38 cardiac muscle tissue diagram
Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Notes: Diagrams... | Osmosis (supports muscle tissue, crisscrossing connective tissue collagen fibers); coronary vessels (lie on outside of heart, penetrate into return → ↑ cardiac output → murmurs from mitral regurgitation, aortic regurgitation, ventricular septal defect → ↑ intensity ▫ Murmur from hypertrophic obstructive... PDF Striated cardiac muscle tissue skeletal muscle tissue •epimysium (muscle) •perimysium (muscle. bundle) •endomysium (muscle fiber). according by Janqueira and Carneiro, 1992. CARDIAC MUSCLE. • localized injury- death of cells • is reapaired by replacement with fibrous conn. tissue- myocardial infarction MI.
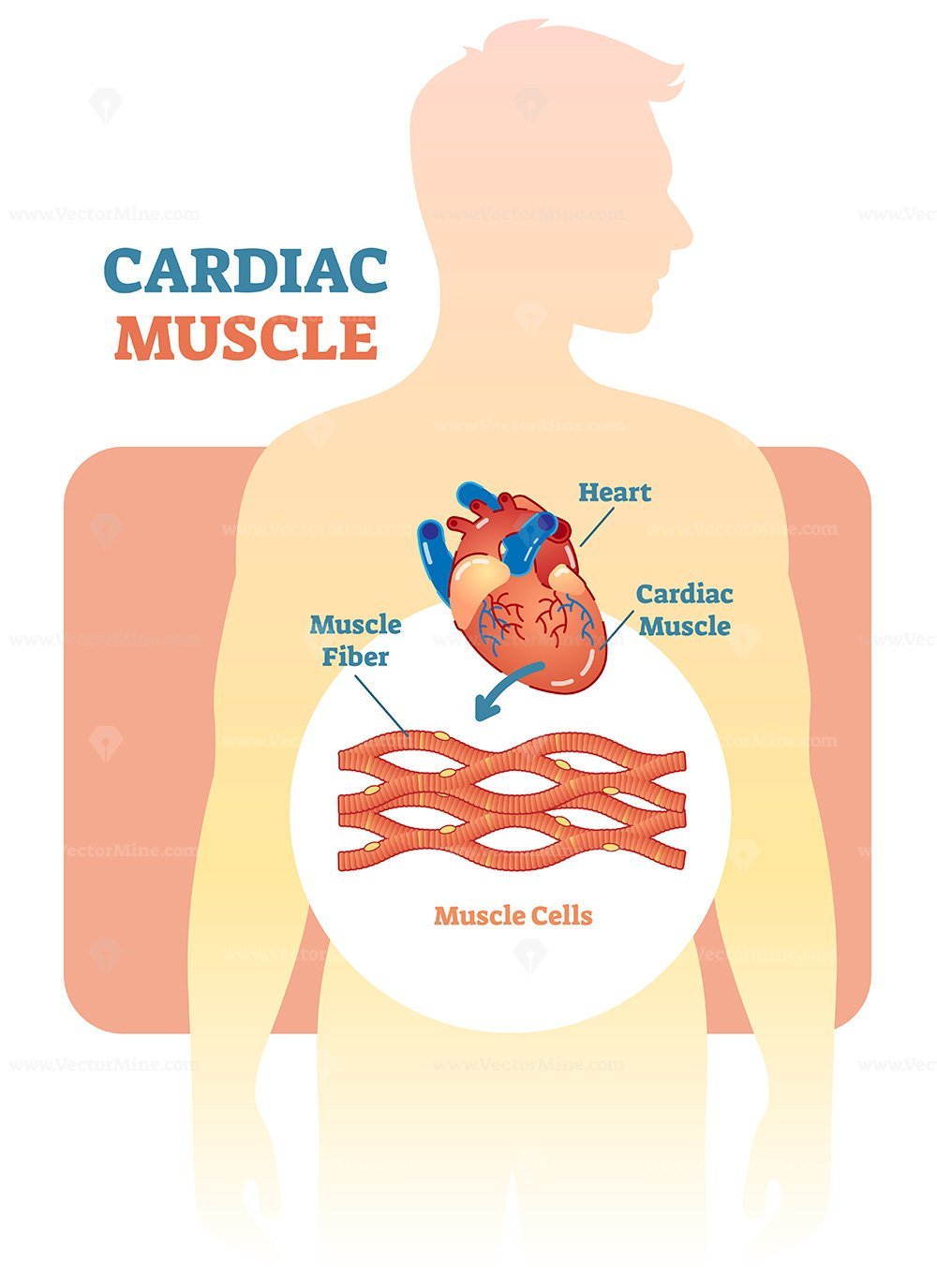
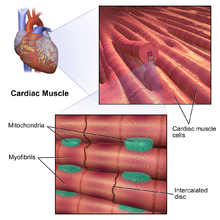
Cardiomyocytes (Cardiac Muscle Cells)- Structure, Function & Histology As previously mentioned, cardiac muscles are constantly contracting and relaxing as the blood is pumped around the body. This requires high levels of energy since these muscles do not rest as is the case with other types of muscles. Here, then, high amounts of mitochondria ensure that the cells get...
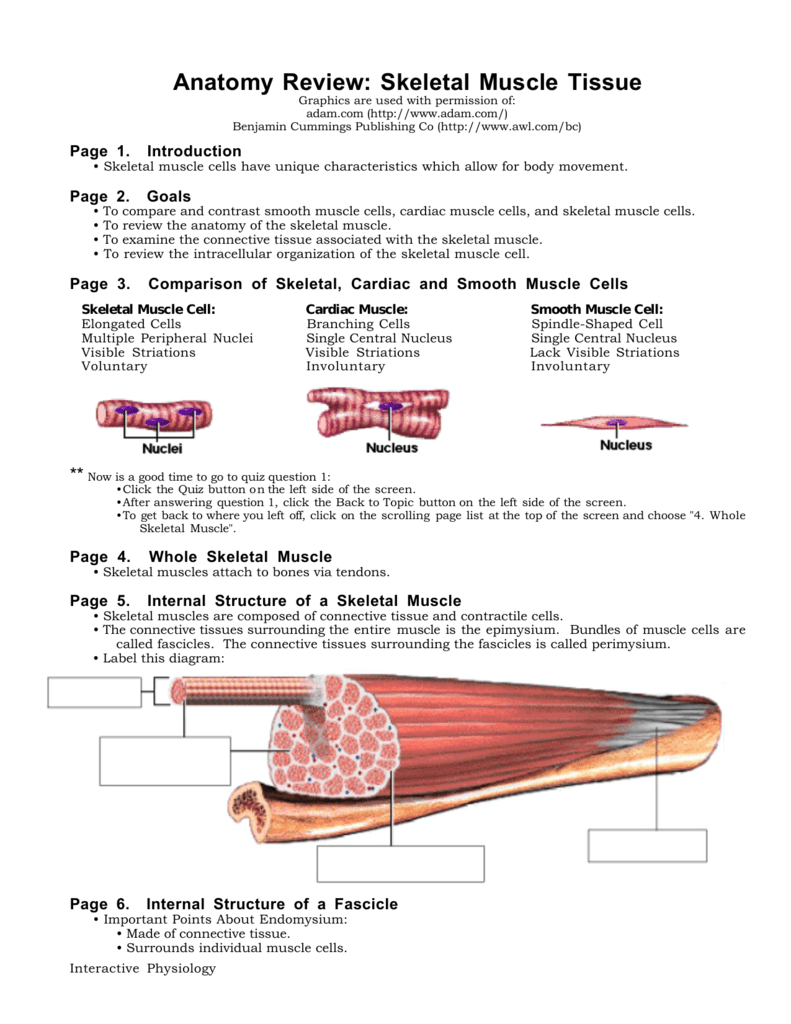
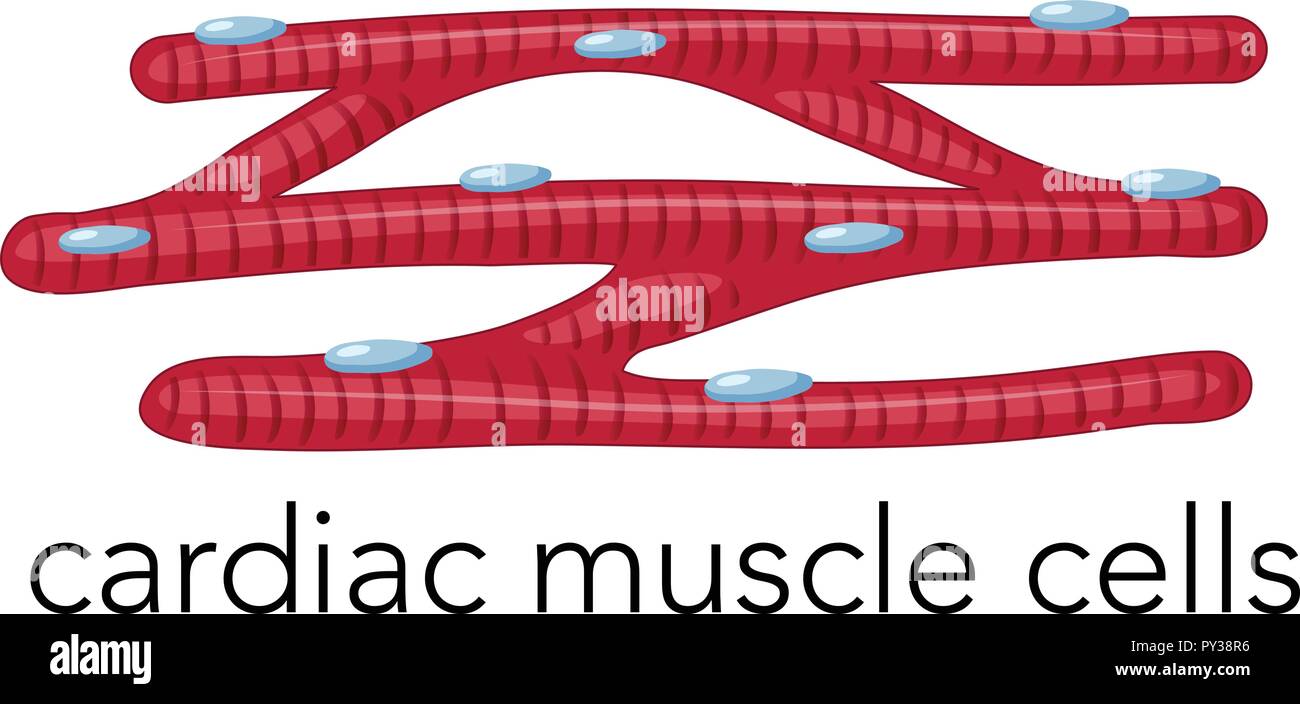
Cardiac muscle tissue diagram
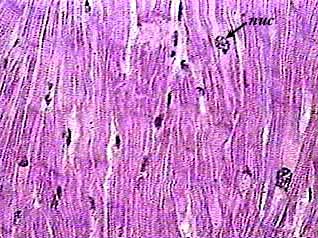
cardiac muscle | Definition, Function, & Structure | Britannica Cardiac muscle, in vertebrates, one of three major muscle types, found only in the heart. Cardiac muscle possesses contractile units known as sarcomeres and exhibits rhythmic contractions. The rhythmic contractions are regulated by the sinoatrial node of the heart and thus are not under... Cardiovascular system - Histology | Muscular arteries The myocardium is a layer of cardiac muscle that has already been described in the chapter about muscular tissue. Notice a nucleus in the middle of the muscle cell enveloped by lightly pink cytoplasm. The epicardium is a layer of connective tissue that lies between the muscle and the... Cardiac muscle tissue histology | Kenhub Cardiac muscle tissue, also known as myocardium, is a structurally and functionally unique subtype of muscle tissue located in the heart, that actually has characteristics from both skeletal and muscle tissues. It is capable of strong, continuous, and rhythmic contractions that are automatically generated.
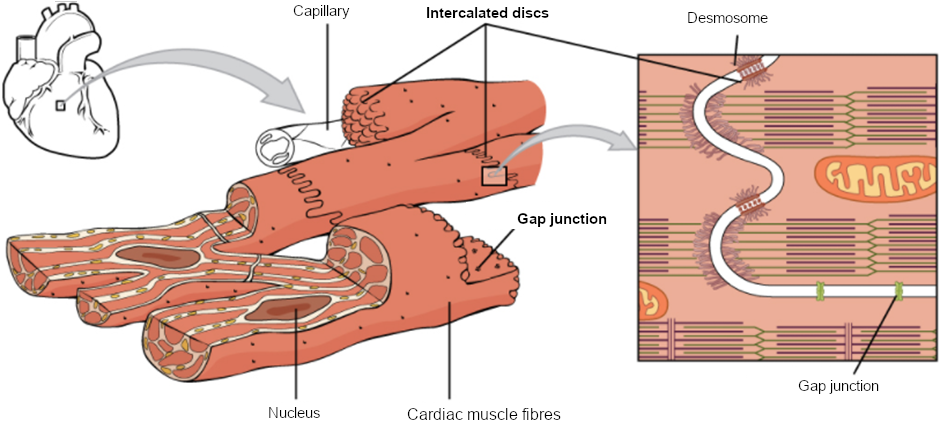
Cardiac muscle tissue diagram. Cardiac muscle - Wikipedia Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. PDF Muscular Tissue Regeneration of Muscle Tissue. • Cardiac muscle has almost no regenerative capacity beyond early childhood. • Skeletal muscle the tissue can undergo limited regeneration. The source of regenerating cells is believed to be the satellite cells. Cardiac Muscle Tissue Review the cardiac muscle cells which make up the myocardium portion of the heart wall in this interactive tutorial, and test yourself in the quiz. They supply the ATP for repeated contractions of the heart. Unlike other types of muscle tissue, cardiac myocytes are joined end to end by intercalated... Cardiac Muscle - Definition, Function and Structure | Biology Dictionary Cardiac muscle, also known as heart muscle, is the layer of muscle tissue which lies between the endocardium and epicardium. These inner and outer layers of the heart, respectively, surround the cardiac muscle tissue and separate it from the blood and other organs.
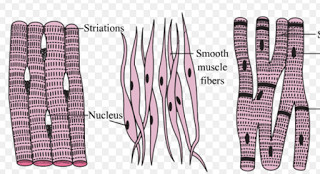
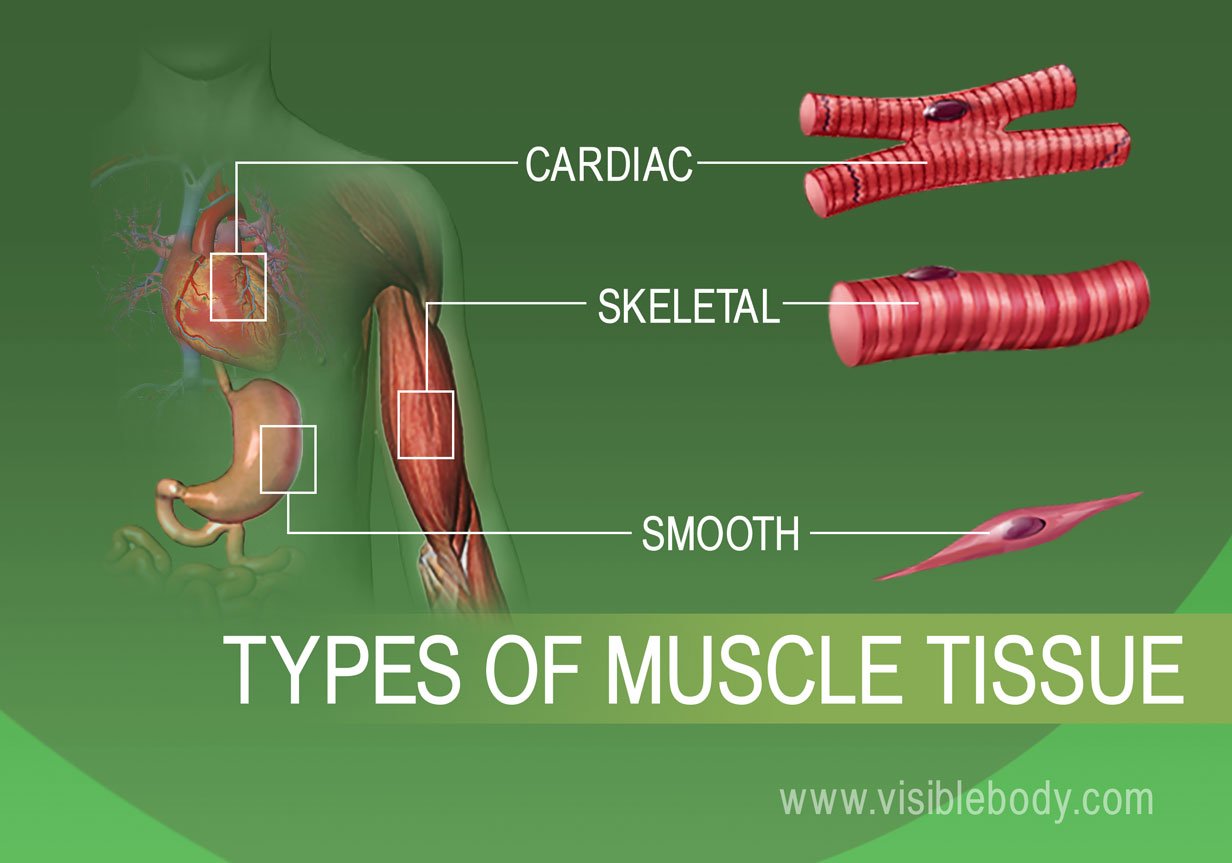
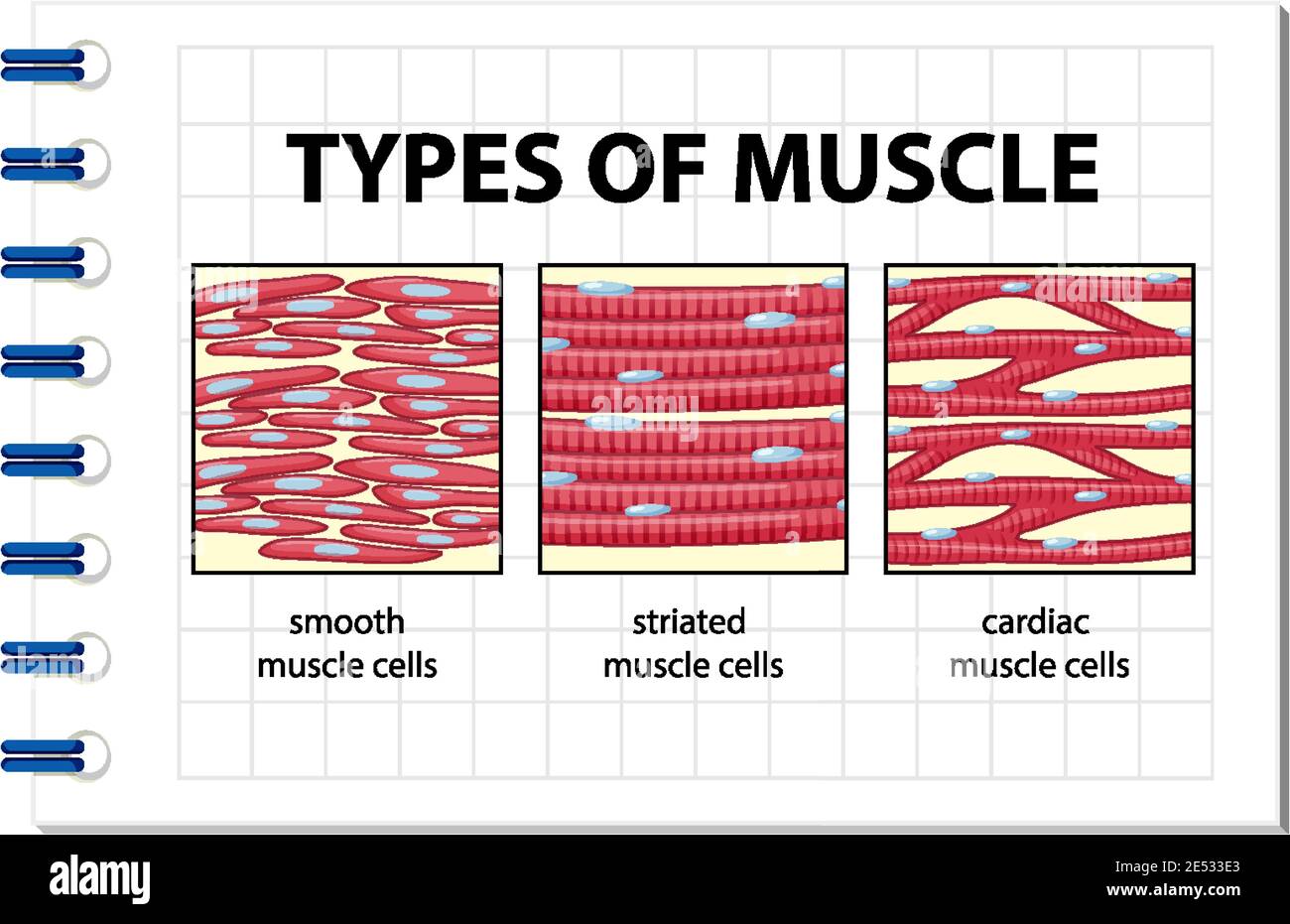
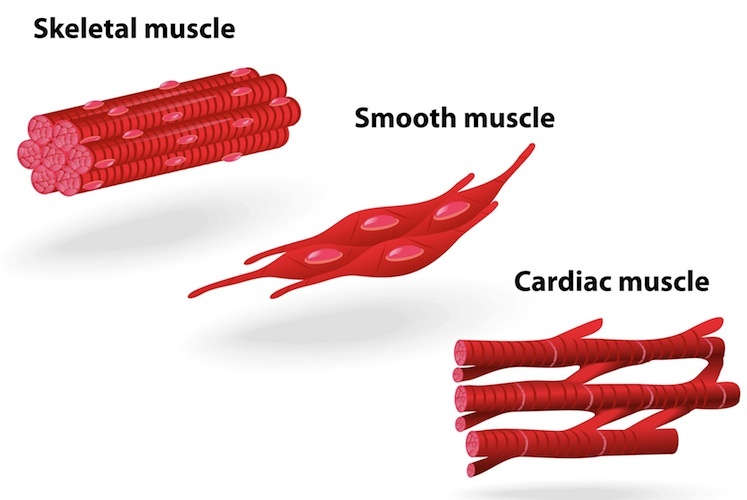
Three Types of Muscle Tissue: Skeletal, Cardiac, and Smooth Muscle Like cardiac muscle tissue, smooth muscle tissue is controlled involuntarily via the autonomic Smooth muscle tissue has a different structure compared to cardiac and skeletal muscle tissue. As you look at this diagram of a smooth muscle fiber, you'll notice the single nucleus in the center. How to draw a Muscle Tissue| Straight | Smooth | Cardiac - YouTube How to draw Xylem Tissue step by step for beginners ! Types of Muscle Tissue | Concise Medical Knowledge Muscle tissue is one of the basic tissue types. Histologically, muscles of the body can be classified into three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. Diagram depicting the microscopic structure of sarcomeres, actin Actin Filamentous proteins that are the main constituent of the thin filaments of... Basic Properties of Cardiac Muscle (With Diagram) | Humans | Biology Like other muscles, the cardiac muscle is excitable by adequate stimuli and responds by contraction. The fundamental contractile unit of the cardiac It has been observed that the different properties of cardiac muscles (Table 7.1) are not developed in all the tissues of heart in the same order.
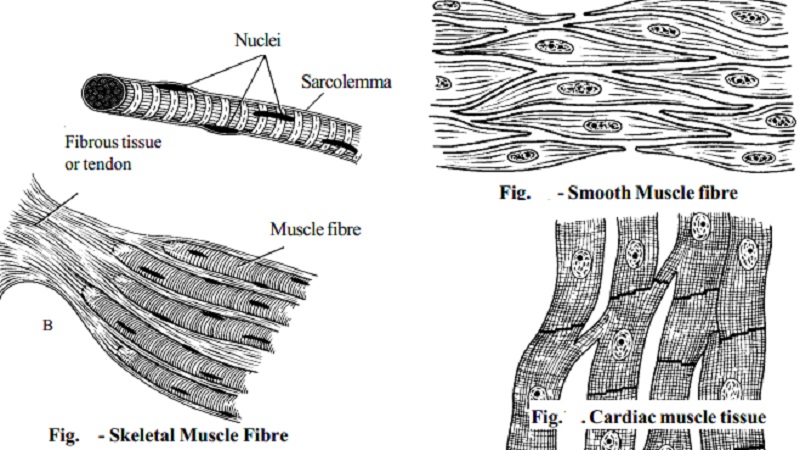
Muscular Tissue - Structure and Functions of Human Tissue Types. Above: Diagram of Cardiac Muscle Tissue. Structure: Cardiac muscle fibers are striated, branched (sometimes described as Y-shaped), and have a single central nucleus. Unlike Skeletal and Cardiac muscle tissue, Smooth muscle is not striated. Smooth muscle fibers are small and tapered - with... 64.5.2.2 Cardiac Muscle Tissue | ScienceDirect Topics Cardiac muscle is an involuntary striated muscle tissue found only in the heart and is responsible for the ability of the heart to pump blood. Cardiac muscle has a low regenerative potential, in case of heart attack the injured area heals and the native tissue is replaced by a scar. Muscle Tissue | Microscope Slides | Histology Guide Muscle tissue is composed of cells specialized for contraction. Muscle is classified into three types according to their structure and function Skeletal and cardiac muscle cells are called striated because they show an alternating series of bands. The repeating arrangement of their basic... Cardiac muscle In the connective tissue between cardiac muscle cells are nuclei of other cells such as fibroblasts and endothelial cells of capillaries. Cardiac muscle cells are joined to each other by junctions called intercalated disks. Arrows in the enlarged image indicate several intercalated disks.
The Cardiac Cycle - Pressures in The Heart - TeachMePhysiology At rest the heart pumps around 5l of blood around the body every minute, but this can increase massively during exercise. In order to achieve this high output efficiently the heart works through a carefully controlled sequence with every heart beat - this sequence of events is known as the cardiac...
Muscle Tissue: Smooth, Skeletal & Cardiac Muscles, Videos... Muscle tissue is a tissue that helps in contraction of muscles. Muscle tissue gives muscles the ability to contract, by applying forces to other body parts. Smooth muscle, skeletal muscle, and cardiac muscles are three types of muscle tissues.
Diagram of Cardiac Muscle Tissue labeled | Quizlet Start studying Cardiac Muscle Tissue labeled. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. Only RUB 2,325/year. Cardiac Muscle Tissue labeled.
Muscular tissue: skeletal, smooth and cardiac... - Online Biology Notes Cardiac muscle cells are closely packed but each cell are nucleated and separated from each other. The cells are joined end to end by the specialised cell junctions called intercalated disks that attach one cell to another with desmosomes, connect the myofibril filaments of adjacent cells and contain gap...
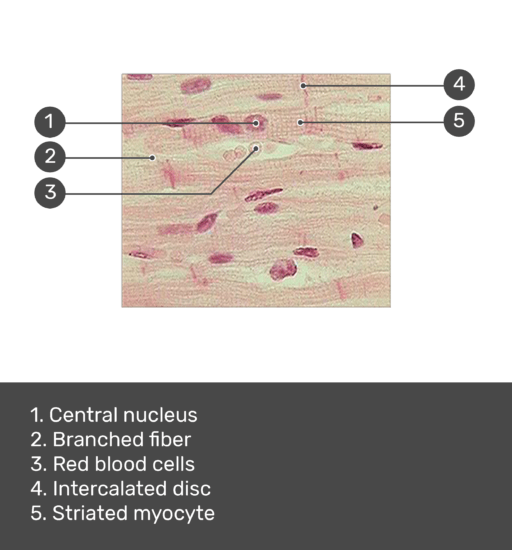
Cardiac Muscle Tissue | Interactive Anatomy Guide Cardiac muscle tissue is made up of many interlocking cardiac muscle cells, or fibers, that give the tissue its properties. Each cardiac muscle fiber contains a single nucleus and is striated, or striped, because it appears to have light and dark bands when seen through a microscope.
Muscle Tissue - Medical Lecture Notes | The Heart: Cardiac Muscle Three types of muscle tissue can be identified histologically: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. The fibres of skeletal muscle Connective tissue elements surround muscle fibres. Individual muscle fibres are surrounded by a delicate layer of reticular fibres called the endomysium.
PDF Muscle Tissue Cardiac muscle tissue. cardiomyocyte (Gr. cardia, heart). three types of cardiac myocytes: contractile, conductive, secretory. Regeneration of muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle has almost no regenerative capacity beyond early childhood: mature cardiac muscle cells do not divide.
Cardiac Muscle Tissue | Boundless Anatomy and Physiology Cardiac muscle, like skeletal muscle, appears striated due to the organization of muscle tissue into sarcomeres. While similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is different in a few ways. Cardiac muscles are composed of tubular cardiomyocytes, or cardiac muscle cells.
15.3: Types of Muscle Tissue - Biology LibreTexts | Cardiac Muscle The cells of cardiac muscle tissue are arranged in interconnected networks. This arrangement allows rapid transmission of electrical impulses, which stimulate virtually simultaneous contractions of the cells. This enables the cells to coordinate contractions of the heart muscle.
Cardiac Muscle Tissue - Anatomy and Physiology Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. Highly coordinated contractions of cardiac muscle pump blood into the vessels of the circulatory system. Similar to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated and organized into sarcomeres, possessing the same banding organization as skeletal...
Cardiomyocytes (Cardiac Muscle Cells) - Structure, Function, Cell... Cardiac muscle cells or cardiomyocytes (also known as cardiac myocytes) are the muscle cells (myocytes) that make up the heart muscle. Cardiomyocytes go through a contraction-relaxation cycle that enables cardiac muscles to pump blood throughout the body.
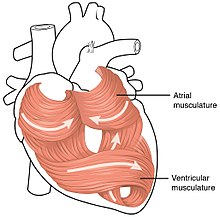
Human Physiology/The cardiovascular system - Wikibooks, open books... The cardiac muscle is self-exciting, meaning it has its own conduction system. The myocardium is composed of specialized cardiac muscle cells with an ability not possessed by muscle tissue elsewhere in the body. The ultimate distribution cannot be completely shown in this diagram.
Cardiac muscle tissue histology | Kenhub Cardiac muscle tissue, also known as myocardium, is a structurally and functionally unique subtype of muscle tissue located in the heart, that actually has characteristics from both skeletal and muscle tissues. It is capable of strong, continuous, and rhythmic contractions that are automatically generated.
Cardiovascular system - Histology | Muscular arteries The myocardium is a layer of cardiac muscle that has already been described in the chapter about muscular tissue. Notice a nucleus in the middle of the muscle cell enveloped by lightly pink cytoplasm. The epicardium is a layer of connective tissue that lies between the muscle and the...
cardiac muscle | Definition, Function, & Structure | Britannica Cardiac muscle, in vertebrates, one of three major muscle types, found only in the heart. Cardiac muscle possesses contractile units known as sarcomeres and exhibits rhythmic contractions. The rhythmic contractions are regulated by the sinoatrial node of the heart and thus are not under...



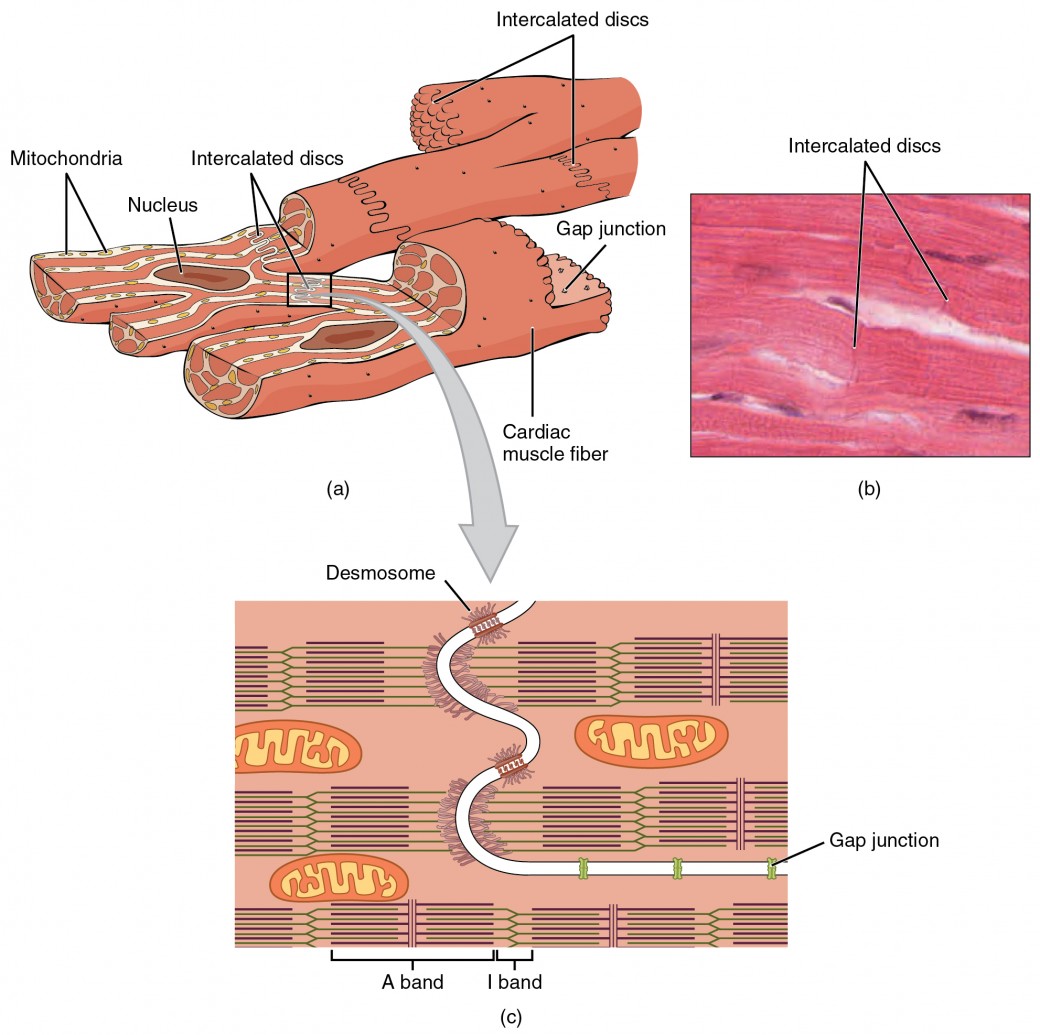







:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3159/W8vCwHUn3D60Kb5xvvzvXQ_Intercalated_discs.png)







0 Response to "38 cardiac muscle tissue diagram"
Post a Comment