39 plane mirror ray diagram
Ray Diagrams for Plane Mirrors - A Plus Topper When you look into a plane mirror, you will see an image of yourself which has the following characteristics The characteristics and the position of the image formed by a plane mirror can be determined by drawing a ray diagram. › 10827 › 3118Convex Mirror - Ray diagram, Images Formed - teachoo Apr 23, 2020 · For a Convex Mirror,The focus and center of curvature is on the right side of the mirrorSo, there will only be 2 cases.They areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Principal axis and InfinityCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object AB is kept far away from mirror (al
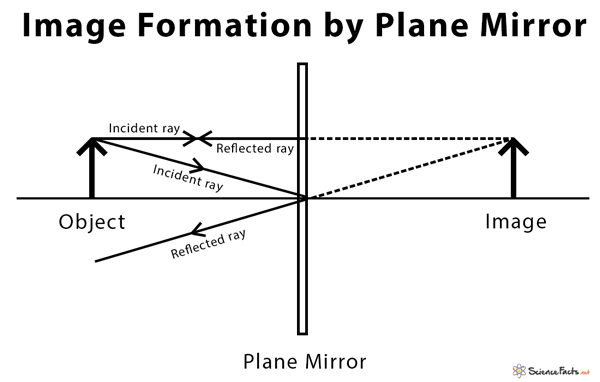
Mirrors | Brilliant Math & Science Wiki | Plane Mirrors The ray diagram shows the image formation, A', of an object placed in front of a plane mirror, A. [1]. Plane mirrors are flat mirrors. The rules of plane mirrors are straight-forward and only explicitly stated so they may be modified for spherical mirrors.
Plane mirror ray diagram
Reflection on a Plane Mirror: Laws, Uses, Image Formation A plane mirror is a mirror with a flat or planar mirror reflective surface. Let us understand the reflection on Plane Mirror with a diagram. Incident Ray: The light rays falling on the surface of the plane mirror is called the incident ray of light. Mirrors | Boundless Physics | Ray Diagrams Plane Mirrors and Reflection. A mirror is a reflective surface that does not allow the passage of light and instead bounces it off, thus producing an image. The image is also the same size as the object. These images are also parity inverted, which means they have a left-right inversion. Ray Diagrams. Physics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams for Plane Mirrors Similarly, ray diagrams are useful tools for determining and explaining what objects might be viewed when sighting into a mirror from a given location. For example, suppose that six students - Al, Bo, Cy, Di, Ed, and Fred sit in front of a plane mirror and attempt to see each other in the mirror.
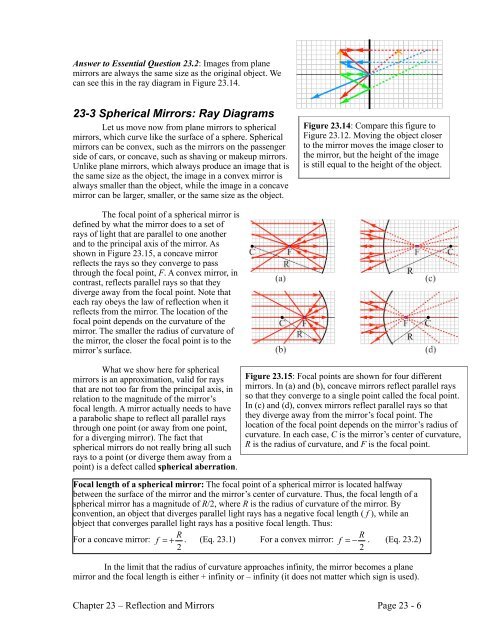
Plane mirror ray diagram. Concave and Convex Mirrors | Ray Diagram for Convex and Concave... Convex Mirror Ray Diagram: When an object is placed at infinity a virtual image will be formed at the focus point. The image will be highly diminished as compared to the object. Plane mirrors and convex mirrors only produce virtual images. courses.physics.ucsd.edu › 2009 › Fall3.1.Image formation by Mirrors and Lenses • A ray passing through the focal point reflects parallel to the mirror axis • A ray striking the center of the mirror reflects symmetrically around the mirror axis • A ray that passes through the center of curvature C reflects and passes back through itself •• Mirror C F axis R F 2 = Law of Reflection The position of the image can be ... Class 12 Physics Revision Notes for Chapter 9 - Ray Optics ... Reflection by a plane surface and a plane mirror has been explained in Ray Optics And Optical Instruments Class 12 Notes with the help of diagrams. Spherical Mirrors Students can strengthen their understanding of spherical mirrors after going through this section in the Physics Class 12 Chapter 9 Notes. Drawing Ray Diagrams for Plane Mirrors - ppt download Presentation on theme: "Drawing Ray Diagrams for Plane Mirrors"— Presentation transcript Once repeated for each extreme, your ray diagram is complete. 6 Drawing Ray Diagrams for Concave Mirrors. 7 Some points to know: C = Centre of Curvature R = Radius of curvature F = Focal point f...
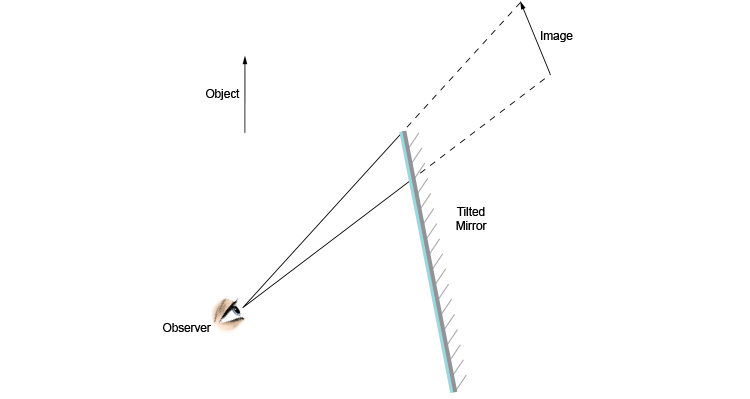
Flat mirror, tilted, ray diagram How do you draw the ray diagram for a flat mirror which has been tilted, an object and an observer, as below: The way to draw the ray diagram for this situation is to carry out the three stages as we have previously learnt as follows: The first stage is to draw an image behind the mirror by marking either... The reflection and refraction of light - Boston University It's relatively straight-forward geometry, all based on similar triangles, but we should review that for a plane mirror. Consider an object placed a certain distance in front of a mirror, as shown in the diagram. To figure out where the image of this object is located, a ray diagram can be used. In a ray diagram, rays of light are drawn from the object to the mirror, along with the rays that ... Optics - Mirrors | Shmoop | Plane Mirrors Mirrors come in two flavors, plane and spherical. Plane mirrors are what we find in any bathroom or department store. All of the glass in the mirror is in the same plane—not in the Boeing 747 sense, but plane, as in Let's redraw our ray diagram including the concept of the mirror's radius of curvature. Physics Optics: Plane Mirrors - University of British Columbia Plane Mirrors III A ray of light is approaching a set of three mirrors as shown in the diagram. The light ray is approaching the first mirror at an angle of 45-degrees with the mirror surface. How many times will the ray reflect before it exits the system?
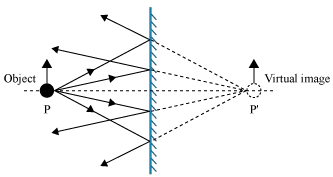
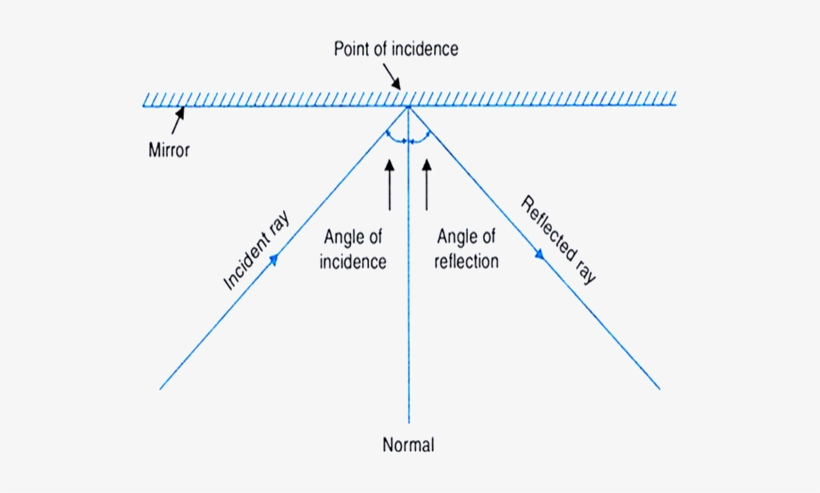
Plane Mirror: Definition, Ray Diagram, Uses and Applications Image formation by a plane mirror using a ray diagram. How does reflection take place. How is the image produced. What are some examples. Ordinary plane mirrors are coated at the back so that the incident ray is reflected from the back surface instead of the front surface. oPhysics Image Formation in Plane Mirrors. Description This is a simulation to illustrate the processes involved in the formation of images in plane mirrors. When the control points are visible, you can move the object (the blue arrow), the four points where the (blue) incident rays strike the mirror, as well as the two ends of the mirror itself. The diagram shows two real rays coming from … How can we show lateral inversion by a plane mirror by a ray diagram? You can see many diagrams showing how the image in a plane mirror is an inversion of the object in the direction normal to the mirror surface. However, that's difficult to show just with ray diagrams, because it's explained in psychological terms (the psychology of visual percepti. The law of reflection - Light and sound - reflection and ... An incident ray of light hits a plane mirror at an angle and is reflected back off it. The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. Both angles are measured from the normal. The ...
Ray Diagram for Point and Extended Objects in Plane Mirror Read formulas, definitions, laws from Image Formed by Plane Mirror here. Click here to learn the concepts of Ray Diagram for Point and Extended Example: A child of height H is standing in front of a straight plane mirror. His father is standing behind him, as shown. The height of the father is...
Plane Mirror Ray Diagram: study guides and answers on Quizlet Plane Mirror Ray Diagram. Quizlet is the easiest way to study, practise and master what you're... Plane Mirror Ray diagram
Spherical lenses: converging, diverging Plane mirrors ... Ray diagram for diverging lens • point object A, source of light • reflected rays appear to come from A’ A’ is image of A • image appears to be located behind the mirror image is virtual Plane mirror • every point of the object acts as light source • every point has an image • collection of image points form image of the object • image is upright, virtual, same size as object ...
Relfection from a Plane Mirror | Light as Rays A ray is the direction of the path taken by light and is represented in diagrams by a straight line with an arrow indicating the direction in which the rays is travelling. However, we do see any reflections as with a plane-mirror. At the microscopic scale the law of reflection is obeyed but the surface is...
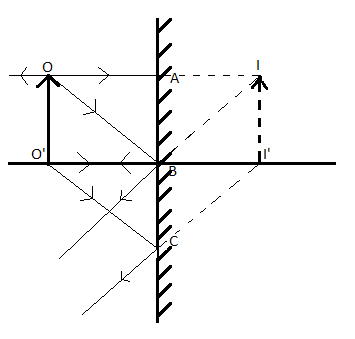
Drawing ray diagrams for plane mirrors - Mini Physics - Learn Physics This is a short tutorial on how to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Click on the images to view a larger version. Initially, we have an object in front of a Lines joining the object to the positions of the reflected rays on the mirror represent the incident rays. Properties of image formed in plane mirror
Ray Diagrams for Plane Mirrors - YouTube Give Mr. H just 6 minutes to explain what a ray diagram is and to demonstrate how to construct a ray diagram for a point object and an arrow object.
PDF The Ray Model of Light describe ray diagrams for plane, concave, and convex mirrors • describe the characteristics of images including size, orientation, and whether they are real or virtual. In this chapter, you will • draw ray diagrams for plane, concave, and. convex mirrors • interpret ray diagrams to predict the.
Ray Diagrams for Mirrors Mirror ray tracing is similar to lens ray tracing in that rays parallel to the optic axis and through... Change to convex mirror Ray diagrams for mirrors
Physics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams - Concave Mirrors While plane mirrors always produce virtual images, concave mirrors are capable of producing both real and virtual images. As shown above, real images are produced when the object is located a distance greater than one focal length from the mirror. A virtual image is formed if the object is located less than one focal length from the concave mirror. To see why this is so, a …
Plane mirror- Definition, Properties and Ray Diagram Plane mirrors in physics have a flat reflecting surface and produce always a virtual image. Geometry prove of plane mirror properties are presented in simple words for high school and college students. Image formation in the plane mirror by ray diagram
Plane mirror - Wikipedia A plane mirror is a mirror with a flat (planar) reflective surface. For light rays striking a plane mirror, the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence. The angle of the incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the surface normal (an imaginary line perpendicular to the surface).
Lesson Explainer: Drawing Ray Diagrams for Concave Mirrors | Nagwa Before starting to draw ray diagrams, it will be useful to first consider a concave mirror as a three-dimensional solid object. It would be easy to mistake how to draw the path for the correct ray by incorrectly comparing a concave mirror to a plane mirror.
The plane mirror - The critical angle and optical fibres - GCSE Physics... Ray diagrams explain reflection in a plane mirror. Beyond a critical angle all waves are totally internally reflected. In a ray diagram, the mirror is drawn as a straight line with thick hatchings to show which side has the reflective coating.
Convex & concave mirror ray diagrams (video) | Khan Academy Practice: Ray diagrams and curved mirrors. Mirror formula derivation. Cartesian sign conventions mirrors. Practice: Concave and convex mirrors. Next lesson. Refraction at plane surfaces.
Plane mirror ray diagram and image formation Geometric ray... Download scientific diagram | Plane mirror ray diagram and image formation Geometric ray diagram of plane mirror shows that object distance (í µí±‘ 0 ) and image distance (í µí±‘ í µí±– ) are the same. í µí±‘ 0 = í µí±‘ í µí±– (1) from publication: A Set of Virtual Experiments of Fluids, Waves...
› Physics-InteractivesPhysics Simulation: Plane Mirror Image The Plane Mirror Images Interactive is shown in the iFrame below. There is a small hot spot in the top-left corner. Clicking/tapping the hot spot opens the Interactive in full-screen mode. Use the Escape key on a keyboard (or comparable method) to exit from full-screen mode. There is a second hot-spot in the lower-right corner of the iFrame.
Plane mirror ray diagrams | Teaching Resources Plane mirror ray diagrams. Subject: Physics. Age range: 14-16. Hand drawn worksheet for practice constructing ray diagrams for a plane mirror. Answer sheet included.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Chandra_X-ray_ObservatoryChandra X-ray Observatory - Wikipedia History. In 1976 the Chandra X-ray Observatory (called AXAF at the time) was proposed to NASA by Riccardo Giacconi and Harvey Tananbaum. Preliminary work began the following year at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO), where the telescope is now operated for NASA at the Chandra X-ray Center in the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics.
Focusing and Collimating - Newport As a first example, we look at a common application, the focusing of a laser beam to a small spot. The situation is shown in Figure 1. Here we have a laser beam, with radius y 1 and divergence θ 1 that is focused by a lens of focal length f. From the figure, we have θ 2 = y 1 /f.The optical invariant then tells us that we must have y 2 = θ 1 f, because the product of radius and …
SNC2D Opt04b Plane Mirror Ray Diagram Instructions... - StuDocu plane mirror ray instructions for drawing ray diagram (plane mirror) measure the shortest distance from the end of the object to the mirror (this will always be. If your diagram is accurate each reflected ray will obey the Law of reflection without you needing to use a protractor.
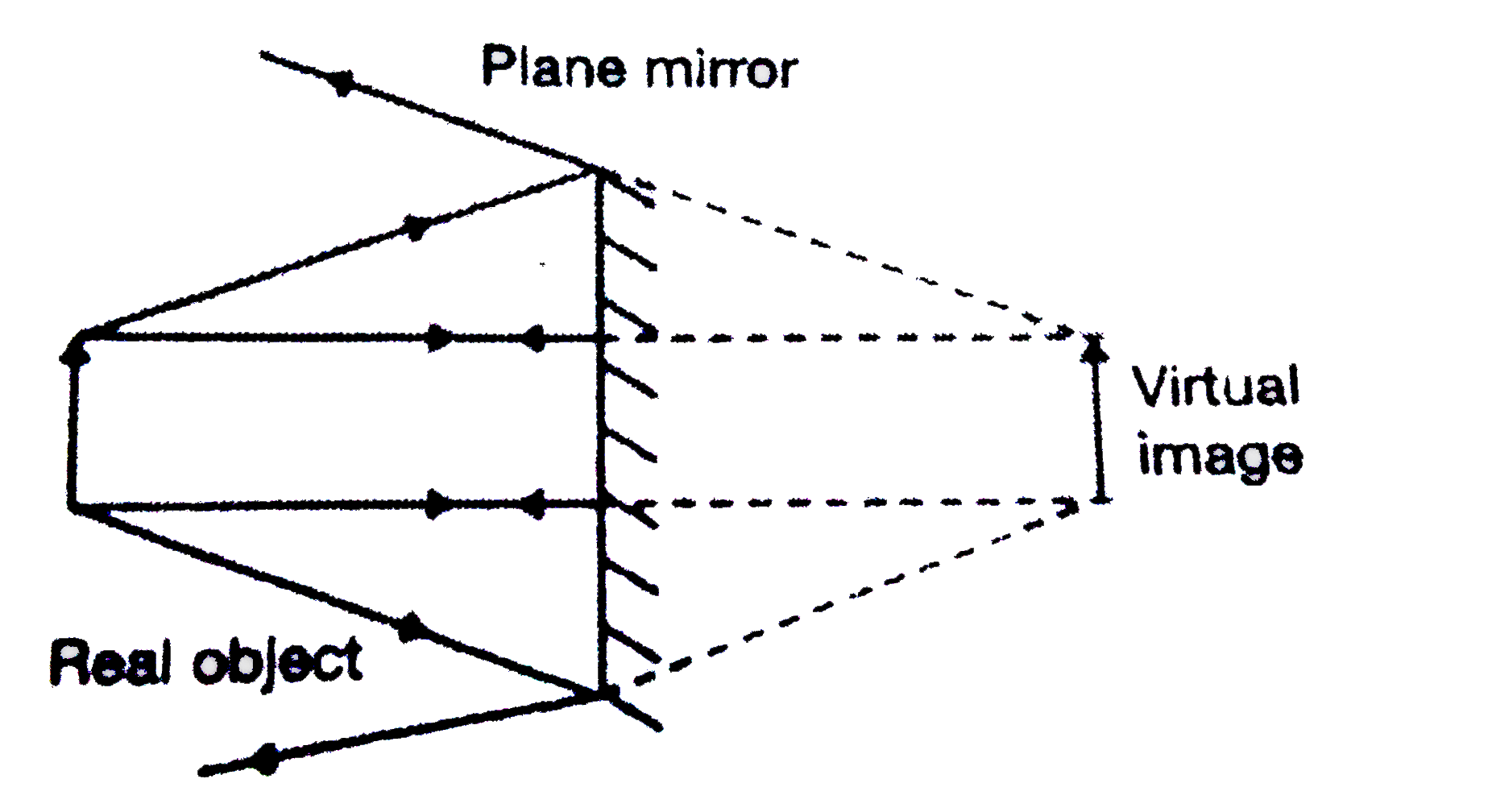
› class › reflnPhysics Tutorial: Image Characteristics of Plane Mirrors Plane mirrors produce images with a number of distinguishable characteristics. Images formed by plane mirrors are virtual, upright, left-right reversed, the same distance from the mirror as the object's distance, and the same size as the object.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum Song - YouTube Emerson Foo ( ) & Wong Yann ( ) made an original music video on the Electromagnet...
Physics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams - Convex Mirrors A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. A ray diagram for a convex mirror shows that the image will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram.
Spherical Mirrors - University Physics Volume 3 Use ray diagrams and the mirror equation to calculate the properties of an image in a spherical mirror. The image in a plane mirror has the same For a plane mirror, we showed that the image formed has the same height and orientation as the object, and it is located at the same distance...
Plane Mirror ray diagrams : Simon Lees : Free... : Internet Archive Plane Mirror ray diagrams. Movies Preview. remove-circle. podcast_physics-light-waves-tutoria_plane-mirror-ray-diagrams_1000336463479. Keywords. episode podcast itunes apple.
Physics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams for Plane Mirrors Similarly, ray diagrams are useful tools for determining and explaining what objects might be viewed when sighting into a mirror from a given location. For example, suppose that six students - Al, Bo, Cy, Di, Ed, and Fred sit in front of a plane mirror and attempt to see each other in the mirror.
Mirrors | Boundless Physics | Ray Diagrams Plane Mirrors and Reflection. A mirror is a reflective surface that does not allow the passage of light and instead bounces it off, thus producing an image. The image is also the same size as the object. These images are also parity inverted, which means they have a left-right inversion. Ray Diagrams.
Reflection on a Plane Mirror: Laws, Uses, Image Formation A plane mirror is a mirror with a flat or planar mirror reflective surface. Let us understand the reflection on Plane Mirror with a diagram. Incident Ray: The light rays falling on the surface of the plane mirror is called the incident ray of light.

























0 Response to "39 plane mirror ray diagram"
Post a Comment