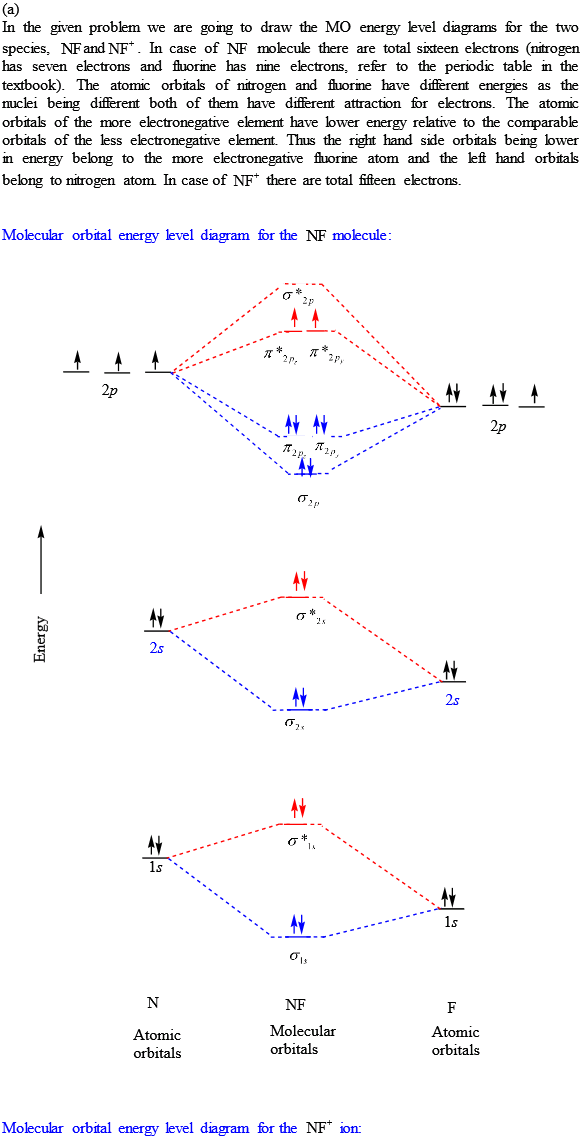
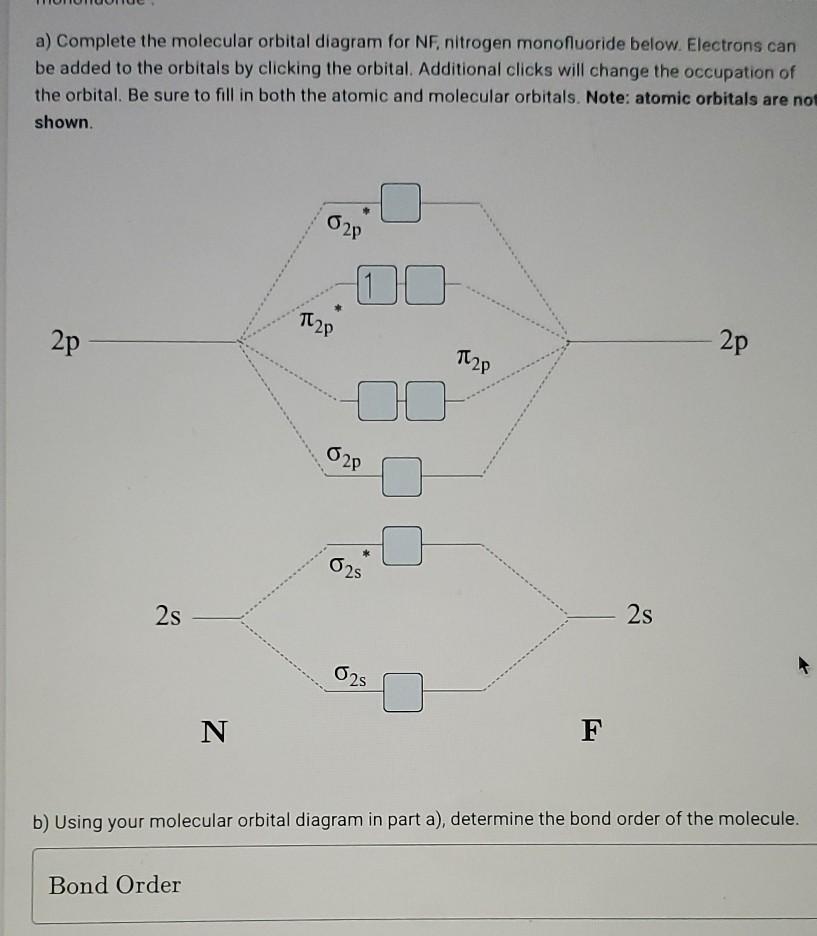
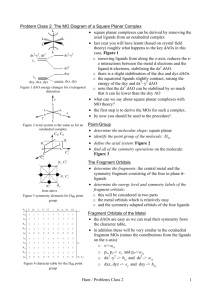
39 nf+ molecular orbital diagram
Transcribed image text: Draw and label a molecular orbital diagram for nitrogen monofluoride,NF. Use atleast half a page Give the bond order Give the magnetism, and explain your choice briefly (a few words are enough) If you ionized NF to give NF+, would the bond be shorter or longer? Explain your reasoning briefly (again a few words are plenty) Learn how to apply molecular orbital theory to determine the shapes of bonded orbitals, recognize molecular orbital diagrams, calculate bond order, and determine relative bond strength.
JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR SPECTROSCOPY 45, 358-365 (1973) Configuration Interaction Studies of NF and NF+ ANDREAS ANDERSENt AND YNGVE OHRN Quantum Theory Project, Departments of Chemistry and Physics, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida 32601 Full potential energy curves and wavefunctions are calculated for NF and NF+ in the Born-Oppenheimer approximation with a configuration interaction ...
Nf+ molecular orbital diagram
NF bond order: NF+ bond order: NF− bond order: Classify each molecule according to its magnetic properties. Diamagnetic Paramagnetic Answer Bank NF NF+ NF−. Use molecular orbital theory to complete the ground state electron configuration for each of the molecules. Determine the bond order of each of the molecules. Structure and Bonding Solutions: #4. 4.* (1997 1 7) Consider the diatomic molecule NF. Draw its molecular orbital energy diagram. A. Using the LCAO-MO scheme, indicate the ground-state MO description for NF, i.e. complete the following: 1(s) 2. . .The LCAO-MO description is: 1s 2 2s 2 3s 2 4s 2 5s 2 1p 4 2p 2. B. john deere sx75.Ask Question Asked 5 years, 6 months ago. Active 5 years, 5 months ago. Viewed 411 times ... Search the URL with "Removing Primary Drive Belt (SX85)" and it will give a diagram and instructions on removing and replacing the drive belt, if that's the issue.The manual covers many other areas as well.
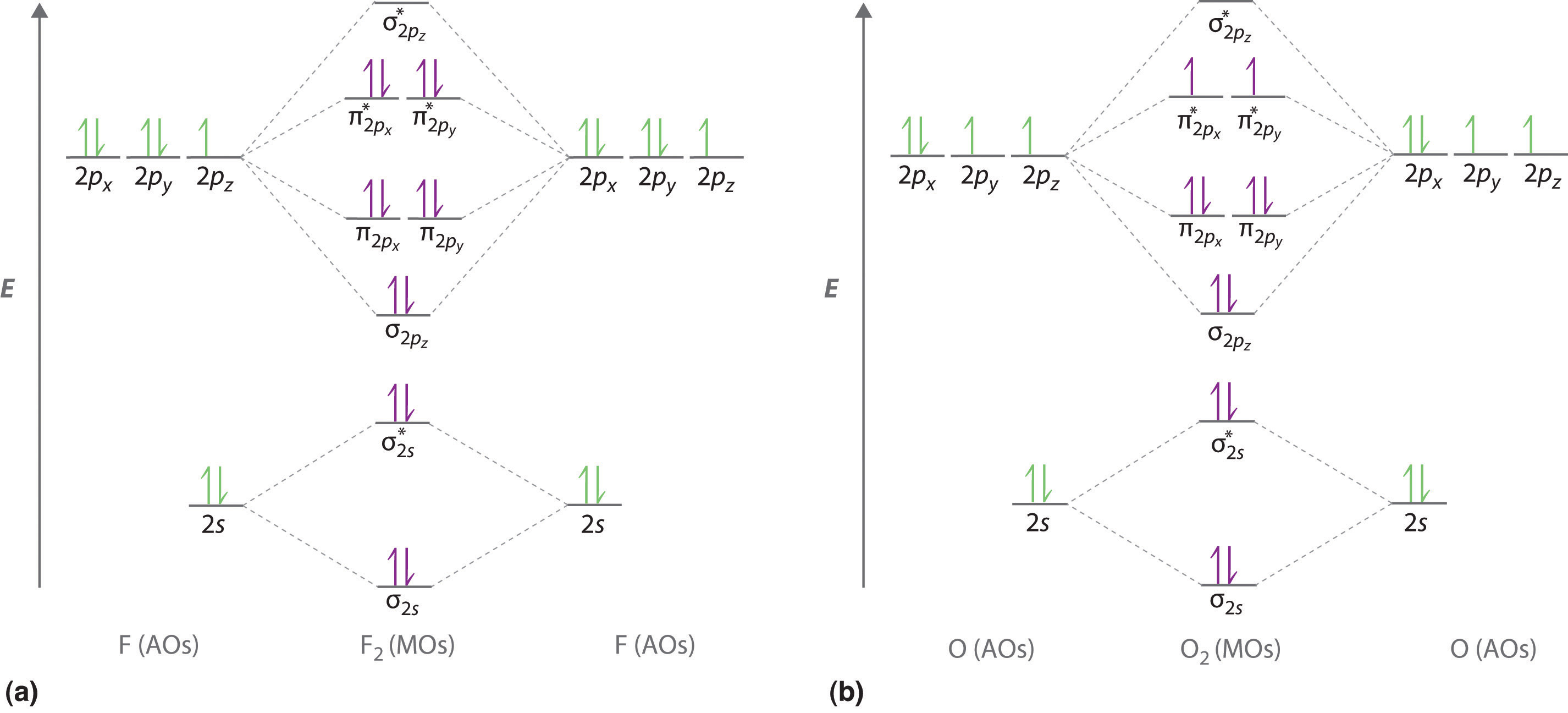
Nf+ molecular orbital diagram. Molecular Orbital Diagram for NF. Post by Christine Van 2E » Thu Nov 05, 2015 6:35 am . Hi! I have a quick question about the molecular orbital diagram for NF. Lavelle said that whenever we have a heteronuclear molecule, if one or both atom(s) has Z<8, then we would use the diagram where the pi px and pi py are lower than the Sigma pz. However ... Density functional theory B3LYP method is used to optimize ground-state structures of NF molecule, NF+ and NF- molecule ions with 6-311++g(df, 3pd), 6-311g(3d, 3p) and 6-311++g(3df, 3pd) basis ... Draw an M0 energy level diagram for the NF+ ion. Use sketches to show clearly how the atomic s and p orbitals interact to form molecular orbitals. What is the HOMO? the LUMO? How is the polarity of the molecular ion indicated in this diagram? Toward which atom would the HOMO be polarized and why? Which MO's correspond to the lone pairs on the ... Answer. Explanation :According to the molecular orbital theory, the general molecular orbital configuration will be,As there are 7 electrons present in nitrogen and 9 electrons in fluorine.(a) The number of electrons present in molecule = 7 + 9 = 16The molecular orbital configuration of molecule will be,The formula of bonding order = The bonding order of = (b) The number of electrons present ...
Gray, Harry B. (1994) Chemical Bonds: An Introduction to Atomic and Molecular Structure. University Science Books , Mill Valley, CA. ISBN 9781600490125. https://resolver.caltech.edu/CaltechAUTHORS:20200902-084538354 · Use this Persistent URL to link to this item: https://resolver.caltech.... ©2021 Prof Adam J Bridgeman | close window : ©2021 Prof Adam J Bridgeman | close windowProf Adam J Bridgeman | close window How are molecular orbitals different from atomic orbitals. because the electrons filling them are under the influence of two or more nuclei rather than just one nucleus. Electron density increases between. 2 nuclei in bonding molecular orbitals. Electron density decreases between. Solved: Use molecular orbital theory to complete the ground state electron configuration for each of the molecules. Molecule Ground state electron configuration NF (σ1s)(σ1s*)(σ2s)(σ2s*)(π2p)(σ2p)(π2p*) NF+ (σ1s)(σ1s*)(σ2s)(σ2s*)(π2p)(σ2p)(π2p*) NF− (σ1s)(σ1s*)(σ2s)(σ2s...
For NF+ and PC1+ the only other low lying doublet bound state is 2II whereas for PF+ it is 2Z+. In each case there is a bound 4H state and a bound 4~- state but the equilibrium bond lengths are very different and one would expect the Franck- Condon factors for the 4~- ~ 4i-[ transition to be unfavourable. ... Molecular orbitals for each spin ... Solutions for Chapter 9Problem 34E: For each of the two species NF and NF+, (a) draw MO energy level diagrams; (b) write out electron configurations; (c) determine bond orders and predict relative stabilities; and (d) predict diamagnetism or paramagnetism. … Method 1Method 1 of 3:Finding Bond Order Quickly. Know the formula. In molecular orbital theory, bond order is defined as half of the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons. Bond order = [ (Number of electrons in bonding molecules) - (Number of electrons in antibonding molecules)]/2 . Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in ...
Use molecular orbital theory to complete the ground state electron configuration for each of the molecules. Molecule Ground state electron configuration. NF (σ1s) (σ1s ) (σ2s) (σ2s ) (π2p) (σ2p) (π2p*)
ANSWERS TO MOLECULAR ORBITALS PROBLEM SET 1. (a) N2 +(13 e-): σ2 1sσ*21sσ22sσ*22sπ22pπ22pσ12p N2 2+(12 e-): σ2 1sσ*21sσ22sσ*22sπ22pπ22p N2 (14 e-): σ2 1sσ*21sσ22sσ*22sπ22pπ22pσ22p N2-(15 e-): σ21sσ*21sσ22sσ*22sπ22pπ22pσ22pπ*12p N2 2-(16 e-): σ21sσ*21sσ22sσ*22sπ22pπ22pσ22pπ*12pπ*12p (b) Bond orders are: N2 + = 2.5 ; N 2 2+ = 2.0 ; N
14 Jul 2021 — Molecule Ground state electron configuration NF GHO.PHP (ou of our NF+ NF (0) (014) (02) (02*) (2p) (2p) (12) Answer Bank Determine the bond ...1 answer · Top answer: Solution:-
When the atomic orbitals of the two atoms combine, the electrons occupy the molecular orbital of lowest energy, the σ1s bonding orbital. A dihydrogen molecule, H2, readily forms because the energy of a H2 molecule is lower than that of two H atoms.
Is there a way to determine if a molecule is diamagnetic or paramagnetic without drawing it's molecular orbital diagram? For example, in the workbook there is a question that asks you to identify the non-paramagnetic molecule out of OF+, NO+, CO+, NF+, and CF.
In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation
Pat's Chemistry Pages · an idea so smart that my head would explode if I even began to know what I was talking about
November 23, 2015 - 12/20: Andy's paper on supported nanocrystal catalysts is published in Chem. Mater.! 10/20: Our joint paper with the Klimov group using ALD to produce CMOS circuit elements from CIS quantum dot films is published in Nature Comms. 9/20: Our paper with Adam Moule's group on electron tomography ...
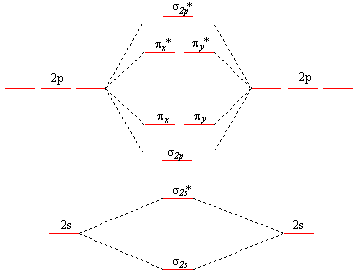
Such orbitals are called molecular orbitals, and this way of looking at molecules is referred to as molecular-orbital (abbreviated MO) theory. The term molecular orbital is mentioned in the discussion of The Covalent Bond when we described formation of a covalent bond in an H 2 molecule as a result of overlap of two 1 s atomic orbitals—one ...
Hund's rules predict that the three electrons in the 2p orbitals of a nitrogen atom all have the same spin, but electrons are paired in one of the 2p orbitals on an oxygen atom. Hund's rules can be understood by assuming that electrons try to stay as far apart as possible to minimize the force of repulsion between these particles.
C. Symmetry Orbitals and Molecular Orbitals The XAO MO's of the homopolar N2 and O2 molecules belong in sets to the irreducible representations of the point group D, h. To obtain proper symmetry for these MO's, symmetry orbit&s (ref. 15) are introduced. The MO's of a given
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
(6 − 0) = B.O. 2 Looking at the molecular orbital diagram, you can see that there are no ... Problem 3 Consider the molecule NF and the ions NF+ and NF- .
1 answerThe MO diagram of the NF molecule can be drawn as below. The energies of the atomic orbital of N and F are different. The atomic orbitals of F are...
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we’ll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in

4 15 Points Use Frontier Molecular Orbital Theory Fmo To Rationalize The Lack Of Reactivity Between Homeworklib
Solutions for Chapter 5Problem 9P: NF is a known molecule! a. Construct a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for NF, being sure to include sketches that show how the valence orbitals of N and F interact to form molecular orbitals. b. What is the most likely bond order for NF? c.
Solutions for Chapter 9 Problem 34E: For each of the two species NF and NF+, (a) draw MO energy level diagrams; (b) write out electron configurations; (c) determine bond orders and predict relative stabilities; and (d) predict diamagnetism or paramagnetism. … Get solutions Get solutions Get solutions done loading Looking for the textbook?
February 19, 2019 -
4. Draw the valence molecular orbital diagram for NF. State the bond order, the molecular orbital configuration and determine whether each of the following molecules/ions is paramagnetic or diamagnetic.
