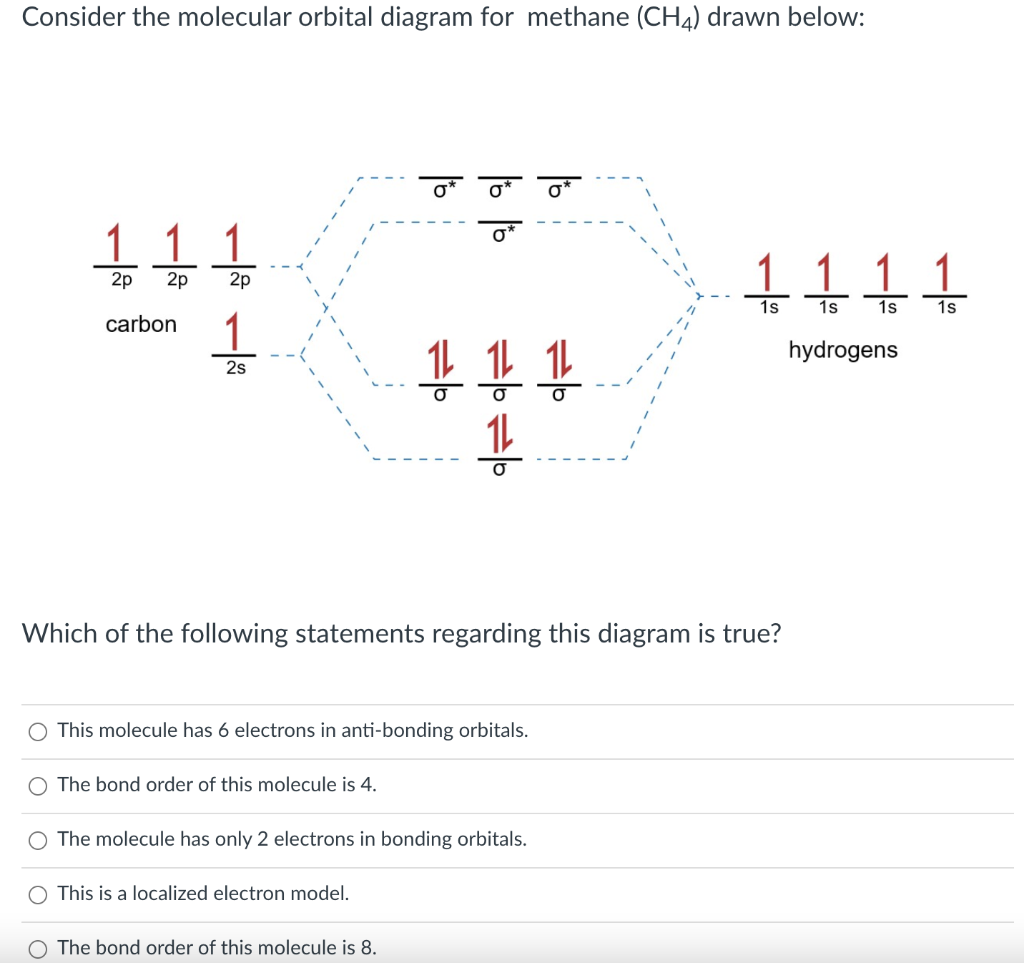
35 methane molecular orbital diagram
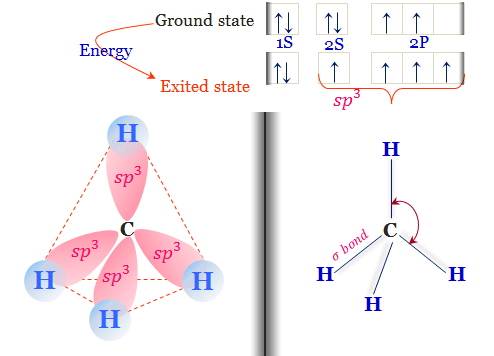
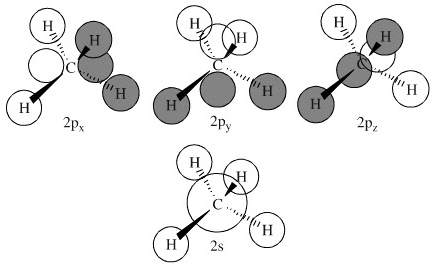
Hi. I was given an assignment about the orbital structure of carbon and the molecular structure of methane. Now i was also asked how does carbon form 4 bonds when the orbital diagram shows that there are only 2 unpaired electrons? My answer was just because of covent bonding resulting of sharing of electrons such as CH4 since each hydrogen atom share electrons with the carbon to satisfy the octate rule Angle and Geometry: Four sp 3 hybridized orbitals formed, repel each other and they are directed towards the four corners of a regular tetrahedron. The Angle between them is 109.5°. Each sp 3 hybrid orbital contains one unpaired electron.; In each sp 3 hybrid orbital, one of the lobes is bigger because of more concentration of electron density. Only bigger lobe is involved in bond formation.
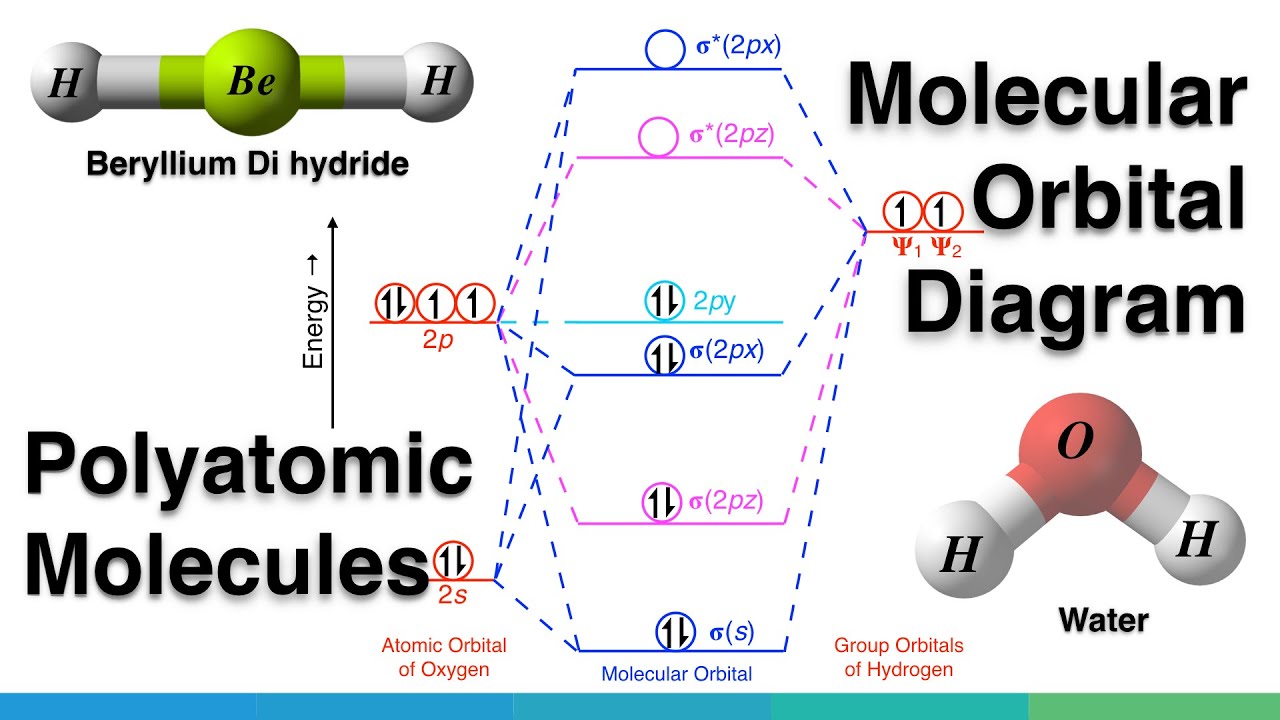
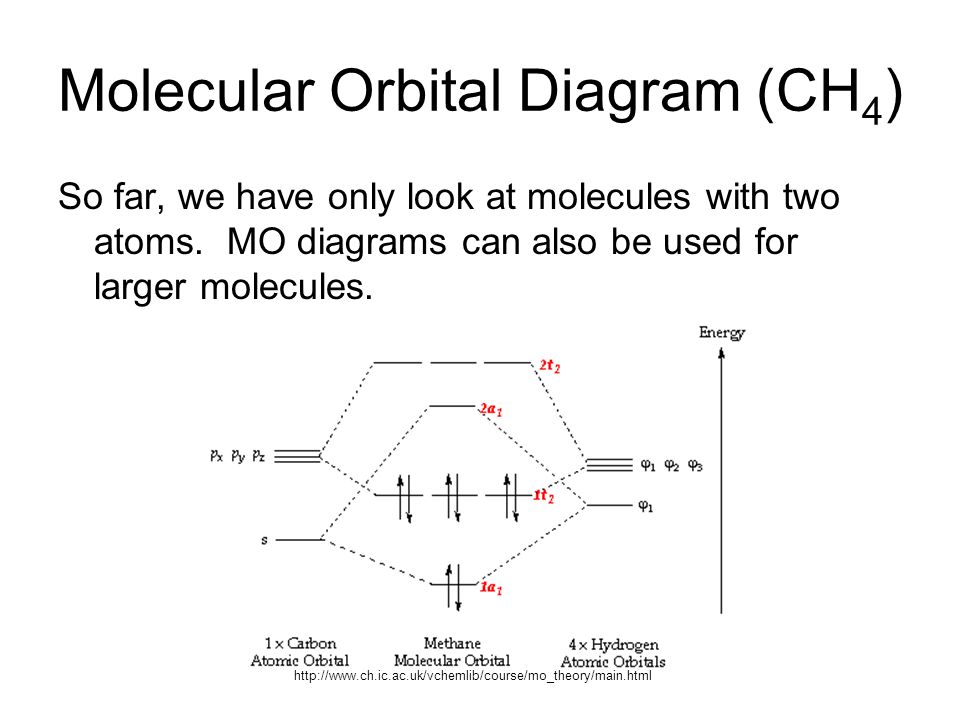
A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. It also helps us to find the bond order, bond length, bond strength of the molecule. In the diagram, the left-hand side consists of the atomic orbitals of carbon. Likewise, the left side has AO's of oxygen. And in the middle is the MO.
Methane molecular orbital diagram
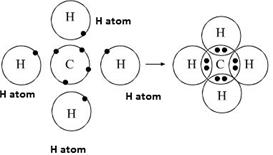
Methane (US: / ˈ m ɛ θ eɪ n /, UK: / ˈ m iː θ eɪ n /) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CH 4 (one atom of carbon and four atoms of hydrogen).It is a group-14 hydride and the simplest alkane and is the main constituent of natural gas.The relative abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel ... Molecular Geometry of Methane. The four hybrid orbitals in methane repel each other and get placed at the corners of a tetrahedron to minimise the force of repulsion between them. Hence, \({{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}}\) has a tetrahedral shape. Answers. There are only two possible bonds when molecular orbitals combine with each other. It can either be sigma bond, or a pi bond. You can differentiate between them by looking at the way they bond together. Sigma bond are much stronger because the orbitals are superimposed on each other. On the other hand, pi bond are overlapped only sideways.
Methane molecular orbital diagram. Answer: because electron excitation is NOT THE ONLY mode for a molecule to absorb energy from electromagnetic radiation. Depending on the energy (frequency) of the electromagnetic radiation, it can be converted to translation (i.e. molecular motion), rotation (molecules that rotate along a speci... The hydrogens bond with the two carbons to produce molecular orbitals just as lock did through methane. The 2 carbon atom bond by merging their staying sp3 hybrid orbitals end-to-end to do a brand-new molecular orbital. The bond developed by this end-to-end overlap is referred to as a sigma bond. CH2Cl2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and MO Diagram. Dichloromethane or methylene chloride, with the chemical formula CH2Cl2, is a colorless, volatile liquid with a boiling point of 39.6 °C. and a melting point of -96.7 °C. It is widely used as a solvent in chemistry laboratories. It is polar because of the presence of ... Molecular Orbital diagram of CH4. The molecular orbital diagram helps with determining how mixing and overlapping have taken place in a molecule to conclude upon the hybridization type. As per the figure, the four sp3 hybrid orbitals of the carbon mixes and overlaps with four 1s atomic orbitals of the hydrogen.
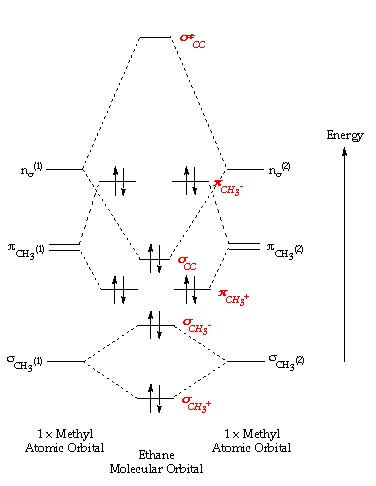
Ethane Formula: We all know that natural gas used as fuel for warming up our homes and for cooking, consists of methane, but do we know Ethane also forms a part of this natural gas. It is the second-largest percentage in natural gas. Ethane is a colourless, odourless, and flammable gas with a chemical formula of \({{\rm{C}}_2}{{\rm{H}}_6}\). CLEAR YOUR CONCEPTUAL DOUBTS ON ETHANE Now the molecular orbitals of methane form from the four 1s orbitals of each hydrogen atom and each of the four hybrid orbitals. Write to me in PM, we will discuss. π Molecular Orbitals of Ethene. There are a total of 6 electrons to add to the molecular orbital diagram, 3 from boron and 1 from each hydrogen atom. π Molecular Orbitals of ... Properties and bonding. Methane is a tetrahedral molecule with four equivalent C-H bonds.Its electronic structure is described by four bonding molecular orbitals (MOs) resulting from the overlap of the valence orbitals on C and H.The lowest-energy MO is the result of the overlap of the 2s orbital on carbon with the in-phase combination of the 1s orbitals on the four hydrogen atoms. The reactivity of (MoO 3 ) 5 O − can be traced back to the appropriate orientation of the lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals (LUMO) that is essentially the 2p orbital of the O b •− atom. This study not only makes up the blank of thermal methane activation by the O b •− radical on negatively charged clusters but also yields new ...
Molecular Orbital diagram of CH4. The molecular orbital diagram helps with determining how mixing and overlapping have taken place in a molecule to conclude upon the hybridization type. As per the figure, the four sp3 hybrid orbitals of the carbon mixes and overlaps with four 1s atomic orbitals of the hydrogen. Orbitals to be combined must have the same symmetry, otherwise, adding and subtracting will not lead to any fruitful result. And these orbitals can explain the photoelectron spectrum of methane. Molecular orbital theory also explains the resonance structure of benzene. Help determining normalisation constant in SALC of methane. We have been told that a symmetry adapted combination of four hydrogen orbitals is used to create localised hydrogen orbitals for methane. These orthonormal combinations are denoted ψa1, ψt'2, ψt''2 and ψt'''2. It then asks to calculate the normalisation constant for ... Figure 1. The hypothetical overlap of two of the 2p orbitals on one oxygen atom (red) with the 1s orbitals of 2 hydrogen atom (blue) would create a bond edge of 90°. This is not constant with experimental evidence.1> Quantum-mechanical calculations suggest why the it was observed bond angles in H2O different from those guess by the overlap that the 1s orbital of the hydrogen atoms with the 2p ...
Molecular Orbital diagram of CH4 The molecular orbital diagram helps with determining how mixing and overlapping have taken place in a molecule to conclude upon the hybridization type. As per the figure, the four sp3 hybrid orbitals of the carbon mixes and overlaps with four 1s atomic orbitals of the hydrogen.
The reactivity of (MoO 3) 5 O − can be traced back to the appropriate orientation of the lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals (LUMO) that is essentially the 2p orbital of the O b.− atom. This study not only makes up the blank of thermal methane activation by the O b .− radical on negatively charged clusters but also yields new insights ...
The hybrid orbitals are more prominent outward so that their ability to overlap is stronger than that of normal orbitals. Molecular Formula: A chemical formula is a brief way of expressing the number and type of atoms that make up a particular chemical compound.
One 2s orbital and three 2p orbitals are hybridized for the Carbon atom. CH4 Molecular Geometry. Molecular geometry helps us understand the arrangement of atoms in 3D for any given molecule. For the Methane molecule, there are four covalent bonds between Hydrogen and Carbon atoms.
Example: Molecular surface and Dot surface. Create models of Atomic orbitals s, p, d and f. Create models of Molecular Orbitals sp3, sp2 and sp. Create molecular orbitals for methane molecule.
The three hybrid orbitals are directed towards the three corners of an equilateral triangle. Thus it is known as trigonal hybridization. sp 3 Hybridization- Here one s- and three p- orbitals get hybridized to form four equivalent hybrid orbitals. These orbitals are directed towards the four corners of a regular tetrahedron.
For example, in methane, the ionized states (CH4+) can be constructed out of four resonance structures attributing the ejected electron to each of the four sp3 orbitals. A linear combination of these four structures, conserving the number of structures, leads to a triply degenerate T2 state and a A1 state.[16]
The molecular orbital diagram helps with determining just how mixing and overlapping have actually taken location in a molecule to conclude upon the hybridization type. As per the figure, the four sp3 hybrid orbitals of the carbon mixes and overlaps with 4 1s atom orbitals the the hydrogen.
The electrical current properties of single-molecule sensing devices based on electronic (tunneling) transport strongly depend on molecule frontier orbital energy, spatial distribution, and position with respect to the electrodes. Here, we present an analysis of the bias dependence of molecule frontier orbital properties at an exemplar case of DNA nucleotides in the gap between H-terminated (3 ...

Methane Orbital Structure Of Methane Preparation Of Methane Chemical Properties Of Methane Physical Properties Of Methane Uses Of Methane
Answer: A simple rule in recombining atomic orbitals to create molecular orbitals. You must end up with the same number of orbitals as you started with. If you're restricting yourself to only the valence shell orbitals then carbon has 4 (2s,2px,2py,2pz) and each hydrogen has 1 (1s). That makes a ...
Quantum-chemical calculation of most important parameters of molecular and electronic structures of octa-carbon C8 having cubic form (bond lengths, bond and torsion angles) using CCSD(T)/QZVP and DFT B3PW91/QZVP methods, has been carried out. NBO analysis data and HOMO/LUMO images for this compound are presented, too. Good agreement was found between the structural data obtained using the ...
Molecular Orbital diagram of CH4 The molecular orbital diagram helps with determining how mixing and overlapping have taken place in a molecule to conclude upon the hybridization type. As per the figure, the four sp3 hybrid orbitals of the carbon mixes and overlaps with four 1s atomic orbitals of the hydrogen.
Answers. There are only two possible bonds when molecular orbitals combine with each other. It can either be sigma bond, or a pi bond. You can differentiate between them by looking at the way they bond together. Sigma bond are much stronger because the orbitals are superimposed on each other. On the other hand, pi bond are overlapped only sideways.
Molecular Geometry of Methane. The four hybrid orbitals in methane repel each other and get placed at the corners of a tetrahedron to minimise the force of repulsion between them. Hence, \({{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}}\) has a tetrahedral shape.
Methane (US: / ˈ m ɛ θ eɪ n /, UK: / ˈ m iː θ eɪ n /) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CH 4 (one atom of carbon and four atoms of hydrogen).It is a group-14 hydride and the simplest alkane and is the main constituent of natural gas.The relative abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel ...















0 Response to "35 methane molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment