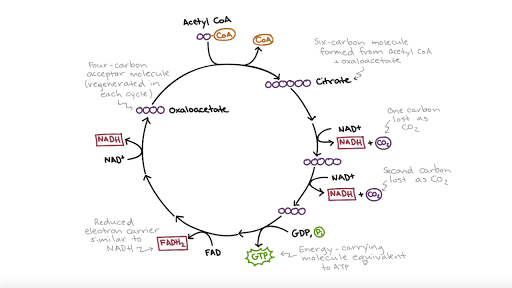
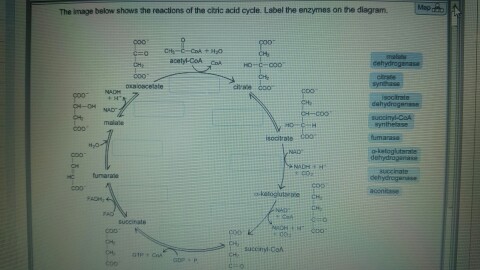
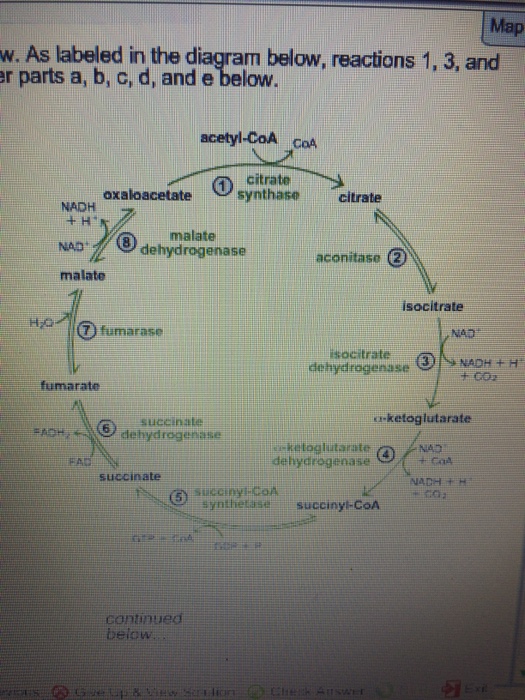
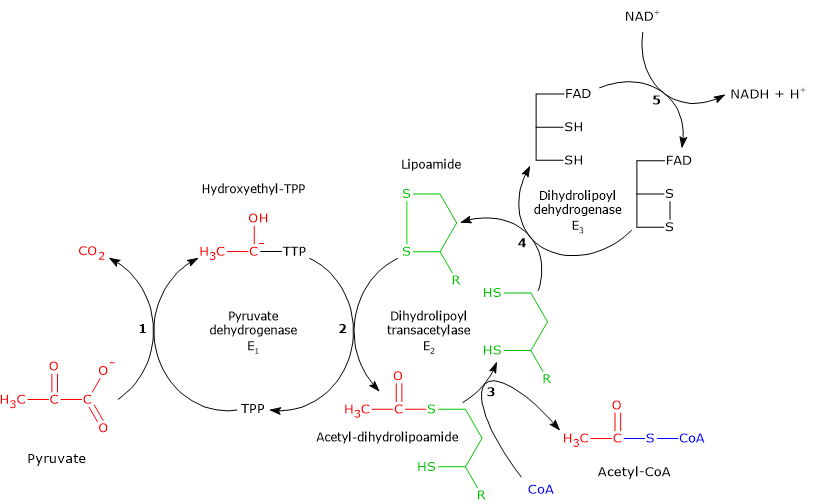
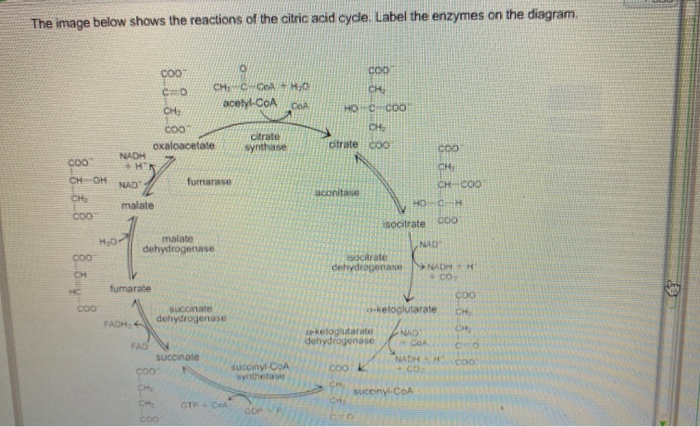
36 the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram.
The citric acid cycle (article) - Khan Academy To start the cycle, an enzyme fuses acetyl CoA and oxaloacetate together so that citric acid is formed (a 2-carbon molecule + a 4-carbon molecule = a 6-carbon molecule!). This is the first molecule that is made in the cycle and is where the cycle gets its name. 5.2: The Light-Dependent Reactions of Photosynthesis ... How Light-Dependent Reactions Work. The overall purpose of the light-dependent reactions is to convert light energy into chemical energy. This chemical energy will be used by the Calvin cycle to fuel the assembly of sugar molecules. The light-dependent reactions begin in a grouping of pigment molecules and proteins called a photosystem.
The Citric Acid Cycle: The Reactions of the Citric Acid ... The first reaction of the citric acid cycle is catalyzed by the enzyme citrate synthase. In this step, oxaloacetate is joined with acetyl-CoA to form citric acid. Once the two molecules are joined, a water molecule attacks the acetyl leading to the release of coenzyme A from the complex. Figure %: Reaction 1.
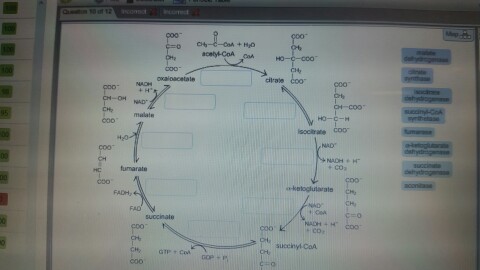
The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram.
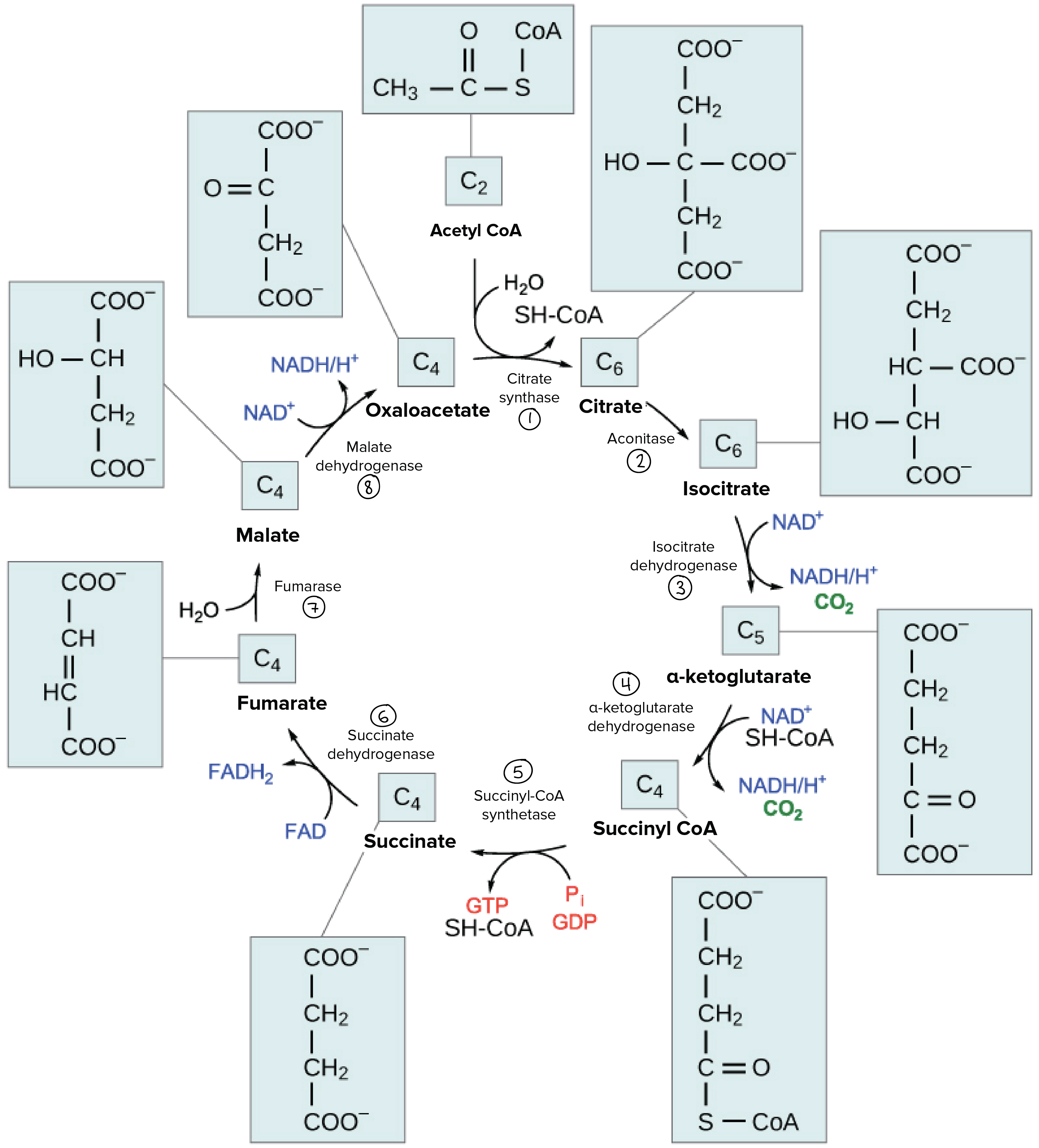
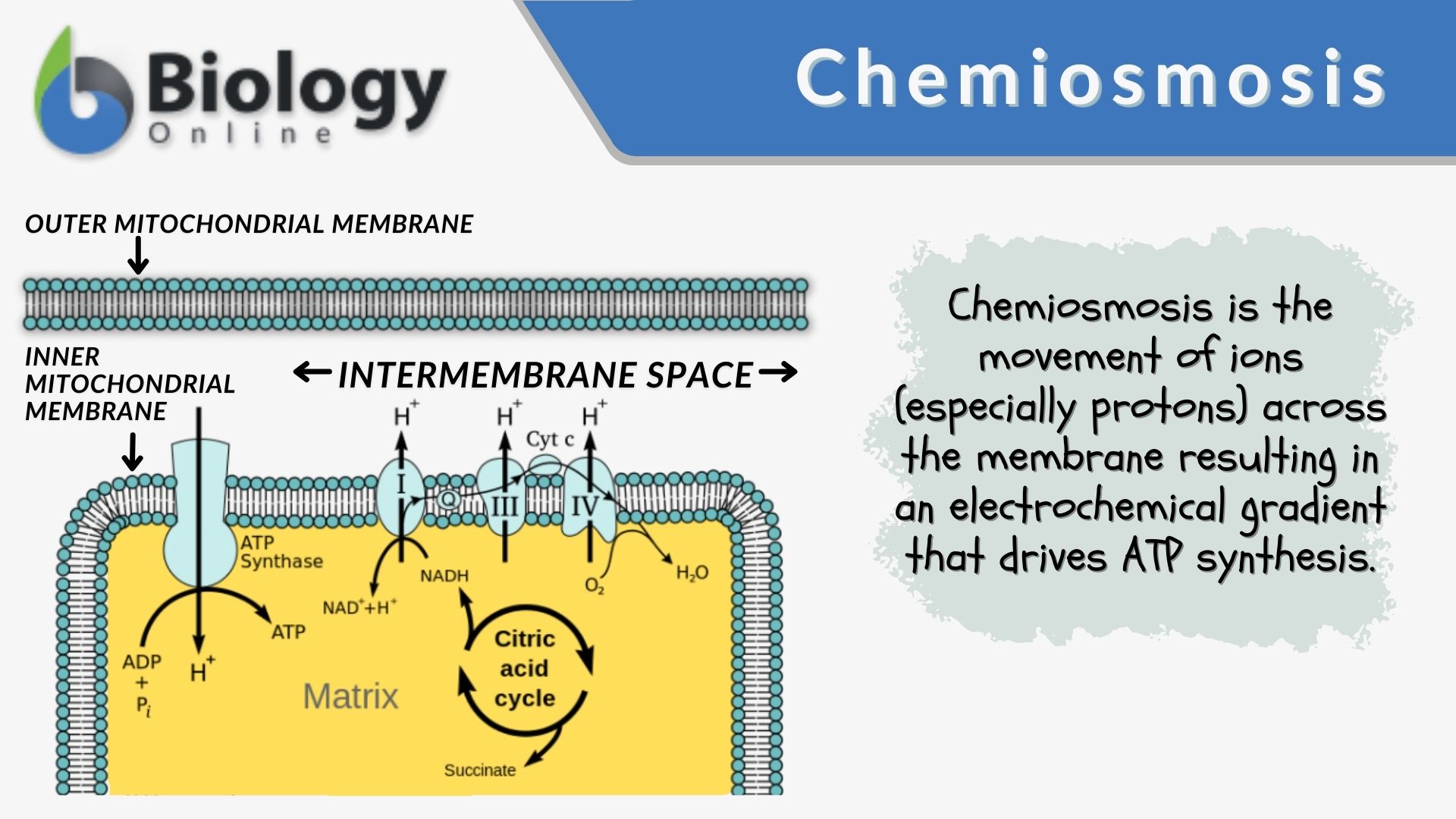
Electron Transport Chain | Biology for Majors I The enzyme in complex I is NADH dehydrogenase and is a very large protein, containing 45 amino acid chains. Complex I can pump four hydrogen ions across the membrane from the matrix into the intermembrane space, and it is in this way that the hydrogen ion gradient is established and maintained between the two compartments separated by the inner mitochondrial membrane. 40 the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid ... The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram Map Coo o CH3-C-CoA+ H20 acetyl-CoA CoA CH2 succinyl-CoA synthetase HO-C-COO CH2 CH2 COO succinate dehydrogenase oxaloacetate citrate COO NADH COO fumarase CH2 CH-OH malate NAD CH COO dehydrogenase CH2 malate citrate synthase COO isocitrate COO H20 ... Glycolysis Explained in 10 Easy Steps (With Diagrams) In aerobic glucose metabolism, the oxidation of citric acid uses ADP and Mg²+, which will increase the speed of reaction: Iso-citric acid + NADP (NAD) — isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) = alpha-ketoglutaric acid. In the Krebs cycle (the citric cycle), IDH1 and IDH2 are NADP+-dependent enzymes that normally catalyze the inter-conversion of D-isocitrate and alpha-ketoglutarate (α-KG).
The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram.. PDF Answer: B - Forest Hills School District is reduced to NADH during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. B) NAD + has more chemical energy than NADH. C) NAD + is reduced by the action of hydrogenases. D) NAD + can donate electrons for use in oxidative phosphorylation. E) In the absence of NAD +, glycolysis can still function. Answer: A Topic: Concept 9.1 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension Citric Acid Cycle Steps: ATP Production - ThoughtCo This cycle is catalyzed by several enzymes and is named in honor of the British scientist Hans Krebs who identified the series of steps involved in the citric acid cycle. The usable energy found in the carbohydrates, proteins, and fats we eat is released mainly through the citric acid cycle. Although the citric acid cycle does not use oxygen directly, it works only when oxygen is present. 4.3 Citric Acid Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation ... Unlike glycolysis, the citric acid cycle is a closed loop: The last part of the pathway regenerates the compound used in the first step. The eight steps of the cycle are a series of chemical reactions that produces two carbon dioxide molecules, one ATP molecule (or an equivalent), and reduced forms (NADH and FADH 2 ) of NAD + and FAD + , important coenzymes in the cell. Cellular respiration - Wikipedia Two low-energy waste products, H 2 O and CO 2, are created during this cycle. The citric acid cycle is an 8-step process involving 18 different enzymes and co-enzymes. During the cycle, acetyl-CoA (2 carbons) + oxaloacetate (4 carbons) yields citrate (6 carbons), which is rearranged to a more reactive form called isocitrate (6 carbons).
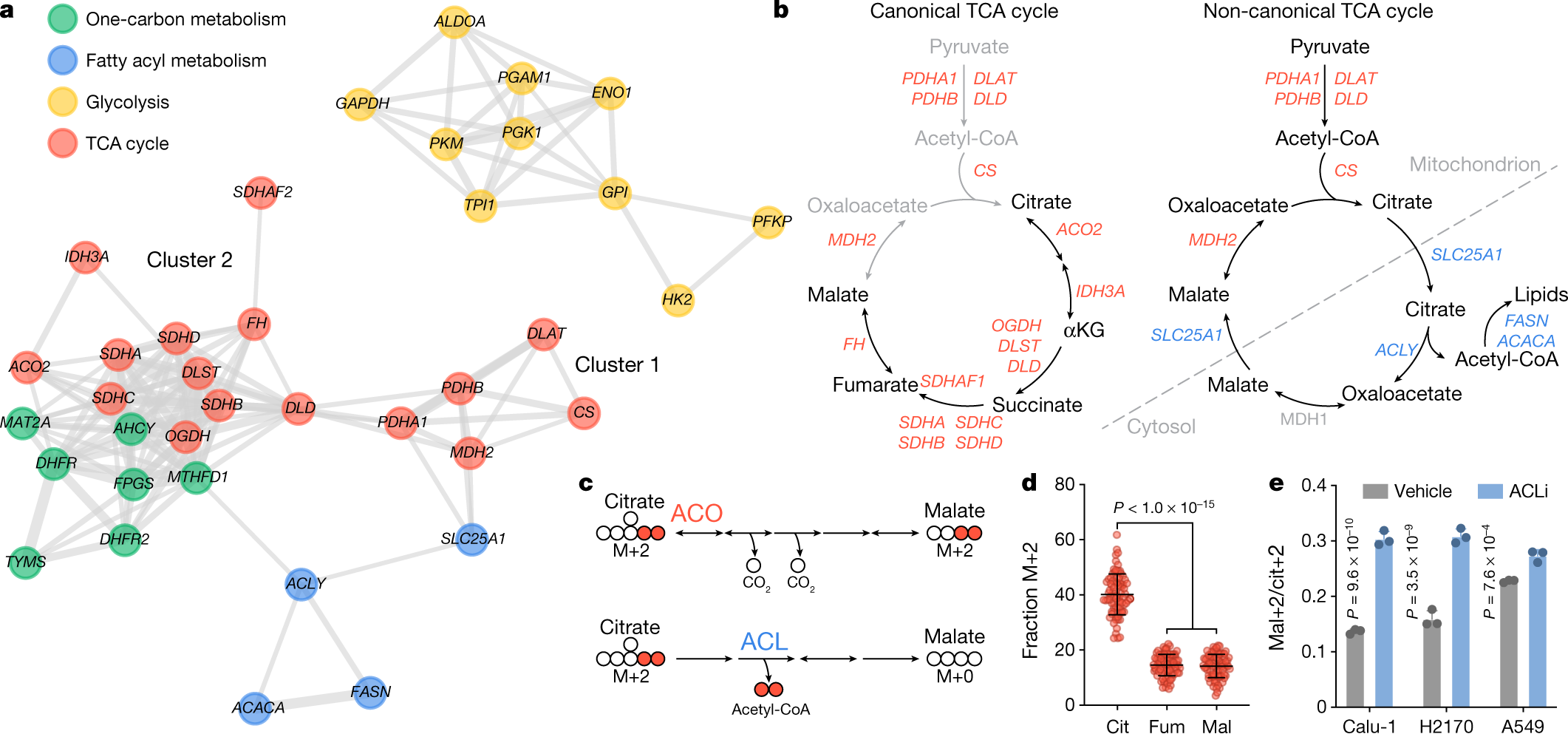
Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis - Biology Dictionary This can be seen in the diagram below. The labels on the right show where the various reactions take place. Cellular Respiration. The Krebs cycle is similar to the Calvin cycle, in that it recycles certain molecules to continually drive the production of electrons and ATP. The electrons are then passed to the inner mitochondrial membrane. Glycolysis - Wikipedia Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C 6 H 12 O 6, into pyruvic acid, CH 3 COCOOH. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes.. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that does not require oxygen. The Glycolytic Pathway, The Gluconeogenic Pathway, The Tca ... The Image Below Shows The Reactions Of The Citric Acid Cycle Label The ... Phytoconstituent regulation of glycolysis and Krebs cycle with sources ... Overview of DEGs in the glycolytic and oxidative metabo | Open-i The Mitochondrion - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI ... The matrix enzymes include those that metabolize pyruvate and fatty acids to produce acetyl CoA and those that oxidize acetyl CoA in the citric acid cycle. The principal end-products of this oxidation are CO 2 , which is released from the cell as waste, and NADH, which is the main source of electrons for transport along the respiratory chain ...
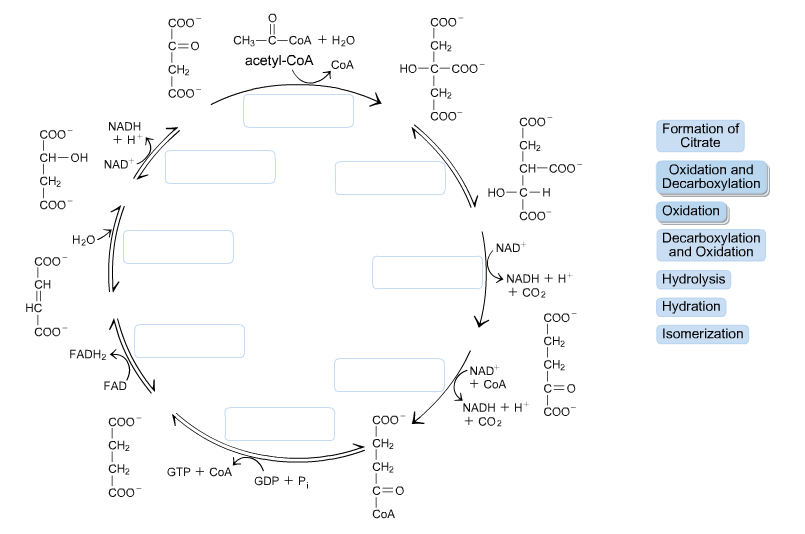
What are the sequence of events in cellular respiration ... NADH gains electrons and carbon is lost, which forms CO2. The second step is the citric acid cycle, which you can see in the image below. Simplified diagram of citric acid cycle: This complex cycle results in eight NADH, two FADH2, two ATP, and six CO2. The last main portion of cellular respiration is oxidative phosphorylation. Solved the image below shows the reactions of the citric ... Chemistry questions and answers. the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram. Question: the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram. Solved The image below shows the reactions of the citric ... The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram Map Coo o CH3-C-CoA+ H20 acetyl-CoA CoA CH2 succinyl-CoA synthetase HO-C-COO CH2 CH2 COO succinate dehydrogenase oxaloacetate citrate COO NADH COO fumarase CH2 CH-OH malate NAD CH COO dehydrogenase CH2 malate citrate synthase COO isocitrate COO H20 isocitrate The image below shows the reaction of the citric acid ... The image below shows the reaction of the citric acid cycle. Label the reaction types on the diagram. COO COO CH2 HO-C-COO CH2 COO acetyl-CoA CoA CH2 COO COO CH2 CH-COO NADH Formation of cOO CH-OH CH2 COO Citrate NAD Oxidation and Decarboxylation Oxidation Decarboxylation HO-C-H Coo H20 NAD+ and...
Glycolysis Cycle - Steps and Enzymes (with Diagrams) In-Detail It can occur with or without the aid of oxygen. In this article, we are going to tackle the steps necessary for the glycolysis process to take place. (1, 2) Image 1: The glycolysis cycle as shown in the diagram. Picture Source: botanystudies.com. Picture 2: The glycolysis process with emphasis on the investment phase and payoff phase.
Learn About the 3 Main Stages of Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration occurs in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells , with most reactions taking place in the cytoplasm of prokaryotes and in the mitochondria of eukaryotes. There are three main stages of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and electron transport/oxidative phosphorylation.
Photosynthesis: ATP and ADP Cycle - bealsscience Below is an image of a worksheet I use in my Biology classes to help students learn the ATP Cycle to mastery. Right click the image below to download the worksheet. Fill it out as you watch the YouTube video "ATP and ADP: Chemical Energy for Cells" and explain what is happening in each step.
CHM 425- Exam 3;Round 2 Flashcards - Quizlet -Electrons generated by the citric acid cycle in the mitochondrial matrix enter the ETC -Electron transfer in the ETC is coupled to proton transfer from the matrix to the intermembrane space -The reactions of the ETC take place in the inner membrane of mitochondria
Types of Mutations - Principles of Biology The types of mutations include: Silent mutation: Silent mutations cause a change in the sequence of bases in a DNA molecule, but do not result in a change in the amino acid sequence of a protein (Figure 1). Missense mutation: This type of mutation is a change in one DNA base pair that results in the substitution of one amino acid for another in ...
Krebs Cycle - Definition, Products and Location | Biology ... The Krebs cycle has 9 main reactions, which happen quickly in succession. The image below shows these reactions. Note that citrate is the first molecule created after acetyl CoA is added. This is why the Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle. The products of the cycle are in the image above.
The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid ... the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram. The image below shows she reactions of the cltric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram dehydragars coo
An Overview of Calvin Cycle - Stages Of C3 Cycle - BYJUS In the first stage of the Calvin cycle, the light-independent reactions are initiated and carbon dioxide is fixed. In the second stage of the C3 cycle, ATP and NADPH reduce 3PGA to G3P. ATP and NADPH are then converted into ATP and NADP+. In the last stage, RuBP is regenerated. This helps in more carbon dioxide fixation. Also Read: C3 and C4 Pathways
The citric acid cycle | Cellular respiration (article ... Step 1. In the first step of the citric acid cycle, acetyl joins with a four-carbon molecule, oxaloacetate, releasing the group and forming a six-carbon molecule called citrate. Step 2. In the second step, citrate is converted into its isomer, isocitrate.
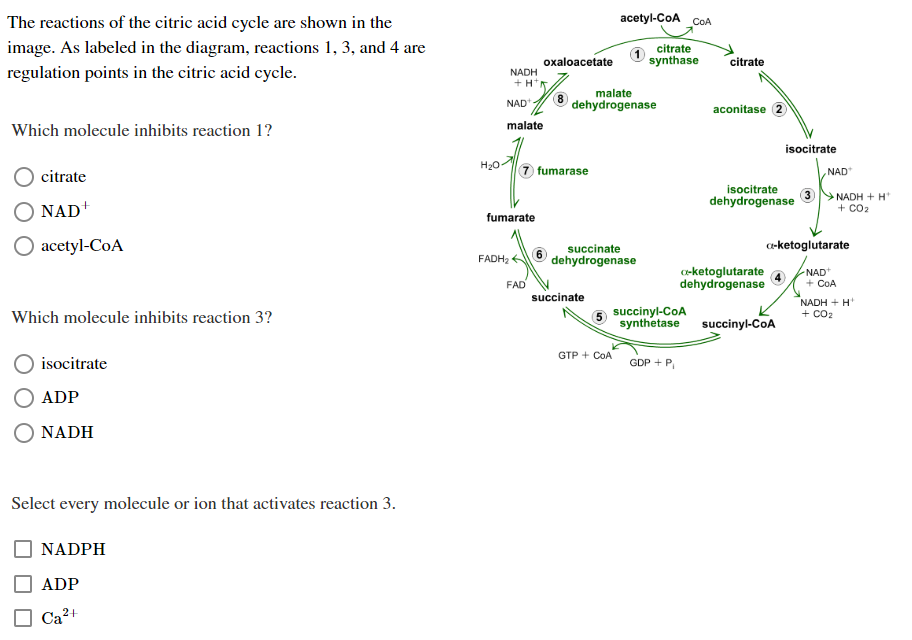
MCB: Exam 4 Sapling Flashcards - Quizlet The reactions of the citric acid cycle are shown in the image. As labeled in the diagram, reactions 1, 3, and 4 are regulation points in the citric acid cycle. Select every molecule or ion that activates reaction 3.
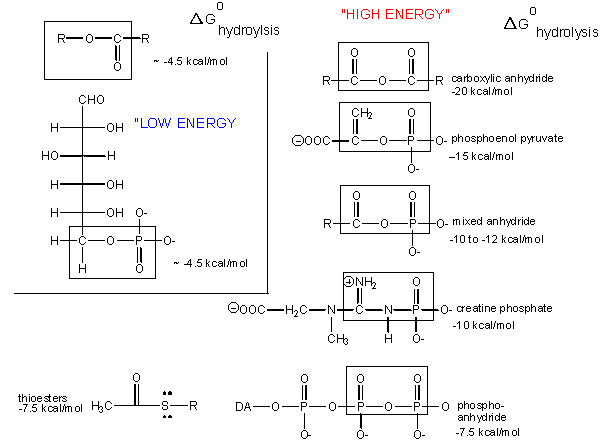
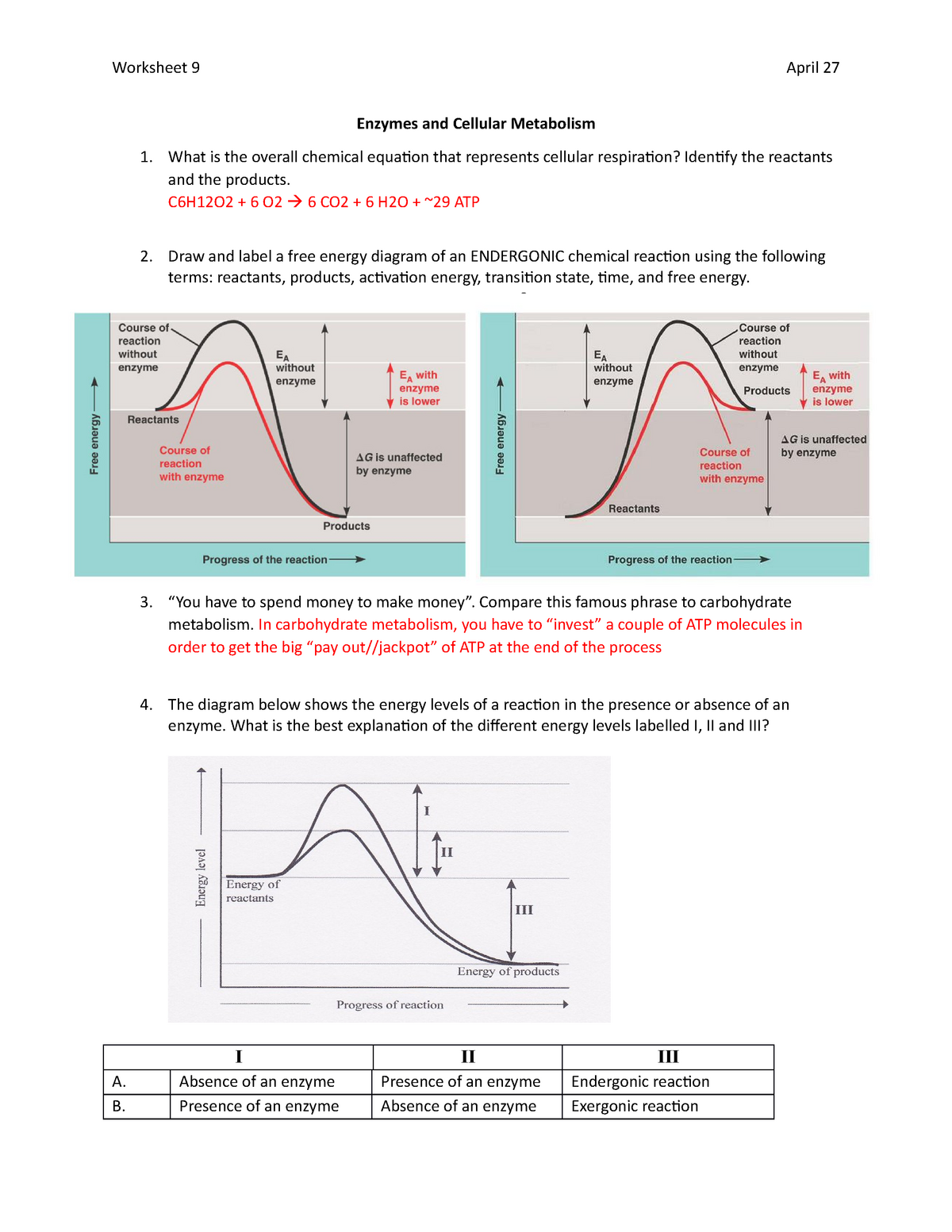
PDF Mcb 102 Spring 2008 Metabolism Final Exam Name: Key MCB 102 - SPRING 2008 - METABOLISM FINAL EXAM NAME:_____ KEY QUESTION 2: CALCULATIONS (7 pts.) The last page of this exam has a log table and a list of equations. (i) Consider the reaction, A B + B, where ΔGº is zero (2 pts.) (a) Explain, in general, how entropy may change during the catabolic reaction depicted above (1 pt.)
Glycolysis Explained in 10 Easy Steps (With Diagrams) In aerobic glucose metabolism, the oxidation of citric acid uses ADP and Mg²+, which will increase the speed of reaction: Iso-citric acid + NADP (NAD) — isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) = alpha-ketoglutaric acid. In the Krebs cycle (the citric cycle), IDH1 and IDH2 are NADP+-dependent enzymes that normally catalyze the inter-conversion of D-isocitrate and alpha-ketoglutarate (α-KG).
40 the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid ... The image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. Label the enzymes on the diagram Map Coo o CH3-C-CoA+ H20 acetyl-CoA CoA CH2 succinyl-CoA synthetase HO-C-COO CH2 CH2 COO succinate dehydrogenase oxaloacetate citrate COO NADH COO fumarase CH2 CH-OH malate NAD CH COO dehydrogenase CH2 malate citrate synthase COO isocitrate COO H20 ...
Electron Transport Chain | Biology for Majors I The enzyme in complex I is NADH dehydrogenase and is a very large protein, containing 45 amino acid chains. Complex I can pump four hydrogen ions across the membrane from the matrix into the intermembrane space, and it is in this way that the hydrogen ion gradient is established and maintained between the two compartments separated by the inner mitochondrial membrane.
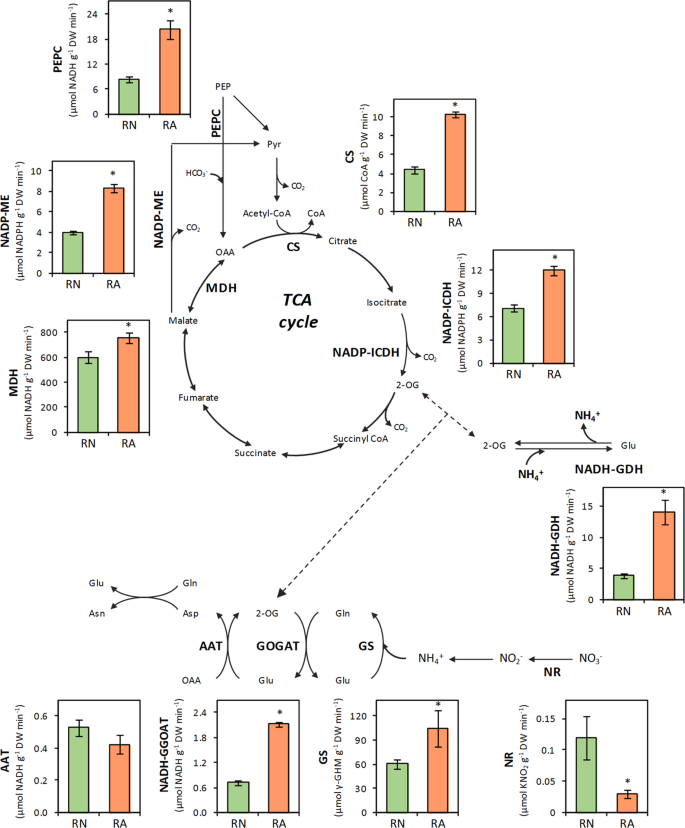
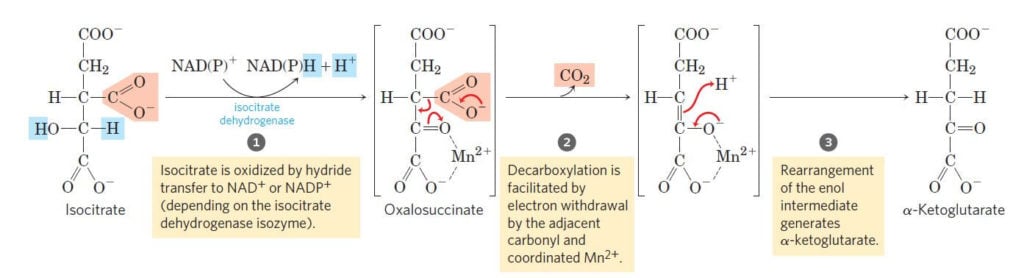
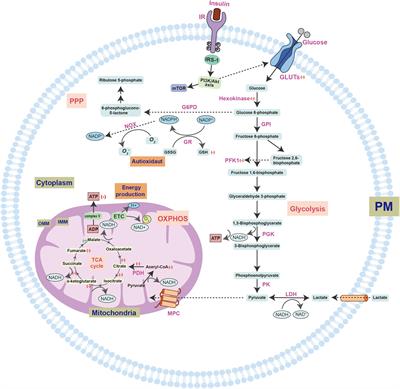















0 Response to "36 the image below shows the reactions of the citric acid cycle. label the enzymes on the diagram."
Post a Comment