38 molecular orbital diagram of h2. Written By Chelsea P. Mariano Monday, November 8, 2021 Add Comment. Edit. 3 Feb 2021 — For H2, bond order = 1/2 (2-0) = 1, which means H2 has only one bond. The antibonding orbital is empty. Thus, H2 is a stable molecule. Again, in ...

Solved Draw The Mo Diagram For Nf Correctly Label As Much As Possible Including Homo Lumo Determine Bond Order And Use The Bond Order To Sketch A Lewis Dot Structure Including Any Formal
Get homework help fast! Search through millions of guided step-by-step solutions or ask for help from our community of subject experts 24/7. Try Study today.
john deere sx75.Ask Question Asked 5 years, 6 months ago. Active 5 years, 5 months ago. Viewed 411 times ... Search the URL with "Removing Primary Drive Belt (SX85)" and it will give a diagram and instructions on removing and replacing the drive belt, if that's the issue.The manual covers many other areas as well.
Structure and Bonding Solutions: #4. 4.* (1997 1 7) Consider the diatomic molecule NF. Draw its molecular orbital energy diagram. A. Using the LCAO-MO scheme, indicate the ground-state MO description for NF, i.e. complete the following: 1(s) 2. . .The LCAO-MO description is: 1s 2 2s 2 3s 2 4s 2 5s 2 1p 4 2p 2. B.
NF bond order: NF+ bond order: NF− bond order: Classify each molecule according to its magnetic properties. Diamagnetic Paramagnetic Answer Bank NF NF+ NF−. Use molecular orbital theory to complete the ground state electron configuration for each of the molecules. Determine the bond order of each of the molecules.
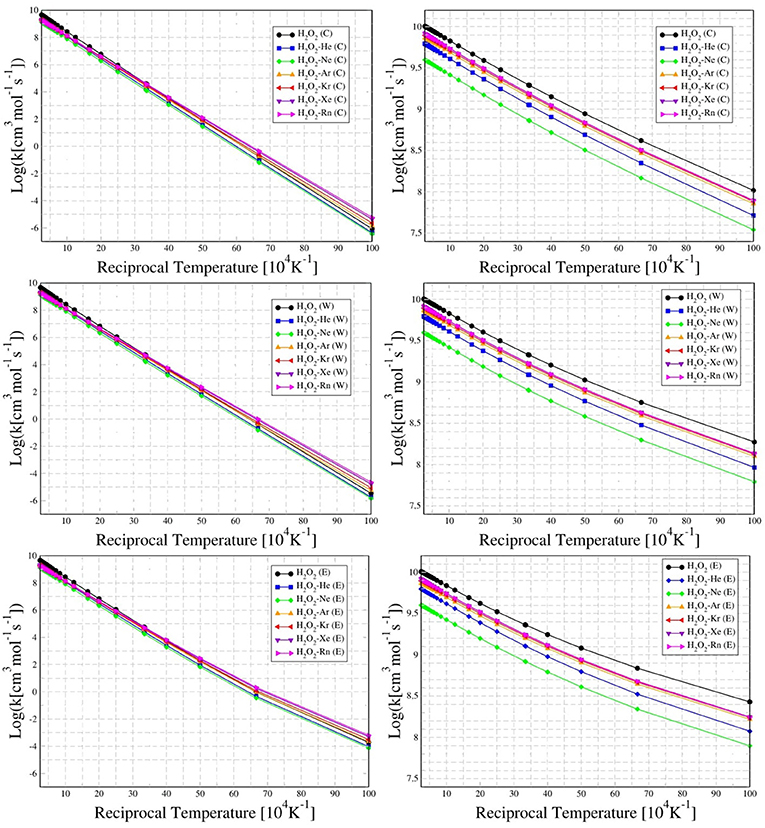
Frontiers Theoretical Investigation On H2o2 Ng He Ne Ar Kr Xe And Rn Complexes Suitable For Stereodynamics Interactions And Thermal Chiral Rate Consequences Chemistry






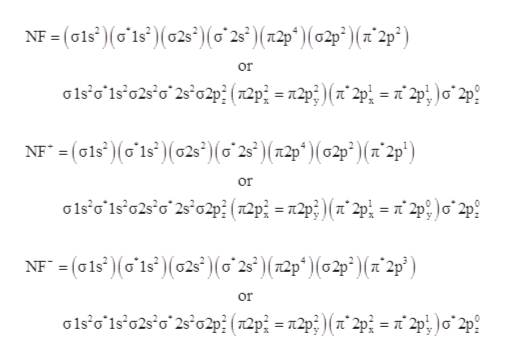











0 Response to "39 nf+ molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment