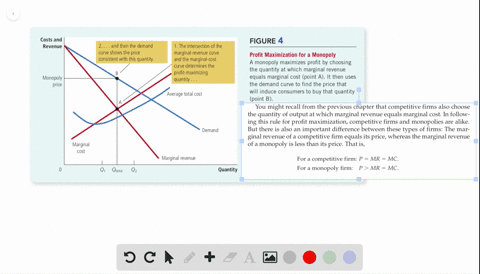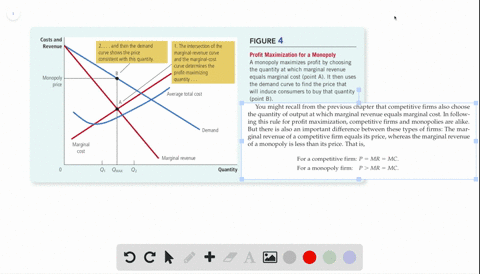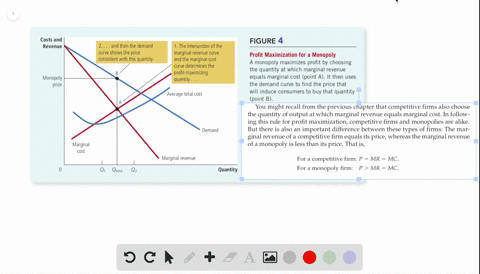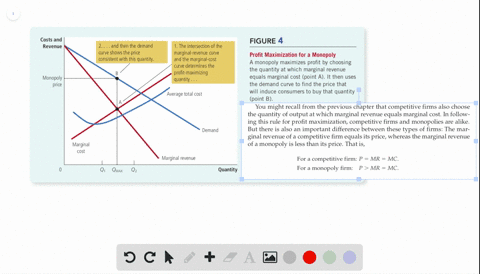
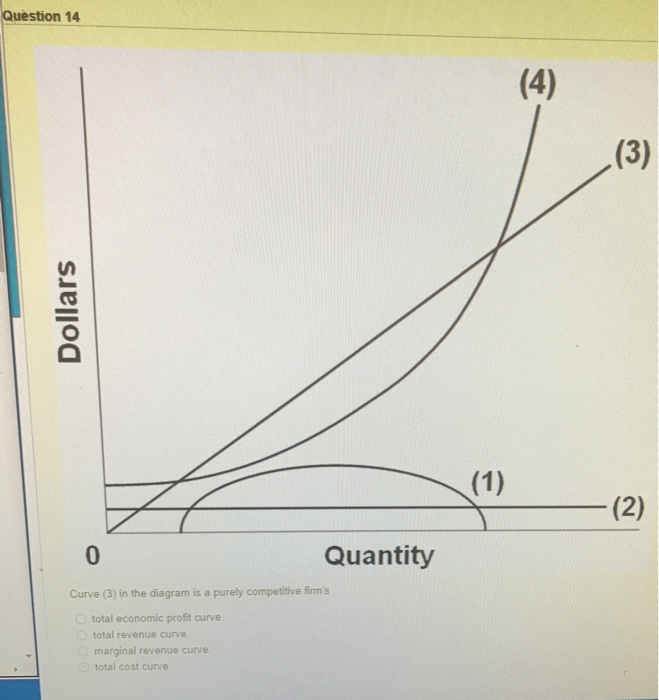
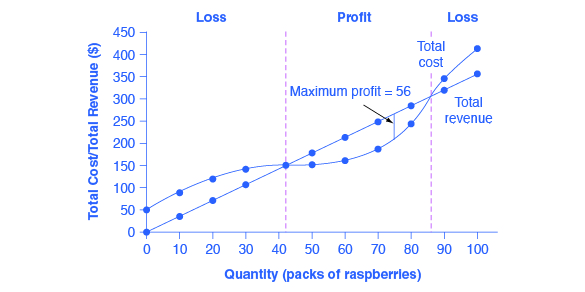
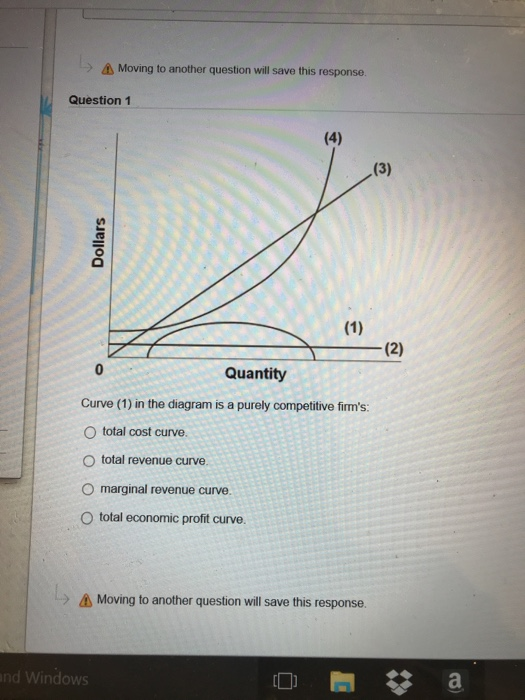
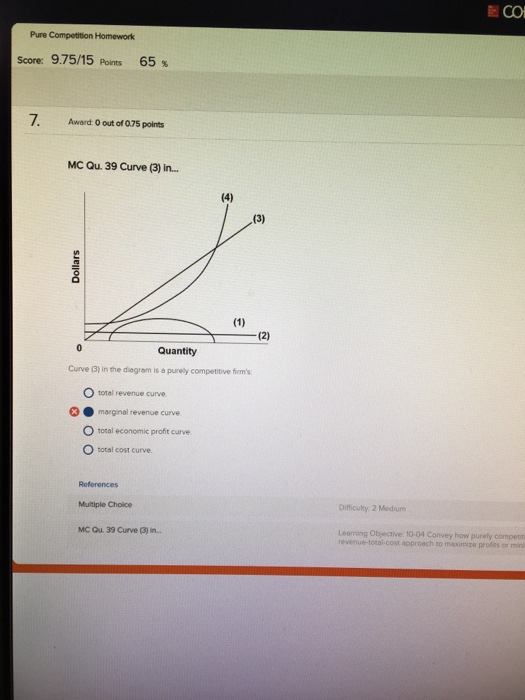
39 curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
Perfect Competition | Boundless Economics The total revenue for a firm in a perfectly competitive market is the product of price and quantity (TR = P * Q). The average revenue is calculated by dividing total revenue by quantity. Marginal revenue is calculated by dividing the change in total revenue by change in quantity. A firm in a competitive market tries to maximize profits. The lowest point on a purely competitive firm's short-run ... Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: The demand schedule or curve confronted by the individual purely competitive firm is; Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. curve a represents; Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's; Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's ...
Fountain - Custom Essay Writing Service - 24/7 ... Undergrad. (yrs 1-2) Psychology. 2. View this sample Research proposal. Writer's choice based on the given 6 options please/thanks. Undergrad. (yrs 1-2)
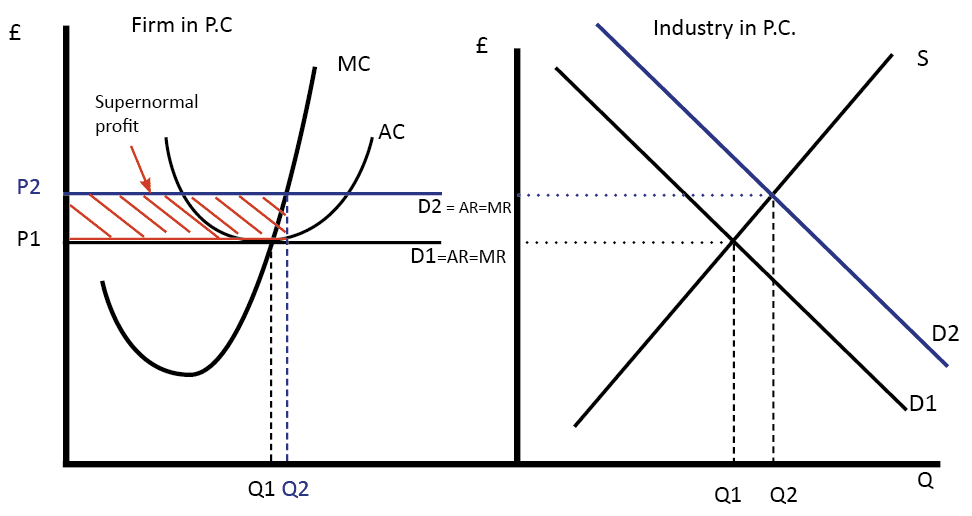
Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's
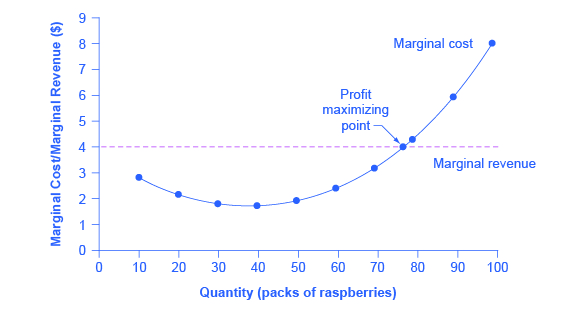
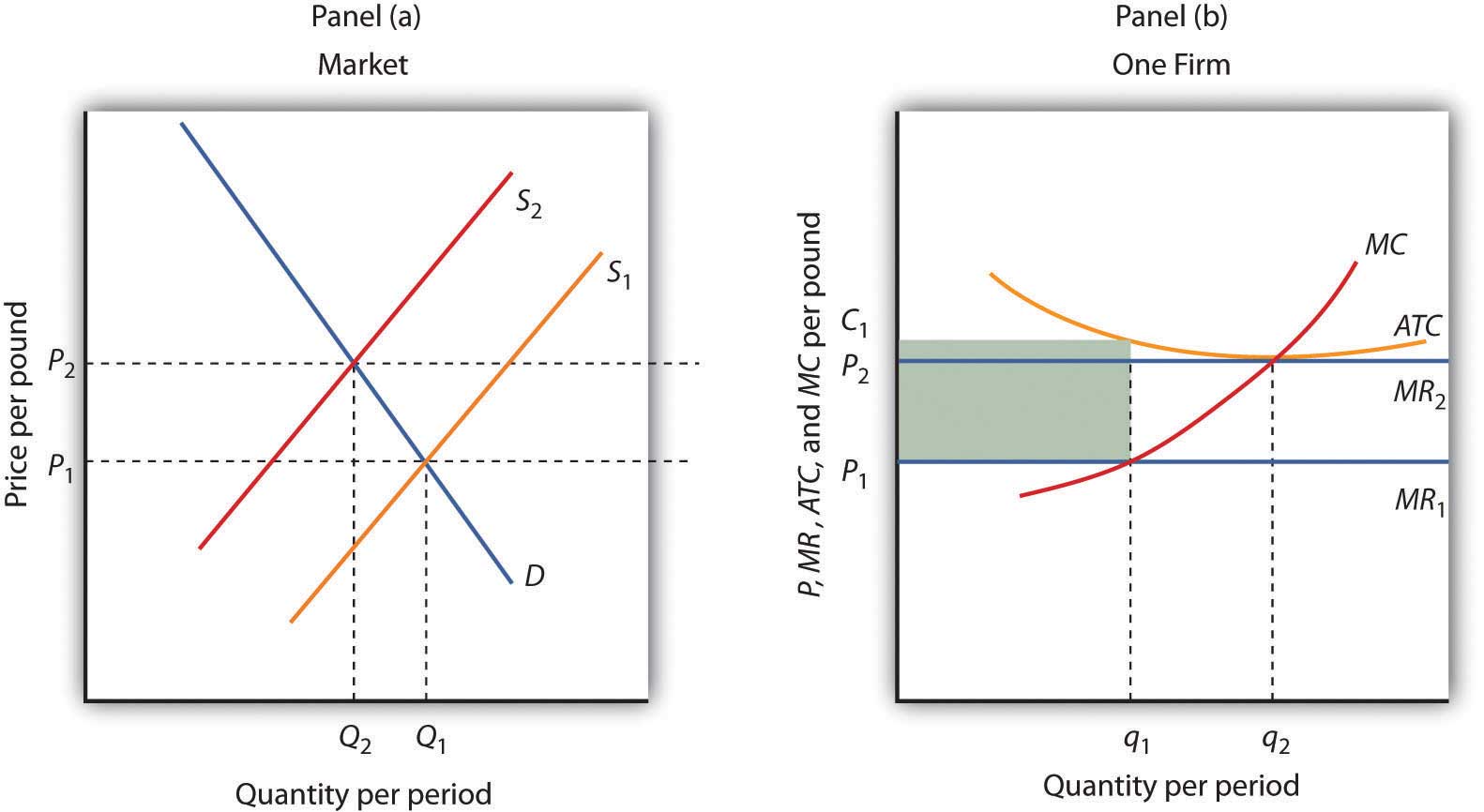
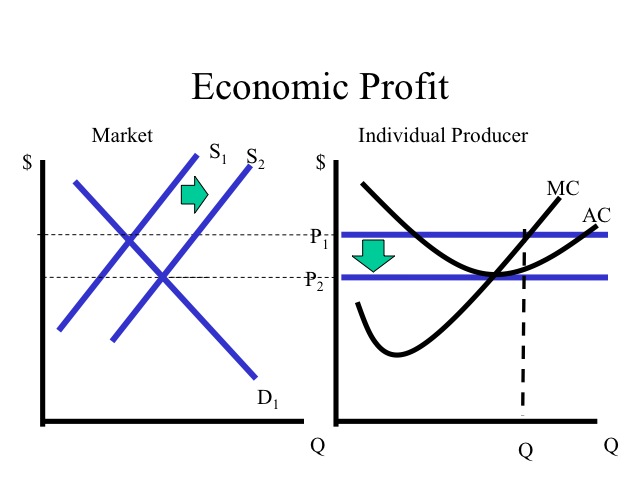
study.com › learn › microeconomics-questions-andMicroeconomics Questions and Answers - Study.com 1. A perfectly competitive firm's marginal cost is MC=75+3q. The firm's short run supply curve is: a. q=-75+3P b. q=25+0.33P c. q=75+3q d. q=-25+0.33P 2. Which of the following market characteristi... DOCX ANSWERS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS - Seneca Valley School ... Explanations and characteristics of the four models are outlined at the beginning of this chapter. Then the characteristics of a purely competitive industry are detailed. There is an introduction to the concept of the perfectly elastic demand curve facing an individual firm in a purely competitive industry. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Transfer_pricingTransfer pricing - Wikipedia There are two markets each with its own price (Pf and Pt in the next diagram). The aggregate market is constructed from the first two. That is, point C is a horizontal summation of points A and B (and likewise for all other points on the net marginal revenue curve (NMRa)). The total optimum quantity (Q) is the sum of Qf plus Qt.
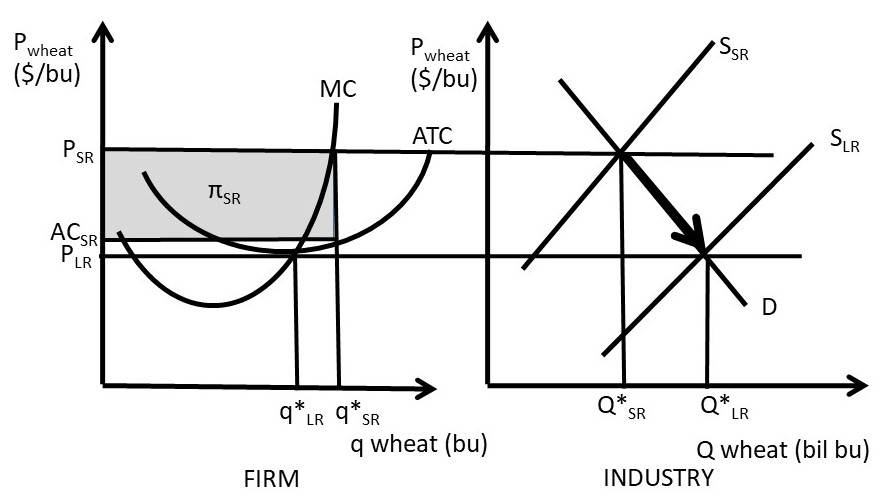
Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's. PDF Econ 103, 2008-2 Answers to Home Work Assignments (a) The industry is purely competitive—this firm is a "price taker." The firm is so small relative to the size of the market that it can change its level of output without affecting the market price. (b) See graph. (c) The firm's demand curve is perfectly elastic; MR is constant and equal to P. Therefore, the marginal Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: The lowest point on a purely competitive firm's short-run supply curve corresponds to A firm operating in a purely competitive resource market faces a resource supply curve that is The short-run supply curve of a purely competitive producer is based primarily on its Solved Question 14 I (3) Dollars - (2) Quantity Curve (3 ... Question 14 I (3) Dollars - (2) Quantity Curve (3) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's total economic profit curve total revenue curve marginal revenue curve total cost curve. Pure Competition A schedule or curve showing the prices at which a purely competitive industry will make various quantities of the product available in the long run. 1. constant cost industry. An industry in which expansion or contraction will not affect resource prices and therefore production costs
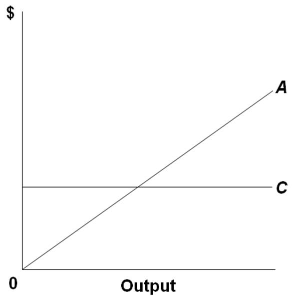
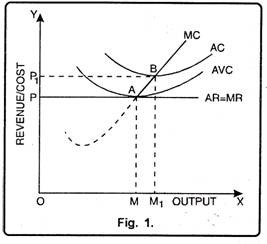
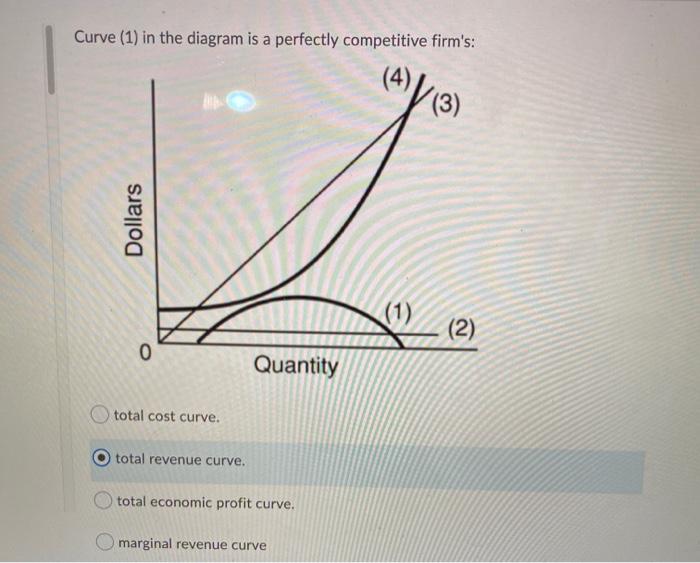
Ch11quiz - paws.wcu.edu is more elastic than that faced by a single purely competitive firm. 27. Suppose that a pure monopolist can sell 10 units of output at $5 per unit and 11 units at $4.90 per unit. Pure Competition: Definition, Characteristics & Examples ... Pure competition is a market condition where the companies providing products offer the same features and price, making the difference between manufacturers minor, if not completely irrelevant ... Equilibrium of the Firm in the Short Run (With Diagram) In figure 5.2 we show the total revenue and total cost curves of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. The total-revenue curve is a straight line through the origin, showing that the price is constant at all levels of output. The firm is a price-taker and can sell any amount of output at the going market price, with its TR increasing proportionately with its sales. The slope of the TR curve is the marginal revenue. Curve 1 in the diagram is a purely competitive firms A ... Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve.
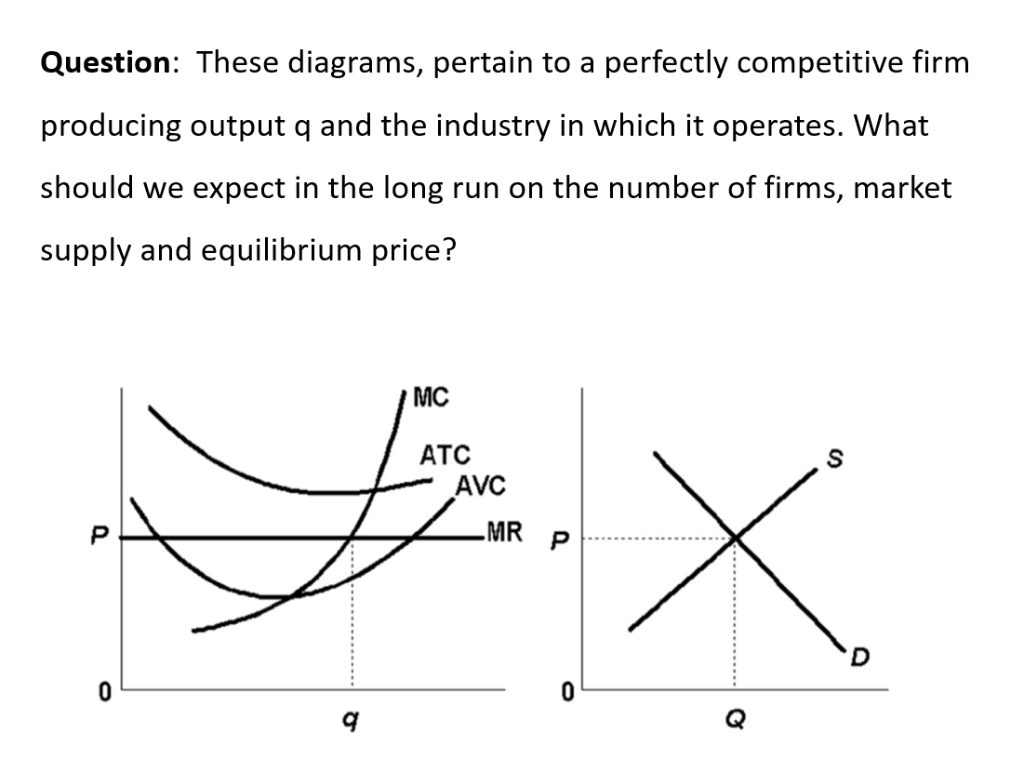
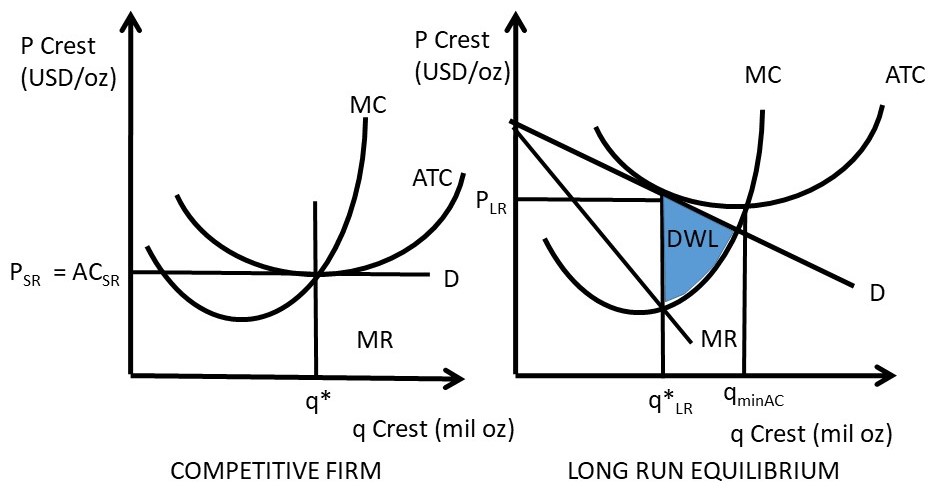
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › ExternalityExternality - Wikipedia Supply and demand diagram. The usual economic analysis of externalities can be illustrated using a standard supply and demand diagram if the externality can be valued in terms of money. An extra supply or demand curve is added, as in the diagrams below. Supply Curve of a Firm and Industry (With Diagram) Thus Long Run Supply Curve of a firm is that portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above the minimum point of the average cost curve. In figure 3 the firm is in equilibrium at point E where MRLMC (=AR). AC is minimum corresponding to this point. This point E is also called optimum point because at this point MR=LMCAR minimum LAC. That portion of LMC which is above E is called long run supply curve. 2. Long Run Supply Curve of an Industry: Microecon Final Exam Practice Test Flashcards - Quizlet Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's marginal revenue curve. An industry comprising a small number of firms, each of which considers the potential reactions of its rivals in making price-output decisions, is called Question: 3. Quantity Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely ... Show transcribed image text 3. Quantity Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: O total revenue curve. total profit curve. total cost curve O total cost curve. O marginal revenue curve. 3. Quantity Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: O total revenue curve. total profit curve. total cost …
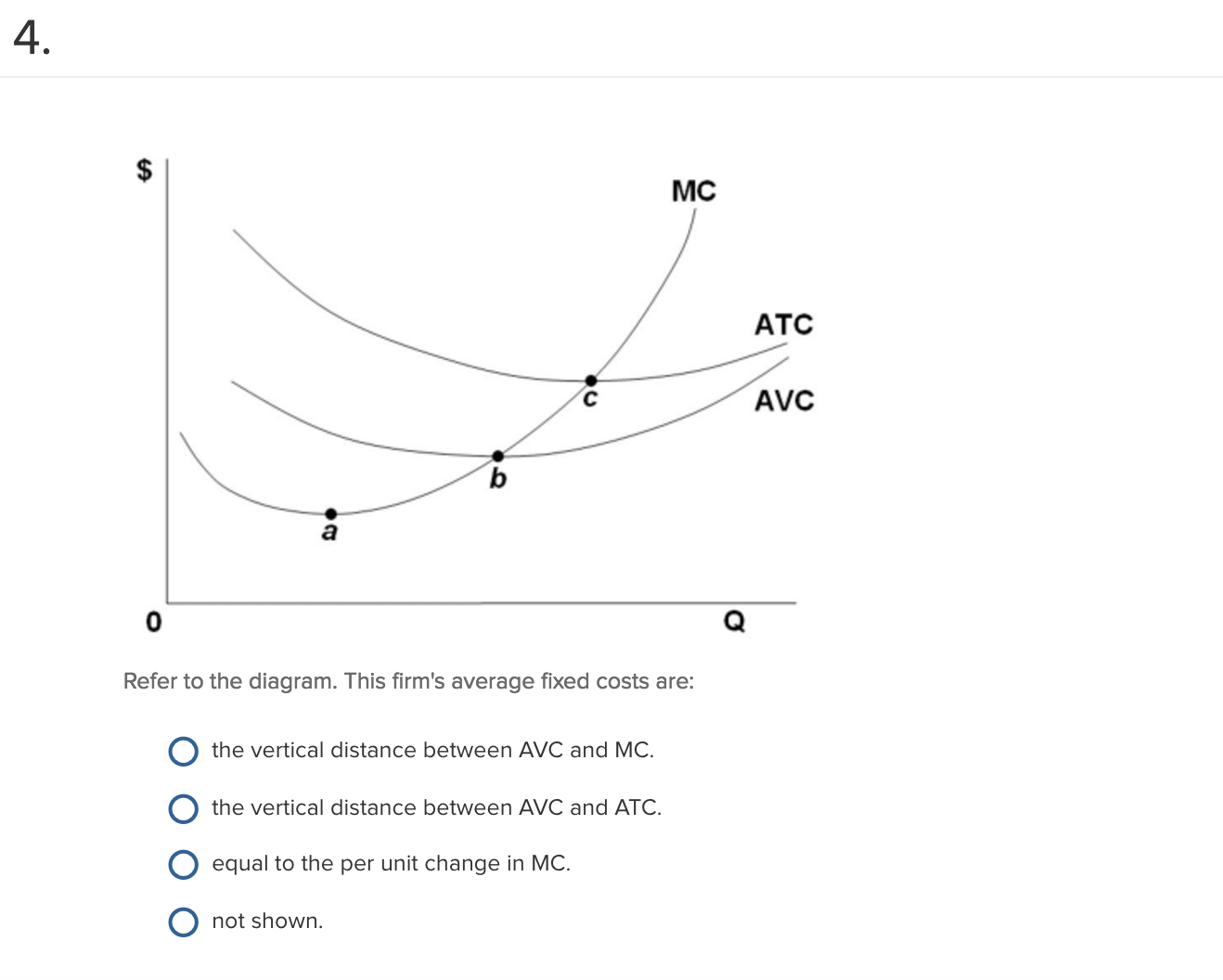
45 refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely ... Get the detailed answer: Refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. What does curve c represent? a) to tal revenue and marginal reve • Question 1 1 out of 1 points Refer to the above diagram, which pertains to a purely competitive firm. Curve represents: C Answer. Selected Answer: average revenue and marginal revenue.
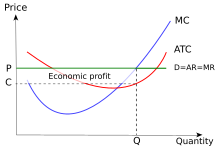
Pure Competition - thismatter.com Economics Pure Competition. A perfectly competitive market is rare, but those that exist are very large, such as the markets for agricultural products, stocks, foreign exchange, and most commodities.Pure competition also offers a simplified economic market model that yields useful insights into the nature of competition and how it provides the greatest value to consumers.
Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's ... Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: May 13, 2020 by sevdaSCO. A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. ANSWER. D. total economic profit curve. Categories economics Post navigation. Refer to the short-run data. The profit-maximizing output for this firm is:
Curve 2 in the above diagram is a purely competitive firms ... 38. Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. Answer: C Topic: Profit maximization in the short run
Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's ... Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: May 13, 2020 by sevdaSCO. A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total profit curve. ANSWER: A. total cost curve. Categories economics Post navigation.
Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer ... Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm's short-run supply curve is: asked Aug 14, 2018 in Economics by universe96. A. the abcd segment and above on the MC curve. B. the bcd segment and above on the MC curve. C. the cd segment and above on the MC curve.
38 refer to the diagram, which pertains to a purely ... Refer to the diagram which pertains to a purely competitive firm curve c represents. A firm is producing an output such that the benefit from one more unit is more than the cost of producing that additional unit. Purely competitive firms monopolistically competitive firms and pure monopolies all earn zero economic profits in the long run ...
revmncmp The demand curve of a monopolistically competitive producer is: A. less elastic than that of either a pure monopolist or a purely competitive seller. B. less elastic than that of a pure monopolist, but more elastic than that of a purely competitive seller. ... In long-run equilibrium the firm shown in the diagram above will: A. earn a normal ...
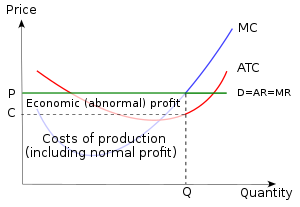
ECON Pure Competition 1 Short run Flashcards | Quizlet The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for this firm's product is $87, it will produce Multiple Choice 8 units at an economic profit of $130.72. 6 units at a loss of $90. 9 units at an economic profit of zero. 9 units at an economic profit of $281.97.
› price-elasticityMarginal Revenue and Price Elasticity of Demand The following one is a perfectly elastic demand curve. This is often used to depict the price and output behaviour of a firm under pure competition. Here dP/dQ = 0. Therefore, the graphing of P in terms of Q in Figure 10.7, has a slope of zero. In other words, the demand curve is completely (perfectly) elastic.
ECON 202 Blanchard Exam 2 - Subjecto.com The demand curve for a purely competitive firm is perfectly elastic, but the demand curve for a purely competitive industry is downsloping. Curve (4) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: a. total cost curve b. total revenue curve c. marginal revenue curve d. total profit curve.
Solved Dollar (1) 0 Quantity 5 Curve (2) in the diagram is ... Question: Dollar (1) 0 Quantity 5 Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's Multiple Choice total cost curve. total economic profit curve. marginal revenue curve. total revenue curve. This problem has been solved!
pure competition questions numbered Curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve. 12. Refer to the diagram. Other things equal, an increase of product price would be shown as: A. an increase in the steepness of curve (3), an upward shift in curve (2), and an upward
PDF UNF PMASON - unf.edu The quantitative difference between areas QIbcQ 2 and PIP2ba in the above diagram measures: marginal cost. total revenue. marginal revenue, D) average revenue. E) price elasticity of demand. A pure monopolist is producing an output such that ATC S4, P SS, MC $2, and MR = $3 This firm is realizing a loss which could be reduced by producing more output,
Curve (1) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's ... A. total cost curve. B. total revenue curve. C. marginal revenue curve. D. total economic profit curve.
DOCX Loudoun County Public Schools / Overview Curve (2) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve.B. total revenue curve.C. marginal revenue curve.D. total economic profit curve. 15. Curve (3) in the above diagram is a purely competitive firm's: A. total cost curve.B. total revenue curve.C. marginal revenue curve.D. total economic profit curve.
› the-economy › bookUnit 9 The labour market: Wages, profits, and unemployment - CORE Figure 9.9 depicts the market’s demand curve and the firm’s isoprofit curves. Based on this information, which of the following statements is correct? The slope of the demand curve is the firm’s marginal rate of substitution. Between points A and C, the firm would prefer point A as the output is higher.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Transfer_pricingTransfer pricing - Wikipedia There are two markets each with its own price (Pf and Pt in the next diagram). The aggregate market is constructed from the first two. That is, point C is a horizontal summation of points A and B (and likewise for all other points on the net marginal revenue curve (NMRa)). The total optimum quantity (Q) is the sum of Qf plus Qt.
DOCX ANSWERS TO END-OF-CHAPTER QUESTIONS - Seneca Valley School ... Explanations and characteristics of the four models are outlined at the beginning of this chapter. Then the characteristics of a purely competitive industry are detailed. There is an introduction to the concept of the perfectly elastic demand curve facing an individual firm in a purely competitive industry.
study.com › learn › microeconomics-questions-andMicroeconomics Questions and Answers - Study.com 1. A perfectly competitive firm's marginal cost is MC=75+3q. The firm's short run supply curve is: a. q=-75+3P b. q=25+0.33P c. q=75+3q d. q=-25+0.33P 2. Which of the following market characteristi...














0 Response to "39 curve (2) in the diagram is a purely competitive firm's"
Post a Comment