36 co2 molecular orbital diagram
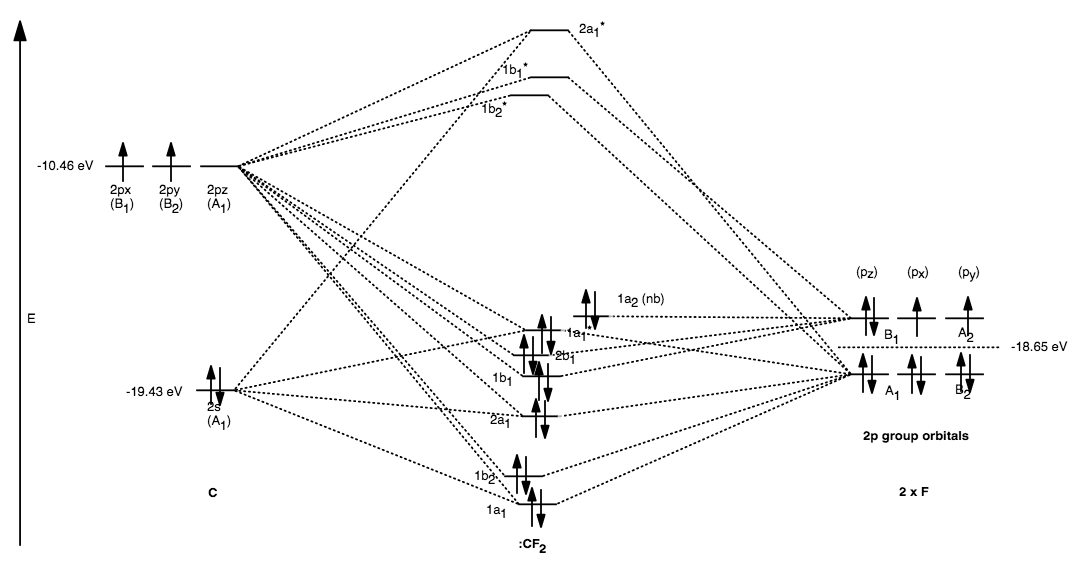
ClO2 is of C2v point group, so I just read off the C2v character table and got the following group orbitals [where z axis is that of the principal axis, and the outer atoms are aligned such that the y-axis points towards the centre atom]: A1 symmetry, two s orbitals B1 symmetry, two s orbitals A1 symmetry, two py orbitals Part B. Draw the orbital diagram for the ion Co2+. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals in order of increasing energy, starting at the bottom with the. Watch the video solution for the question: Draw the orbital diagram for ion Co 2+.. . can be accommodated in the metal d orbitals. • d0 ions •d7 ions - Fe1+, Ru1+, Co2 ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. . combinations such as CO and NO show that the 3σg MO is higher in energy. Mulliken came up with theory known as Molecular Orbital Theory to explain questions like above.

Co2 molecular orbital diagram
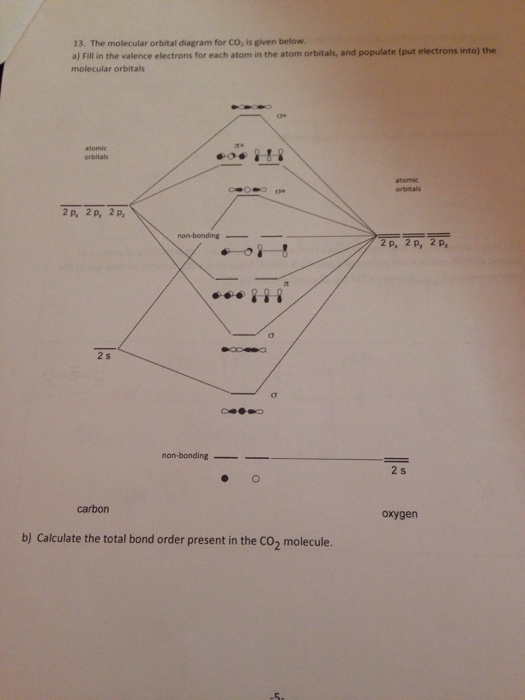
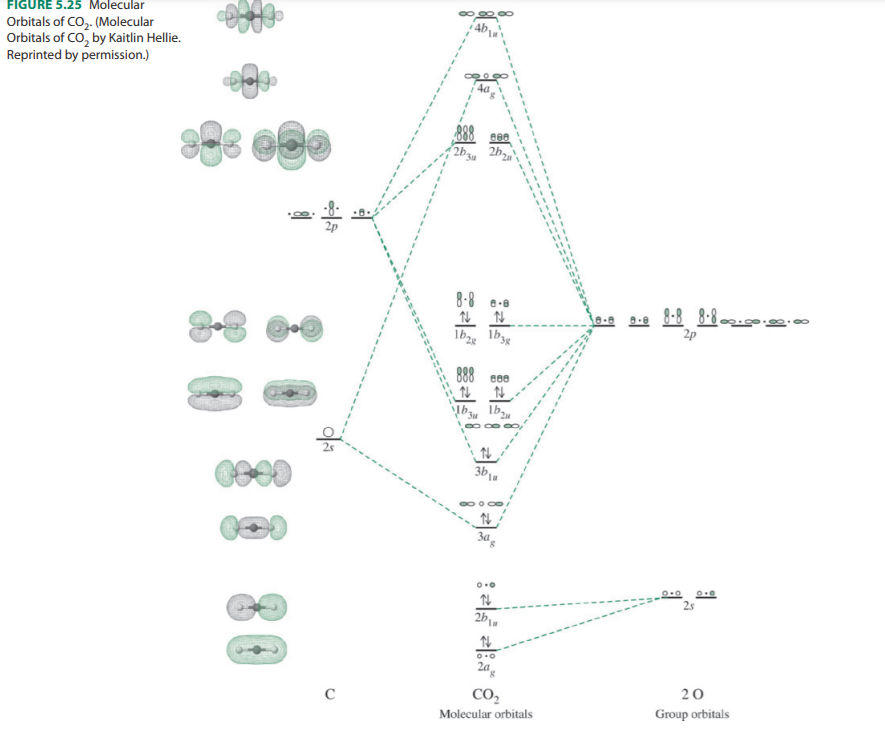
In a Molecular Orbital Diagram, the 2s orbital of oxygen is nonbonding because of the high energy difference between carbon and oxygen atoms. Based on the rules of the Lewis Structure, all 16 electrons are filled upon bond formation, but the nonbonding orbitals remain vacant, as in the case of CO2. Bond Angle The molecular orbital diagram of CO2 is as below. A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. It also helps us to find the bond order, bond length, bond strength of the molecule. In the diagram, the left-hand side consists of the atomic orbitals of carbon. Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
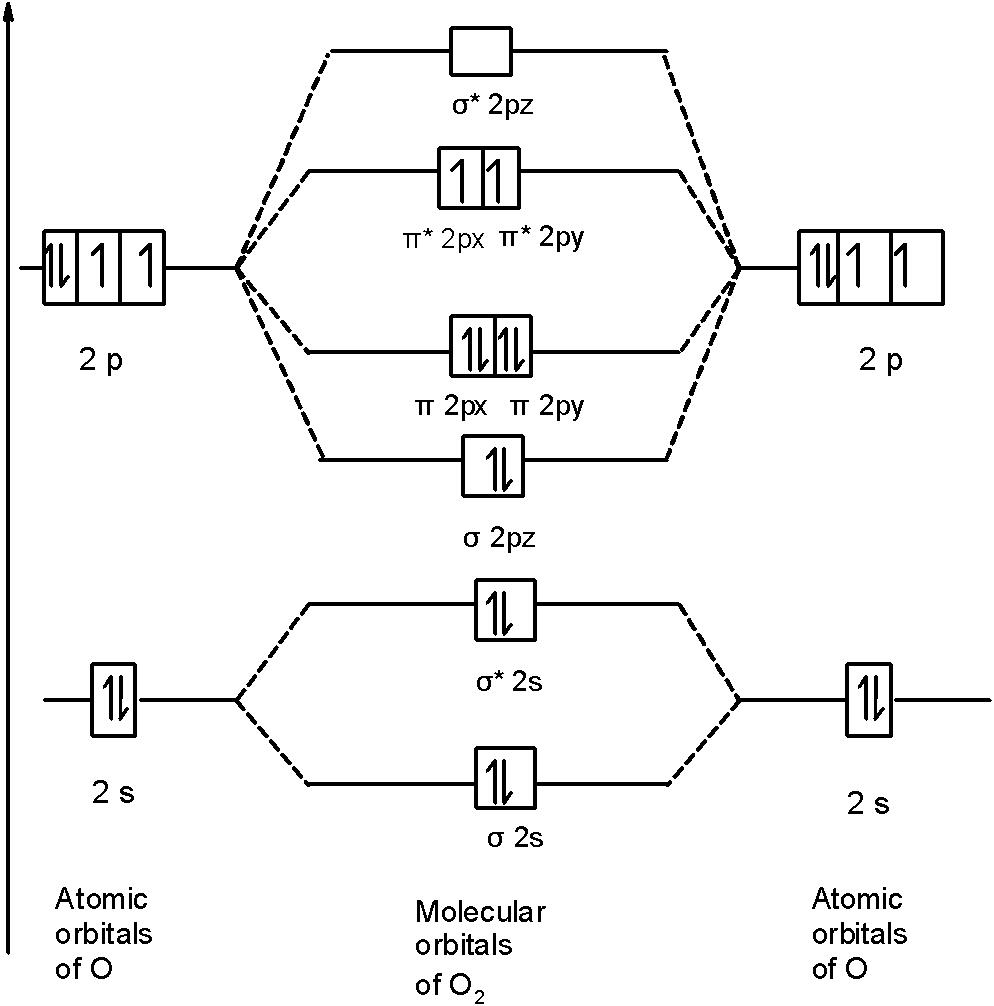
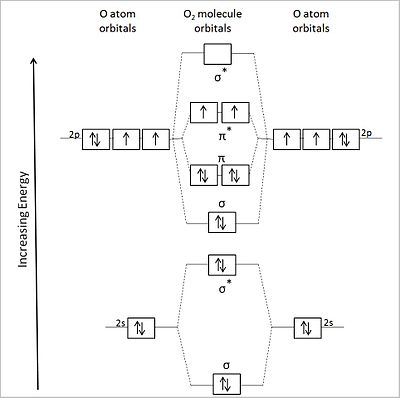
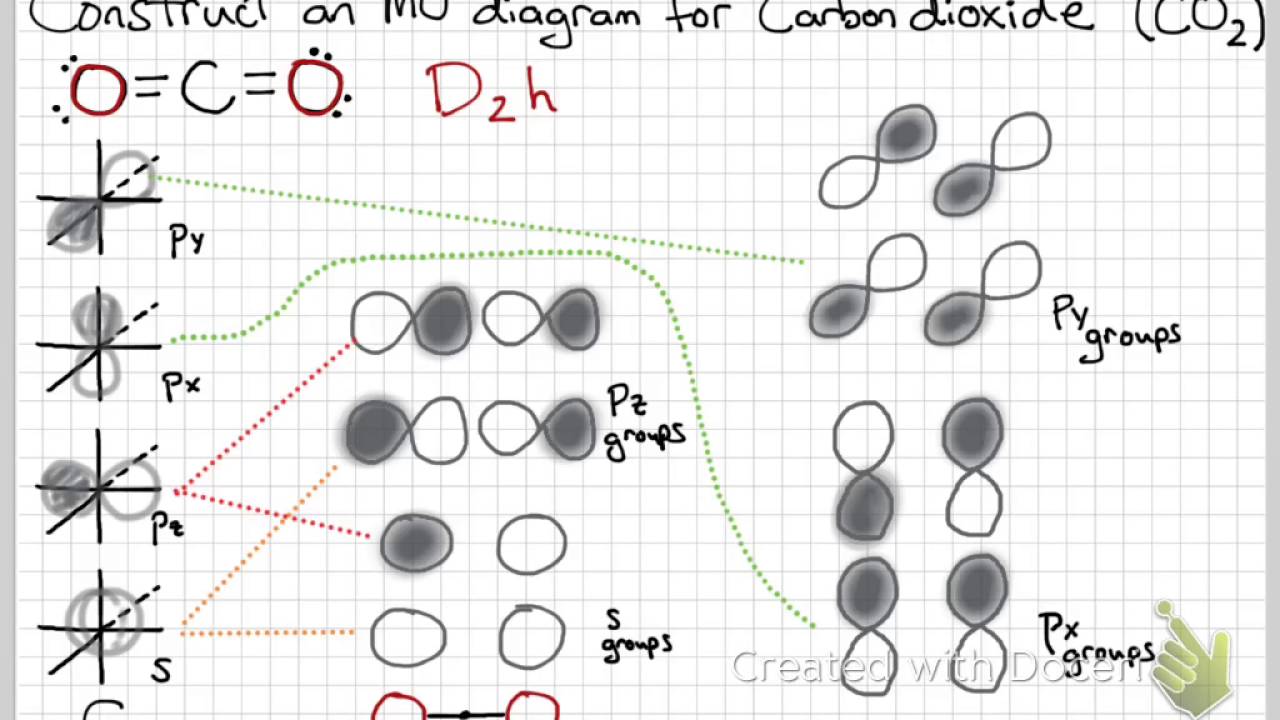
Co2 molecular orbital diagram. Molecular Orbitals for Larger Molecules 1. Determine point group of molecule (if linear, use D2h and C2v instead of D∞h or C∞v) 2. Assign x, y, z coordinates (z axis is principal axis; if non-linear, y axes of outer atoms point to central atom)3. Find the characters of the reducible representationfor the combination of 10. in the schematic sketches on the left of the energy level diagram and in the calculated molecular orbital images on the right.* 1 because the molecular orbital is the sum of two atomic orbitals, 3c (1sa) + 2 2c (1sb) 4 , and results in an increased concentration of electrons between the two nuclei, it is a bonding molecular orbital and has a … Molecular orbitals for CO2 using the pictorial method. Here I look at determining the symmetries of the possible combinations of orbitals. Part 2 will look... The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxideis very similar to that of molecular nitrogen. Carbon, with 4 valence electrons, and oxygen with 6 valence electrons, together have the same number of electrons as dinitrogen.
Carbon dioxide (CO2), molecule is triatomic and linear like Beryllium di hydride (BeH2) However, unlike hydrogen as peripheral atoms in BeH2, there are oxyge... Bonding in Carbon Dioxide From the Lewis structure we can see that the carbon in CO2must make 2 sigma bonds and it has no lone pairs. This atom will be 2sp hybridized with remaining 2pxand 2pyatomic orbitals. Each oxygen makes 1 sigma bond and also needs 2 orbitals for lone pairs of electrons. Home / Structure and Bonding / Atomic Orbitals / Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide CONTROLS Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals The angular overlap diagrams for the molecular orbitals with high d orbital .. For Co2+: High-spin octahedral d7 has LFSE = -∆o. Tetrahedral d7 has. As it is sometimes explained, the statement that 4 s orbital is lower in energy than 3 d But while you fill 3 d orbital with electrons it becomes lower and lower in. Part B.
What is the molecular orbital diagram of co2? The carbon dioxide MO diagram is based on a C atom and an O-O ligand fragment. Carbon has 2S and 2Px,y,z orbitals and the O-O fragment has 2S and 2Px,y,z orbitals that are involved in the formation of molecular orbitals. Part 2 of molecular orbitals of carbon dioxide. Drawing the molecular orbital diagram.Link to part 1: https://youtu.be/ec4kDcI0Hzc English: Molecular orbital diagram of CO2. Source: Own work. Vectorized from File:MO Diagram CO2.jpg: Author: Tjb26 / Orionist: Licensing . I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby publish it under the following license: This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. Carbon dioxide. The molecule is very symmetric and one of only a few with the point group D ∞ h. That also imposes constraints on how the spatial distribution looks like. Along the molecular axis ( O − C − O) is a rotational axis of infinite fold, C ∞, as the molecule is linear. Perpendicular to that axis there is a horizontal mirror ...
Carbon dioxide (CO2) molecular orbital diagram (Jmol visualization) for important MOs. The HOMO-1, HOMO and LUMO+1 are degenerate and the HOMO-5, HOMO-4 and HOMO are non-bonding lone pairs. Firefly 8.2.0 DFT B3LYP 6-311++G (d,p) geometry-optimized structure (energy minimum, no imaginary frequencies).
Molecular Orbitals for CO2. Jmol models of wavefunctions calculated at the RHF/3-21G* level. To view a model, click on an orbital in the energy level correlation diagram shown Mouse Control of Models. Left mouse drag rotate; Shift Left drag resize; Shift Right drag z-rotate; Right click for menu Notes
Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
The molecular orbital diagram of CO2 is as below. A molecular orbital diagram of any compound gives us an idea about the bonding of the orbitals. It also helps us to find the bond order, bond length, bond strength of the molecule. In the diagram, the left-hand side consists of the atomic orbitals of carbon.
In a Molecular Orbital Diagram, the 2s orbital of oxygen is nonbonding because of the high energy difference between carbon and oxygen atoms. Based on the rules of the Lewis Structure, all 16 electrons are filled upon bond formation, but the nonbonding orbitals remain vacant, as in the case of CO2. Bond Angle













0 Response to "36 co2 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment