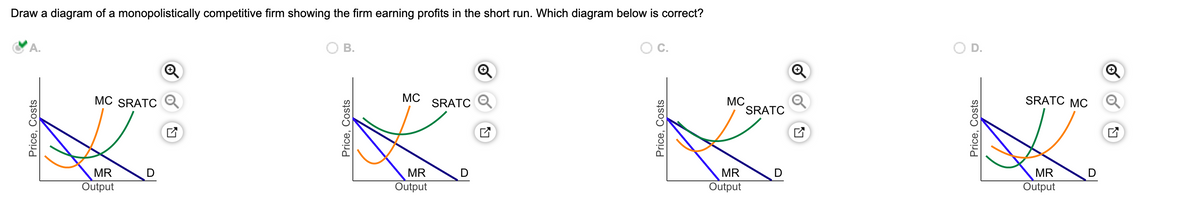
37 the monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is
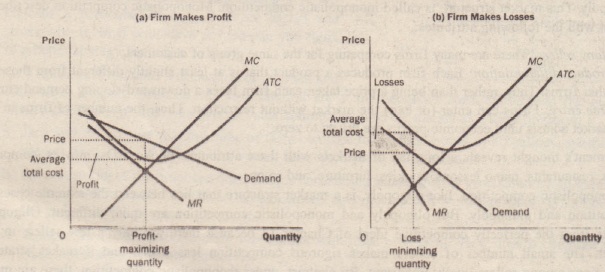
Monopolistic competition - LegitWriting Welcome to Legit Writing. Draw the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm, label the level of output it will choose to produce in the short-run, and label the profit of the firm. Draw the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in the long-run and label its long-run level of output. Solved The figure below depicts a monopolistically | Chegg.com The figure below depicts a monopolistically competitive firm operating in the short run. Label the diagram with the items listed to the right of the figure. You will have to decide whether the firm is making a profit or a loss.
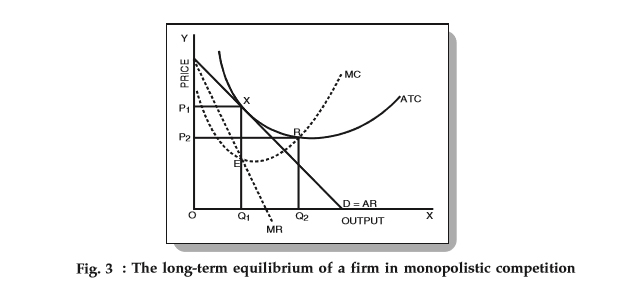
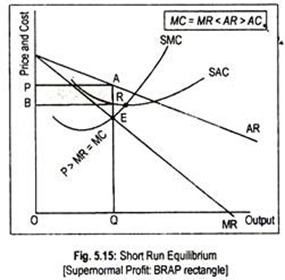
Microeconomics Chapter 13 Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. This firm is experiencing excess capacity of DE. Assume the top six firms comprising an industry have market shares of 10, 8, 8, 5, 5, and 4 percent. The remaining 20 firms each have market shares of 2 percent. The Herfindahl index for this industry is 374.
