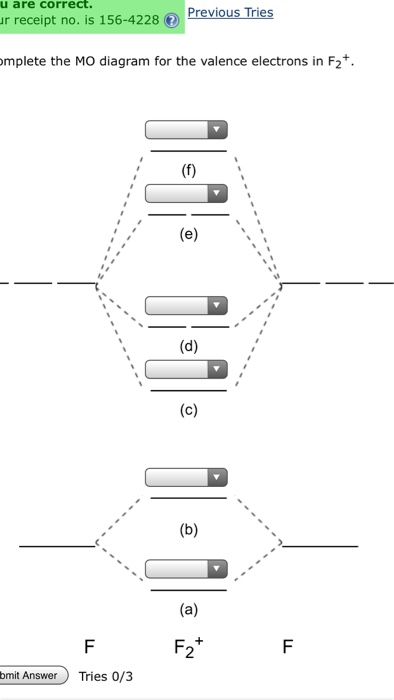
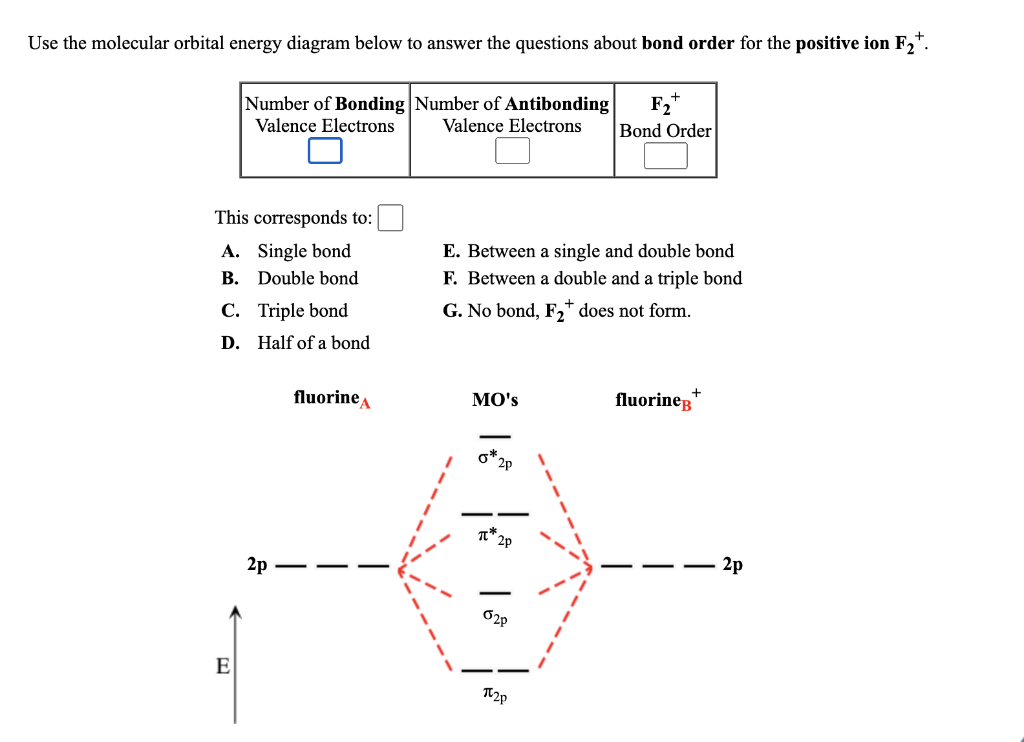
37 f2+ molecular orbital diagram
In Molecular orbital diagram, we just need to calculate the number of electrons in anti-bonding orbital and bonding orbital, then we can use the formula in order to calculate bond order is: Bond order = (No. of electrons in anti-bonding MO) - (No. of electrons in bonding MO) / 2 Answer (1 of 6): Here is the solution, > * For O2 molecule, > * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading.
Chemistry questions and answers. Complete the molecular orbital diagram of F2 and F2-. What type of orbital contains the highest energy electron (s) in F2? pi, antibonding sigma, bonding sigma, antibonding pi, bonding Which atom is larger in size (radius), Cr or Cr3+? Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram of F2 and F2-.

F2+ molecular orbital diagram
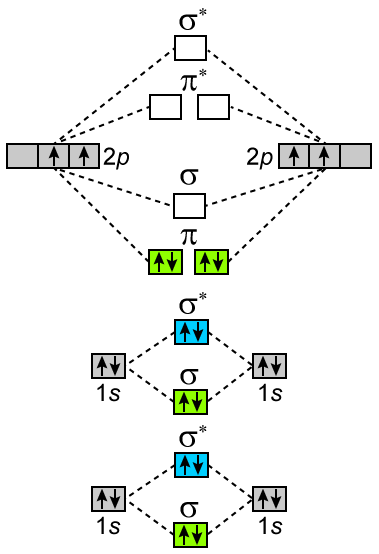
LCAO, Molecular orbitals of di-atomic molecules: Molecular orbital energy level diagrams of diatomic molecules (N 2, O & F2). 1.22 in text) The pictures below are intended to help you visualize pi bonds in double and triple bonds. The number of molecular orbitals = the number of atomic orbitals combined. Draw the molecular orbital diagram of dioxygen and calculate bond order. Medium. View solution > Explain the molecular orbital structure, bond order, stability and magnetic behavior of Hydrogen molecule on the basis of molecular orbital theory. ... Draw molecular orbital diagrams for o2 o22 and o2. If2- Lewis Structure How