39 orbital diagram for p
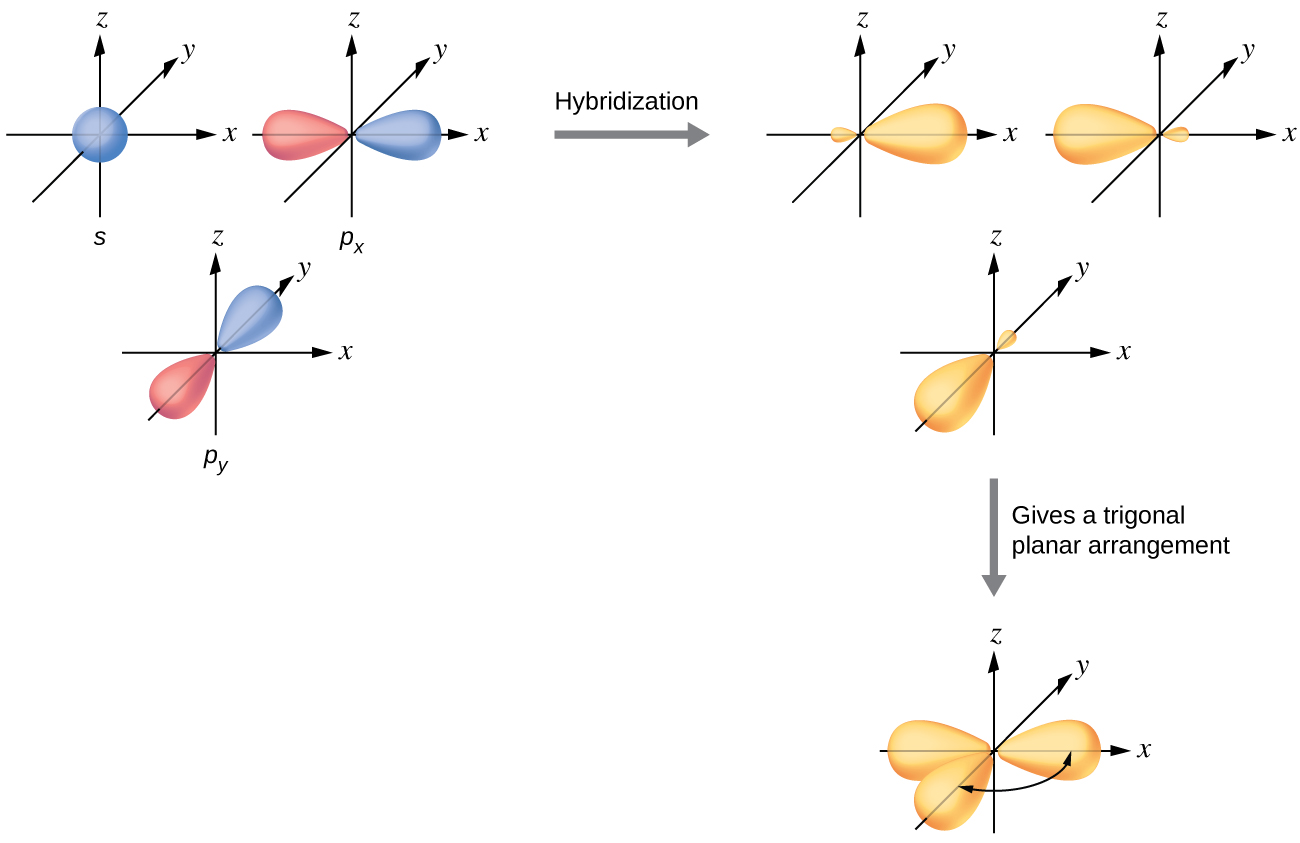
Orbital hybridisation - Wikipedia In chemistry, orbital hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals (with different energies, shapes, etc., than the component atomic orbitals) suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory.For example, in a carbon atom which forms four single bonds the valence-shell s orbital combines with three ... 9.8: Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry LibreTexts 20-02-2022 · The three p orbitals correspond to the three directions of Cartesian space, and are frequently designated p x, p y, and p z, to indicate the axis along which the orbital is aligned. Of course, in the free atom, where no coordinate system is defined, all directions are equivalent, and so are the p orbitals.
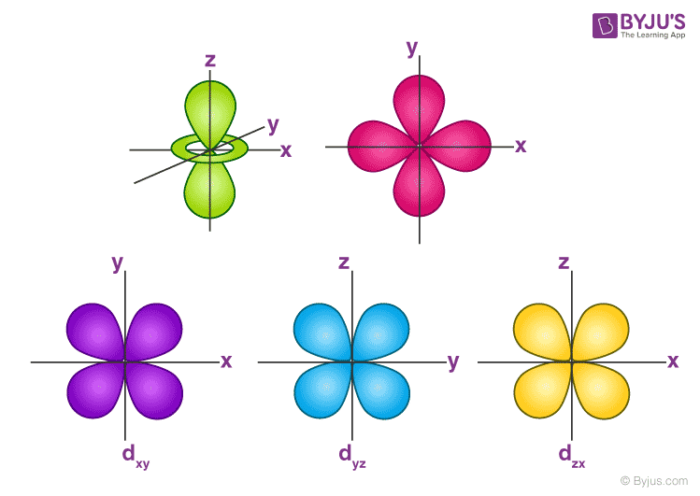
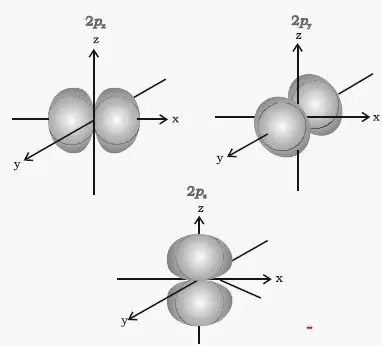
Atomic orbital - Wikipedia The p z orbital is the same as the p 0 orbital, but the p x and p y are formed by taking linear combinations of the p +1 and p −1 orbitals (which is why they are listed under the m = ±1 label). Also, the p +1 and p −1 are not the same shape as the p 0, since they are pure spherical harmonics.

Orbital diagram for p
Orbital Diagram of All Elements (Diagrams given Inside) Orbital diagram of Hydrogen (H) 2: Orbital diagram of Helium (He) 3: Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11 ... Degenerate Orbitals - Explanation With Diagram, Examples ... p orbital has 3 degenerate orbitals. All three have the same energy levels. Each orbital is first assigned with only one electron. The second electron will be of opposite spin. Each orbital is filled and the total is six electrons. Explanation of Degenerate Orbitals with Diagram Orbital filling diagrams - The Cavalcade o' Chemistry The orbital filling diagram of boron. I skipped past beryllium because I was getting bored. The electron configuration of boron is 1s²2s²2p¹, which means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and one electron in the 2p orbitals. This gives us an orbital filling diagram of:
Orbital diagram for p. Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine … Carbon Orbital diagram, Electron configuration, and ... The orbital diagram for Carbon is drawn with 3 orbitals. The orbitals are 1s, 2s, and 2p. The Carbon orbital diagram contains 2 electrons in 1s orbital, 2 electrons in 2s orbital, and the rest two electrons in 2p orbital. Orbital diagram for a ground-state electron configuration of Carbon atom is shown below- Orbital Box Diagram Phosphorus - schematron.org The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two electrons in the 3s. Since the 3s if now full we'll move to the 3p where we'll place the remaining three electrons. Therefore the Phosphorus electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 3. A molecular orbital diagram or MO diagram for ...
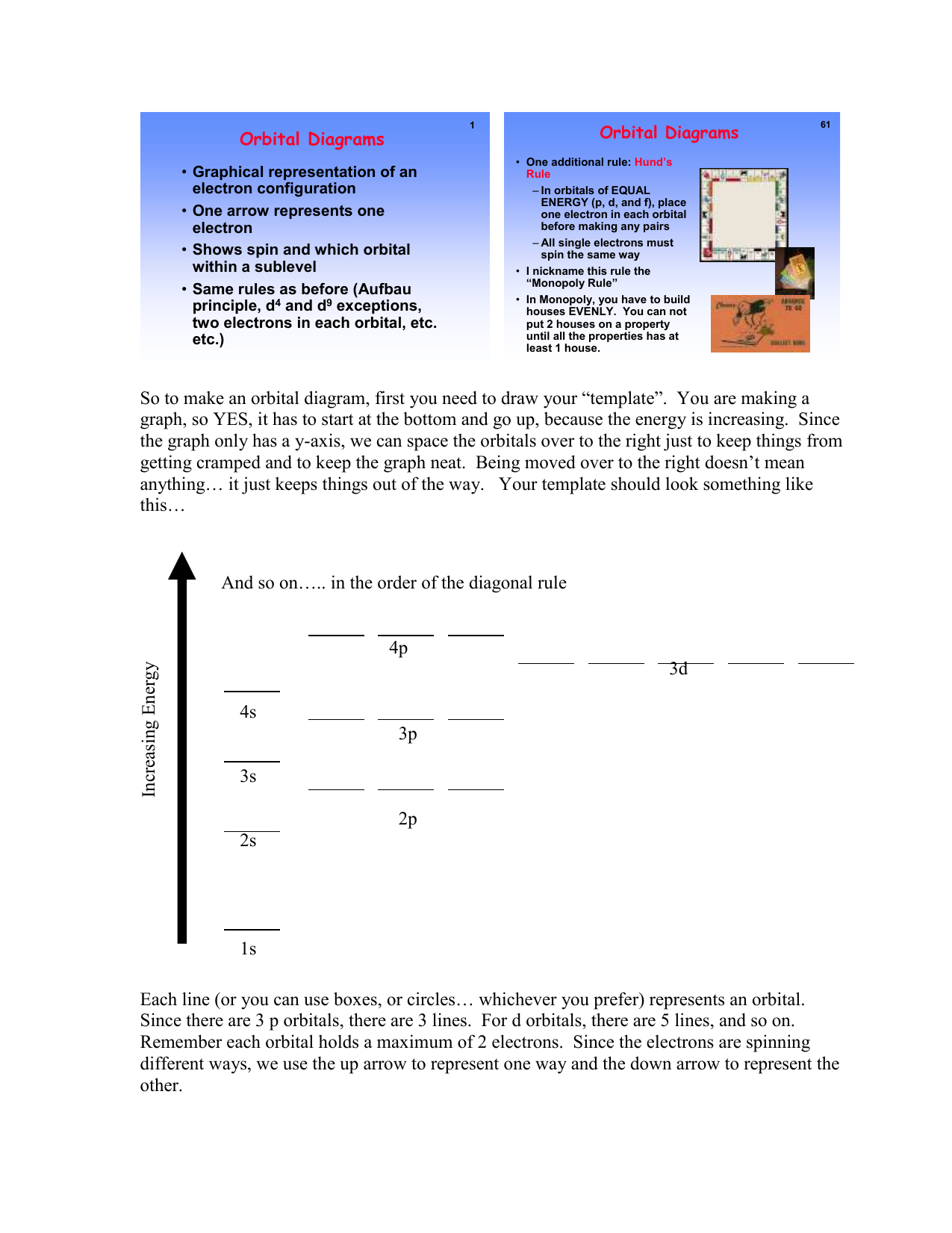
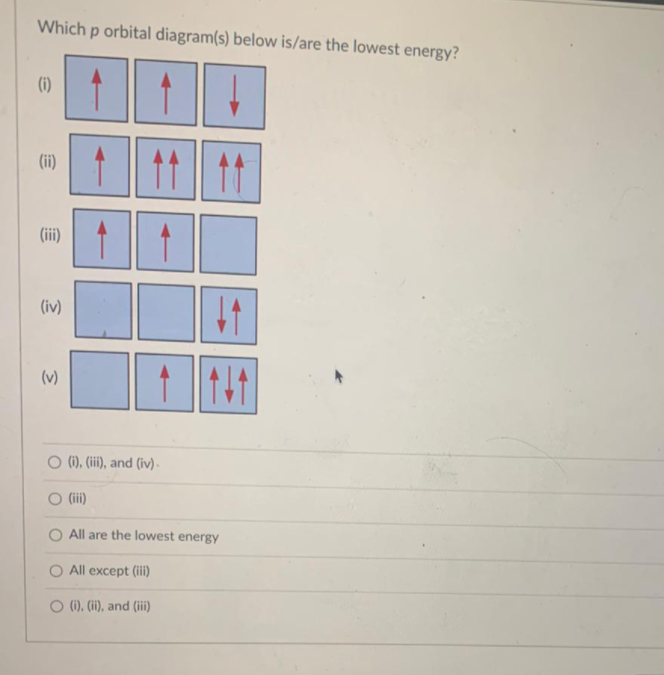
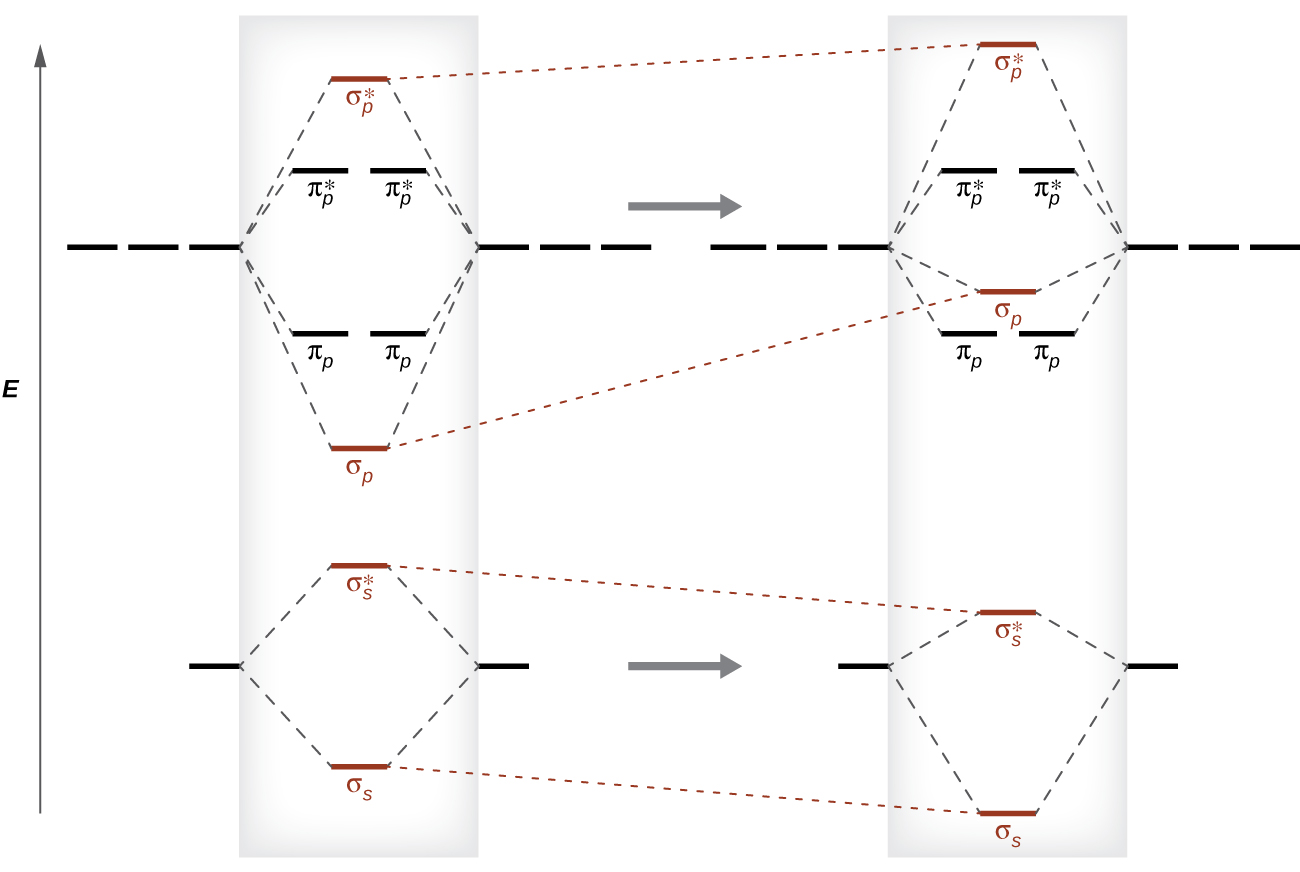
What Are The 3 Rules For Orbital Diagrams An orbital diagram is a clear way of showing exactly how many paired and unpaired electrons there are in a particular atom's electronic configuration. ... When a single p orbital contains a pair of electrons, the act of pairing the electrons raises the energy of the orbital. Thus the 2p orbitals for O, F, and Ne are higher in energy than the ... Orbital Diagrams - Concept - Chemistry Video by Brightstorm Orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. Three rules are useful in forming orbital diagrams. According to the Auf Bau Principle, each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital. The Pauli Exclusion Principle says that only two electrons can fit into an single orbital. s,p,d,f Orbitals - Chemistry | Socratic The p orbitals at the second energy level are called 2px, 2py and 2pz. There are similar orbitals at subsequent levels: 3px, 3py, 3pz, 4px, 4py, 4pz and so on. All levels except the first have p orbitals. d ORBITALS 7.7 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Fundamentals Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 7.7.9). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right.
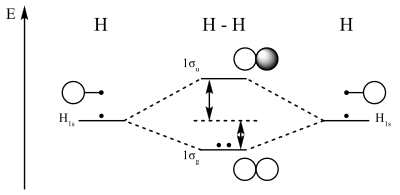
Electron Configuration for Phosphorus (P) - UMD The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two electrons in the 3s. Since the 3s if now full we'll move to the 3p where we'll place the remaining three electrons. Therefore the Phosphorus electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 3. Orbital Diagram For Arsenic - schematron.org Orbital Diagram For Arsenic. Because the 4p section has 3 orbitals, but Arsenic ends with 4p3. It'll want to leave as few orbitals empty, so you have three arrows pointing up. The orbital diagram of arsenic can be written as 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6 4s2 3d10 4p3. Arsenic has 33 electrons, including 3 in itsoutermost shell. schematron.org! Molecular Orbitals - Introductory Chemistry - 1st Canadian ... The head-to-head overlap giving σ molecular orbitals results in greater overlap, making its bonding molecular orbital the most stable and lowest energy, while the σ* antibonding is least stable and has the highest energy (Figure 9.24 "Molecular orbital energy diagram for homonuclear diatomic molecules made from atoms of atomic number 8-10"). Orbitals Chemistry (Shapes of Atomic Orbitals) - Shape of ... Each p orbital consists of two sections better known as lobes which lie on either side of the plane passing through the nucleus. The three p orbitals differ in the way the lobes are oriented whereas they are identical in terms of size shape and energy.
CN- lewis structure, molecular orbital diagram, and, bond order Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3.
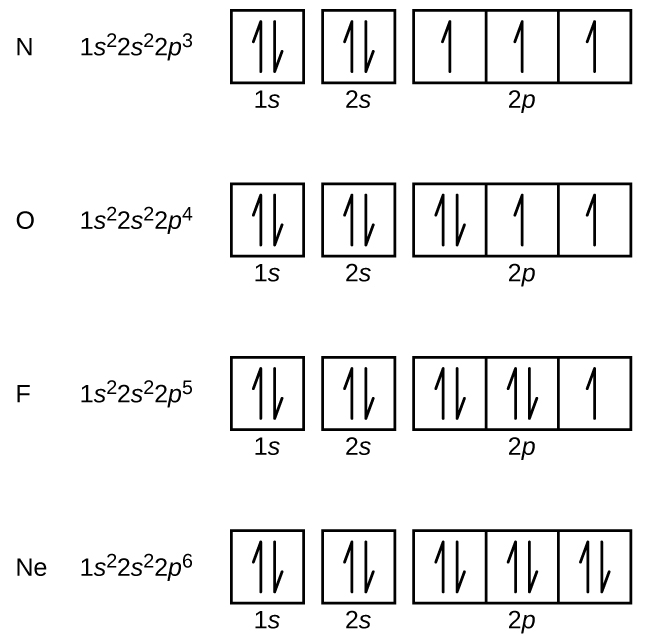
Chlorine(Cl) electron configuration and orbital diagram The p-orbital has three sub-orbitals. The sub-orbitals are p x, p y, and p z. Each sub-orbital can have a maximum of two electrons. In the chlorine(Cl) ground-state electron configuration, the five electrons of the 3p orbital are located in the p x, p y, and p z sub-orbitals.
What is orbital diagram in chemistry? - Frequentlyasked An orbital filling diagram is the more visual way to represent the arrangement of all the electrons in a particular atom. In an orbital filling diagram, the individual orbitals are shown as circles (or squares) and orbitals within a sublevel are drawn next to each other horizontally.
Krypton Orbital Diagram What does this tell us about electrons in p orbitals? An orbital diagram is similar to electron configuration, except that instead of indicating the atoms by total numbers, each orbital is shown with up and down arrows to represe nt the electrons in each orbital. Refer to the related link to see an illustration of an orbital diagram for aluminum.
How to Do Orbital Diagrams - Sciencing The first number is the principal quantum number (n) and the letter represents the value of l (angular momentum quantum number; 1 = s, 2 = p, 3 = d and 4 = f) for the orbital, and the superscript number tells you how many electrons are in that orbital. Orbital diagrams use the same basic format, but instead of numbers for the electrons, they ...
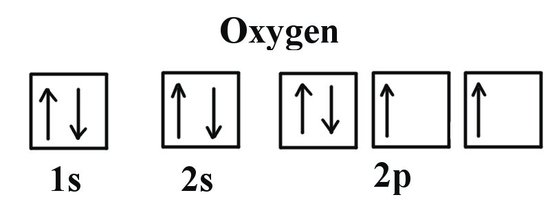
Oxygen(O) electron configuration and orbital diagram The p-orbital can have a maximum of six electrons. So, the remaining four electrons enter the 2p orbital. Therefore, the oxygen(O) electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4. How to write the orbital diagram for oxygen(O)? To create an orbital diagram of an atom, ...
Memahami Konfigurasi Elektron dan Diagram Orbital Lebih ... Diagram Orbital. Nah sekarang kita akan menggambarkan konfigurasi elektron memakai diagram orbital, teman. Sebenarnya gambarnya cukup mudah kok. Suatu subkulit punya sejumlah orbital. Orbital itu digambarkan sebagai persegi dan berisi garis setengah panah yang mewakili elektron. Subkulit s punya 1 orbital, p punya 3 orbital, d punya 5 orbital ...
Oxygen(O) electron configuration and orbital diagram The Aufbau principle is that the electrons present in the atom will first complete the lowest energy orbital and then gradually continue to complete the higher energy orbital. These orbitals are named s, p, d, f. The electron holding capacity of these orbitals is s = 2, p = 6, d = 10 and f = 14.
Phosphorus(P) electron configuration and orbital diagram Phosphorus (P) orbital diagram 1s is the closest and lowest energy orbital to the nucleus. Therefore, the electron will first enter the 1s orbital. According to Hund's principle, the first electron will enter in the clockwise direction and the next electron will enter the 1s orbital in the anti-clockwise direction.
Hund's Rule and Orbital Filling Diagrams | Chemistry for ... Orbital filling diagram for carbon. Oxygen has four 2 p electrons. After each 2 p orbital has one electron in it, the fourth electron can be placed in the first 2 p orbital with a spin opposite that of the other electron in that orbital. Figure 4. Orbital filling diagram for oxygen. Summary
S P D F orbitals Explained - 4 Quantum Numbers, Electron ... This video explains s, p, d, and f orbitals, sublevels, and their shapes. It discusses the 4 quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms. n represents the energy leve...
Electron Configuration for Phosphorus (P) - UMD The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next two electrons in the 3s. Since the 3s if now full we'll move to the 3p where we'll place the remaining three electrons. Therefore the Phosphorus electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 3. Video: Phosphorus Electron Configuration Notation
8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams — Flux Science You can also add the number of each orbital type's electrons; they should also be equal. Organizing Molecular Orbitals These diagram reveal just how complementary the MO theory and VB theory are through the presence of the sigma (σ) and pi (π) symbols.
How to Write the Orbital Diagram for Phosphorus (P) - YouTube To write the orbital diagram for the Phosphorus atom (P) first we need to write the electron configuration for just P. To do that we need to find the number...
Orbital Mechanics II - Practice – The Physics Hypertextbook The satellite is initially in an elliptical orbit as shown in the diagram to the right. At perigee (the point of closest approach) the distance from the center of the satellite to the center of the Earth is r p and the speed of the satellite is v p.
Degenerate orbitals definition: - BYJU'S Online learning Programs … p orbital has 3 degenerate orbitals. All three have the same energy levels. Each orbital is first assigned with only one electron. The second electron will be of opposite spin. Each orbital is filled and the total is six electrons. Explanation of Degenerate Orbitals with Diagram
Orbital Filling Diagram For Sulfur Show the orbital-filling diagram for (bromine).Status: Resolved. Show the orbital-filling diagram for S (sulfur). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top%(15). 1. Describe the two differences between a 2p x orbital and a 3p y orbital.
Molecular Structure & Bonding - Michigan State University Likewise, the orbital correlation diagram for methane provides another example of the difference in electron density predicted by molecular orbital calculations from that of the localized bond model. Click on the compound names for these displays. A cartoon of the p and π orbitals of a double bond may be examined by .
Orbitals - Department of Chemistry & Biochemistry 1) An orbital is a three dimensional description of the most likely location of an electron around an atom. Below is a diagram that shows the probability of finding an electron around the nucleus of a hydrogen atom. Notice that the 1s orbital has the highest probability. This is why the hydrogen atom has an electron configuration of 1s 1 .
Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry In p orbitals, the wave function gives rise to two lobes with opposite phases, analogous to how a two-dimensional wave has both parts above and below the average. We indicate the phases by shading the orbital lobes different colors. When orbital lobes of the same phase overlap, constructive wave interference increases the electron density.
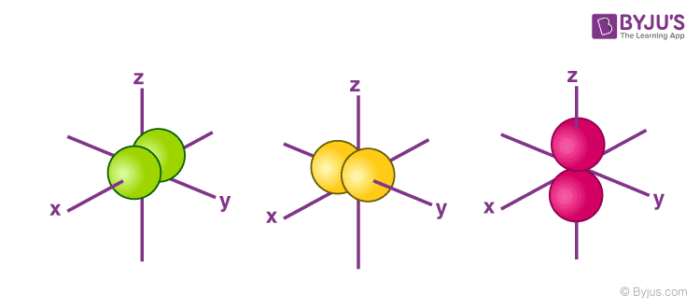
Atomic Orbitals Definition, Shapes, Examples And Diagrams p-orbitals. The p-orbitals are dumb-bell shape contains two lobes just like two identical balloons tied together. The two lobes stay away from each other along the axial line. When n = 1, there are no p-orbitals, it has only s-orbital. When n = 2 and l = 1, the magnetic quantum number m = +1, 0, -1. Thus three dumb-bell shape p-orbitals are ...
Orbital filling diagrams - The Cavalcade o' Chemistry The orbital filling diagram of boron. I skipped past beryllium because I was getting bored. The electron configuration of boron is 1s²2s²2p¹, which means that there are two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and one electron in the 2p orbitals. This gives us an orbital filling diagram of:
Degenerate Orbitals - Explanation With Diagram, Examples ... p orbital has 3 degenerate orbitals. All three have the same energy levels. Each orbital is first assigned with only one electron. The second electron will be of opposite spin. Each orbital is filled and the total is six electrons. Explanation of Degenerate Orbitals with Diagram
Orbital Diagram of All Elements (Diagrams given Inside) Orbital diagram of Hydrogen (H) 2: Orbital diagram of Helium (He) 3: Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11 ...






















0 Response to "39 orbital diagram for p"
Post a Comment