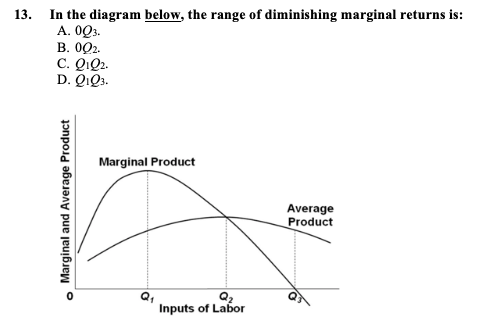
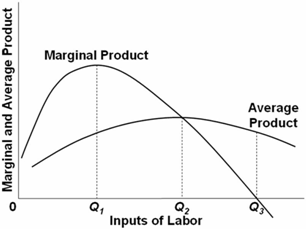
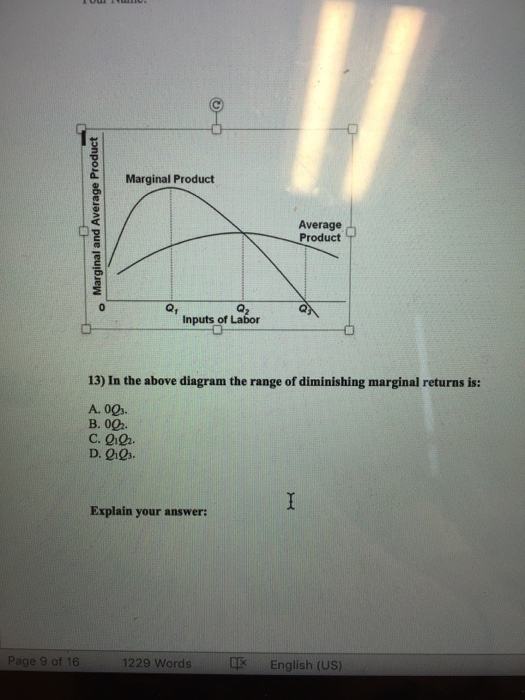
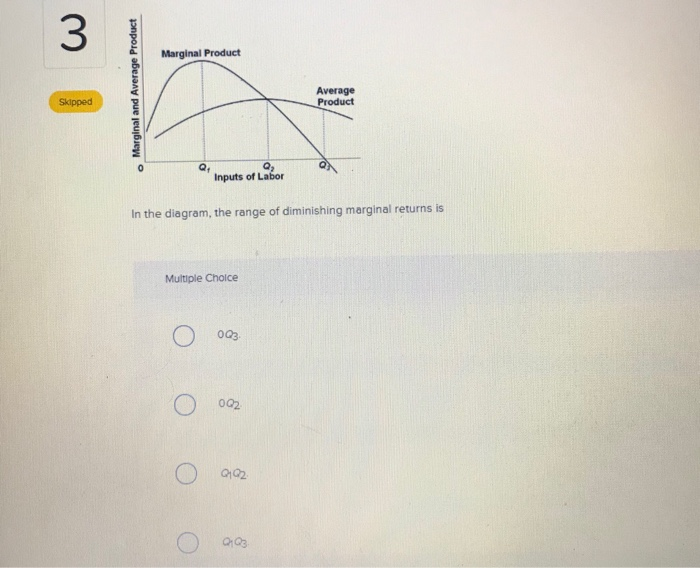
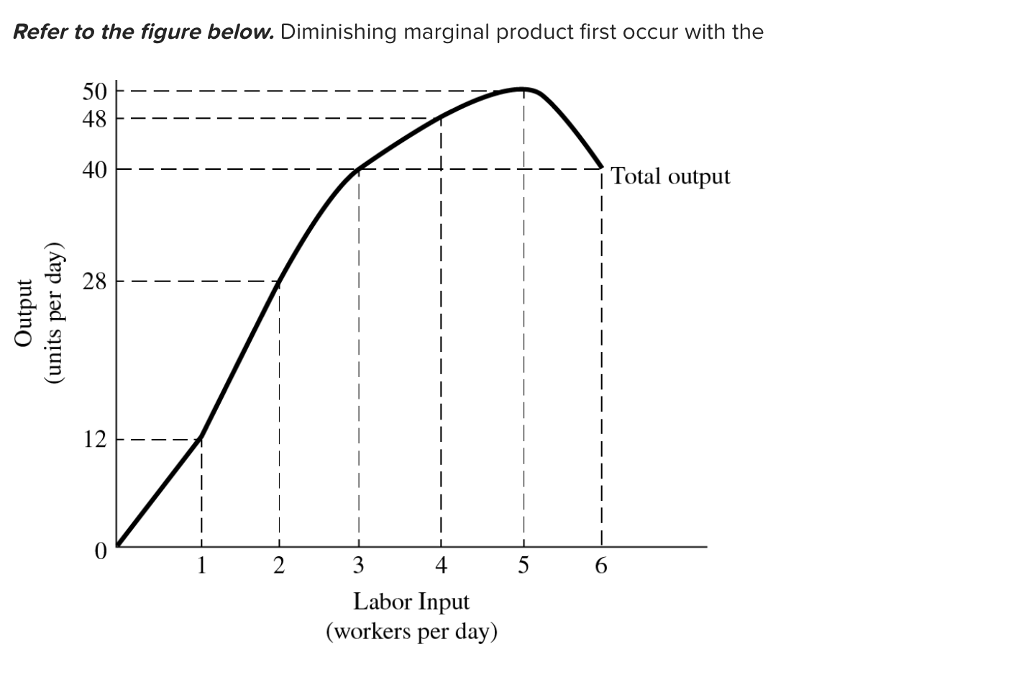
40 in the diagram, the range of diminishing marginal returns is:
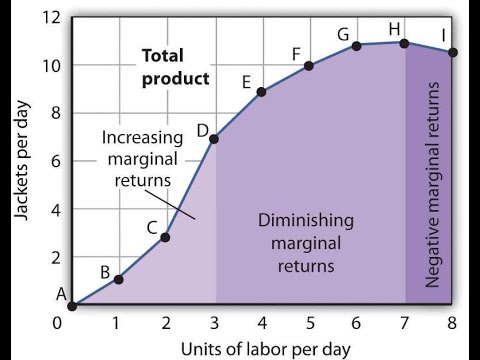
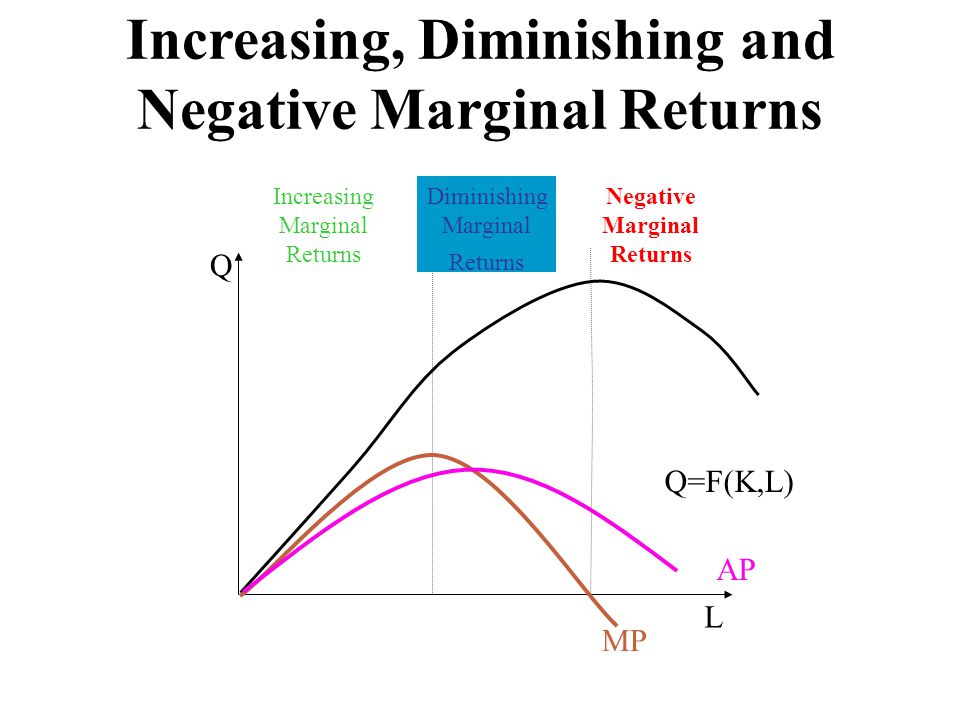
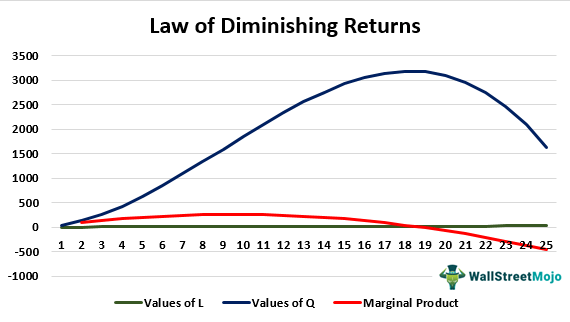
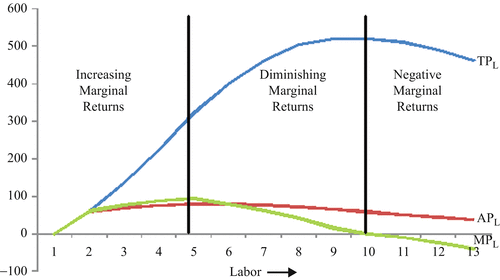
Stage II: Diminishing Returns. Throughout the stage of diminishing returns, the total product keeps on increasing. However unlike the stage of increasing returns, here the total product increases at a diminishing rate. This happens because the marginal product falls and becomes less than the average product, which also sees a downwards slope.
A decreasing marginal costs B diseconomies of scale C increasing returns to scale D the law of diminishing returns 15 To increase the number of cleaners at a local school from 10 to 11, the employer has to raise the hourly rate of pay from $8.00 to $8.50. What is the marginal cost of labour per hour to the employer?
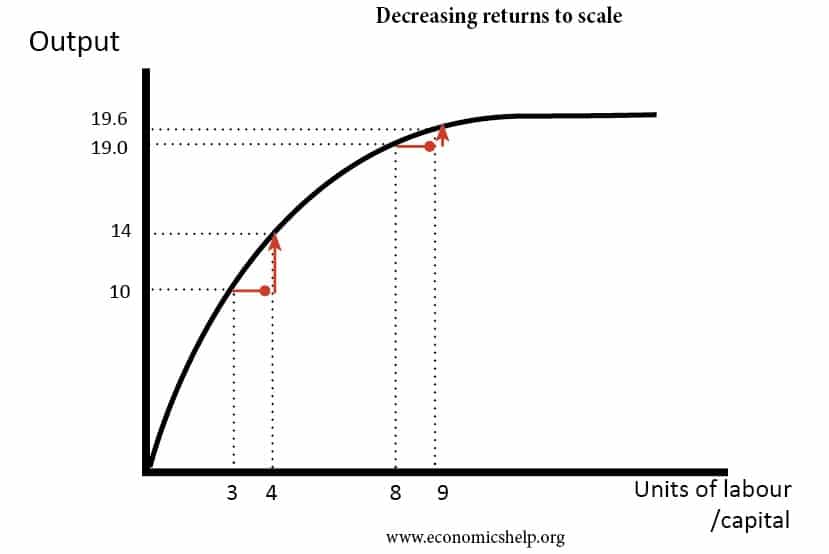
Diminishing marginal returns are an effect of increasing input in the short-run, while at least one production variable is kept constant, such as labor or capital. Returns to scale, on the other...
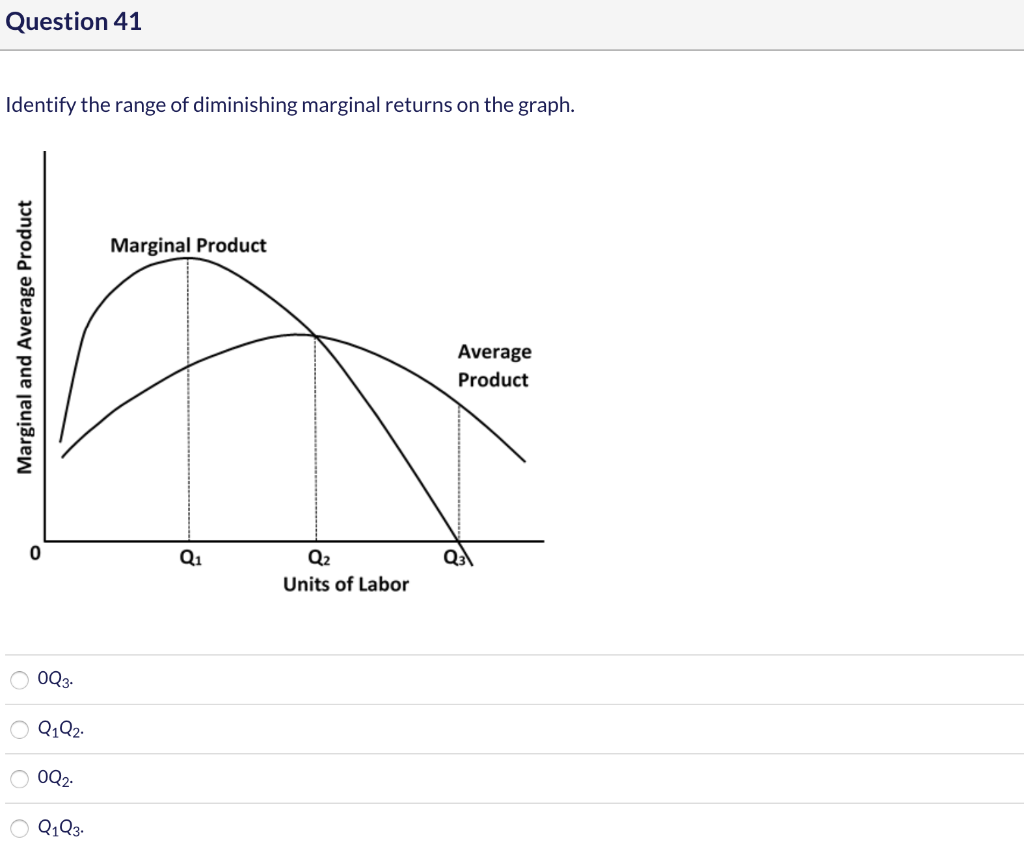
In the diagram, the range of diminishing marginal returns is:
The marginal cost is shown in relation to marginal revenue (MR), the incremental amount of sales revenue that an additional unit of the product or service will bring to the firm. This shape of the marginal cost curve is directly attributable to increasing, then decreasing marginal returns (and the law of diminishing marginal returns).
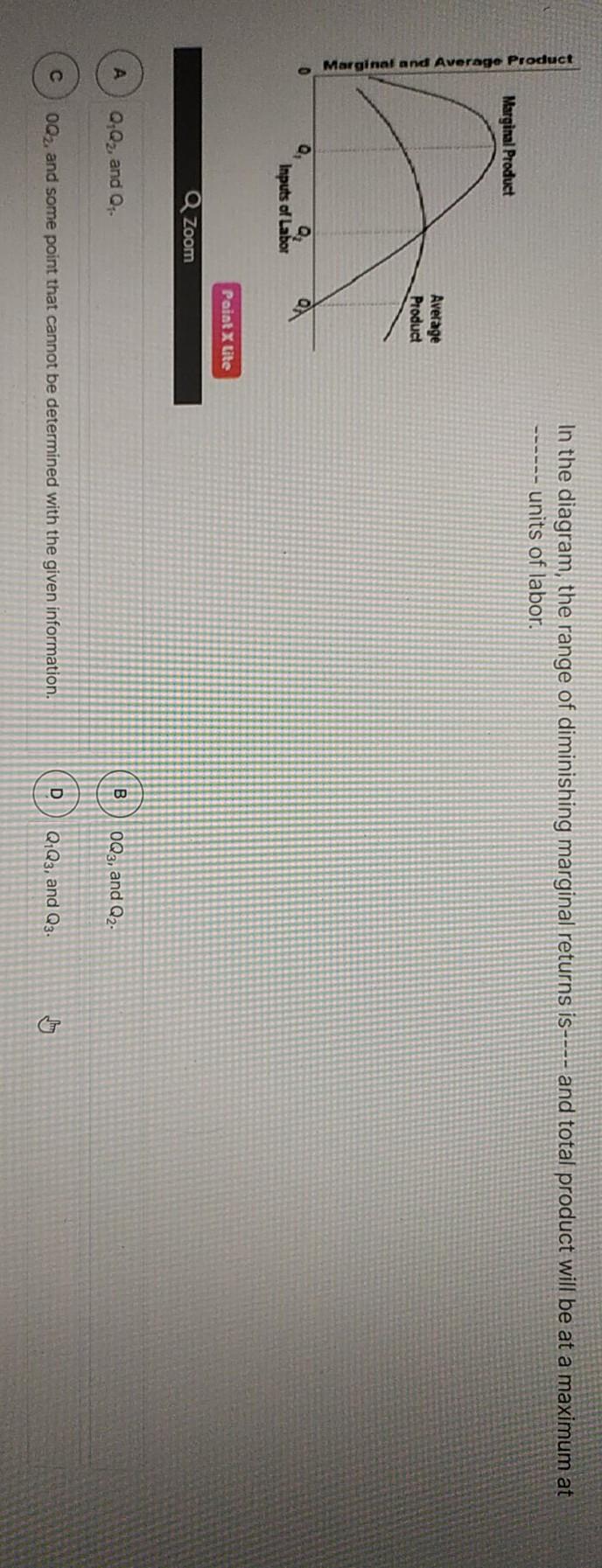
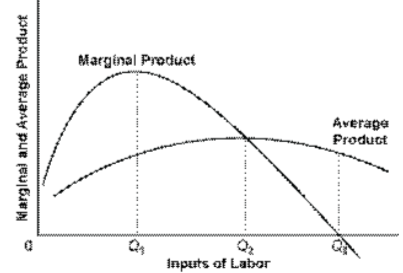
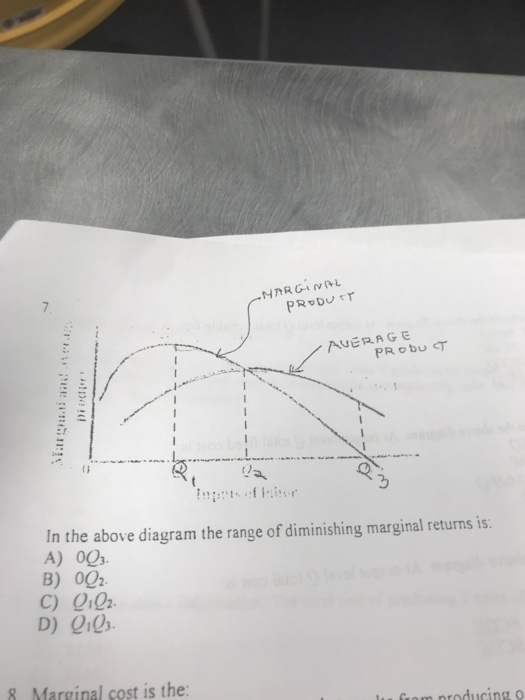
Question 41 Identify the range of diminishing marginal returns on the graph. Marginal Product Marginal and Average Product Average Product Margin - Q1 Q2 Units of Labor 0Q3. O Q1Q2. O 0Q2. O Q1Q3 Question 42 Use the output data below to answer the question. Assume that all non-labor resources are fixed.
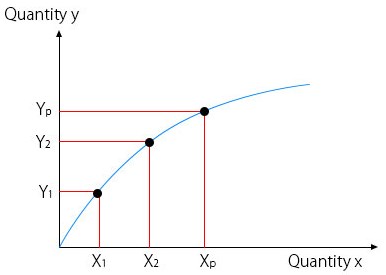
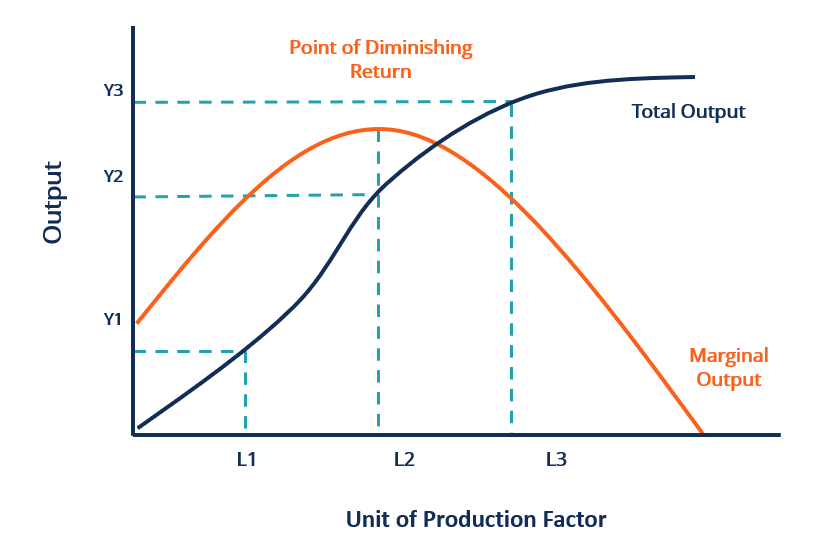
Factor of Production - Any input that generates a desired quantity of output. With regard to the law of diminishing returns, only one factor at a time is considered. Marginal Product - With every additional input, the increase in total product is referred to as the marginal product. In the graph above, Y 2-Y 1 is the marginal product.; Total Product - When an input is applied through a ...
In the diagram, the range of diminishing marginal returns is:.
Over this range marginal product is diminishing. 4. Finally, a point will be reached beyond which total output itself will actually fall, indicating a negative marginal product. In Fig. 13.4, this occurs for employment levels greater than 5.6. iii. The Average-Marginal Relationship: There is also a very close relation between MP L and AP L ...
Law of diminishing returns explains that when more and more units of a variable input are employed on a given quantity of fixed inputs, the total output may initially increase at increasing rate and then at a constant rate, but it will eventually increase at diminishing rates.
The law of diminishing marginal returns states: A) As the size of a plant increases, marginal product eventually decreases. B) As the size of a firm's plant increases, average cost eventually decreases. C) As a firm uses more of a variable factor of production, with a given quantity of the fixed factor of production, the marginal product of the variable factor eventually diminishes. D) …
MC When the marginal cost (MC) increases, it SRAC Q means the cost of producing one additional unit of the good becomes higher. The MC rises due to diminishing marginal returns. This is because if we are gaining less output from raw materials (factors of production e.g. labour), this means we need more of it to produce the next unit,
Define The Law of Diminishing Return. The law is also known as the law of increasing costs. It is one of the important laws of microeconomics. The law of diminishing return indicates that if the number of variable inputs is increased with some fixed inputs, the total output will first increase but then start to decline.
In the above diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is: A) 0Q3. B) 0Q2. C) Q1Q2. D) Q1Q3. A: D. Refer to the above data. When total product is increasing at an increasing rate, marginal product is: A) positive and increasing. ... diminishing marginal returns B) an increase in the wage rate C) a decrease in the wage rate D) increasing ...
The marginal product (MP) and average product (AP) initially increase and then decrease due to the operation of the Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns. As long as MP is higher than AP, AP increases. At the highest point of AP, i.e. when AP is at its maximum, MP is equal to AP. When MP becomes lesser than AP, AP also starts to fall.
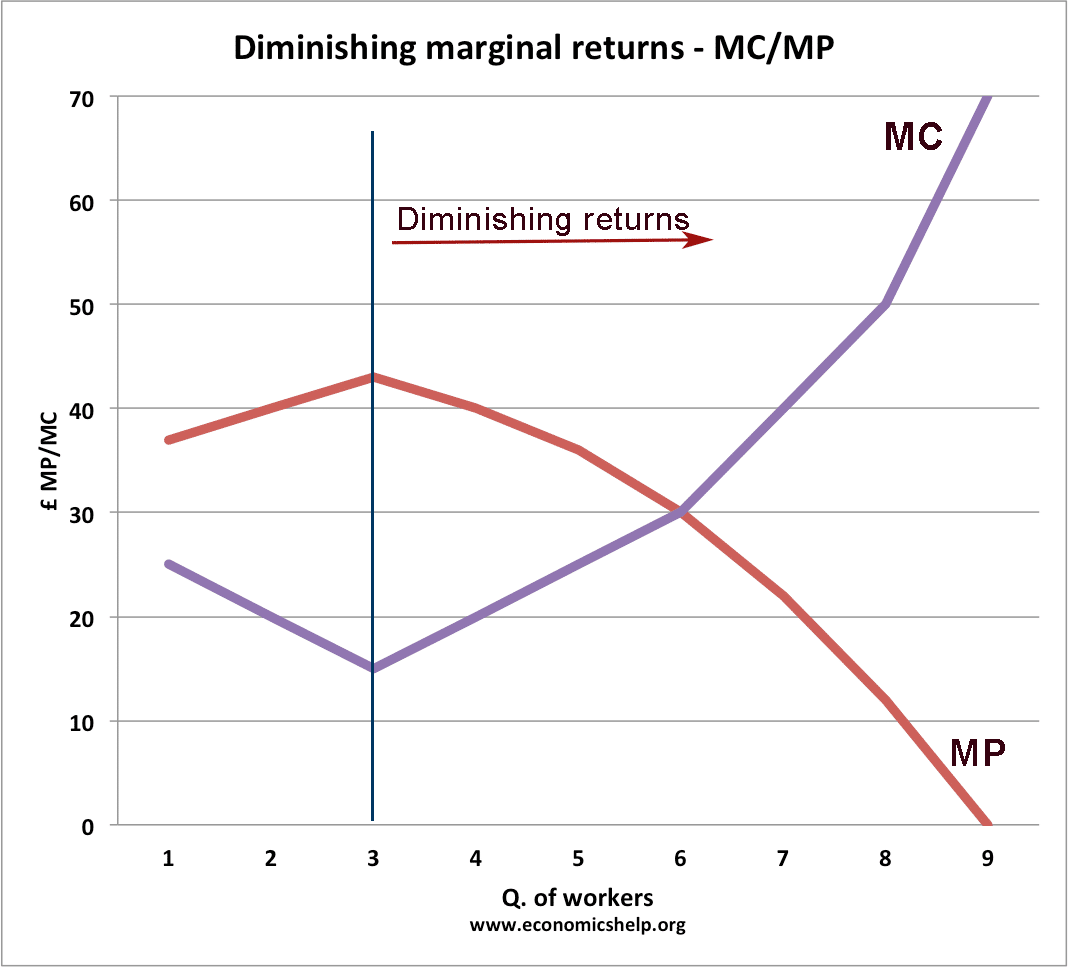
Diminishing Marginal Returns Diagram. As we can see from the diagram, at 3 workers, the gap between marginal profit and marginal cost is at its maximum. However, at 4 workers, the marginal cost of producing an additional unit starts to become more expensive. At this point, we start to see diminishing marginal returns.
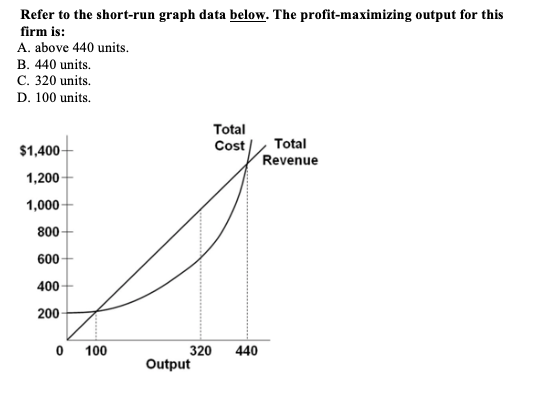
C. the law of diminishing returns determines the shape of the cost curve. D. marginal product first falls, but ultimately rises as output is increased. D. CH 8 #35 Refer to the above diagram. The profit-maximizing level of output for this firm: A. is at point a. B. is at point b. C. is at point c. D. cannot be determined from the information given. C. CH8 #29 In the above figure, curves 1, …
A the law of diminishing returns applies in the long run but not in the short run. Diagram of diminishing returns. In the above diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is. In the above diagram total product will be at a maximum at. Law of diminishing returns helps mangers to determine the optimum labor required to produce maximum output.
Law of diminishing returns (explained with diagram) law of diminishing returns explains that when more and more units of a variable input are employed on a given quantity of fixed inputs, the total output may initially increase at increasing rate and then at a constant rate, but it will eventually increase at diminishing rates. in other words.
Increasing returns mean lower costs per unit just as diminishing returns mean higher costs. Thus, the law f of increasing return signifies that cost per unit of the marginal or additional output falls with the expansion of an industry. As more and more units of the commodity are produced, the cost per unit goes on steadily falling.
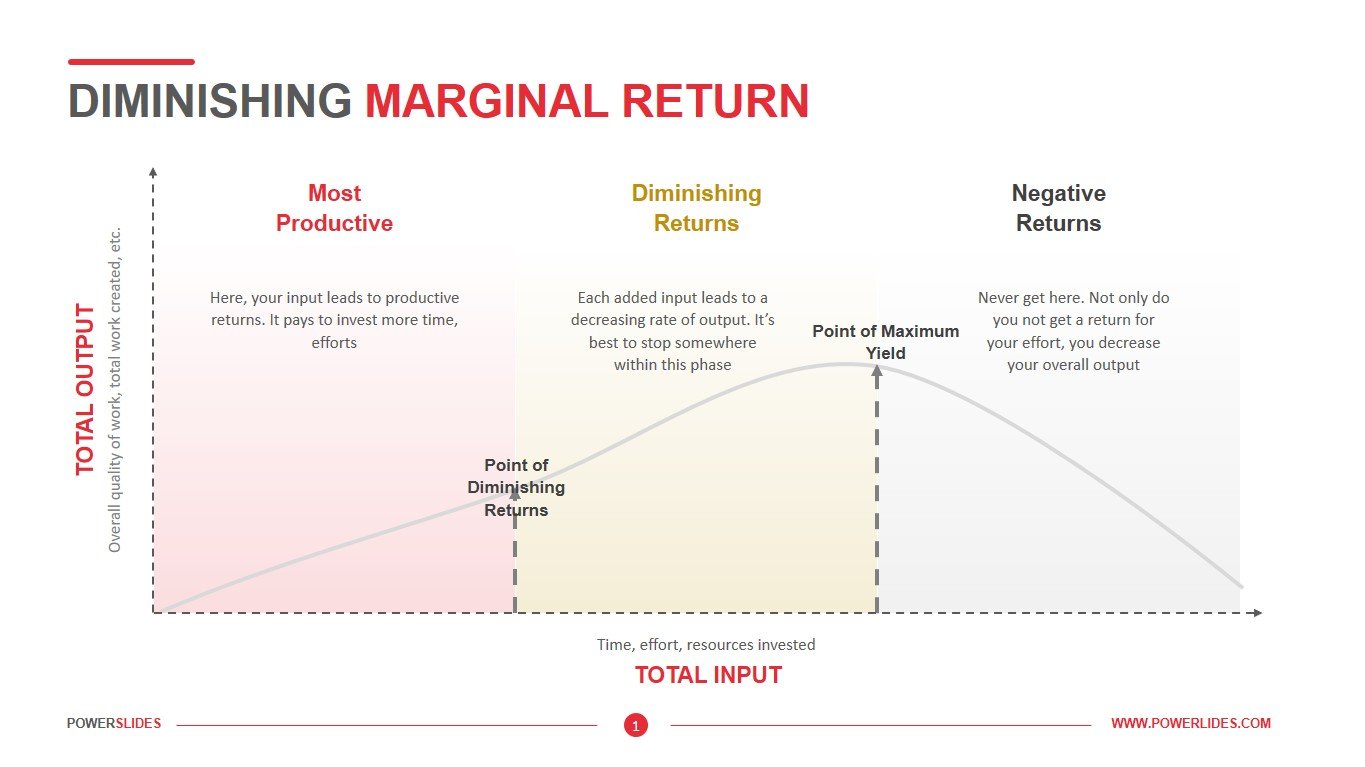
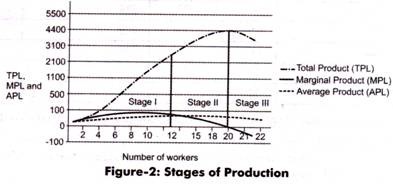
Economists recognize three distinct stages of production, which are defined by a concept known as the law of diminishing marginal returns. This law holds that as you add more workers to the production process, output will increase, but the size of that increase will get smaller with each worker you add.
According to the law of constant returns when a firm employs more and more factors, output increases at a constant rate. Therefore, the average cost curve as well as marginal cost curve remains parallel to horizontal axis. This can be made clear with the help of diagram 13. In the diagram 13 output has been measured on OX- axis while costs on ...
Q (1) Explain and illustrate with diagrams the differences between diminishing marginal returns and decreasing economies of scale and cite causes and examples. Ans. The law of diminishing returns is also called the law of variable proportion, as the proportions of each factor of production employed keep changing as more of one factor is added.
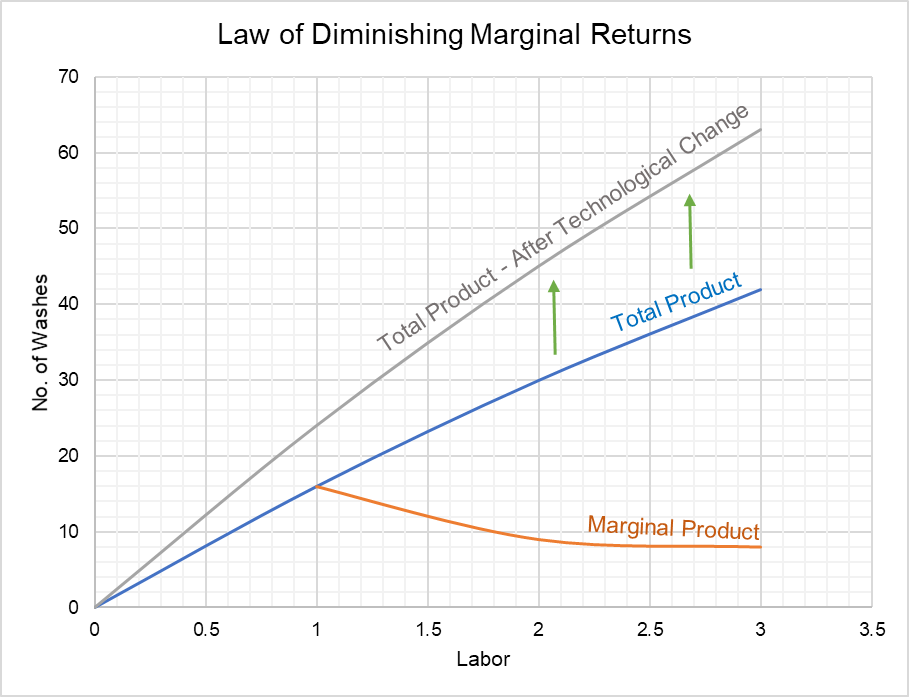
The law of diminishing marginal returns states that additional inputs will eventually lead to a negative impact on outputs. For it to be valid, some assumptions need to be made: All the technology involved is constant. Changing the technological tools used in production would change the marginal and average cost and value of a product.
When an additional unit of labor and capital is employed, the marginal productivity comes down from 10 tons to 8 tons and so on decreasing. This tendency of marginal productivity to decrease as successive units of variable factors are employed to fixed factor is called the law of diminishing returns. Diagram: Application:
Your diagram should have the same general characteristics as Figure 6-2 in the textbook. (c). MP is the slope ... Over the 0 to 4 range of output, the TVC and TC curves slope upward at a decreasing rate because of increasing marginal returns. The slopes of the curves then increase at an increasing rate as diminishing marginal returns occur.' (b) See the graph. AFC (= …
The law of diminishing marginal returns. As per economists, there are three stages of production. All of the stages are defined under the concept of diminishing marginal returns. This is not merely a concept but the law of diminishing marginal returns according to which during production process as input (capital, workers, etc.) is increased, output will also …
Answer (1 of 6): We know that a firm is at equilibrium when it produces such units of output that the Marginal Cost of producing the additional unit = Marginal Revenue that can be earned by its sale. > Equilibrium condition : MC = MR However, in …
Three stages of production and law of diminishing Download Now Download. Download to read offline. Economy & Finance. Sep. 05, 2015 57,486 views Economic stages Read more ... Law of diminishing returns Arun Roy. Theory of Production Cedrick Abadines. MelissaCamilo2 Dec. 4, 2021. AkashMaurya83 Nov. 30, 2020. ZibusisoMoyo2 ...
and illustrate with diagrams the differences between diminishing marginal returns and decreasing economies of scale and cite causes and examples. Ans. The law of diminishing returns is also called the law of variable proportion, as the proportions of each factor of production employed keep changing as more of one factor is added.
In the diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is. Micro econ ch12 25 terms. The above diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is. In the above diagram total product will be at a maximum at. In the above diagram total product will be at a maximum at.
20.12.2021 · Diminishing marginal returns. Log of educational materials fit the data better than its simpler, linear counterpart, consistent with the view that school inequality of educational materials operates through diminishing marginal returns (inefficient resource allocation)—thereby supporting H-2c. Log of hours spent in mathematics classes per ...
Law of Diminishing Returns (Explained With Diagram) Law of diminishing returns explains that when more and more units of a variable input are employed on a given quantity of fixed inputs, the total output may initially increase at increasing rate and then at a constant rate, but it will eventually increase at diminishing rates. In other words ...
Diminishing marginal returns primarily looks at changes in variable inputs and is therefore a short-term metric. Variable inputs are easier to change in a short time horizon when compared to fixed...
Diminishing marginal returns occur when each additional unit of a variable factor input (e.g. labour) is adding less to total output than the previous additional unit. This occurs due to over-utilisation of the fixed factor inputs (e.g. capital). Diminishing marginal returns set in when the fifth unit of labour is employed. Furthermore, the seventh unit of labour is actually redundant. …
In the diagram, the range of diminishing marginal returns is: D. Q1Q3. 3. In the diagram, total product will be at a maximum at: A. Q3 units of labor. 4. Use the following data to answer the question: Refer to the data. The average product (AP) when two units of labor are hired is:
As extra workers produce less, the MC increases. Diagram of diminishing returns In this example, after three workers, diminishing returns sets in. After employing 4 workers or more - the marginal product (MP) of the worker declines and the marginal cost (MC) starts to rise. Difference between diminishing returns and dis-economies of scale
Expert Answer Answer - Q1Q3 The whole range from Q1 to Q3 represents the diminishing marginal returns. At this range, it … View the full answer Transcribed image text: In the diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is. 0Q_3 0Q_2 Q_1Q_2 Q_1Q_3 Previous question Next question
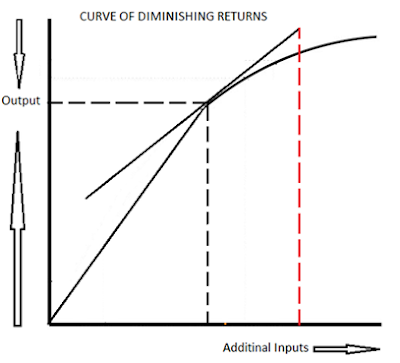
It is known as the point of diminishing returns. At such a point, the marginal output is maximized but will decrease if the units of a production factor continue to increase. As the diagram above shows, the point of diminishing return is at L2.
The law of increasing returns is the opposite of the legislation of decreasing returns. Wherein the legislation of diminishing return operates, every additional investment the capital and labour yields much less than proportionate returns. But, in the situation of the regulation of raising returns, the return is more than proportionate.
In the above diagram the range of diminishing marginal returns is: Q1Q3. In the above diagram, total product will be at a maximum at: Q3 units of labor. Refer to the above diagram. At output level Q total variable cost is: ... The above diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is. not 4.
/dotdash_Final_Law_of_Diminishing_Marginal_Productivity_Oct_2020-01-d3c30a9c6ba442b9bccc7b99158251e3.jpg)
/dotdash_Final_Law_of_Diminishing_Marginal_Productivity_Oct_2020-01-d3c30a9c6ba442b9bccc7b99158251e3.jpg)








0 Response to "40 in the diagram, the range of diminishing marginal returns is:"
Post a Comment