To Draw The Lewis Structure For If2- In 2021 Positivity Math Molecules . Out of eight electrons six go to bonding molecular orbitals and two to the antibonding molecular orbitals. How to draw molecular orbital diagram of o2. I.e., one is bond and one p bond.
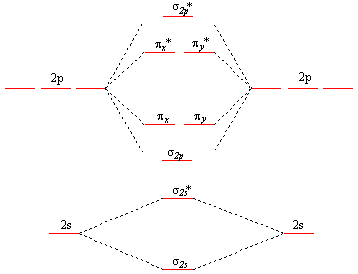
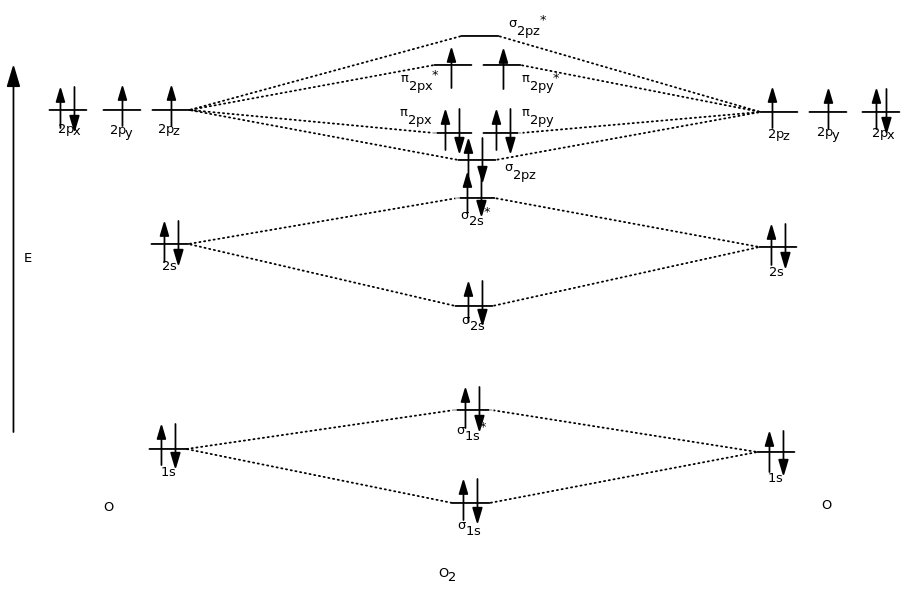
F2+ molecular orbital diagram. Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) ... There would be four electrons to fill into our molecular orbital diagram and that would force us to fill in the bonding sigma MO and the anti-bonding sigma-star MO. Molecular orbital diagram ne2 28.12.2018 28.12.2018 7 comments on molecular orbital diagram ne2 even rather simple molecular orbital (mo) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how mo diagrams are constructed, from n2, o2, f2, ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways. Molecular Orbital Diagram For F2 - Analysis The Magnetically Induced Current Density Molecules molecular orbital diagrams of diatomic molecules chem