35 what is orbital diagram
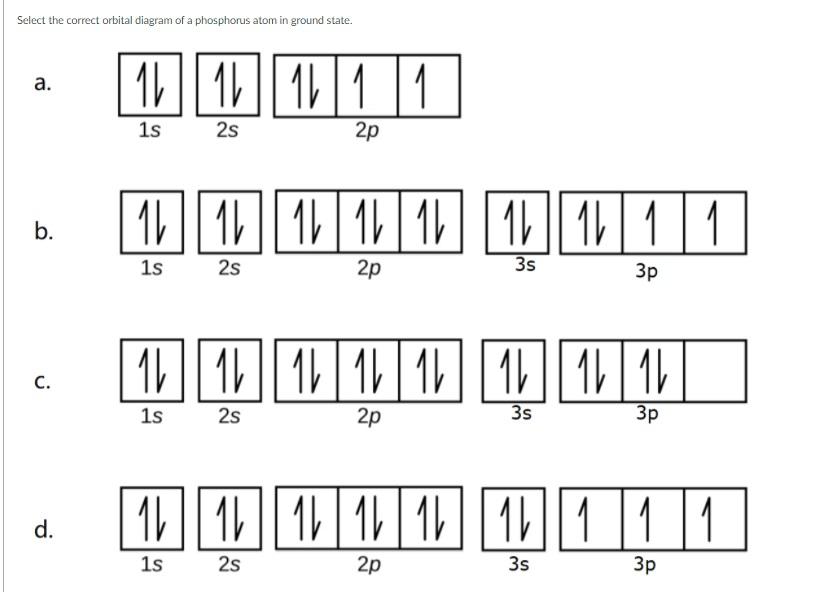
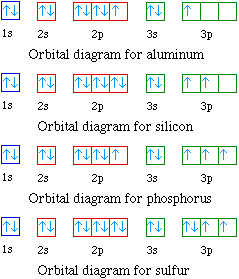
What is the orbital diagram for phosphorus? In writing the electron configuration for Phosphorus the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for Phosphorous go in the 2s orbital. The next six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. 8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams. Abstract (TL;DR) Molecular orbital diagrams are a fantastic way of visualizing how molecular orbitals form using what we already understand about sigma and pi bonds. Depending on if it is a homonuclear case, where the bonding atoms are the same, or a heteronuclear case, where the bonding atoms are ...
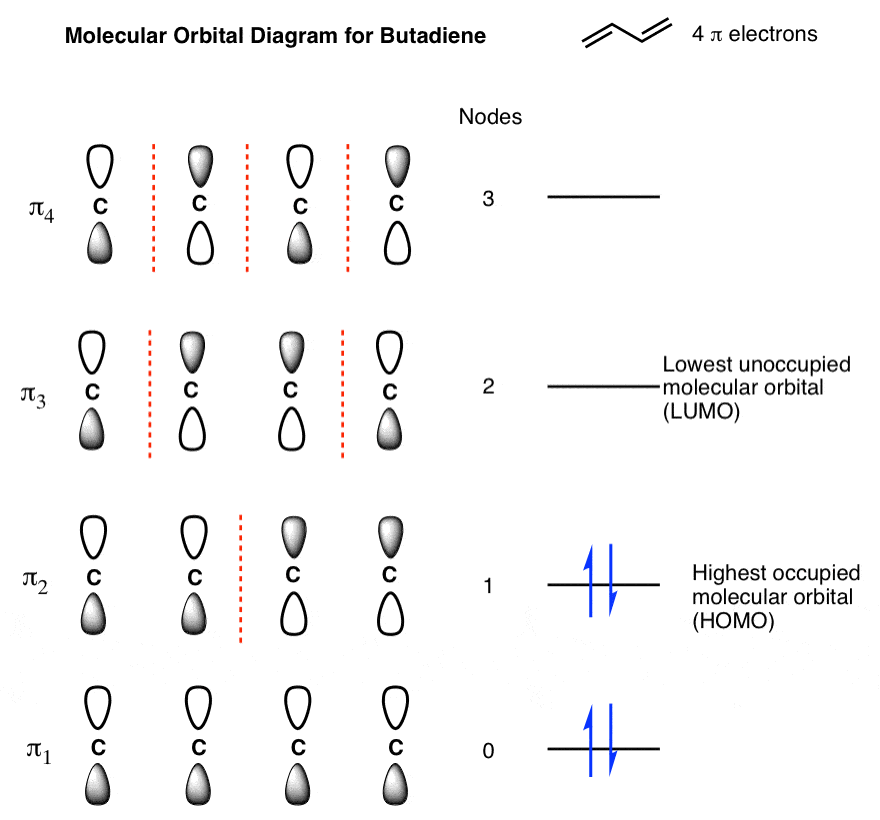
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.

