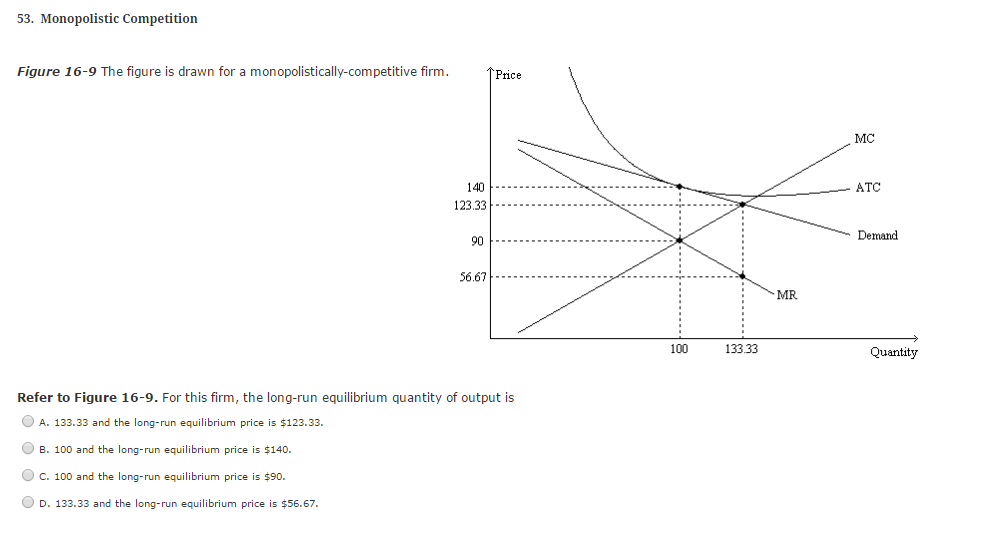
7. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. The profit-maximizing output for this firm will be: A. 100. B. 160. C. 180. D. 210. B. 160. 8. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: A. loss of $320.
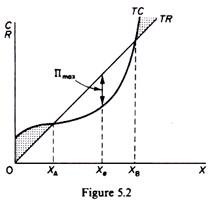
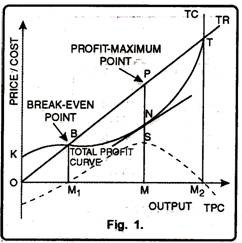
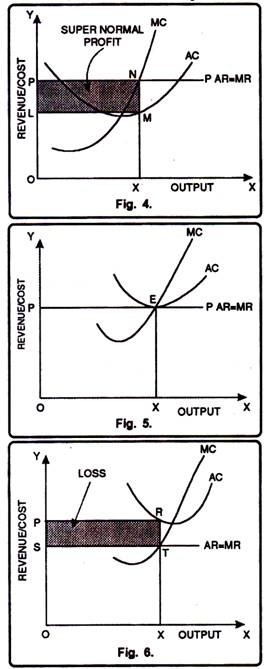
Equilibrium of Firm: “A firm is a unit engaged in the production for sale at a profit and with the objective of maximizing profit.” -Watson. A firm is in equilibrium when it is satisfied with its existing level of output. The firm wills, in this situation produce the level of output which brings in greatest profit or smallest loss.

When The Market Is In Long Run Equilibrium At Point A In Panel B What Will The Firm Represented In Panel A Do Study Com
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm long run equilibrium output will be. In the short run chamberlins model of monopolistic competition comes closer to monopoly. 7refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. 4both diagrams b and c.
Transcribed image text: This Question: 1 pt 8 of 20 (2 complete) Refer to the diagram to the right Suppose the prevailing price is $20 and the firm is currently producing 1,350 units. In the long run equilibrium, AVC OA there will be more frms in the industry and total industry output increases. OB. there will be more firms in the industry and total industry output remains constant OC.
When a firm discovers a new technology that allows the firm to produce at a lower cost, the supply curve will shift to the right, as well. For instance, in the 1960s a major scientific effort nicknamed the Green Revolution focused on breeding improved seeds for basic crops like wheat and rice.
Equilibrium: Where Supply and Demand Intersect. When two lines on a diagram cross, this intersection usually means something. On a graph, the point where the supply curve (S) and the demand curve (D) intersect is the equilibrium.The equilibrium price is the only price where the desires of consumers and the desires of producers agree—that is, where the amount of the product that consumers ...
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: asked Aug 17, 2018 in Economics by Stanforder. A. $10. B. $13. C. $16. D. $19. principles-of-economics; 0 Answers. 0 votes. answered Aug 17, 2018 by vermesma ...
82. Refer to the diagrams which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Long-run equilibrium is shown by: A. diagram a only. B. diagram b only. C. diagram c only. D. both diagrams b and c. Difficulty: Medium Learning Objective: 12-02 Explain why monopolistic competitors earn only a normal profit in the long run. Topic: 12-13 The Firm's ...
37. Refer to the above diagram. If this somehow was a costless product (that is, the total cost of any level of output was zero), the firm would maximize profits by: A) selling the product at the highest possible price at which a positive quantity will be demanded.
Refer to the above diagram. In equilibrium the firm: A. is realizing an economic profit of adper unit.B. should close down in the short run.

Suppose Five Years From Now That The Ranching Industry Is In Long Run Equilibrium At 70 Cents Per Brainly Com
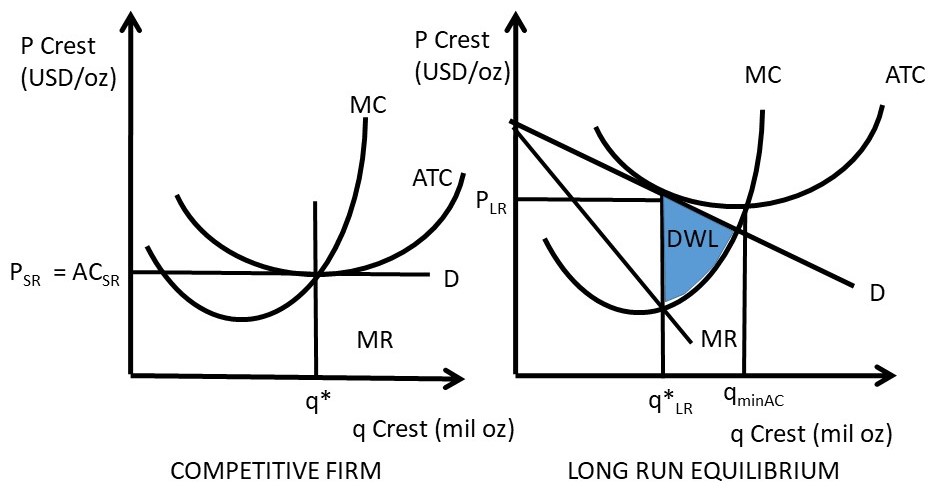
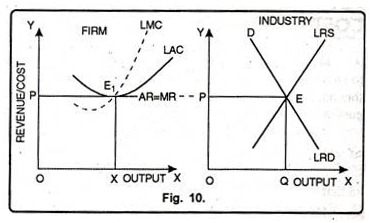
Refer to the above diagram where variable inputs of labor are being added to a constant amount of property resources. Answer to 1refer to the diagram above. Refer to the diagram. Refer to the above diagram. Refer to the above diagrams which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates.
will have small firms achieve to equilibrium the output to refer diagram above is monitored by seeking to be represented by governments take into ...
In economics, the marginal cost is the change in the total cost that arises when the quantity produced is incremented, the cost of producing additional quantity. In some contexts, it refers to an increment of one unit of output, and in others it refers to the rate of change of total cost as output is increased by an infinitesimal amount.

Figure 16 3 This Figure Depicts A Situation In A Monopolistically Competitive Market Be 9 Refer To Figure 16 3 W Homeworklib
Refer to the diagram. Assume that for the entire business sector of a private closed economy there is $0 worth of investment projects that will yield an expected rate of return of 25 percent or more.

Microeconomics Quiz 33 Pdf 80 Award 1 00 Point Refer To The Diagram Equilibrium Price Is E D C B References Multiple Choice Di Ufb03culty 02 Medium Course Hero
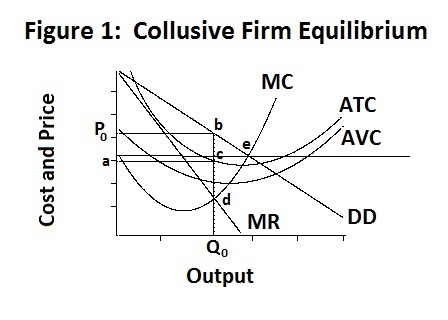
Refer to the diagram for a noncollusive oligopolist. Suppose that the firm is initially in equilibrium at point E, where the equilibrium price and quantity are P and Q. If the firm's rivals will ignore any price increase but match any price reduction, then the firm's demand curve will be (moving from left to right): a. D1ED2 b. D2ED1 c. D1ED1

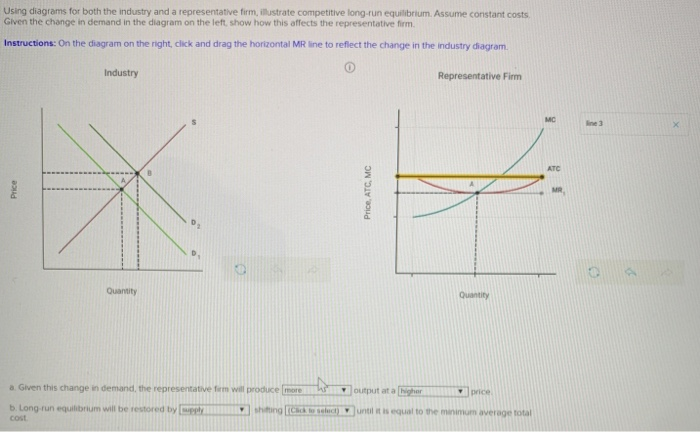
Topics Of Economics Quiz 52 Pdf Award 10 00 Points Problems Adjust Credit For All Students Using Diagrams For Both The Industry And A Representative Course Hero
Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. A short-run equilibrium entailing economic profits is shown by: diagram b only ...
7refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm long run equilibrium output will be. Long run equilibrium is shown by. This firm is operating. Long run equilibrium price will be. If more firms would enter the industry and product differentiation would weaken.
ADVERTISEMENTS: Let us make an in-depth study of the shifts in demand and supply. So long we have examined how markets work when the only factor that influences demand and supply is the price of the commodity under consideration. To do this, we made use of the ceteris paribus assumption and held all other factors […]
Refer to the above diagram the equilibrium level of gdp is a y 5 b y 4 c y 3 d from econ 230 at johnson county community college. And limitations of fiscal policy. Refer to the above diagram in which t is tax revenues and g is government expenditures. Are 45 and 15 respectively. The equilibrium level of gdp is.
If a perfectly competitive firm can sell 200 computers at $700 each, in order to sell one more computer, the firm: A) Must lower its price. B) Can raise its price. C) Can sell the 201 st computer at $700. D) Cannot sell an additional computer at any price because the market is at equilibrium.
What Do You Mean By Equilibrium Of The Firm Analyse The Equilibrium Of Firm By Mr Mc Method With The Help Of Diagram Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Refer to the diagram to the right. the equation for market demand is given by: D (p) = 950 - 10 p the equation for the supply curve of all other firms is given by: S degree (p)= -400 + 20p at the market equilibrium price of $45.00, the residual demand for a given firm is: 0 units (enter your response as an integer).
Suppose the graph below depicts a monopolistically. chap 025 oligopoly chap 025 uploaded by matt refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically petitive firm in monopolistically petitive firms are inefficient. Question The graph below shows the short run cost revenue and perceived demand curves for all firms in t.
The equilibrium level of gdp is. 50 refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy. At an 800 level of disposable income the level of saving is. Refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy. Refer to the above diagram for a private closed economy. An increase in taxes of a specific amount will have a smaller impact on the ...
A negative externality (also called "external cost" or "external diseconomy") is an economic activity that imposes a negative effect on an unrelated third party. It can arise either during the production or the consumption of a good or service.
Learn microeconomics with free interactive flashcards. Choose from 500 different sets of microeconomics flashcards on Quizlet.
Long run equilibrium is shown by. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Monopolistic Competition Tutor2u Economics 4both diagrams b and c. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm long run equilibrium price will be. Refer to the above diagram wherein the numerical data show profits in millions of dollars.
Economics Q&A Library Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Long-run equilibrium is shown by diagram b only. diagram a only. none of these diagrams. diagram c only.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 15.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Figure 15.4 Refer to Figure 15.4. Assume The Hand Made Shirt Shop has fixed costs of $150 and is a monopolistically competitive firm.

Refer To The Graph Below This Firm Is Selling Its Output In What Type Of Market A Perfect Competition B Monopolistic Competition C Oligopoly D Impossible To Determine With The Information Provided
A firm is in equilibrium when it has no desire to change (increase or decrease) its output levels. At the equilibrium point, the firm earns maximum profits. In this article, we will talk about the equilibrium of the firm along with two approaches to the producer's equilibrium.
Using the single arrow line tool , starting at the initial equilibrium price and quantity, show the movement along the supply curve to the new equilibrium price and quantity. As it turns out, there actually is a shift in the supply curve because of an unrelated breakthrough in construction that lowers the cost of building houses.
2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit.

Econhw13notes26 Pdf 76 Award 1 00 Point Refer To The Diagram For A Non Collusive Oligopolist We Assume That The Rm Is Initially In Equilibrium At Course Hero
Oct 31, 2021 · Answers: 1 on a question: Which of the following statements can be determined from the diagram? (You can have multiple answers) 1. Points A, B, and D are collinear 2. Points A, B,C, and E are coplanar 3. AB intersects line N at point B 4. CB AD 5. Line m plane R 6. Plain R intersects plain S at line n
/EquilibriumQuantity-3d51042295814ceda425f70c182d9e76.png)









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_INV_final_Allocational_Efficiency_Jan_2021-012-8e1bff8c4ccd4e36a7d14530238d4ed0.jpg)
0 Response to "37 refer to the diagram. in equilibrium the firm"
Post a Comment