in chemistry molecular orbital mo theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule The total number of electrons present in the ${N_2}$ molecule is 14. Number of electrons in bonding orbitals : 8 Number of electrons in antibonding orbitals : 2 So, the formula to find bond order is Bond order = $\dfrac{1}{2}$ (Number of electrons in BMO) - (Number of electrons in ABMO) Bond order = $\dfrac{1}{2}$ (8) - (2)
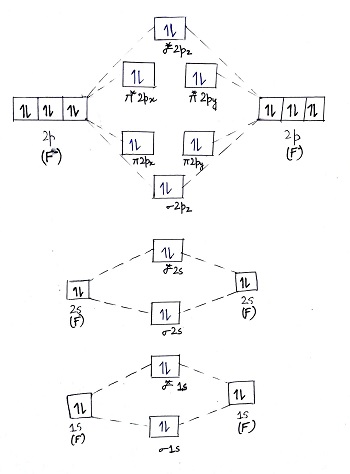
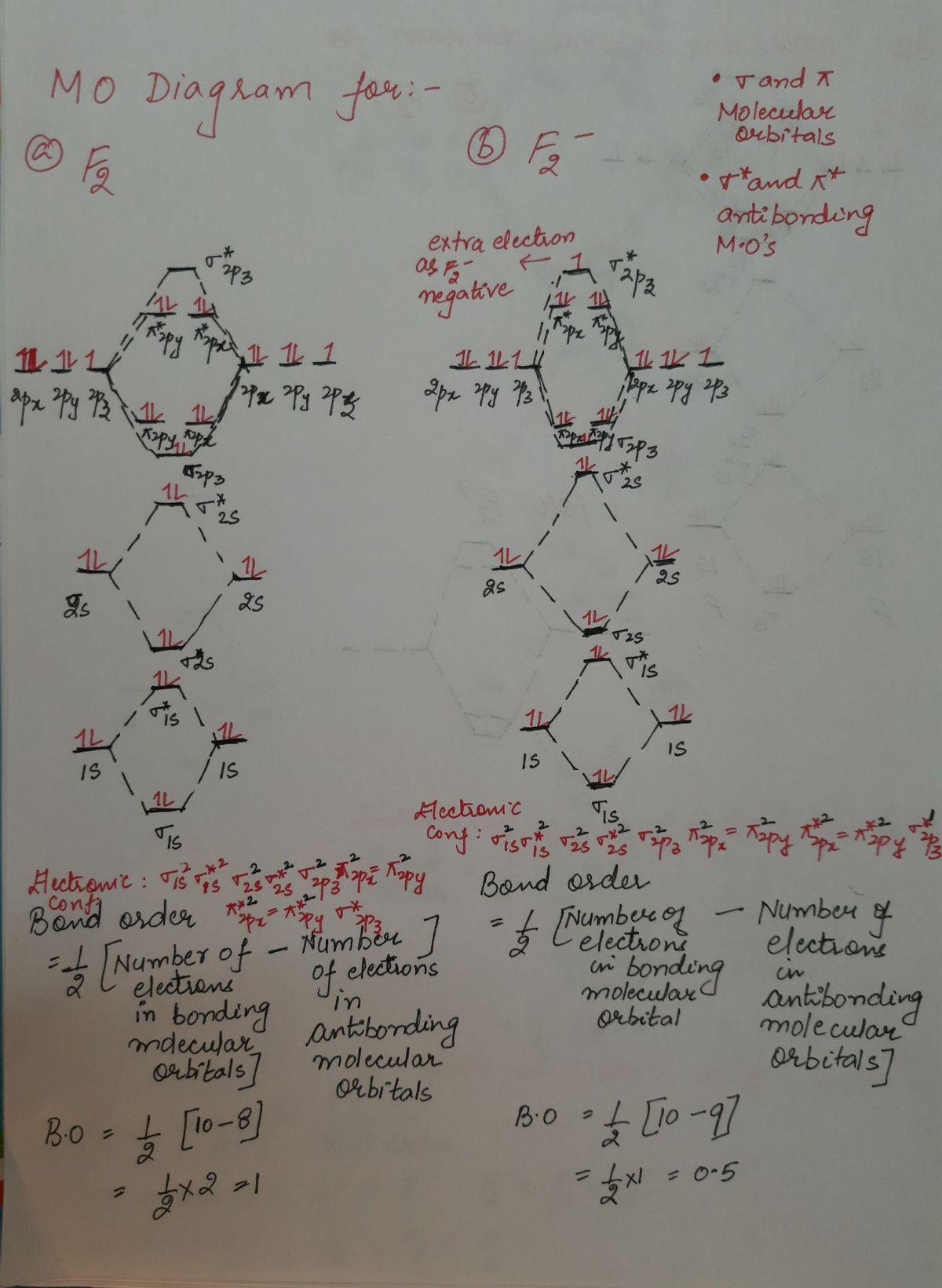
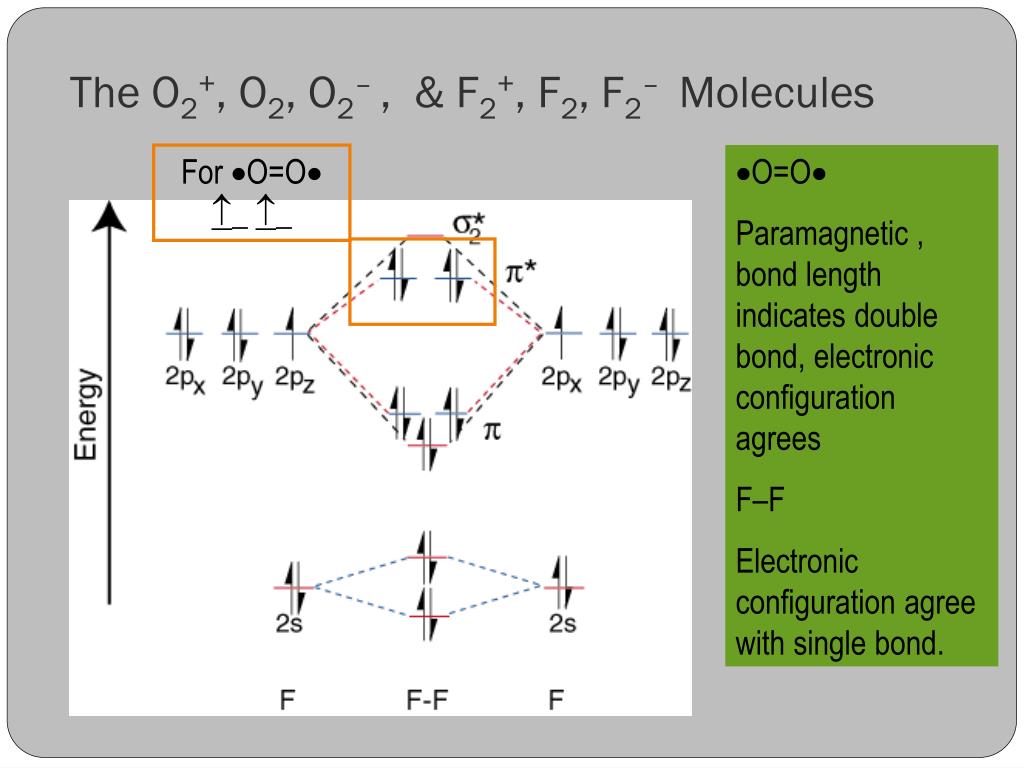
Hey there! We have to draw a molecular orbital diagram for the F 2-ion, determine bond order and decide whether the molecule is diamagnetic or paramagnetic.. For this, we need to do the following steps: Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons present. Step 2: Draw the molecular orbital diagram. Step 3: Calculate the bond order of the molecule. The Molecular Orbital Theory (often abbreviated to MOT) is a theory on chemical bonding developed at the beginning of the twentieth century by F. Hund and R. S. Mulliken to describe the structure and properties of different molecules. The valence-bond theory failed to adequately explain how certain molecules contain two or more equivalent bonds ... 37. Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following: A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
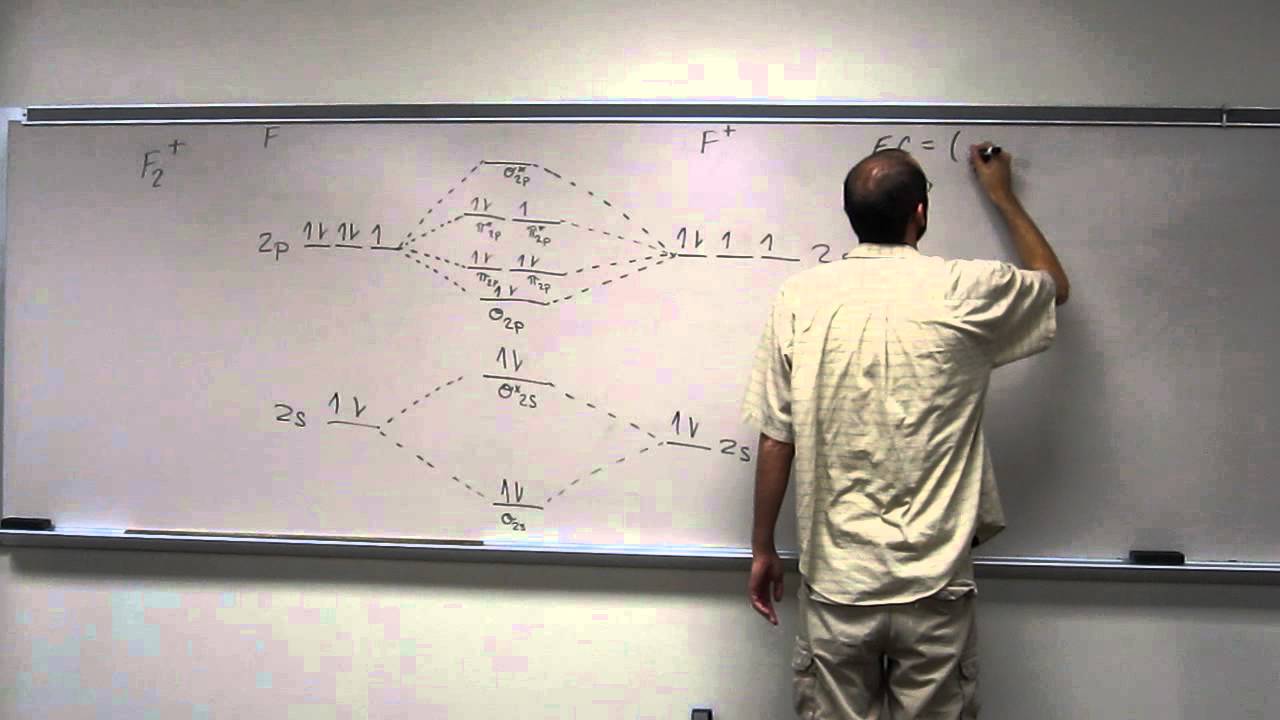
Molecular orbital diagram and bond order of fluorine molecule Fluorine molecule is formed by the combination of atomic orbitals of two fluorine atoms, each having nine electrons, thus making 18 electrons. Click here to get an answer to your question ✍️ 37. Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, ... A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.Second-Row Diatomic Molecules - Chemistry LibreTextsMolecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia For the ion F2+:a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram.b) Calculate the bond order.c) Would this ion exist?d) Write the electron configuration of the ion.————...
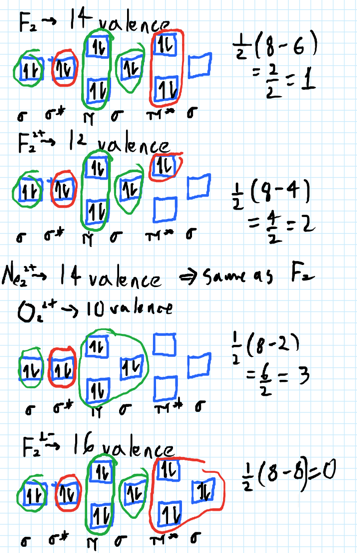
We can calculate for the bond order using: Bond Order = 1 2[# of e - in bonding MO - # of e - in antibonding MO] bonding MOs → without an asterisk ( e.g., σ 1s) antibonding MOs → those with an asterisk ( e.g., σ 1s*) a. F22+. Group Valence Electrons. F 7A 2 × 7 e- = 14 e-. From +2 charge: - 2 e-.
#sigma# molecular orbitals are singly-degenerate, and #pi# molecular orbitals are doubly-degenerate. #sigma# molecular orbitals, in principle, get more stabilized upon overlap than #pi# molecular orbitals do. For example, an #ns//ns# overlap for a homonuclear diatomic molecule gives rise to a partial MO diagram like this:
The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To find the bond order, add th... The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons).
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we’ll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
The Lewis theory of chemical bonding helps us visualize the arrangement of atoms—how they are attached or bonded—in molecules. The valence electrons in each atom are the ones that participate in the bonding, and hence they are the only ones displayed in the Lewis structures. It is to be noted though that this theory about the electronic structure is quite primitive and most limited. In a typical Lewis structure, each valence electron is represented as a dot, and a covalent bond between two atoms (formed as a result of sharing of two electrons) is represented as a line. Several atoms tend to seek eight electrons in their valence shell through chemical bonding; this is referred to as the octet rule and is reflected in the Lewis structure of a molecule. Hydrogen is an exception, though; it seeks a duplet, not octet, because it has only one electron in its K shell, and thus needs only one more to achieve the maximum capacity of K shell. Noble gases already have completely filled valance...
Nov 01, 2021 · When we make the molecular orbital energy level diagram of f2 molecule then, we will get this configuration: 1σs 2, 1σ*s 2, 2σs 2, 2σ* 2, σ2pz 2, π2p x 2, π2p y 2, πp x * 2, π2p y * 2. From this electronic configuration, we can see that there are a total of ten bonding molecular orbitals and eight antibonding molecular orbitals.
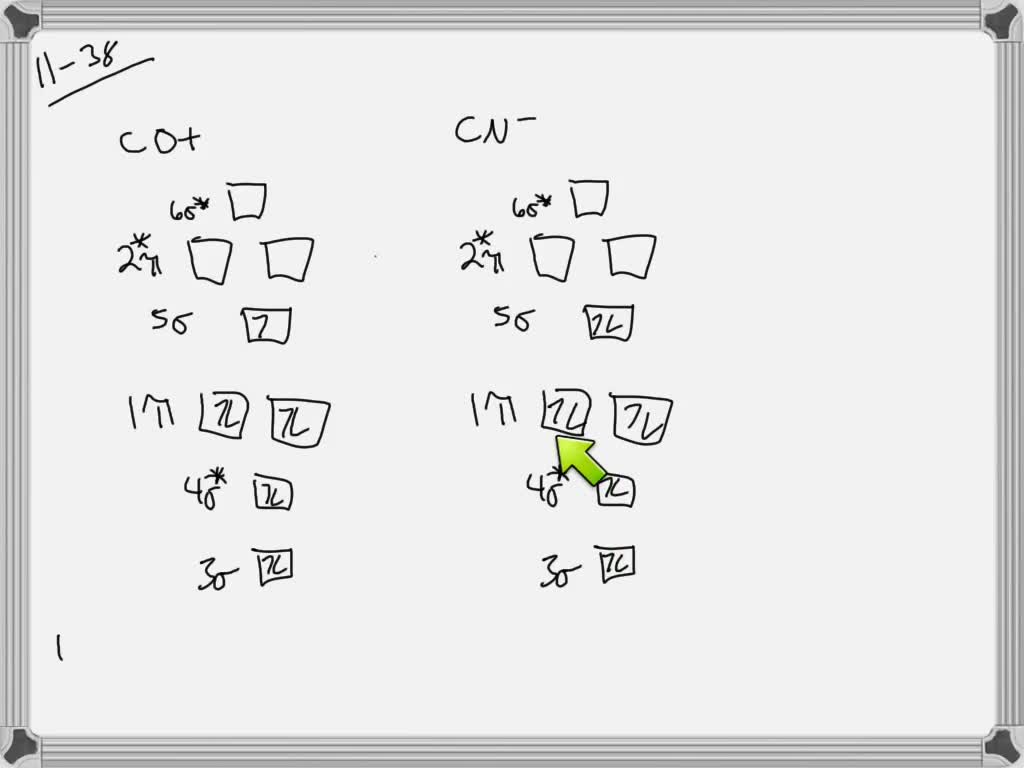
A) F2; B) F2^2+ C) Ne2^2+ D) O2^2+ E) F2^2-2) Use molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2^2-B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic.
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F 2 molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT). The bond order calculations are feasible using MOT and so is the description of electronic ...
Basis of molecular orbital (MO) approach: Overlap of orbitals occurs for the whole molecule-bonding is thereforeDELOCALISED. Atomic orbitals: Orbitals that are localized on single atoms. Molecular orbitals: Orbitals that span two or more atoms. These are constructed by overlapping atomic orbitals (AOs) which match in symmetry and size. In principle, To construct MO diagram of a any Molecule, first, set up
Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram for F2 (2+) Watch later. Share. Copy link. Info. Shopping. Tap to unmute. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. Up next.
Solved Draw the MO diagram for F2. What is the bond order of | Chegg.com. Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Draw the MO diagram for F2. What is the bond order of this molecule?
molecular orbital diagram for octahedral complexes. grade 5 diagnostic test with tos and answer key / 2012 new york knicks roster / molecular orbital diagram for octahedral complexes. February 3, 2022February 3, 2022. by in blue plaid crochet baby blanket.
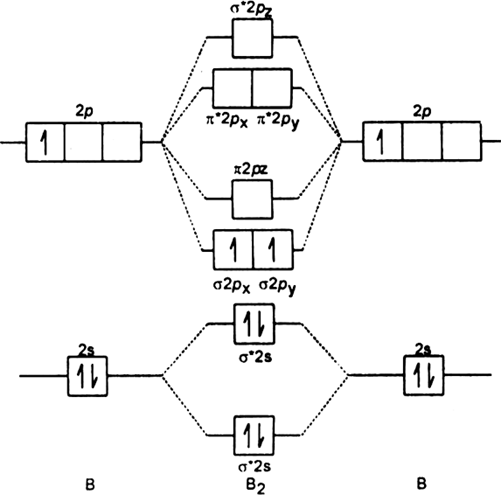
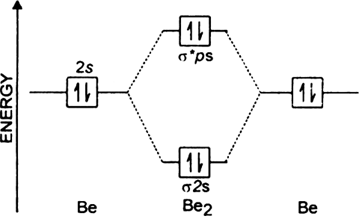
Explain why the relative energy levels diagrams for Li2, Be2, B2, C2, N2 are different The molecular orbital theory of Li2 to F2 gives a graphical explanation. Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. May 25, By Mrs Shilpi Nagpal 9 . It is paramagnetic in nature. 6)Li2. Molecular orbital energy level of Li2.Molecular orbitals of Li 2, Be 2 ...