What is orbital diagram
Molecular orbital diagram for b2. B2 molecular orbital diagram. This also causes a large jump in energy in the 2p σ orbital. For example when two hydrogen atoms bond a σ1s bonding molecular orbital is for med as well as a σ1s antibonding molecular orbital. Valence bond model vs. Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8. Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9. Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10. Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11. Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na) Energy-Level Diagrams. Because electrons in the σ 1 s orbital interact simultaneously with both nuclei, they have a lower energy than electrons that interact with only one nucleus. This means that the σ 1 s molecular orbital has a lower energy than either of the hydrogen 1s atomic orbitals. Conversely, electrons in the \( \sigma _{1s}^{\star } \) orbital interact with only one hydrogen ...
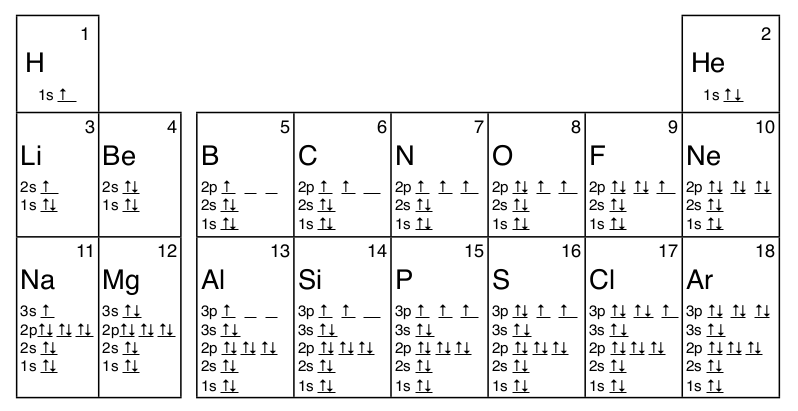
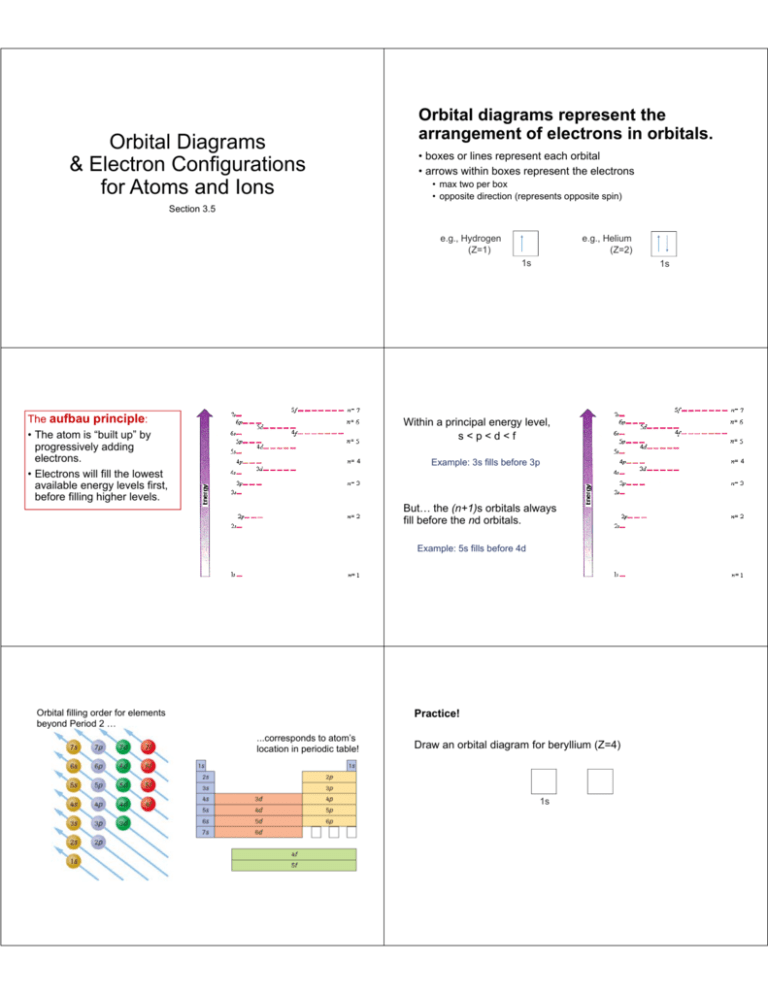
What is orbital diagram. An orbital diagram naturally leads to the writing of an electron configuration. Pool Automatic Filler Spare. Truth be told, it's just an alternative method to draw the configuration in a way to easily identify how. The bond between the metal ion and the ligand, where the ligand supplies both electrons, is known as a coordinate covalent bond ... In an orbital diagram, orbitals are represented as boxes and electrons are represented by arrows (↑ or ↓), with two electrons occupying each orbital/box. Orbitals are labeled according to their principle energy levels and sublevels (1s, 2p, etc..). Helium, with two electrons in the 1s orbital has the following orbital diagram. Orbital Diagrams. Another way to represent the order of fill for an atom is by using an orbital diagram often referred to as "the little boxes": The boxes are used to represent the orbitals and to show the electrons placed in them. The order of fill is the same but as you can see from above the electrons are placed singly into the boxes ... The anti bonding molecular orbital σ*2 s is empty . Thus . Bond order = Number of electrons in BMO - Number of electrons in ABMO . 2. Bond order = 2-0. 2. Bond order = 1. Bond order 1 shows that there is a single covalent bond between the lithium atoms in Li 2 molecule. How to draw the molecular orbital diagram of Li 2, Li 2 +, Li 2 -?
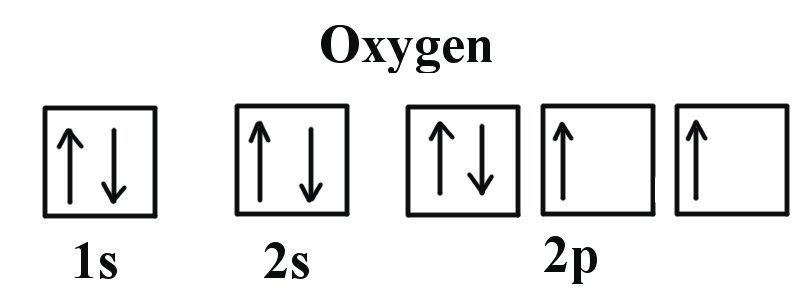
Definition of atomic orbital diagram for oxygen: An orbital is the region of space around the nucleus within which the probability finding an electron of given energy is maximum. The diagram of this region gives the diagram of the orbital. The plot of angular wave function or square of angular wave functions give us the diagram of orbitals. Molecular Orbital Diagrams. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic ... An orbital filling diagram is the more visual way to represent the arrangement of all the electrons in a particular atom. In an orbital filling diagram, the ... An orbital diagram, or orbital filling diagram, is a type of notation which illustrates an atom's electron distribution and electron spin within orbitals.
The famous nitrogen molecule, N 2 , can also be perfectly described using molecular orbital diagrams: OM diagram for the N2 molecule. Source: Gabriel Bolívar. Note that this diagram is exactly the same as for the C 2 2- anion . This means that N 2 and C 2 2- are isoelectronic. However, this fact does not imply that both species behave in the ... Mar 28, 2018 — Orbital diagrams use the same basic format, but instead of numbers for the electrons, they use ↑ and ↓ arrows, as well as giving each orbital ... The molecular orbital diagram of CO2 is as below. A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. It also helps us to find the bond order, bond length, bond strength of the molecule. In the diagram, the left-hand side consists of the atomic orbitals of carbon. Now the next topic to cover is the molecular orbital diagram of nitrous oxide. N2O Molecular Orbital Diagram. Molecular orbital diagrams say about the mixing of orbitals in a compound. Using a MO diagram, the bond order of a compound can be determined which gives us an idea about bond length, bond stability as well.
Its primary value is the rapid establishment of d-orbital degeneracies (or lack thereof) and relative energies. It provides a guide to the metal-ligand orbital interactions as a basis of geometric and electronic structure and reactivity of ML n complexes. The model utilizes two parameters:
Answer (1 of 3): I modified the picture from this post: What's the MOT diagram of O2 +2 ion? and modified it to be O2 2+ (since sadly enough I am about as advanced with artistic programs on pc as a rock). How you basically do these questions is by first drawing the empty AO and MO, then counting ...
Orbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration, showing the individual orbitals and the pairing arrangement of electrons. AbstractAs a new class of fluorescent carbon materials, graphene quantum dots GQDs have attracted tremendous attention due to their outstanding properties and potential applications in ...
Two p-atomic orbitals (one from each nitrogen) atom combine to form two molecular orbitals, the bonding molecular orbital σ2px and antibonding molecular orbital σ*2px. The other four p-atomic orbitals (two from each nitrogen) atom combine to give four molecular orbitals, two bonding molecular orbitals i.e. π2py and π2pz, while two ...
What is the orbital diagram of CO 27? In this case of Cobalt there are 27 electrons which are present in 4 orbits and their distribution on the orbit that is electronic configuration can be written as: 1s22s22p63s23p63d74s2.
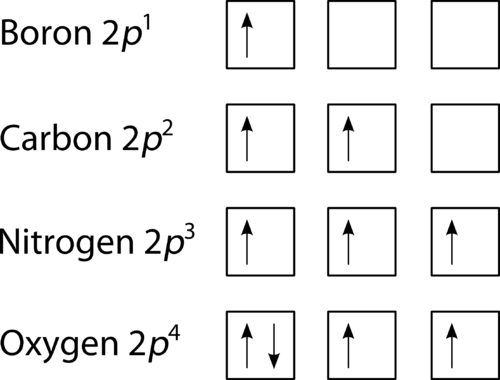
What is the Orbital Diagram For Nitrogen? When we talk about the orbital diagram, we first need to understand what exactly it means. Therefore, during exams, the student can expect questions related to this topic so it is important that the students must go through it.
An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. Arrows (or half arrows) are used to represent the electrons occupying the orbitals. What is more reactive Fe2+ or Fe3+? In an oxidative solution, Fe2+ will be. In a reductive environment, Fe3+ will be more reactive.
Carbon Electron Dot Diagram. If we talked about the electronic configuration of the element then, carbon is an element whose electronic configuration is given as 1s22s22p2. Now the main thing here is what electronic configuration actually means, so the solution/ answer is that in simple words, by knowing the electronic configuration of any ...
Molecular Orbital Theory An approach, known as Molecular Orbital Theory, was established primarily by Hund and Mulliken in \(1932\) to explain the features of molecules such as their relative bond strengths, paramagnetic and diamagnetic properties, etc.
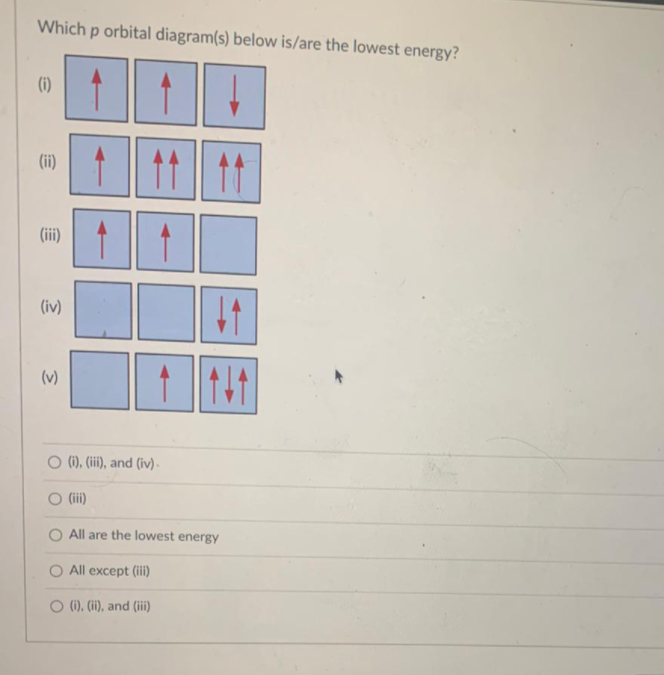
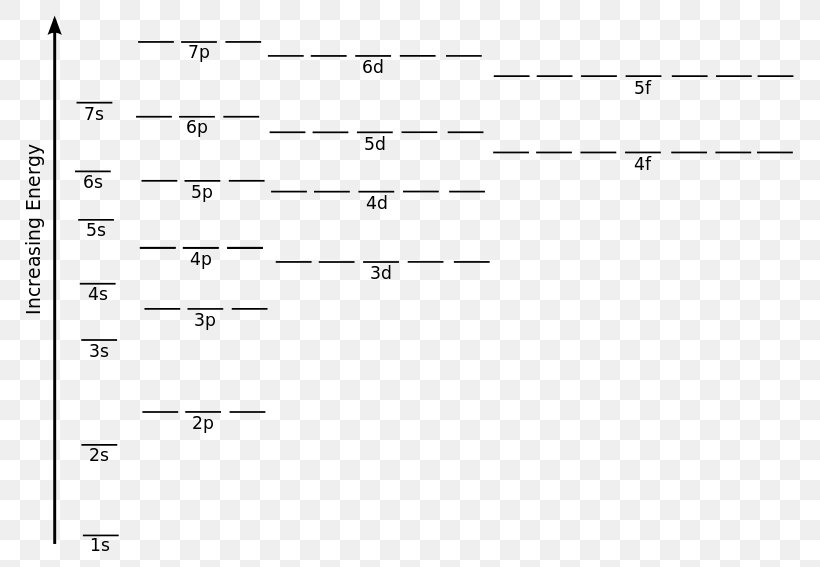
Orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. Three rules are useful in forming orbital diagrams.
Dec 8, 2019 — The orbital diagram is a type of diagram which shows the distribution of electrons in the orbitals of an atom and indicates the spin of those ...
What is the orbital diagram? Orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. Three rules are useful in forming orbital diagrams. According to the Auf Bau Principle, each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital. Orbital diagrams are a pictorial description of electrons in an atom.
Energy-Level Diagrams. Because electrons in the σ 1 s orbital interact simultaneously with both nuclei, they have a lower energy than electrons that interact with only one nucleus. This means that the σ 1 s molecular orbital has a lower energy than either of the hydrogen 1s atomic orbitals. Conversely, electrons in the \( \sigma _{1s}^{\star } \) orbital interact with only one hydrogen ...
Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8. Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9. Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10. Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11. Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na)
Molecular orbital diagram for b2. B2 molecular orbital diagram. This also causes a large jump in energy in the 2p σ orbital. For example when two hydrogen atoms bond a σ1s bonding molecular orbital is for med as well as a σ1s antibonding molecular orbital. Valence bond model vs.
















0 Response to "35 what is orbital diagram"
Post a Comment