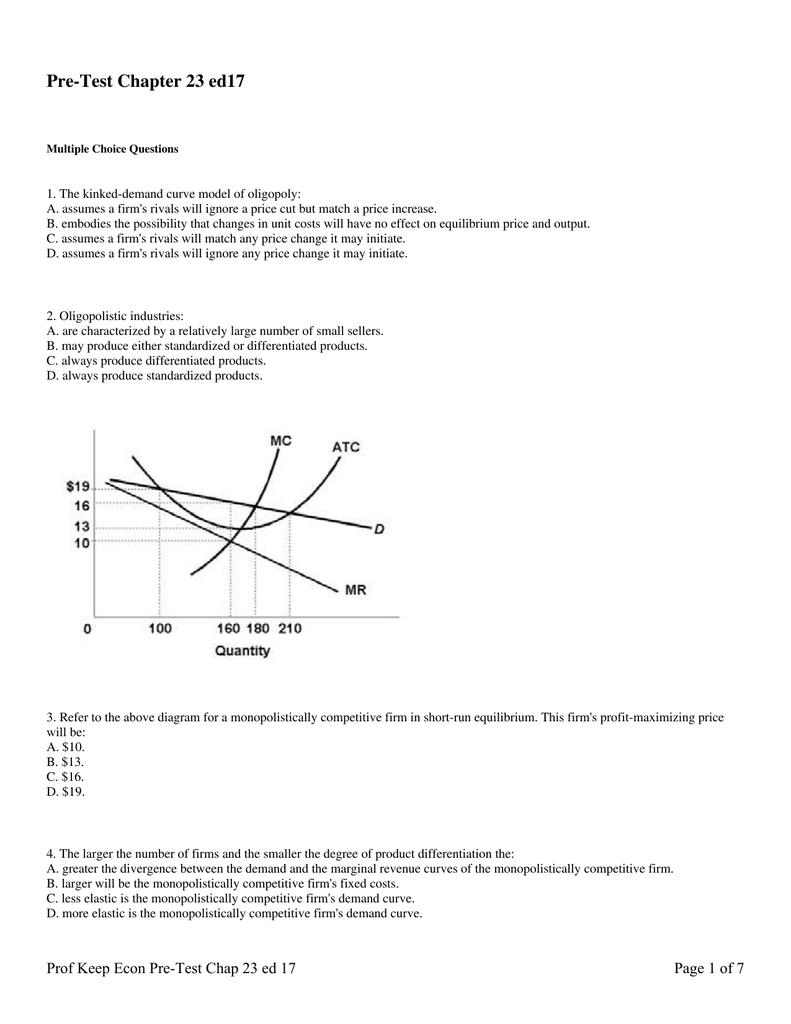
The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is
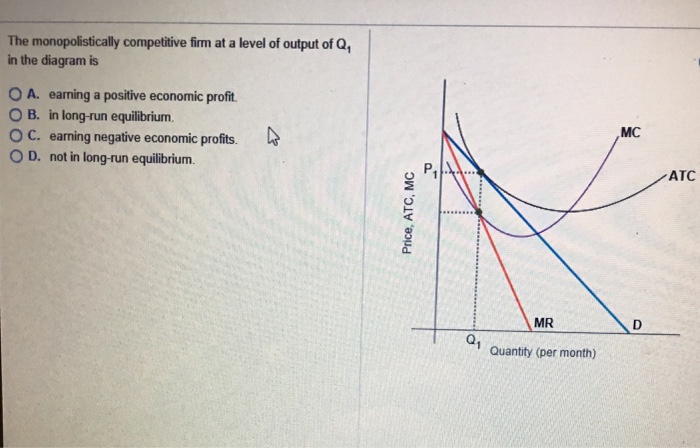
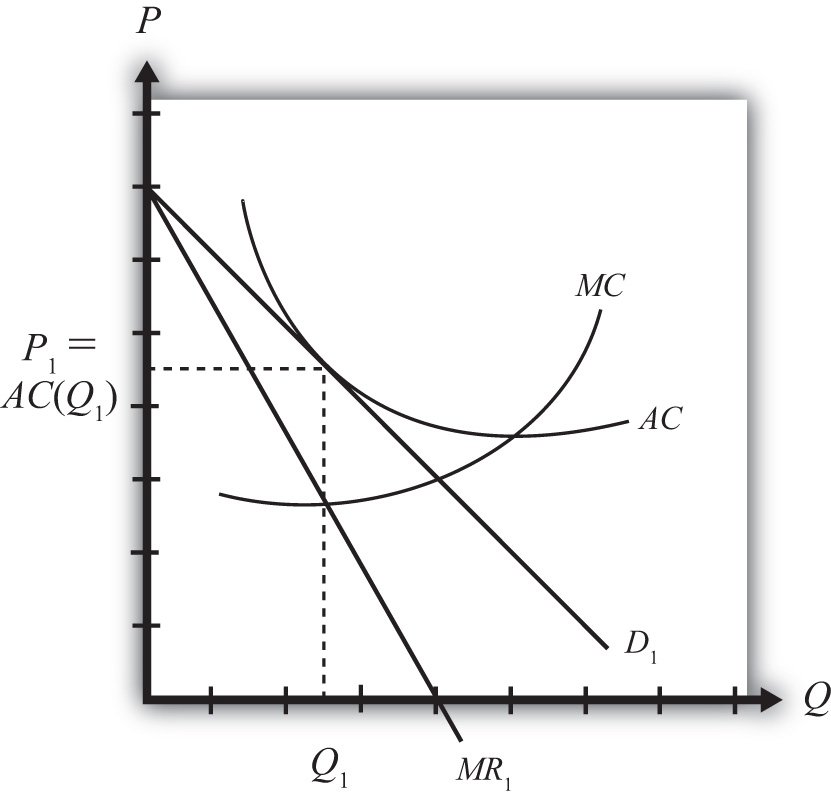
Monopolistic Competition - tutor2u Monopolistic competition is a form of imperfect competition and can be found in many real world markets ranging from clusters of sandwich bars, other fast food shops and coffee stores in a busy town centre to pizza delivery businesses in a city or hairdressers in a local area. Monopolistic Competition, short-run analysis: Revision Video Chapter 25 Homework Flashcards - Quizlet The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of Q1 in the diagram is A.not in long-run equilibrium. B.in long-run equilibrium. C.earning a positive economic profit. D.earning negative economic profits. A.not in long-run equilibrium. Correct B.in long-run equilibrium. C.earning a positive economic profit. Ch13 Flashcards - Quizlet In monopolistic competition there is an underallocation of resources at the profit-maximizing level of output, which means that Multiple Choice ATC is not equal to MC. price is greater than MR. price is greater than minimum ATC. price is greater than MC. price is greater than MC.
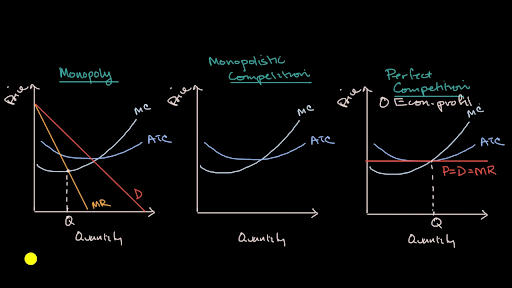
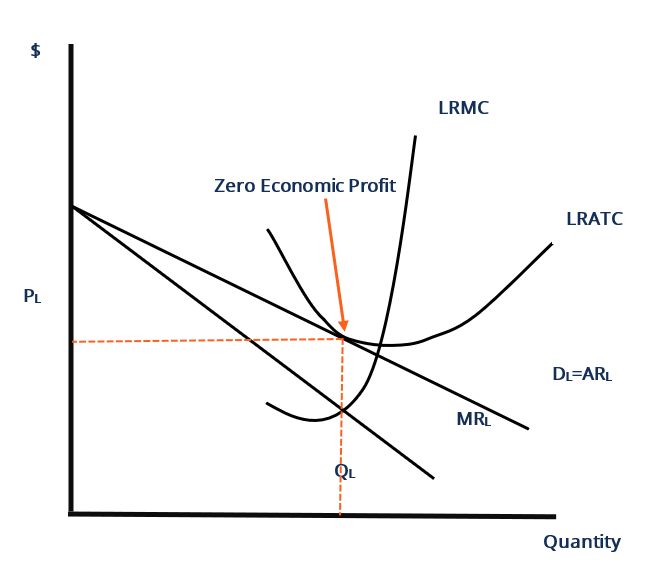
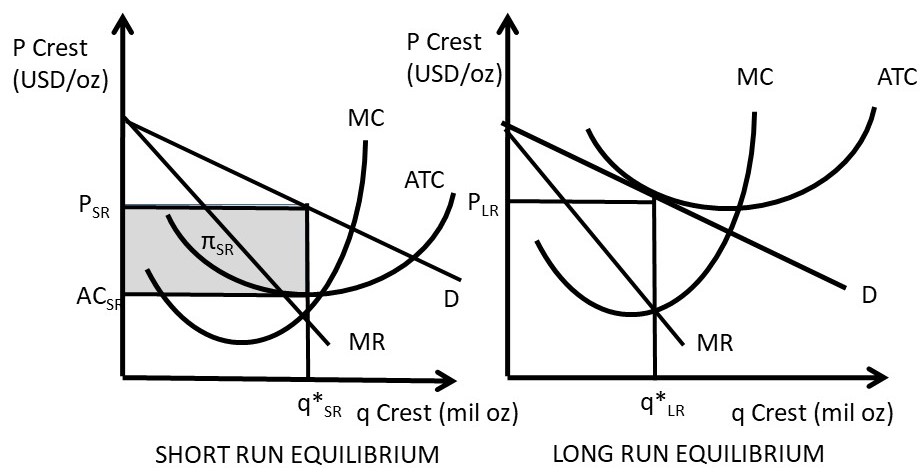
The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is. Answered: Microeconomic Question QUESTION ONE… | bartleby The major difference between monopolistic competition and monopoly is a. how the quantity of output is determined. b. only a monopoly can earn an abnormal profit in the long run. c. monopoly is a price taker, and a firm in monopolistic competition is a price maker d. only firms in monopolistic competition are protected by barriers to entry Monopolistic Competition in the Long-run Monopolistic Competition in the Long-run The difference between the short‐run and the long‐run in a monopolistically competitive market is that in the long‐run new firms can enter the market, which is especially likely if firms are earning positive economic profits in the short‐run. Monopoly diagram short run and long run - Economics Help The diagram for a monopoly is generally considered to be the same in the short run as well as the long run. Profit maximisation occurs where MR=MC. Therefore the equilibrium is at Qm, Pm. (point M) This diagram shows how a monopoly is able to make supernormal profits because the price (AR) is greater than AC. Monopolistic Competition Flashcards | Quizlet The demand schedule or curve confronted by the individual, purely competitive firm is: A. relatively elastic, that is, the elasticity coefficient is greater than unity. B. perfectly elastic. C. relatively inelastic, that is, the elasticity coefficient is less than unity. D. perfectly inelastic. B. perfectly elastic. 16.
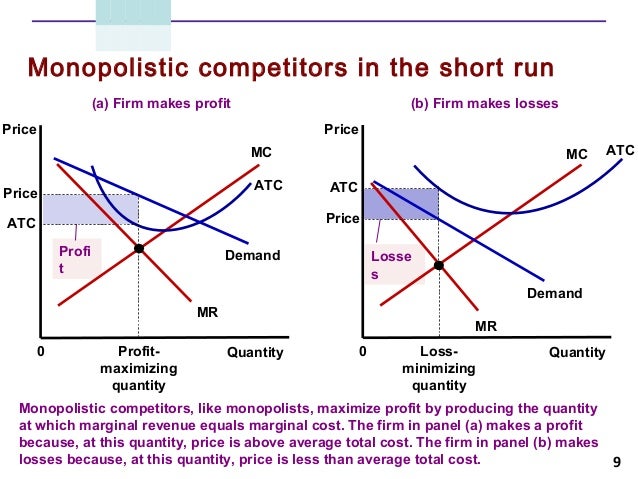
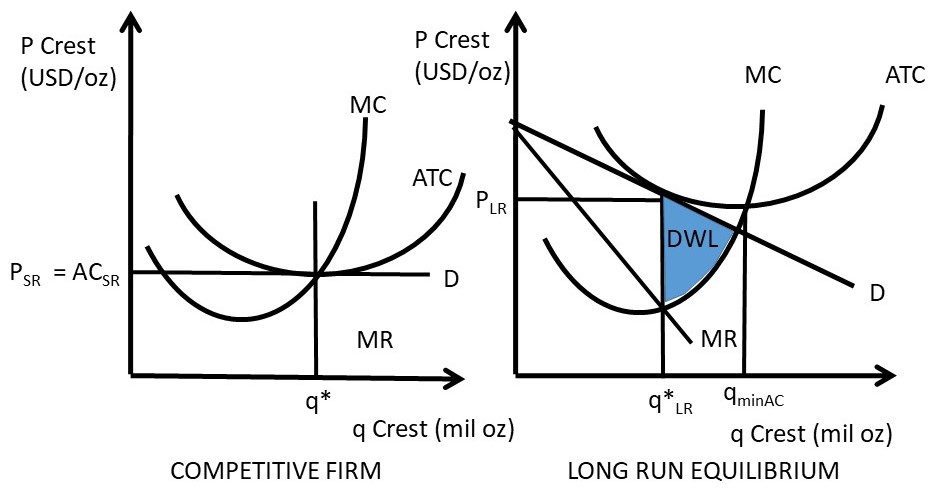
Monopolistic Competition Diagram | Quizlet Firms in monopolistic competition determine the profit-maximizing level of output by producing where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. If the market for tires is monopolistically competitive: sellers can influence the market price of the product. Suppose that the men's suit business is monopolistically competitive. Monopolistic Competition - Overview, How It Works, Limitations The short-run equilibrium under monopolistic competition is illustrated in the diagram below: Profits are maximized where marginal revenue (MR) is equal to marginal cost (MC). The point determines the company's equilibrium output. Monopolistic Competition - Managerial Economics In other words, a Monopolistic Competitive firm resembles a monopoly in the short run but displays outcomes similar to Perfect Competition in the long run.. b. Monopolistic Competition has a smaller output sold at a higher price as compared to Perfect Competition. The following diagram shows the comparison. 8.4 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Microeconomics The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price similar to the way that a monopolist does. Since they face a downward sloping demand curve, the same considerations about how elasticity affects revenue are relevant, and the firm will maximize profits where MR = MC when P > MR. Step 1.
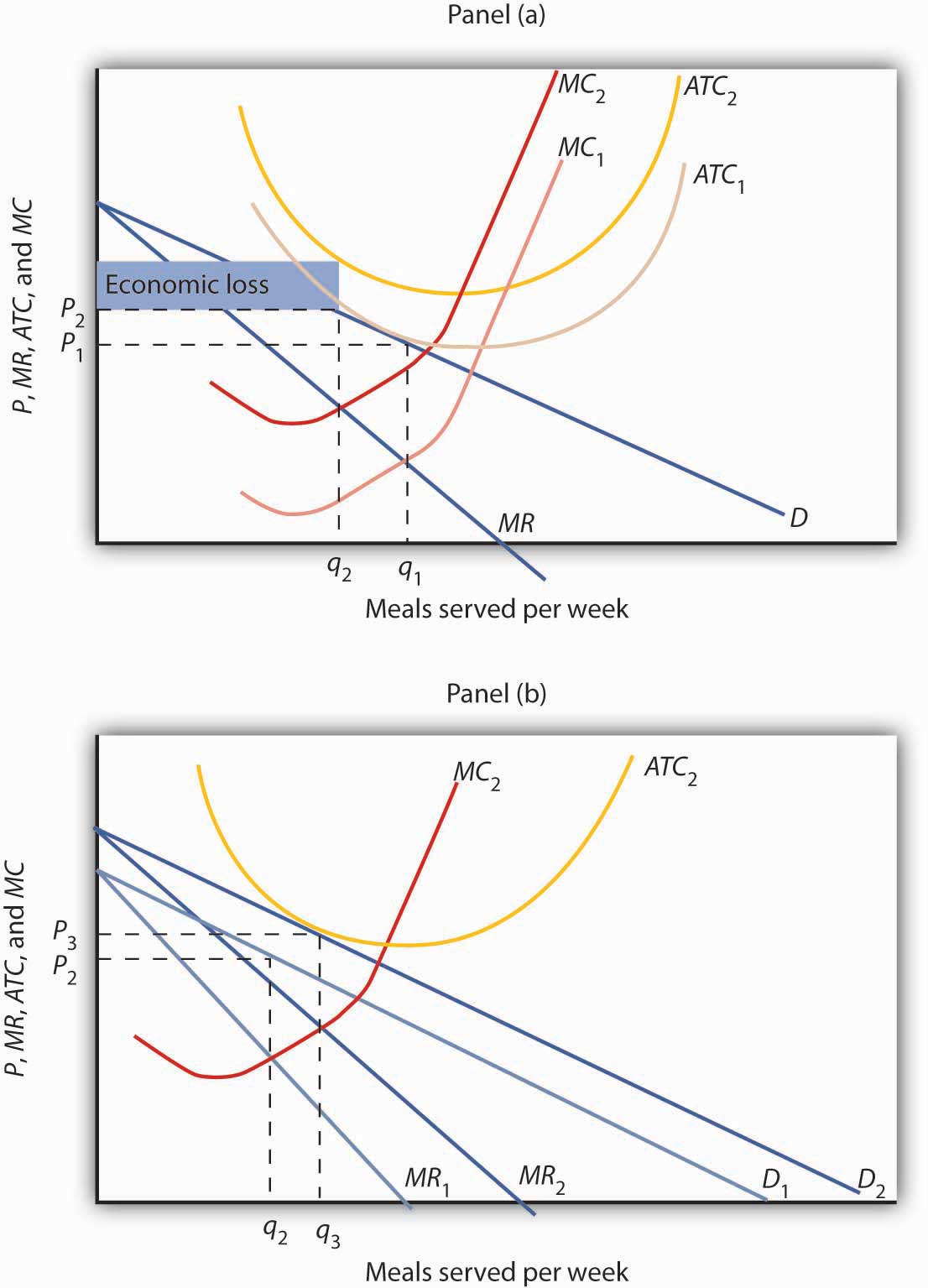
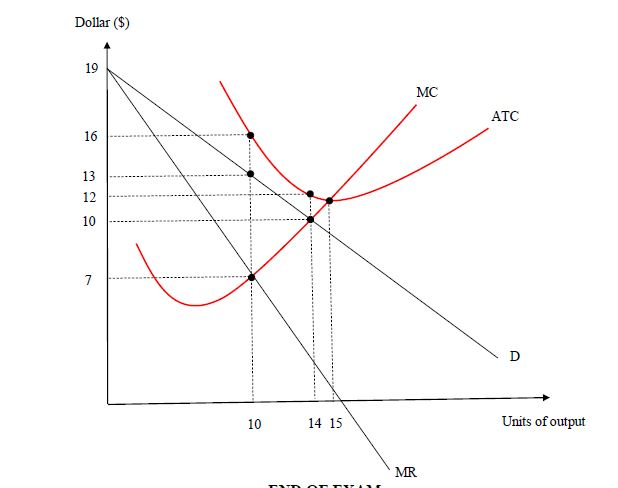
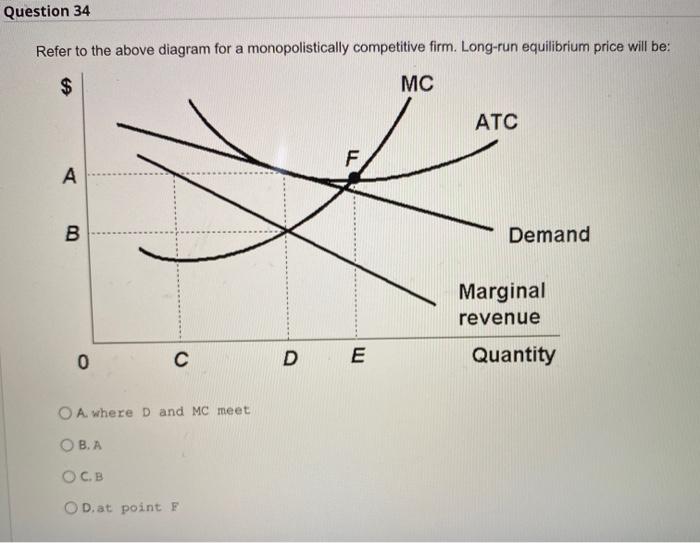
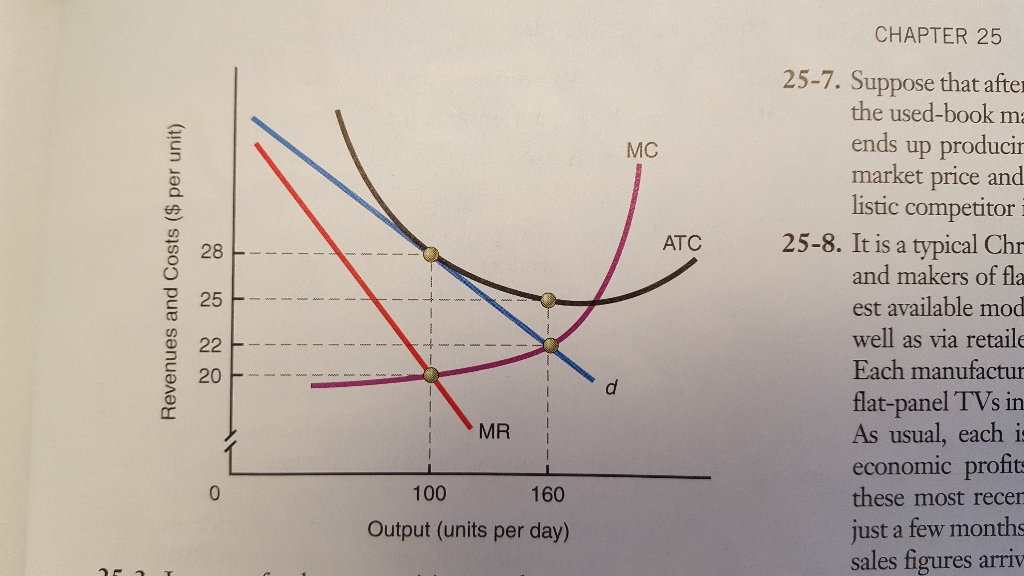
Solved The diagram to the right shows a typical | Chegg.com Question: The Diagram To The Right Shows A Typical Monopolistically Competitive Firm When The Industry Is In Long-run Equilibrium. Monopolistically Competitive Firm A. The Long-run Equilibrium Is At Point A Because Economic Profits There Are MC Any Nonzero Value For Profits Induces A Change In The Industry's Of Firms. PDF Chap 13 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly MULTIPLE ... 29)In the above figure, the monopolistically competitive firm earns an economic profit of A)between $50.01 and $100 per day. B)greater than $100.01 per day. C)$0. D)between $0 and $50 per day. 29) 30)The above figure is for a firm in monopolistic competition. The diagram represents the short run rather than the long run because PDF Characteristics of Monopolistic competition Output and Price in Monopolistic Competition Diagram at right shows long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm. economic profits? price mark-up (P vs ... a firm in monopolistic competition must be in a state of continuous product development. New product development allows a firm to gain a competitive edge, if only temporarily ... Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically ... 2 8. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Assume the firm is part of an increasing-cost industry. In the long run firms will: A.leave this industry, causing both demand and the ATC curve to shift upward. B.enter this industry, causing demand to rise and the ATC curve to shift downward.
10.1 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Economics The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price in much the same way as a monopolist. A monopolistic competitor, like a monopolist, faces a downward-sloping demand curve, and so it will choose some combination of price and quantity along its perceived demand curve.
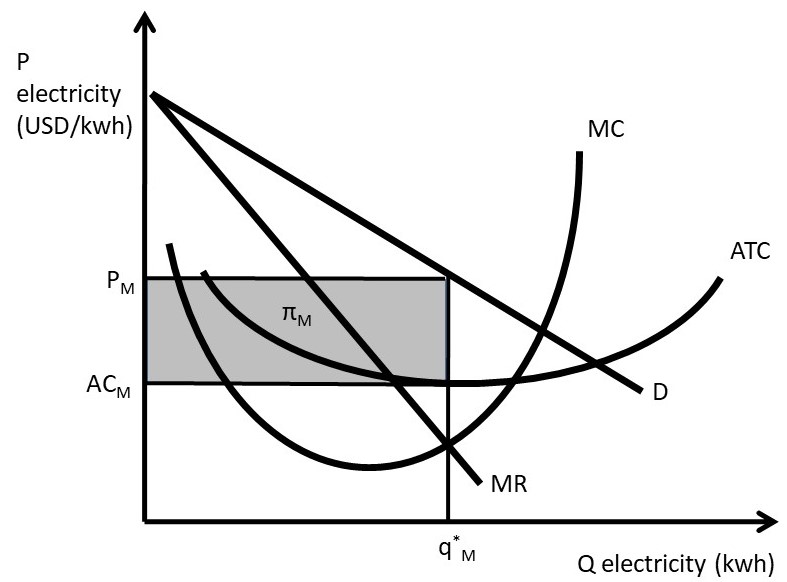
Monopolistic Competition - definition, diagram and ... Diagram monopolistic competition short run. In the short run, the diagram for monopolistic competition is the same as for a monopoly. The firm maximises profit where MR=MC. This is at output Q1 and price P1, leading to supernormal profit. Monopolistic competition long run. Demand curve shifts to the left due to new firms entering the market.
The Effects of Trade in a Monopolistically Competitive ... Use a monopoly diagram for a representative monopolistically competitive firm to depict a long-run equilibrium. Understand how the market equilibrium changes upon opening to free trade. Assume that there are two countries, each with a monopolistically competitive industry producing a differentiated product.
Monopolistic competition - Economics Online Monopolistically competitive markets exhibit the following characteristics: Each firm makes independent decisions about price and output, based on its product, its market, and its costs of production. Knowledge is widely spread between participants, but it is unlikely to be perfect.
Monopolistic competition - Wikipedia Monopolistic competition is a type of imperfect competition such that there are many producers competing against each other, but selling products that are differentiated from one another (e.g. by branding or quality) and hence are not perfect substitutes.In monopolistic competition, a firm takes the prices charged by its rivals as given and ignores the impact of its own prices on the prices of ...
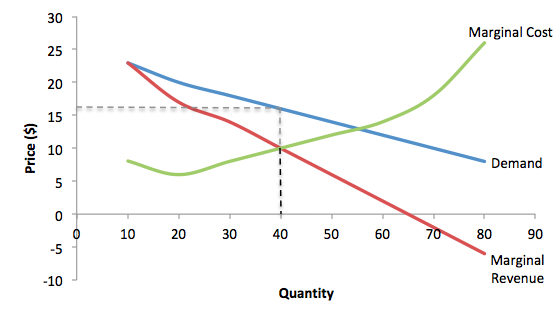
microeconomics chapter 25 Flashcards - Quizlet Monopolistic competition is similar to monopoly because in both industry structures, the firm's demand curve is downward sloping. Consider the diagram at the right depicting the revenue and cost conditions faced by a monopolistically competitive firm. What are the total revenues experienced by this firm? $2800
Chapter 13 (Monopolistic Competition) Homework Flashcards ... Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. If this firm were to realize productive efficiency, it would - also realize an economic profit. - incur a loss. - also achieve allocative efficiency. - have to produce a smaller output. incur a loss. 15. A
Refer to the diagram The monopolistically competitive firm ... Refer to the diagram the monopolistically competitive 62. Refer to the diagram. The monopolistically competitive firm shown A. will realize allocative efficiency at its profit-maximizing output. B. cannot operate at a loss. C. is in long-run equilibrium. D . is realizing an economic profit.
Monopoly Vs Monopolistic Competition (With Diagram) It means small fall in price, will lead to big increase in demand. Fig. 14 represents AR and MR under monopolistic competition. 6. Decision-Making: Under monopoly and monopolistic competition, a firm cannot determine both price and output at the same time. Under monopolistic competition, the firm has to spend more on selling costs.
Ch13 Flashcards - Quizlet In monopolistic competition there is an underallocation of resources at the profit-maximizing level of output, which means that Multiple Choice ATC is not equal to MC. price is greater than MR. price is greater than minimum ATC. price is greater than MC. price is greater than MC.
Chapter 25 Homework Flashcards - Quizlet The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of Q1 in the diagram is A.not in long-run equilibrium. B.in long-run equilibrium. C.earning a positive economic profit. D.earning negative economic profits. A.not in long-run equilibrium. Correct B.in long-run equilibrium. C.earning a positive economic profit.
Monopolistic Competition - tutor2u Monopolistic competition is a form of imperfect competition and can be found in many real world markets ranging from clusters of sandwich bars, other fast food shops and coffee stores in a busy town centre to pizza delivery businesses in a city or hairdressers in a local area. Monopolistic Competition, short-run analysis: Revision Video















0 Response to "37 the monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is"
Post a Comment