Draw molecular orbital diagrams for o2 o22 and o2. If2- Lewis Structure How To Draw The Lewis Structure For If2- In 2021 Positivity Math Molecules . Out of eight electrons six go to bonding molecular orbitals and two to the antibonding molecular orbitals. How to draw molecular orbital diagram of o2. I.e., one is bond and one p bond.
Draw the molecular orbital diagram of dioxygen and calculate bond order. Medium. View solution > Explain the molecular orbital structure, bond order, stability and magnetic behavior of Hydrogen molecule on the basis of molecular orbital theory. ...
LCAO, Molecular orbitals of di-atomic molecules: Molecular orbital energy level diagrams of diatomic molecules (N 2, O & F2). 1.22 in text) The pictures below are intended to help you visualize pi bonds in double and triple bonds. The number of molecular orbitals = the number of atomic orbitals combined.
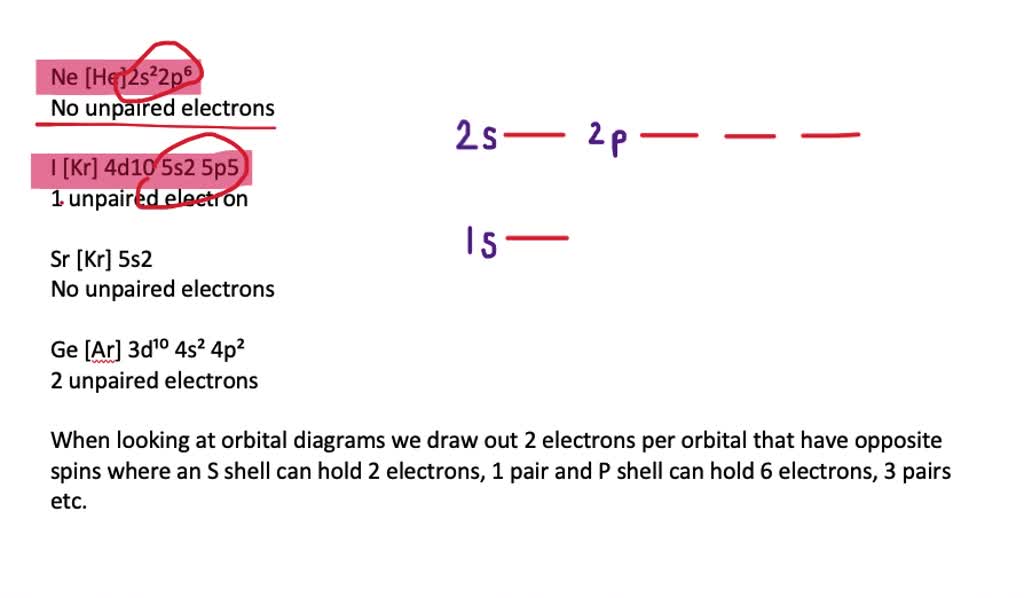
a draw the shape of the atomic valence orbitals formed by the overlaping of two fluoride 2p atomic orbitals 4 marks b draw the molecular orbital diagrams for f2 and f2 identify their bond or 30506













0 Response to "37 f2+ molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment