40 molecular orbital diagram h2
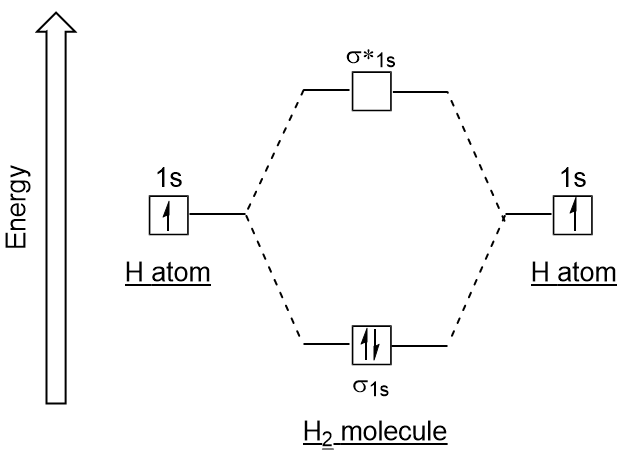
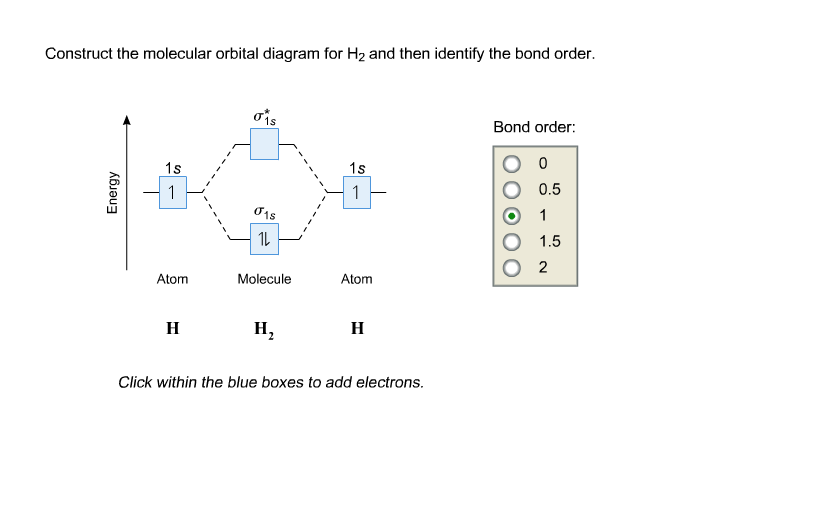
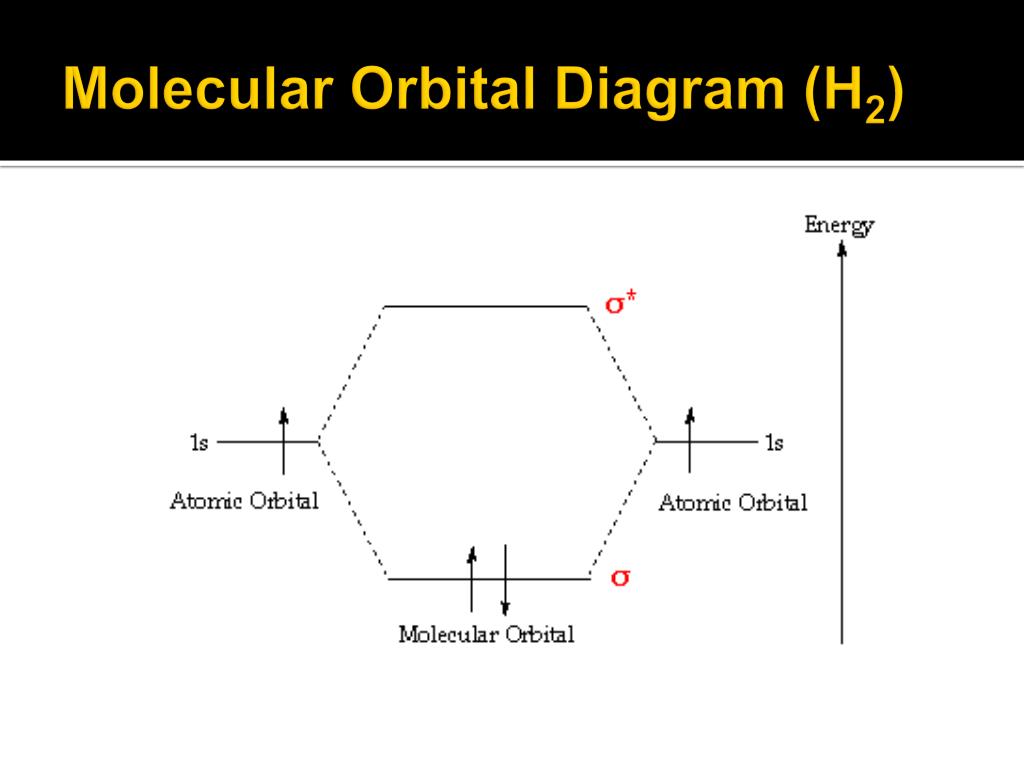
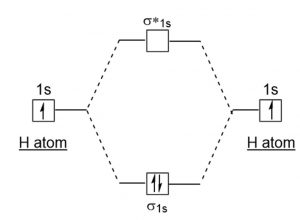
How to draw the Molecular Orbital Diagram of H2 ( Hydrogen molecule ) ? Bond order = Number of electrons in BMO - Number of electrons in ABMO = 2 - 0 = 1 As bond order in H 2 is one so one bond i.e is a single bond is formed between two hydrogen atoms. Further more as there is no unpaired electron in H 2 molecule hence it is diamagnetic.
a molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbital s (lcao) molecular orbital method in particular.the hydrogen molecule ion h2 + molecular orbital diagram s of diatomic molecules - chem …
H2S Molecular geometry Hybridization of the given molecule H2S is sp3; the Sulfur atom is in center bonding with two Hydrogen atoms forming the bond angle less than 180 degrees. According to the VSEPR theory, the lone pairs of electrons repel each other, but as the Sulfur atom is less electronegative, the bond angle decreases to 104.5 degrees.

Molecular orbital diagram h2
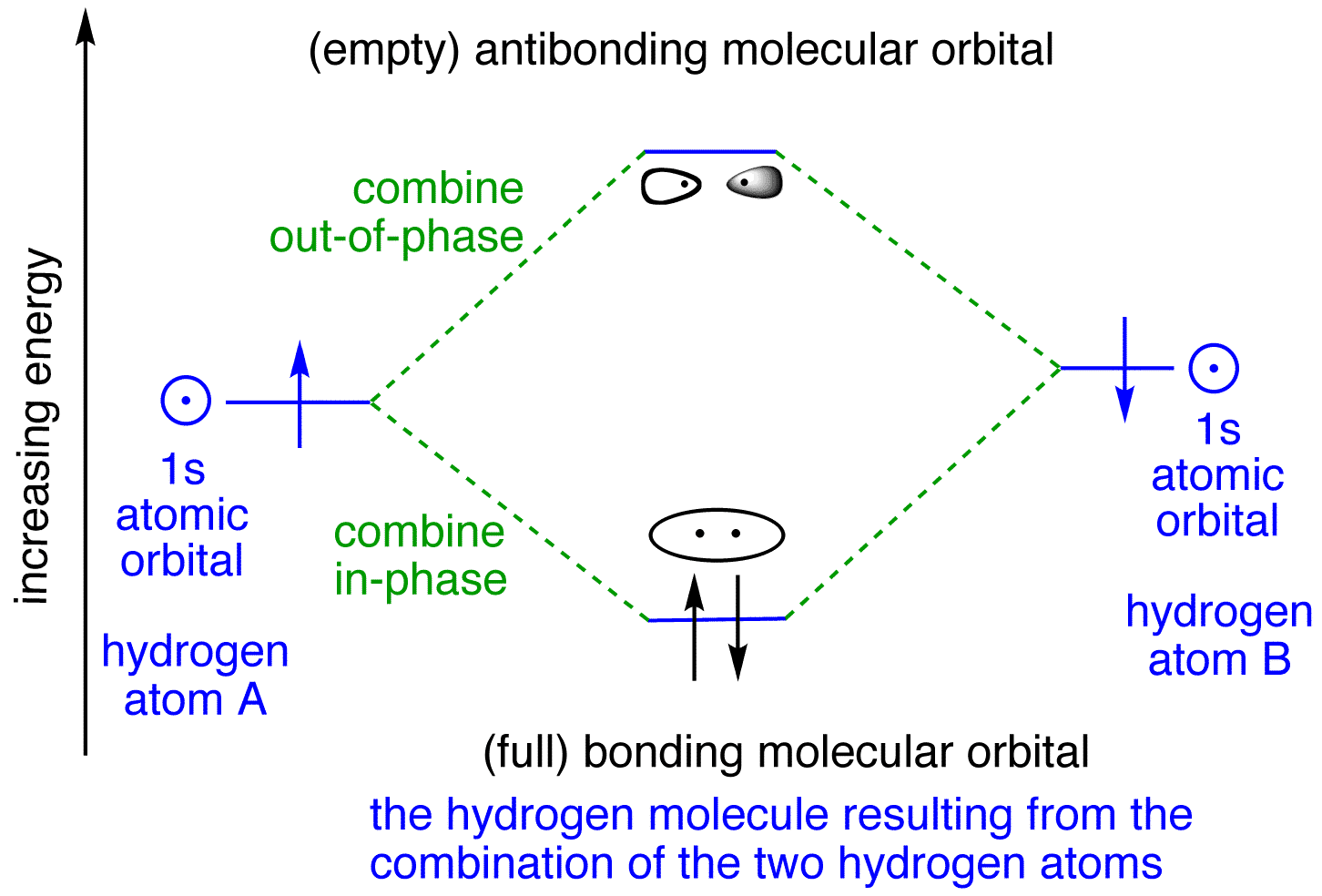
(a) This diagram shows the formation of a bonding σ 1s molecular orbital for H 2 as the sum of the wave functions (Ψ) of two H 1 s atomic orbitals. (b) This plot of the square of the wave function (Ψ 2) for the bonding σ 1s molecular orbital illustrates the increased electron probability density between the two hydrogen nuclei.
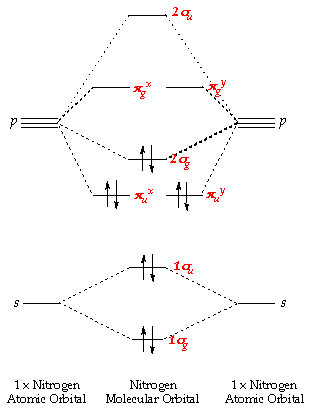
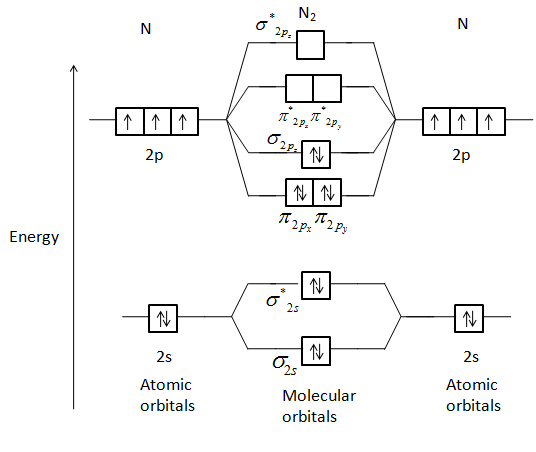
Fig. No. 1 Molecular Orbital Diagram for H2 molecule. Comparison of N2 and N2+ ion N 2 + ion is for med when one electron is removed from N 2 molecule. This electron will be lost from 2p z M.O. Hence the electronic configuration of N 2 + ion will be. N2 molecular orbital diagram and titled.
Apr 1, 2017 · 1 answerI'm assuming you mean H−2 vs. H+2 . Well, build the molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, ...
Molecular orbital diagram h2.
The MO diagram or Molecular Orbital diagram is an extension of the 3-dimensional molecular design and gives a better understanding of the structure of an atom. Molecular Diagram also reflects upon bond length, bond shape, bond energy, and the bond angle between 2 atoms. Br2 is a simple compound as it is formed by 2 atoms of the same element.
Molecular orbital diagram for o2- ion 1918 (Venn's diagram is from 1904), named for English logician John Venn (1834-1923) of Cambridge, who explained them in the book "Symbolic Logic" (1881). 1834, introduced by English physicist and chemist Michael Faraday (suggested by the Rev. William Whewell, English polymath), coined from Greek ion ...
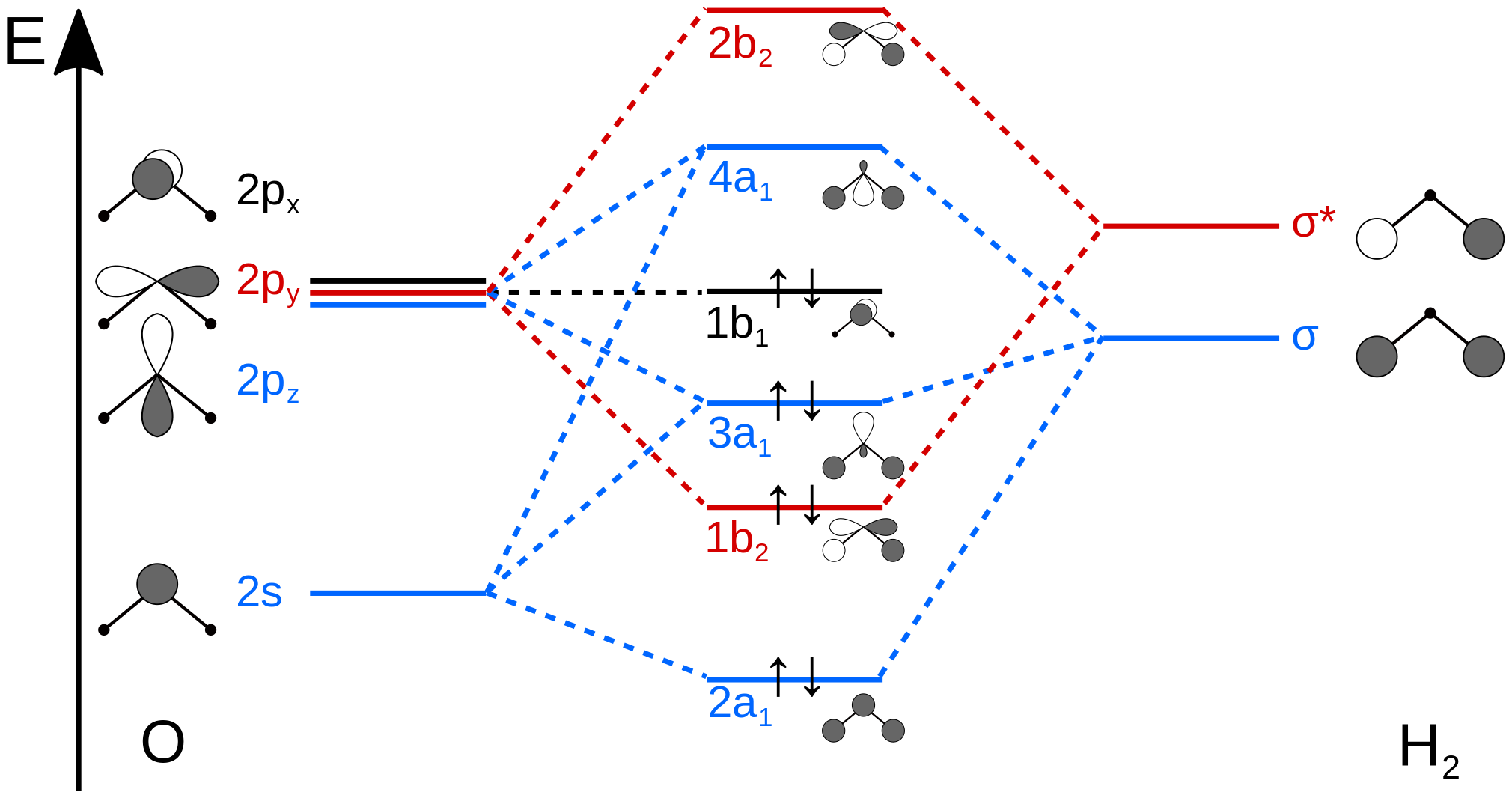
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mo stly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine The energy curves for ψ + and ψ-reveal the following properties of the ion H 2 +.
using the molecular orbital diagram for an h2 molecule, what is the bond order for a neutral h2 molecule? using the molecular orbital diagram for an h2 molecule, what is the bond order for a neutral h2 molecule? Categories Question-Answer. Leave a Reply Cancel reply. Your email address will not be published.
Figure 9. The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that H2 will be a stable molecule with lower energy than the separated atoms. Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. Learn how to draw a Molecular Orbital diagram.
he2 when the bond order is equal to 0, a molecule is predicted to not exist. bond order = [ (# of bonding elections# of anti bonding electrons) / 2] for he2, the number ... ⇒ a homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital in which the same atoms combine together. example- n2, o2, b2, etc. ⇒ a hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital in which …
A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao n2 molecular orbital diagram.
Answer (1 of 2): Rate of a reaction is change in concentration per unit time. If we represent it for the reactants than a negative sign should be there because in case of reactants the change (final-initial) is always comes negative because their concentration is decreases as the time increases....
Explain about the molecular orbital diagram of hydrogen molecule. chemical bonding; class-11; Share It On Facebook Twitter Email. 1 Answer +1 vote . answered Dec 22, 2020 by Taashi (15.8k points) selected Dec 24, 2020 by Aashi01 . Best answer. 1. Electronic ...
B2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both boron atoms. A number of valence electrons of each boron atom = 3. In the formation of B2 molecule, three valence electrons of each boron atom i.e. 6 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies.
14+ H2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. A molecular orbital diagram, or mo diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals.
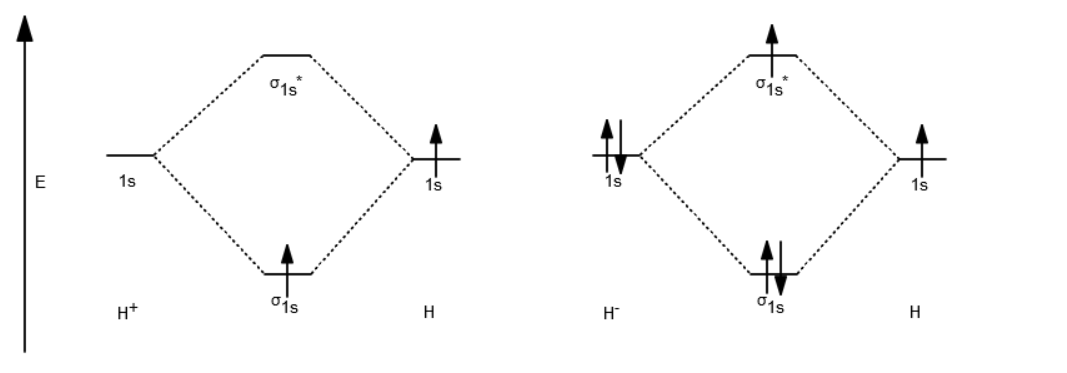
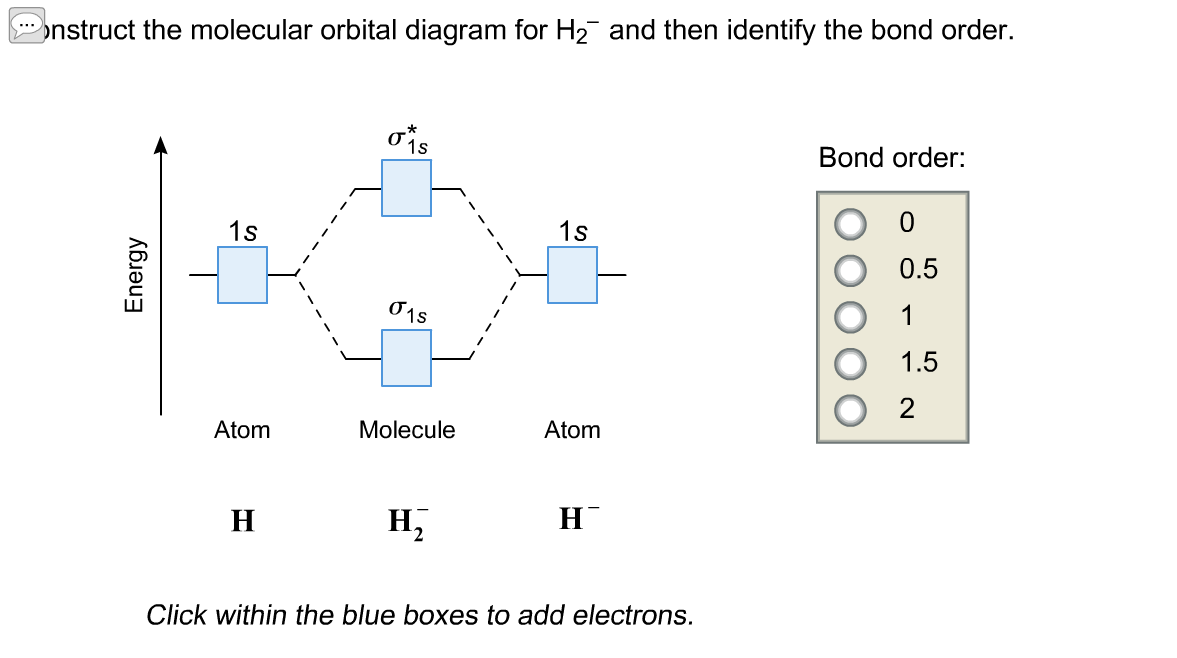
The Answer (1 of 2): In order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2 - is to be drawn. According to MOT number of atomic orbital s combined is equal to total number of molecular orbital s formed.Electronic configuration of H is 1s1. when two hydrogen atoms come closer, then on combi... Science. Chemistry.
He2+ molecular orbital diagram. Draw a molecular orbital diagram for He2. Use this diagram and bond order calculations to explain if He2 is more or less stable than the ions He2+ and He2−. I have done He2 and He2+ and the bond order calculations for both.
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagram s He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+.The energy-level diagram for He2 is shown above, the two electrons in each of the 1s atomic orbital give total of 4 electrons in this molecule.
C2H6 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram The molecular orbital theory, a quantum mechanical model, is used to draw the molecular orbital (MO) diagram of the ethane molecule. It is based on the linear combination of atomic orbitals, which lead to the formation of the molecular orbital. The molecular orbital diagram of ethane would be:
Question: Use Molecular Orbital Theory To Determine Whether He2 Or He2+ Is More Stable. These properties can be explained by the molecular orbital diagram of BN". The bond order of two suggests that the oxygen molecule is stable. Correct option (a) O-2. Diamagnetic Metals + properties give you a broad overview of these metals from multiple angels.
4- Theoretically it would not be possible to form a molecule from two hydrides because the anti-bonding and bonding orbitals would cancel each other out. So, the bond order is zero. Because the antibonding ortibal is filled, it destabilizes the structure, making the "molecule" H 2 2-very non-stable. Bond order = 1/2 (2-2) = 0 ---> no bond ...
In order to predict the bond order, molecular orbital diagram for H2- is to be drawn. According to MOT number of atomic orbitals combined is equal to total number of molecular orbitals formed.Electronic configuration of H is 1s1. when two hydrogen atoms come closer, then on combining two 1s orbitals,two molecular orbitals are formed among which one is bonding and other is antibonding molecular ...
a) The point at which the solid, liquid and gaseous phases for a substance co-exist. b) The triple point exists for a substance at a specific temperature and pressure. c) The triple point exists at a single temperature and is not related with pressure. d) The system must be closed so that no vapor can escape.
The MOT diagram for H2 H 2 is formed by the overlap of 1s atomic orbitals. Its shell has two molecular orbitals. one is bonding (σ 1s) and the other is anti-bonding (σ *1s ). The H 2 molecule has two electrons and these can be accommodated in the σ 1s molecular orbital.
Molecular Orbital Theory. Molecular orbitals are formed by the combination of atomic orbitals of the bonded atoms. For example, the formation of the hydrogen molecule. A hydrogen molecule is formed by the combination of atomic orbitals of hydrogen \({\rm{A}}\) and \({\rm{B}}\) Each hydrogen atom has one electron in \({\rm{ 1s }}\) orbital.
You are watching: Construct the molecular orbital diagram for h2 and then identify the bond order A molecular orbital diagram is used to define chemical bonding in a molecule. This chart is based ~ above the molecular orbital theory.
Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for H2 - and then identify the bond order. Bond order: Click thin the blue boxes. The hydrogen atom is the simplest atom, and its molecule \ (\ce { H2 }\) is get a sigma (s) bonding orbital, denoted as s1s in the diagram here.
Molecular orbitals are of two types - bonding and antibonding. The two types of bonds are σ - bond and π − bond. The s -orbitals of one atom can overlap with the s, p, d, f, orbital of another atom such that the overlapped region is symmetrical about the internuclear axis. Similar symmetrical overlaps are also possible among p, d and f ...



















0 Response to "40 molecular orbital diagram h2"
Post a Comment