40 mo diagram of f2
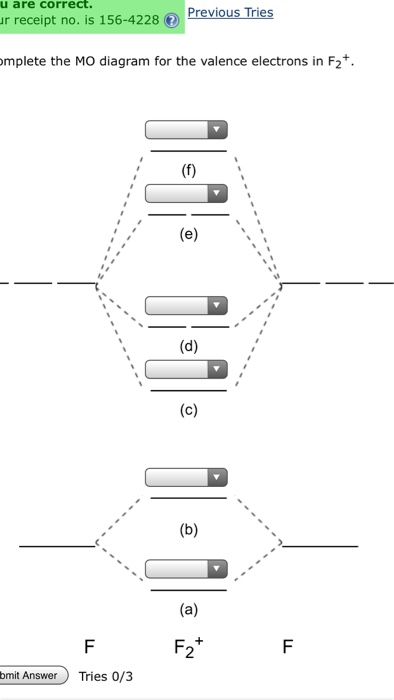
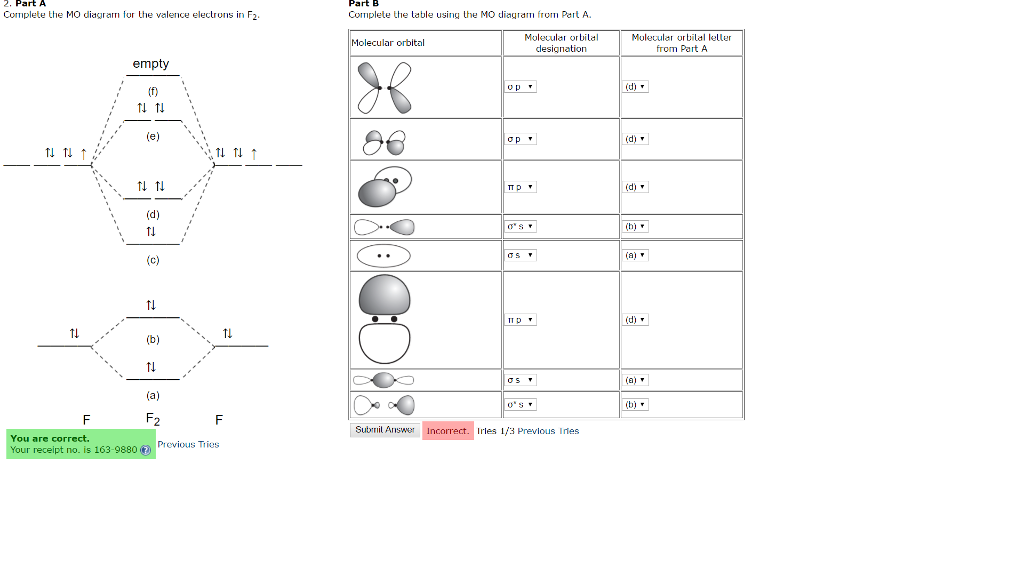
Draw an MO diagram for the valence electrons in F2. What is the bond order? How many o and π bonds are there? What is the HOMO and LUMO? What is the magnetism of the species? FREE Expert Solution 83% (476 ratings) Sign up for free to view this solution Sign up for free. 561,816. students enrolled. 97%. ... Here is a video that discusses over the Molecular Orbital Diagram for F2+ and F2+. Then compare their bond length, strength, bond order etc. And explaining a...
For this, we need to do the following steps: Step 1: Calculate the total number of valence electrons present. Step 2: Draw the molecular orbital diagram. Step 3: Calculate the bond order of the molecule. The molecular orbital diagram for F2- ion will be like this: Step 1: Total number of valence electrons. 88% (20 ratings)

Mo diagram of f2
This video is about MO Diagram #2 - F2 0:21 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Oxygen Molecule3:30 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Florine Molecule5:25 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Neon MoleculeSo as we d... Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following: Open in App. Solution. Verified by Toppr. Solve any question of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure with:-Patterns of problems >
Mo diagram of f2. For the ion F2+:a) Draw the molecular orbital diagram.b) Calculate the bond order.c) Would this ion exist?d) Write the electron configuration of the ion.————... Answer (1 of 5): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To find the bond order, add th... MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine Why isn't the media OR why aren't people in general conversation talking about HOW covid kills people anymore? Where are the hospitals full of patients being ventilated? Where are any of these actually scary horrifying things that were the original reason people were panicking? All I see now is a discussion of cases, but it's almost like the fear porn is gone. What happened? And I mean this sincerely: any doctors or nurses who can weigh in? Edit: Are covid death rates wildly inflated? A...
There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc).One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen (start... #3. Draw the MO diagram for `O_2^+` This is a bit of a curveball, but a perfectly valid problem. Recall that a cation indicates a loss of `1` electron. `O_2^+` is just the ionized form of `O_2`; that is, it's `O_2` with `1` missing electron. The MO diagram will be the same as the MO diagram of `O_2`, except with `1` less electron. When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so ... Hello everyone, I am teaching MO diagrams next week and would like to make a proper Figure for the corrections of my exercises. Since I am no Picasso, doing it by hand seems tedious for the students. How do you do that guys? I am looking at doing it with Tikz but since I am doing BF3, that gets messy quite fast. Python perhaps? I would be thankful if someone had advices or a working script, bonus cookie points if it is on one of the molecules I will make the students suffer on. Cheer...
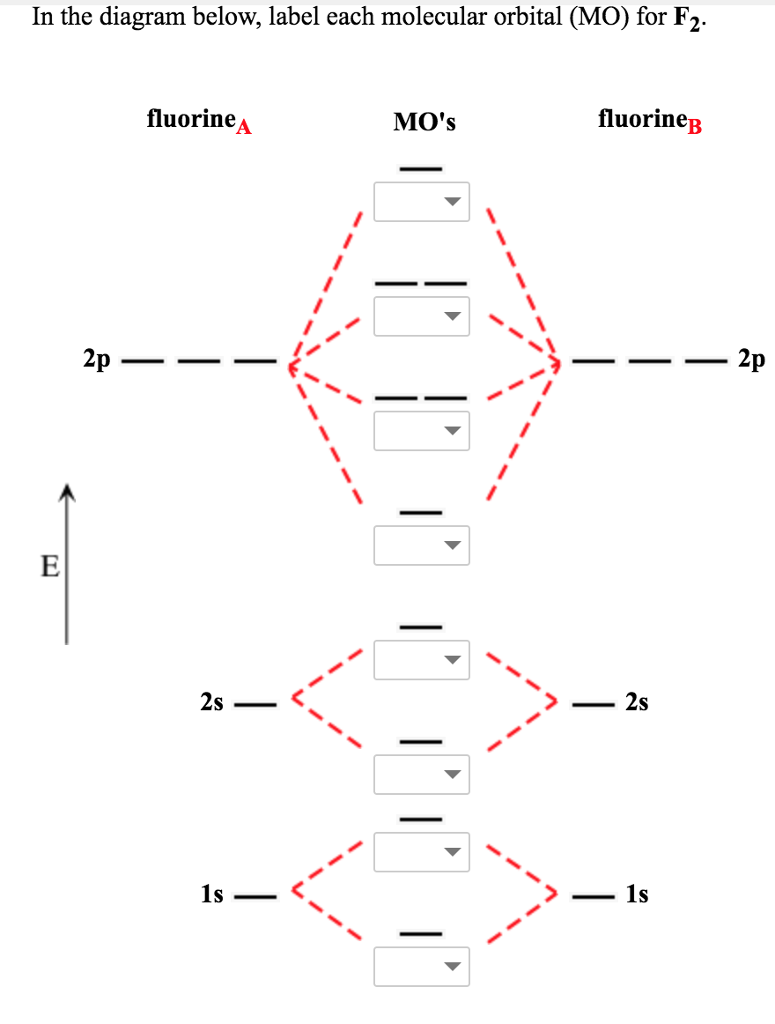
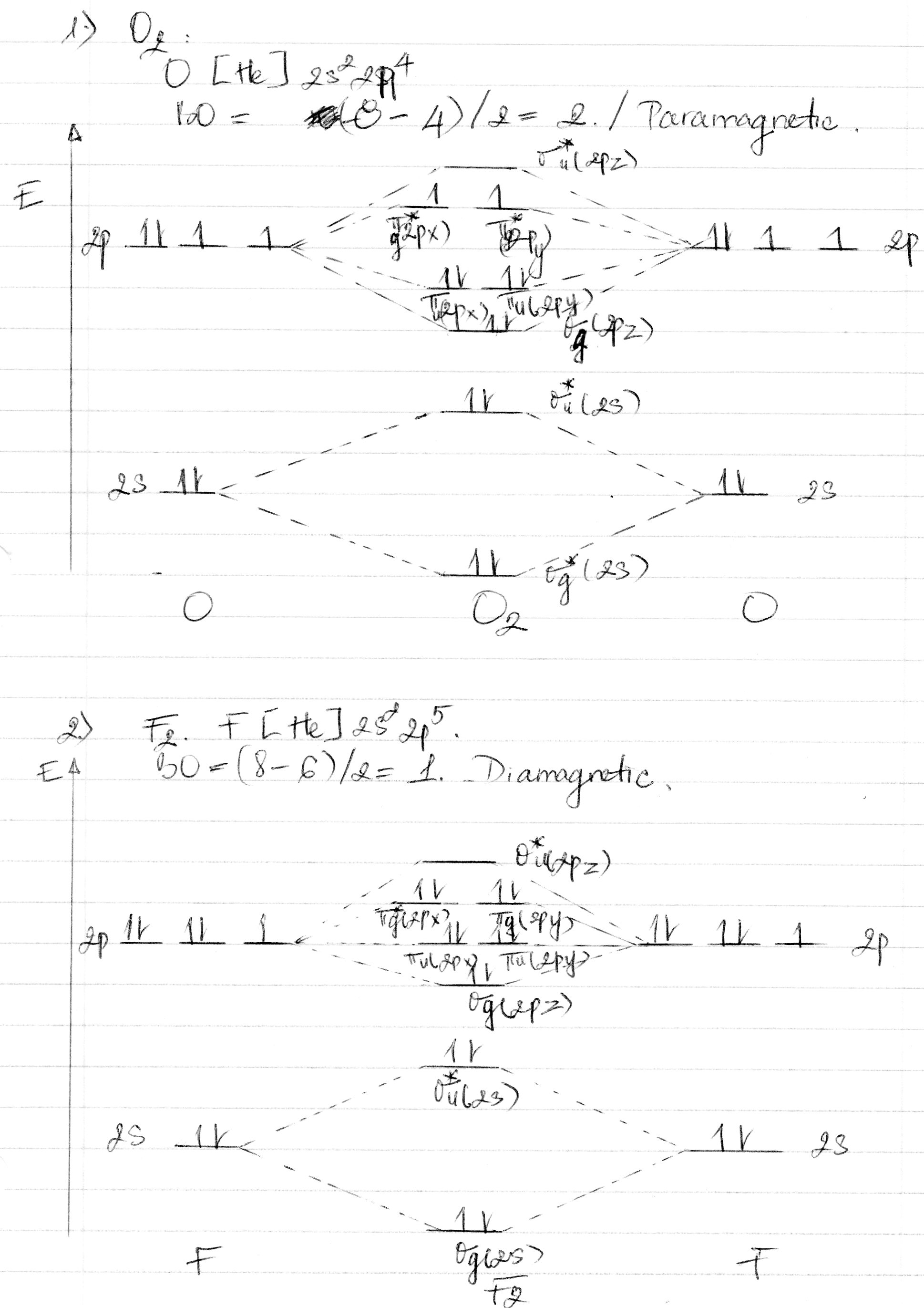
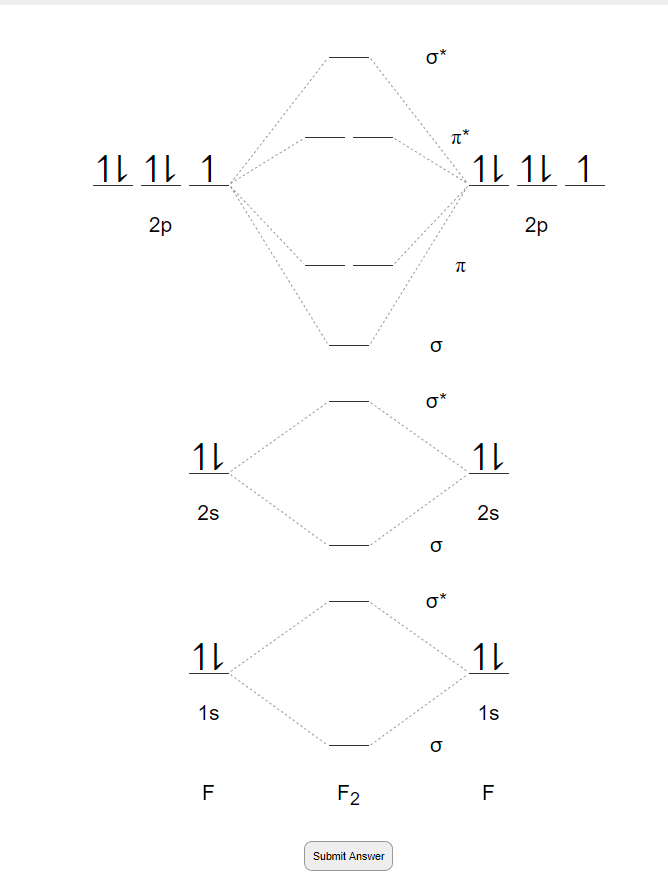
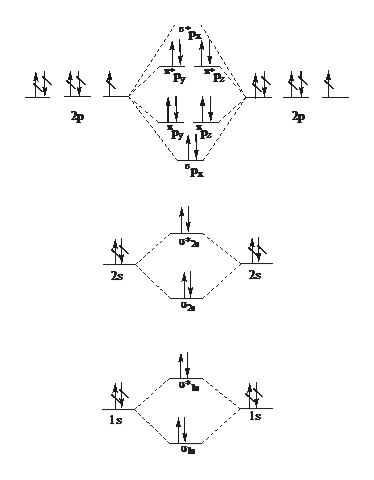
Whereas, presence of unpaired electrons shows that the substance is paramagnetic i.e. can be attracted by magnetic field. Now, let us see the MO diagram of F 2 molecule- -Molecular orbital electronic configuration is given by, MOEC = K K ( σ 2 s) 2 ( σ ∗ 2 s) 2 ( σ 2 p z) 2 [ ( π 2 p x) 2 = ( π 2 p y) 2] [ ( π ∗ 2 p x) 2 = ( π ∗ 2 p y) 2] 3. Construct the MO diagram for F2 (containing atomic orbitals, molecular orbitals, lines denoting which atomic orbitals contribute to which molecular orbitals, symbols for each molecular orbital, and placing electrons in the correct molecular orbitals)(10 points) a. Originally Answered: When doing molecular orbitals the pi-bonds come before sigma for B2,C2, N2 and for O2,F2 and N2 the sigma bond comes first then the pi- ... Arrange the following in order of decreasing stability. a blank molecular orbital diagram (part a 1 figure) has been provided to you. rank the fluorine species from most to least stable. to rank items as equivalent, overlap them. f2, f2+, f2-
Alright, so nobody can explain the nature of the big bang, why the universe is expanding, etc. Here's my nutjob theory that's been in my head for about a year now: [So this is the best I could do with my bad art skills, represented in 2d](https://i.imgur.com/vZafR3Z.png) Basically, I think our universe is the result of a 4d hypersphere passing through an area of 3d space. This could explain the nature of our universe constantly expanding, we're just still on the 1st "half" of the sphere. Event...
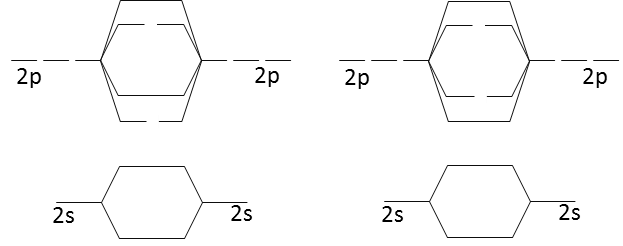
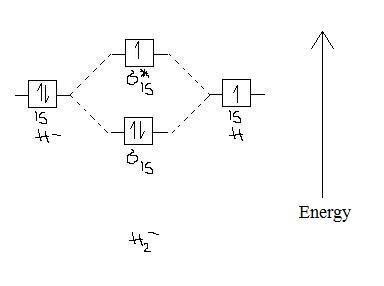
For example, an ns/ns overlap for a homonuclear diatomic molecule gives rise to a partial MO diagram like this: and an np/np overlap for O2 and F2 gives: So, the full MO diagram is: Thus, the valence electron configuration is: (σ2s)2(σ* 2s)2(σ2pz)2(π2px)2(π2py)2(π* 2px)2(π* 2py)2. Answer link.
Identify the MO diagram for F2. F2 valence e−: diagram A 6 diagram A 8 diagram A 10 diagram B 12 diagram B 14 Solution In B2, C2, and N2, the 𝜎2𝑝 orbital is higher in energy than the 𝜋2𝑝 orbitals as shown in diagram A.
Building the MO diagram of fluorine based on the allowed combinations of atomic orbitals on fluorine. For more free educational content, visit http://www.in...
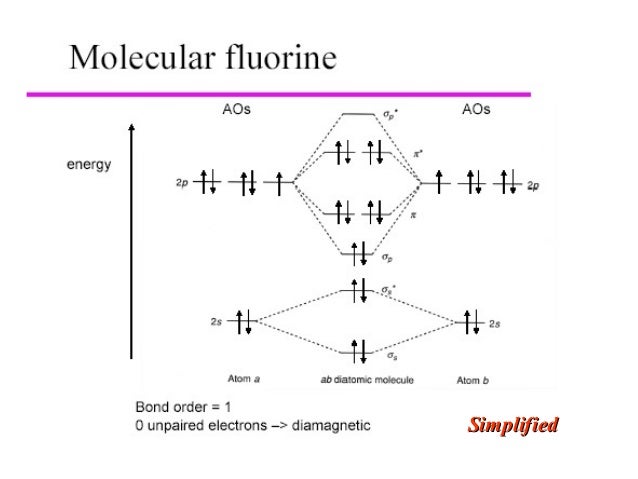
Molecular orbital diagram and bond order of fluorine molecule . Fluorine molecule is formed by the combination of atomic orbitals of two fluorine atoms, each having nine electrons, thus making 18 electrons.; These 18 electrons are filled in various molecular orbitals, in the increasing order of their energies (aufbau principle) and on the basis of Hund's rule and Pauli's exclusion principle as ...
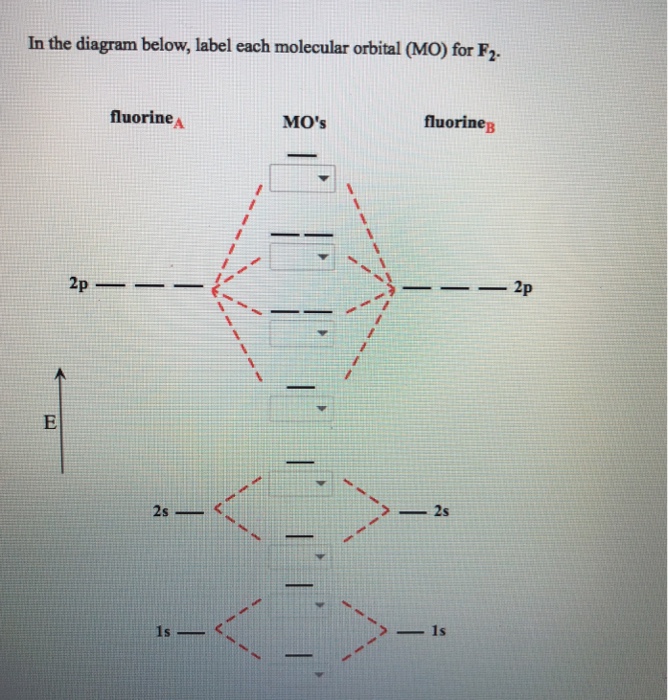
Question: VI VI IC 100wing molecular orbital (MO) diagram represent F2 molecule? 11/11 - 11/11* | OMO diagram C O MO diagram A O MO diagram B . This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Show transcribed image text Expert Answer. Who are the experts?
As discussed in class the MO diagram for B 2 shows that it has two unpaired electrons (which makes it paramagnetic) and these electrons are in bonding molecular orbitals resulting in the equivalent bond strength of one bond. As discussed in class it is not a bond. This example was covered in class to show the rare exception that this single bond is a bond.
So I just got this CBR 600F 1993 from a friend for super cheap because he had crashed it. I'm restoring it and changing parts, which is going just fine, but the electricity is where I'm confused. So if anyone knows about a diagram it would be appreciated. My specific problem atm is the two wires that come from the choke switch on the left handlebar and connect behind the radiator to two wires that come from the motor/carburetor. I made a beginner mistake and didn't memorize the colors when I to...
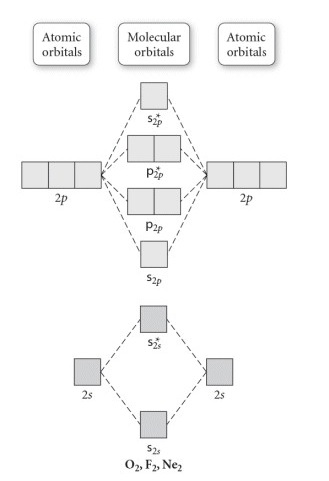
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
Answer (1 of 5): The atomic number of fluorine is 9, so a (neutral) F2 molecule has a total of 18 electron, or 14 valence electrons (excluding the four 1s electrons). The (F2)- ion has one more valence electron, or 15. The orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule is To find the bond order, add th...
The molecular orbital diagrams of , and are drawn in the attached image. There is no unpaired electron present in the MO diagram of and all the electrons are paired up so it is diamagnetic in nature. There is one unpaired electron present in the MO diagram of and therefore it is paramagnetic in nature.
When we make the molecular orbital energy level diagram of f2 molecule then, we will get this configuration: 1σs 2, 1σ*s 2, 2σs 2, 2σ* 2, σ2pz 2, π2p x 2, π2p y 2, πp x * 2, π2p y * 2. From this electronic configuration, we can see that there are a total of ten bonding molecular orbitals and eight antibonding molecular orbitals.
If you draw the molecular orbital diagram for F2, you can see that the highest energy electrons are in pi anti-bonding orbitals. Removing one of these is relatively easier since the orbital is anti-bonding, or higher energy than a normal orbital in F. On the other hand, fluorine is one of the hardest elements to remove an electron from because ...
The Lewis theory of chemical bonding helps us visualize the arrangement of atoms—how they are attached or bonded—in molecules. The valence electrons in each atom are the ones that participate in the bonding, and hence they are the only ones displayed in the Lewis structures. It is to be noted though that this theory about the electronic structure is quite primitive and most limited. In a typical Lewis structure, each valence electron is represented as a dot, and a covalent bond between two atoms (formed as a result of sharing of two electrons) is represented as a line. Several atoms tend to seek eight electrons in their valence shell through chemical bonding; this is referred to as the octet rule and is reflected in the Lewis structure of a molecule. Hydrogen is an exception, though; it seeks a duplet, not octet, because it has only one electron in its K shell, and thus needs only one more to achieve the maximum capacity of K shell. Noble gases already have completely filled valance...
Answer (1 of 6): Here is the solution, > * For O2 molecule, > * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading.
I get the meaning of MO for diatomic molecules such as O2 F2 and similar, but i'm stuck on how to know which orbitals have more energy and how to identify anti-bonding ones. I searched on internet but it's not quite helpful
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following: Open in App. Solution. Verified by Toppr. Solve any question of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure with:-Patterns of problems >
0:21 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Oxygen Molecule3:30 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Florine Molecule5:25 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Neon MoleculeSo as we d...
This video is about MO Diagram #2 - F2


















0 Response to "40 mo diagram of f2"
Post a Comment