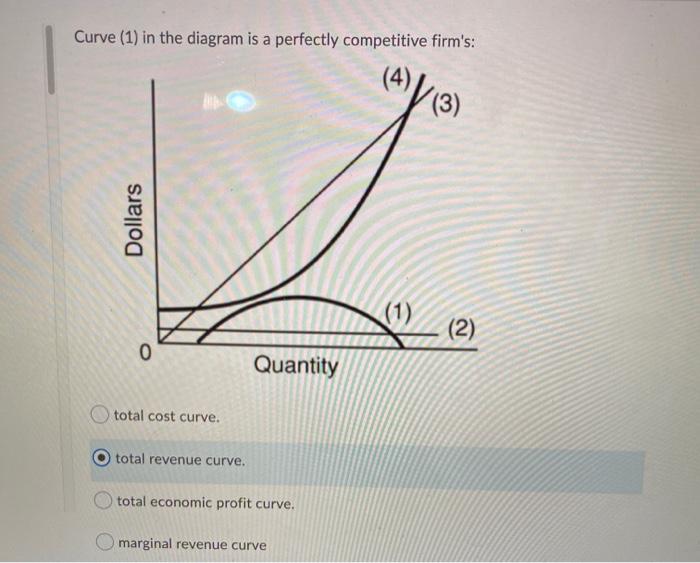
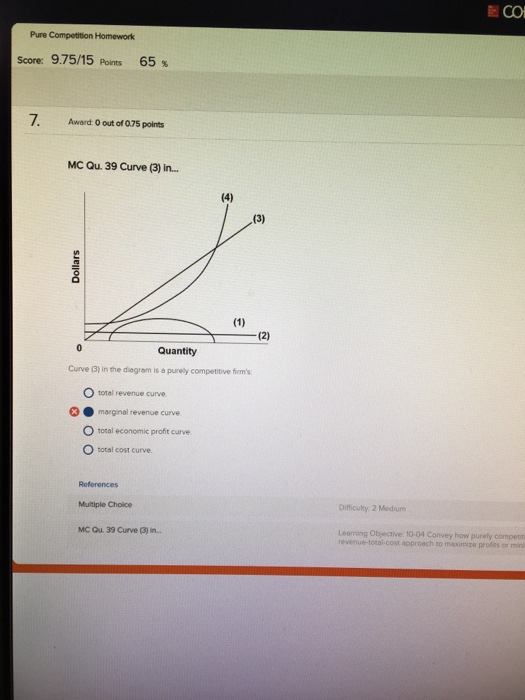
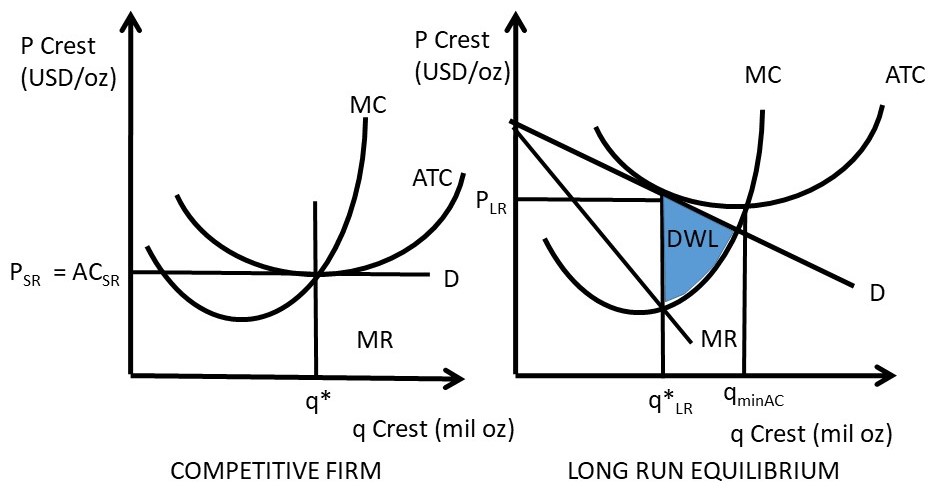
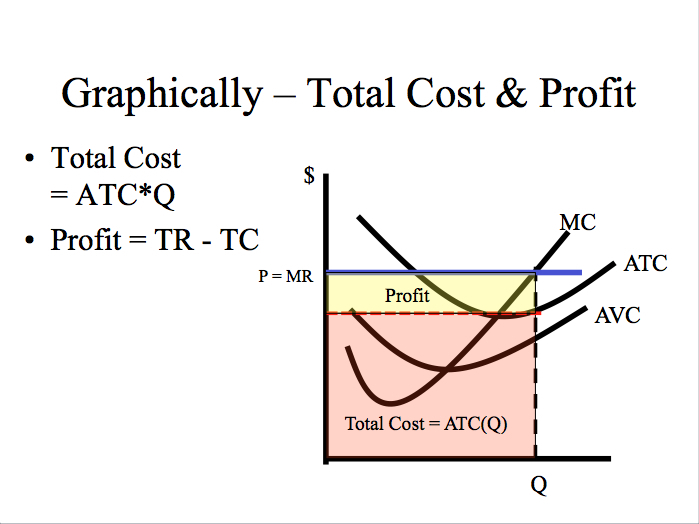
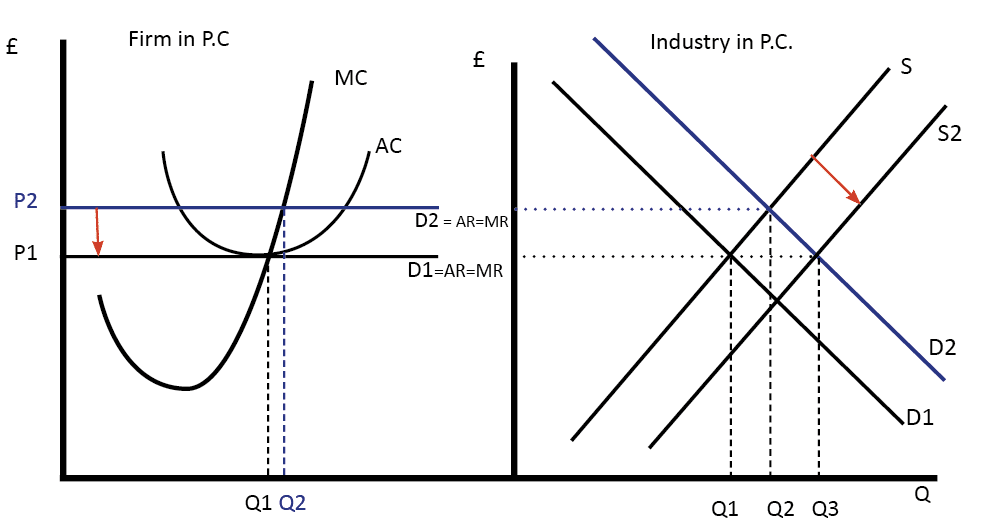
37 curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
42 at p3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will - Wiring ... Apr 03, 2022 · Refer to the diagram. the firm's supply curve is the segment of the: Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve c represents; Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. this firm is experiencing; Refer to the diagram. at p3, this firm will: Refer to the diagram. to maximize profit or minimize ... Curve 3 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms A ... 39. Curve (3) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. B. total revenue curve . 40. Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve.
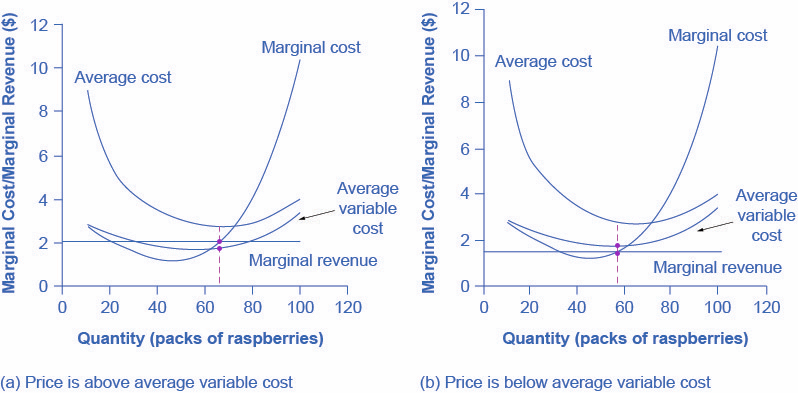
Answered: What is the short run Supply Curve for… | bartleby "That segment of a competitive firm's marginal-cost curve that lies above its average-variable-cost curve constitutes the shortrun supply curve for the firm." Explain using a graph and words. arrow_forward

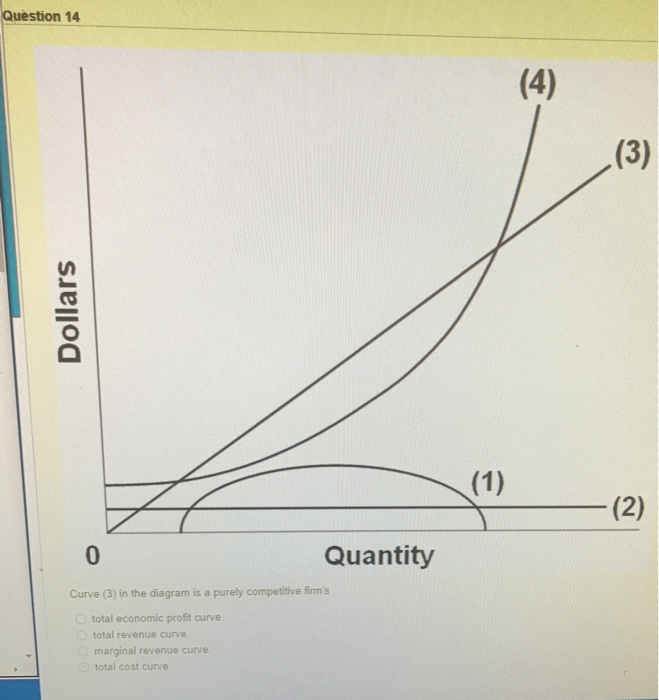
Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
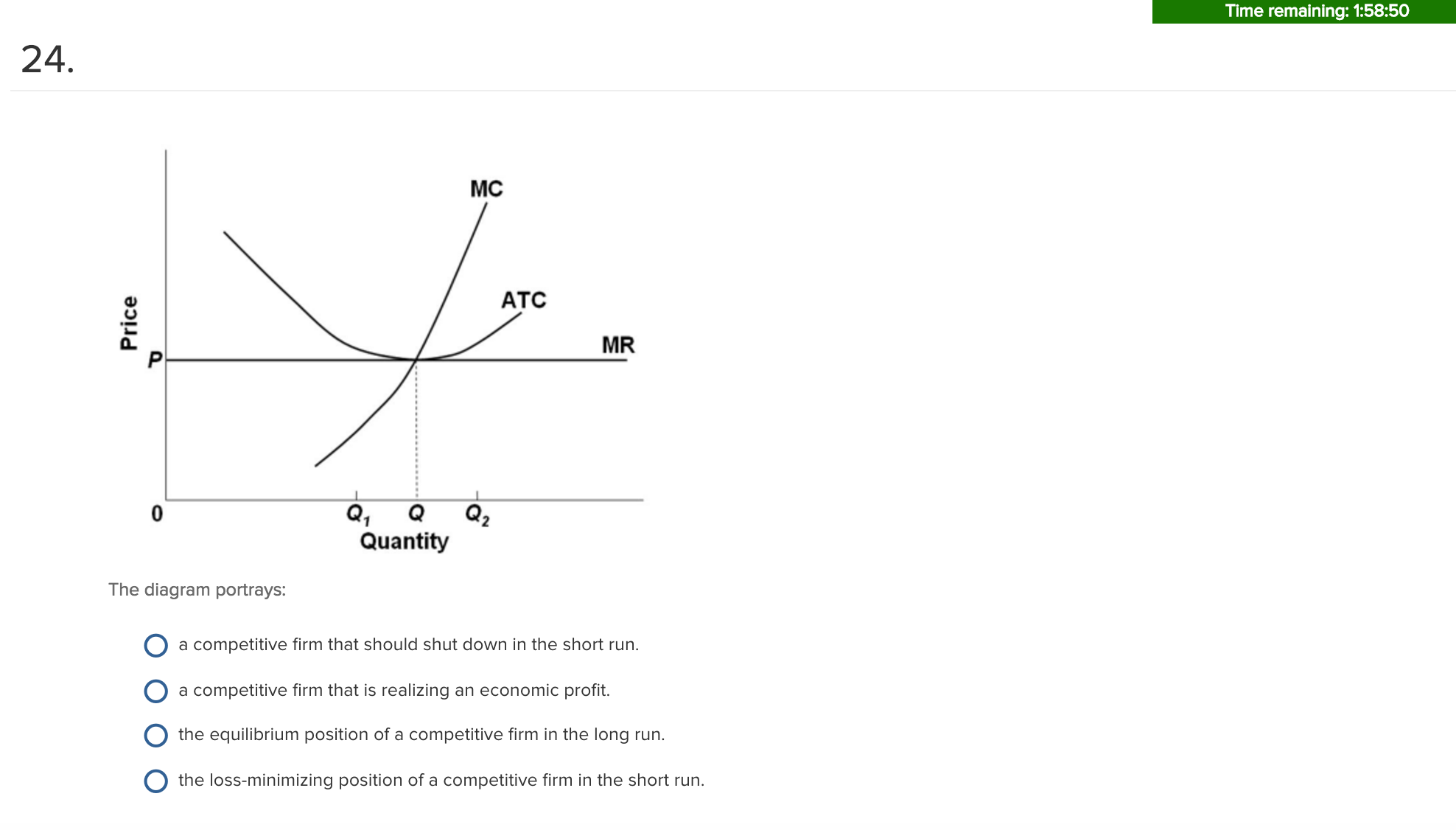
Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... 38. Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. Answer: C Topic: Profit maximization in the short run. Learning Objective: 11-03: Convey how purely competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run. PDF ECO 211 Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit. Econ exam 3 Flashcards - Quizlet The demand and supply curves for the lawnmower market intersect at a market price of $500. In a perfectly competitive market, a profit-maximizing quantity requires that P = MC. In the cost diagram, a horizontal line at a price of $500 intersects the MC curve at a …
Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. Your grades could look better! - Fountain Essays We have writers who are always ready to work and take up orders with a short deadline. We deliver papers as early as after 3 hours of ordering. You only have to indicate the short deadline and our support team will help pick the best and most qualified writer in your field. ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com If a firm in a purely competitive industry is confronted with an equilibrium price of $5, its marginal revenue: a. may be either greater or less than $5 b. will also be $5 c. will be less than $5 d. will be greater than $5. b. will also be $5. Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: a. total cost curve b. total revenue curve ECON202 CH10 Heath Flashcards - Quizlet A purely competitive firm's total revenue (TR) is a straight line that slopes _____ and to the _____. upward; right In a perfectly competitive market, the demand curve for an individual firm is perfectly __________ at the market price. Ch10quiz - paws.wcu.edu neither its demand nor its marginal revenue curve. 3. The short-run shut-down point for a purely competitive firm occurs: A. at any point where price is less than the minimum AVC. B. between the two break-even points. C. at any point where total revenue is less than total cost. D. at any point where the firm is not making an economic profit.
Solved Question 14 I (3) Dollars - (2) Quantity Curve (3) in ... Question: Question 14 I (3) Dollars - (2) Quantity Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's total economic profit curve total revenue curve marginal revenue curve total cost curve This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (5 ratings) Curve 3 is the total revenue curve. Chapter 10 Homework Flashcards | Quizlet Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: total cost curve ... the vertical distance between curves (3) and (4) is the greatest. Econ160: Practice Questions Chapters 7, 9 10 & 11 - Quizlet The average fixed cost of 3 units of output is: $13.33. ... Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: total revenue curve. MICROECONOMICS Flashcards | Quizlet The diagram shows two product supply curves. It indicates that over range q1q2, price elasticity of supply is greater for s1 than for s2 Refer to the diagram and assume that price decreases from $10 to $2. The coefficient of the price elasticity of supply (midpoint formula) relating to this price change is about 1, and supply is unit elastic
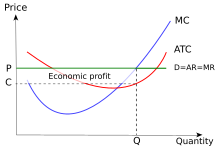
Pure Competition A supply curve which shows the quantity of a product a firm in a purely competitive industry will offer to sell at various prices in the short run; the portion of the firm's short-run marginal cost curve which lies above its average variable cost curve. revmncmp Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: A. loss of $320. B. loss of $280. C. profit of $480. D. profit of $600. E. profit of $360. 7. R-2 F25037 Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to Explain why profit maximization is not the best goal for a ... 23.3.2022 · Explain why profit maximization is not the best goal for a company Supply Curve of a Firm and Industry (With Diagram) Short run supply curve of a perfectly competitive firm is that portion of marginal cost curve which is above average variable cost curve. According to C.E. Ferguson, "The short run supply curve of a firm in perfect competition is precisely its Marginal Cost Curve for all rates of output equal to or greater than the rate of output associated with minimum average variable cost."
The Psychological Contract - BusinessBalls.com Here are a couple of diagram interpretations, offered here as useful models in understanding Psychological Contracts. Venn diagram Here is a Venn diagram representing quite a complex view of the Psychological Contract, significantly including external influences, which are often overlooked in attempting to appreciate and apply Psychological Contracts theory.
DOC Chapter 9: Four Market Models 2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit. 3.
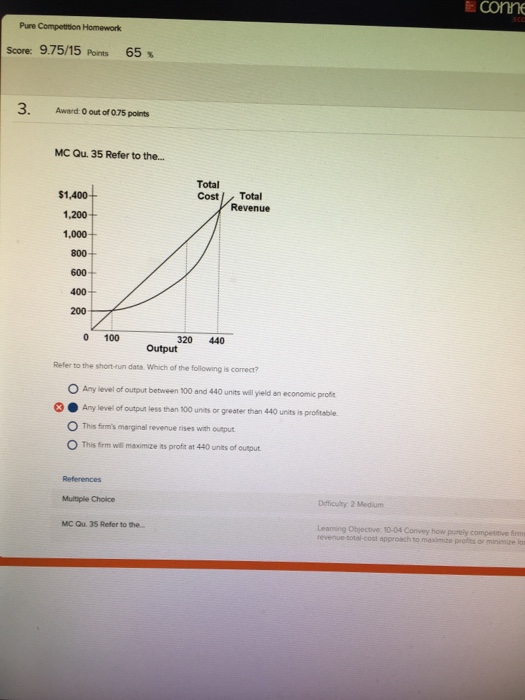
Econ test 2 Flashcards - Quizlet Any level of output between 100 and 440 units will yield an economic profit. Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. total economic profit curve. Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. marginal revenue curve. Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. total revenue curve.
DOCX Loudoun County Public Schools / Overview Price is constant or given to the individual firm selling in a purely competitive market because: A. the firm's demand curve is downsloping.B. of product differentiation reinforced by extensive advertising.C. each seller supplies a negligible fraction of total supply.D. there are no good substitutes for its product. 9.
PDF UNF PMASON - unf.edu the demand curve in a purely competitive industry is while the demand curve to a single firm in that indllstry is perfectly inelastic, perfectly elastic downsloping, perfectly elastic c) downslopmg, perfectly inelastic d) peffectly elastic, dowllsloptng usc the following to answer questions 6-7: in answering the next question(s), assume a graph …
Type: D... - Martinsville Indiana Computer Repair - 46151 ... 73. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm's short-run supply curve is: A) the abcd segment of the MC curve. C) the cd segment of the MC curve. B) the bcd segment of the MC curve. D) not shown. Answer: B. Type: A Topic: 3 E: 424 MI: 180 74. The short-run supply curve of a purely competitive producer is based on ...
For a purely competitive seller price equals? - All Famous ... The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, but the demand curve for a purely competitive industry is downsloping. Marginal revenue is the. change in total revenue associated with the sale of one more unit of output. Firms seek to maximize. total profit.
Monopolistic Competition Questions and Answers | Study.com Get help with your Monopolistic competition homework. Access the answers to hundreds of Monopolistic competition questions that are explained in a way that's easy for you to understand. Can't find ...
ECON Pure Competition 1 Short run Flashcards | Quizlet The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for this firm's product is $87, it will produce Multiple Choice 8 units at an economic profit of $130.72. 6 units at a loss of $90. 9 units at an economic profit of zero. 9 units at an economic profit of $281.97.
Curve 3 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms A ... Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total profit curve. AACSB: Reflective Thinking Bloom's: Level 3 Apply Difficulty: 2 Medium Learning Objective: 08-03 Convey how purely competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run.
Curve 3 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms A ... Curve (4) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total profit curve. 41. Refer to the above diagram. Other things equal, an increase of product price would be shown as: A. an increase in the steepness of curve (3), an upward shift in curve (2), and upward ...
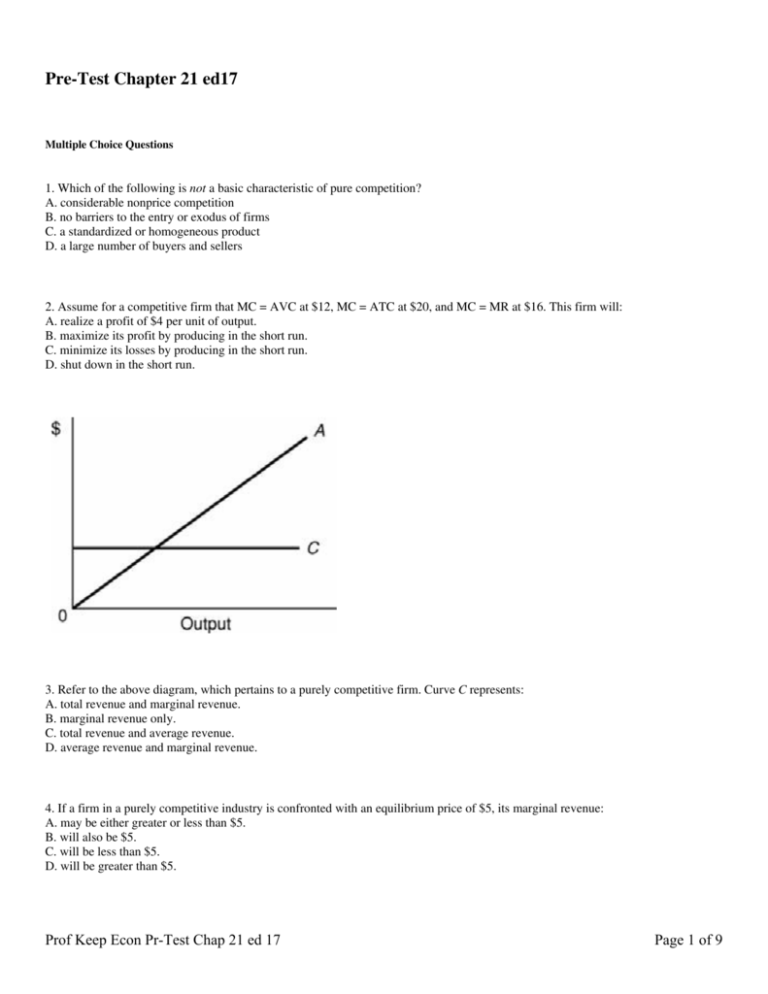
Chapter 10 Pure Competition Econ 1 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve C represents: average revenue and marginal revenue.
Ch11quiz - paws.wcu.edu Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Marginal revenue will be zero at output: A. q 4. B. q 3. C. q 2. D. q 1. 7. ... is less elastic than a purely competitive firm's demand curve. B. is perfectly elastic. C. coincides with its marginal revenue curve. D.
ECON Chap. 4: Market Failures; Chap. 6: Elasticity; Chap ... A. the demand for goods produced by purely competitive industries is downsloping. B. because of economies and diseconomies of scale, a competitive firm's long-run average total cost curve will be U-shaped.
Curve 1 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... 43. Curve (1) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A) total cost curve. C) marginal revenue curve B) total revenue curve. D) total economic profit curve. Answer: D. D ) total economic profit curve . McConnell/Brue: Economics, 16/e Page 695. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 416 MI: 172 44.
AGB 144 Ch. 8 quiz Flashcards | Quizlet Curve (3) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. B. total revenue curve. The MR = MC rule applies: A. to firms in all types of industries. B. only when the firm is a "price taker."
Unit 9 The labour market: Wages, profits, and ... - CORE Exercise 9.3 The price-setting curve. In your own words and using a diagram like Figure 9.9, ... The elasticity of the firm’s demand curve is greater the more competition the ... A good way to review these differences is to contrast the market for bread that we used to illustrate the model of a competitive equilibrium of price takers in the ...
Principles of Micro Economics Flashcards | Quizlet A purely competitive firm's short-run supply curve is: upsloping and equal to the portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the average variable ...
Economies of Scale and International Trade - GitHub Pages A secondary assumption is that the additional savings (or economies) fall as the scale increases. Graphically, this means that the slope of the curve in Figure 6.1 "Unit-Labor Requirement with Economies of Scale" becomes less negative as the scale of production (output) rises. Economists sometimes refer to this feature by saying the function is concave to the origin; that …
Chapter 10 Quiz Flashcards | Quizlet Technological advance improves productivity in a purely competitive industry. This change will result in a shift A. down of the individual firm's MC curve, causing the market supply curve to shift to the left. B. down of the individual firm's MC curve, causing the market supply curve to shift to the right.
PDF exam: 060205RR - Product Markets - JustAnswer 4. Curve (3) in the diagram above is a purely competitive firm's A. total cost curve. B. marginal revenue curve. C. total economic profit curve. D. total revenue curve. € 5. Which of the following is a characteristic of a pure monopoly economic system? A. Price taker B. Many sellers C. Free entry D. Blocked entry € 6. If production is ...
Martinsville Indiana Computer Repair - 46151 - Facebook 43. Curve (1) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A) total cost curve. C) marginal revenue curve B) total revenue curve. D) total economic profit curve. Answer: D. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 416 MI: 172 44. Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's A) total cost curve. C) marginal revenue curve B) total revenue ...
Chapter 8 Microeconomic DD2013 Flashcards | Chegg.com An industry comprised of 40 firms, none of which has more than 3 percent of the total market ... The marginal revenue curve of a purely competitive firm:.
Econ exam 3 Flashcards - Quizlet The demand and supply curves for the lawnmower market intersect at a market price of $500. In a perfectly competitive market, a profit-maximizing quantity requires that P = MC. In the cost diagram, a horizontal line at a price of $500 intersects the MC curve at a …
PDF ECO 211 Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit.
Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... 38. Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. Answer: C Topic: Profit maximization in the short run. Learning Objective: 11-03: Convey how purely competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses in the short run.













0 Response to "37 curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's"
Post a Comment