38 uniform circular motion free body diagram
S4P-1-21 Draw free-body diagrams of an object moving in uniform circular motion. S4P-1-22 Experiment to determine the mathematical relationship between period and frequency and one or more of the following: centripetal force, mass, and radius.
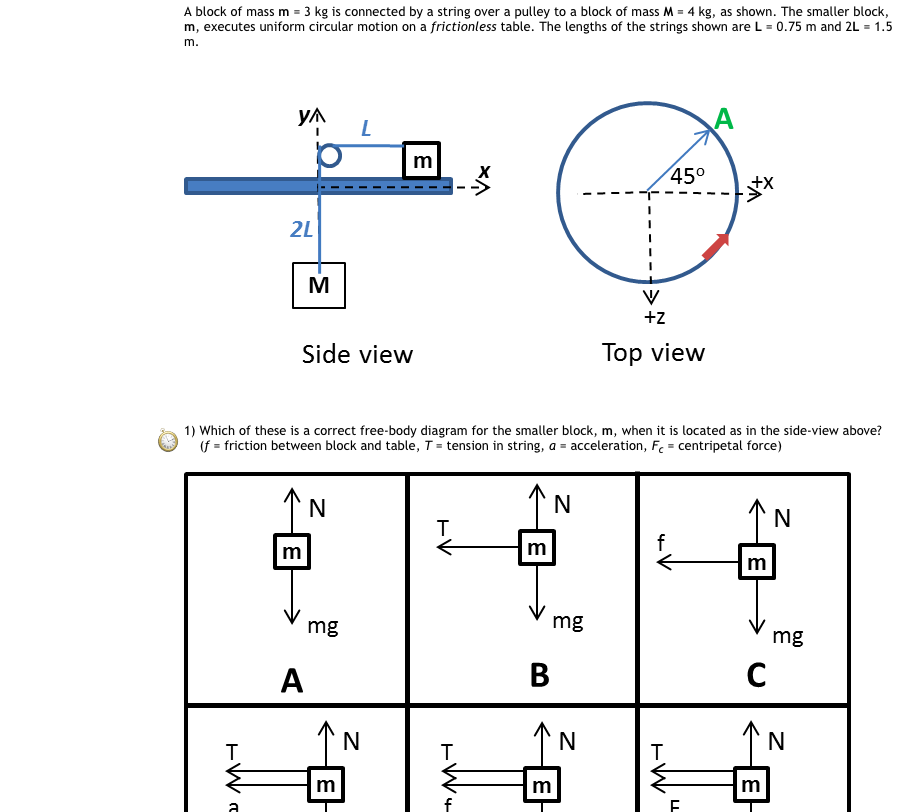
A conical pendulum consists of an object moving in uniform circular motion at ... A free-body diagram of the object is shown in Figure 2. represents the tension in the string and the gravitational force on the object is where m is the object's mass and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
The actual question is easy to solve using uniform circular motion equations (and has nothing to do with my question). ... In the free-body diagram below, what is the balancing force in the question mark? centripetal-force. Share. Cite. Improve this question. Follow edited May 6 '17 at 15:00. blackened. asked May 6 '17 at 13:56.
Uniform circular motion free body diagram
http://www.physicseh.com/Free simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website.
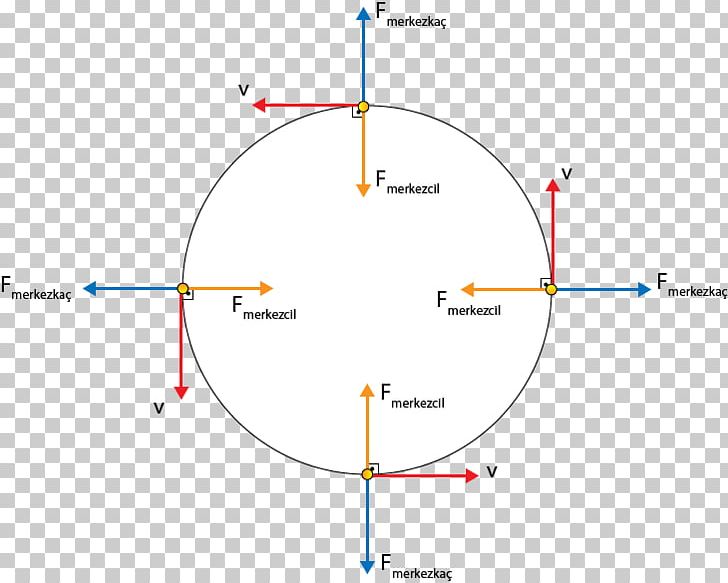
you should be able to maintain uniform circular motion. Figure 3a shows the free body diagram for the rotating bob in uniform circular motion. The weight of the mass is balanced by the tension in the suspending string. The centripetal force is provided by the tension in the spring attaching the bob to the shaft.
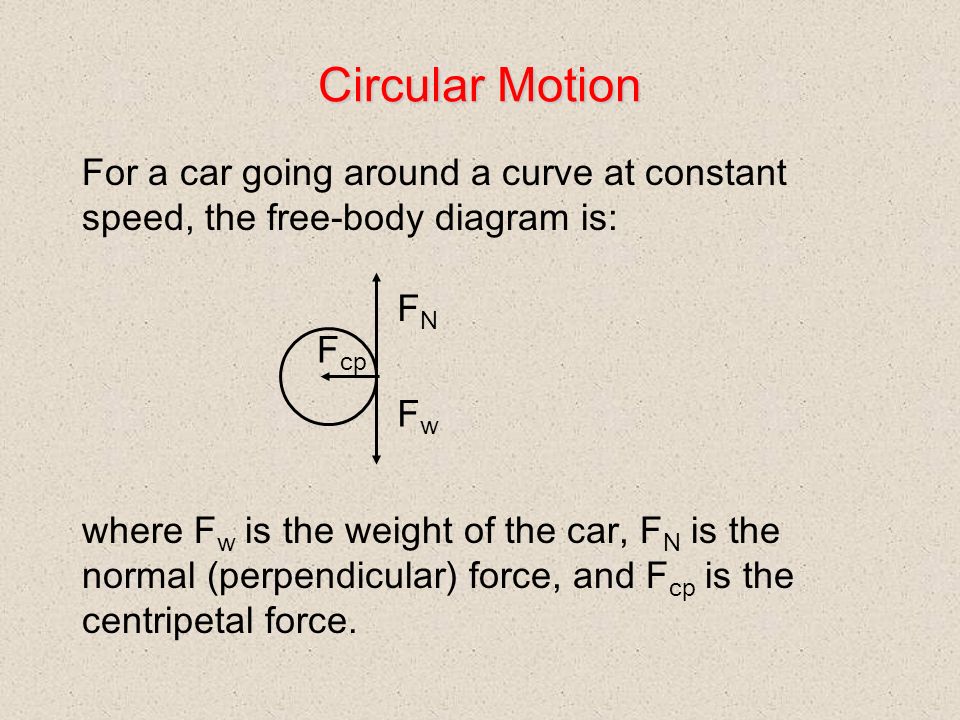
Solution: The free-body diagram below (side view) shows all forces acting on the car. (a) Centripetal acceleration is found by the following formula \[a_c=\frac{v^2}{r}=\frac ... Uniform circular motion is an example that shows the acceleration and velocity are not always in the same direction. ...
Uniform circular motion free body diagram.
The concept of uniform circular motion means that the speed of the object moving in the circle is constant. There are many examples of uniform circular motion. A car moving on a curve at 50 miles per hour, a child on a merry-go- ... The figure below shows a free body diagram of the forces acting on Ozobot while in uniform circular motion. Since ...
Check your understanding of free-body diagrams for uniform circular motion in this set of free practice questions aligned to AP Physics I standards. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
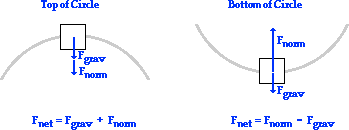
An object in uniform circular motion has constant speed, v, centripetal acceleration, a c ... Draw a free body diagram showing all the forces acting on the rotating penny e) What is the minimum coefficient of static friction required to keep the penny from sliding off the ... Force Diagram for top Force Diagram for bottom Note that at the top ...
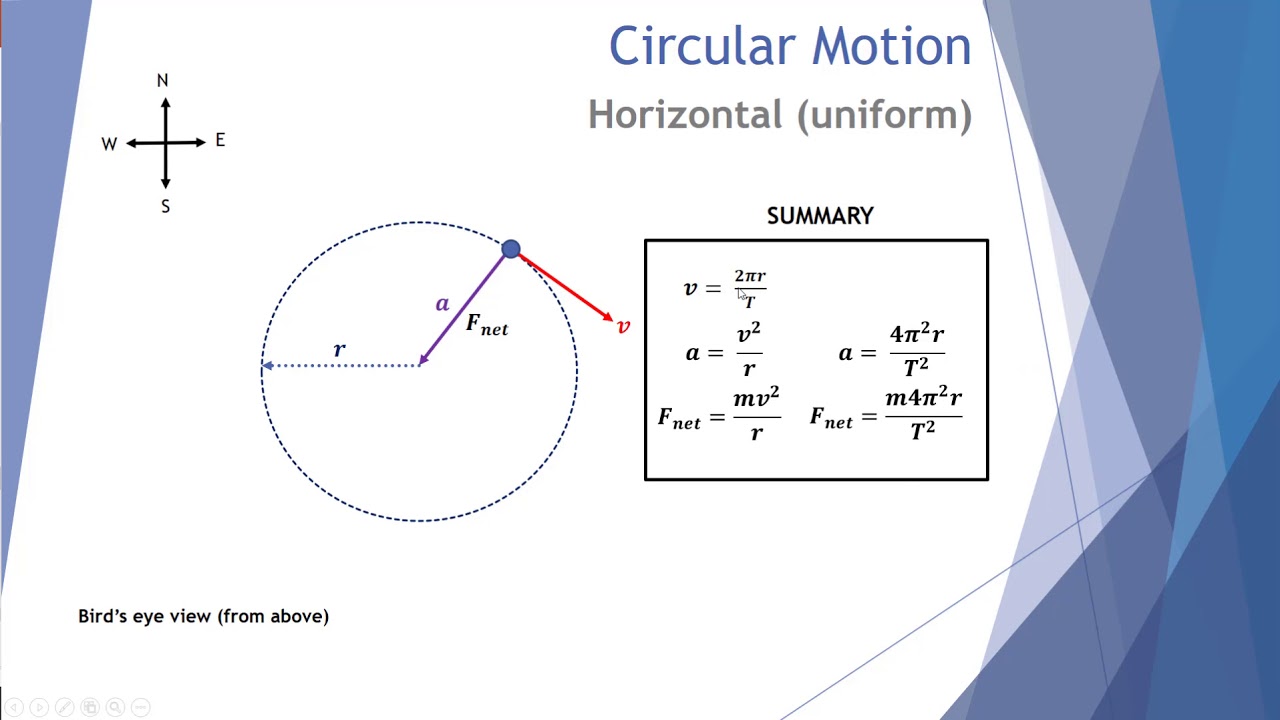
Uniform circular motion. Review: An object moving in a circle of radius r with constant speed v is accelerating. The direction of its velocity vector is changing all the time, but the magnitude of the velocity vector stays constant. ... A free- body diagram of the car is shown. The only forces acting on the car moving with constant speed are ...
The Forces and Free-Body Diagrams in Circular Motion Concept Builder is an adjustable-size file that displays nicely on smart phones, on tablets such as the iPad, on Chromebooks, and on laptops and desktops. ... It is called Uniform Circular Motion. When combined with the accompanying activity sheet, it makes for an excellent activity to help ...
The complete free-body diagram, in Figure 5.15, also shows an upward force of friction opposing the force of gravity. This force of friction is static friction because there is no relative motion between the person and the wall. Key ideas for circular motion: In uniform circular motion, there is a net force directed toward the center of the circle.
So if a particle is moving in a uniform circular motion: 1) Its speed is constant. 2) Velocity is changing at every instant. 3) There is no tangential acceleration. 4) Radial (centripetal) acceleration = ω2r. 5) v=ωr.
Circular Motion Free Body Diagram - Coefficient Friction The Ratio Between The Force Necessary To. circular motion in physics uniform circular motion describes the motion of a body traversing a circular path at constant speed since the body describes circular motion. Mechanics of Solids S S Bhavikatti Pages 51 100 Text Version.
Uniform circular motion is ... the free-body diagram. The centripetal acceleration has to be provided by some other force (tension, friction, normal force) in order for circular motion to occur. 10
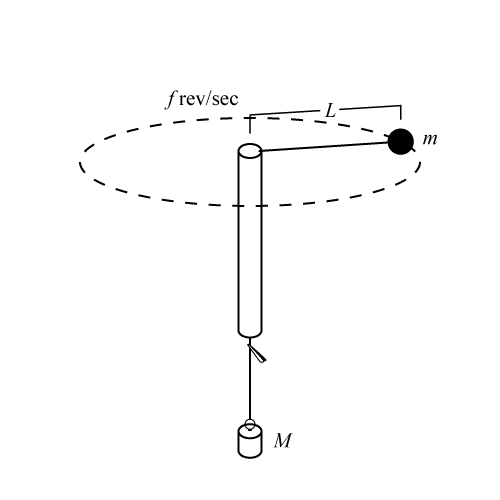
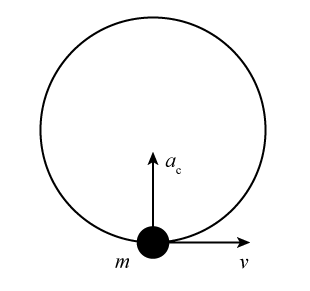
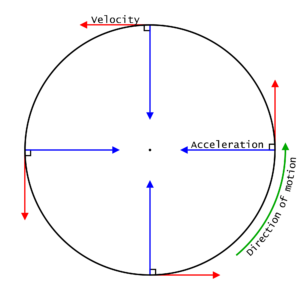
Uniform Circular Motion Figure 1: The diagram here shows the directions of the velocity and acceleration of an object in ccw uniform circular motion. At all times the velocity is tangent to the circle and the acceleration ... Make a free body diagram for the stationary bob, i.e. when the spring and weight hanger over the pulley are attached ...
very powerful statement, for an object to be in uniform circular motion there must be a very ... Let's draw the free-body diagram for an example such as this, specifically the swinging bucket. rope g r v a a parallel a perpendicular F T. There are two forces on the bucket, gravity and the tension due to the rope. We can resolve these
Uniform Circular Motion For an object to move along a curved path, the direction of its velocity must change. A change in velocity means that there must be an acceleration that is not in the same direction as the velocity. ... Circular motion free body diagrams can be shown in different ways. One way is to show a view of the rotation from a ...
Uniform circular motion. 9-29-99 Sections 5.1 - 5.2 ... In this case, the free-body diagram has three forces, the force of gravity, the normal force, and a frictional force. The friction here is static friction, because even though the objects are moving, they are not moving relative to the turntable. ...
Uniform Circular Motion Free Body Diagrams Thread starter archelon; Start date Feb 8, 2012; Feb 8, 2012 #1 archelon. 1 0. Homework Statement A circular-motion addict of mass 82.0 kg rides a Ferris wheel around in a vertical circle of radius 14.0 m at a constant speed of 7.10 m/s. (a) What is the period of the motion?
Uniform circular motion is the motion of an object traveling at a constant speed on a circular path. r ... Draw a free-body diagram and apply Newton's Second Law. r. Driving on a hilly road. As you drive at relatively high speed . v. over the top of a hill curved in an arc of radius . r
https://www.positivephysics.org/
Acceleration in Uniform Circular Motion v 1 v 2 ... On a piece of paper, draw a Free Body Diagram (FBD) for the car. The net force on the car is f W F N A. Zero B. Pointing radially inward C. Pointing radially outward F Net = ma = mv2/R R . Physics 101: Lecture 8, Pg 7 ACT
The kinematics of uniform circular motion were introduced in Sections 4.4- 4.5, and a review is highly recommended. ... The free-body diagram, drawn from behind the car, shows the static friction pointing toward the center of the circle. Slide 8-48
Uniform Circular Motion (free-body diagram) Thread starter Joshuarr; Start date May 16, 2012; May 16, 2012 #1 Joshuarr. 23 1. Homework Statement Curved portions of highways are always banked (tilted) to prevent cars from sliding off the highway. When a highway is dry, the frictional force between the tires and the road surface may be enough to ...
As we saw in Chapter 4, "uniform circular motion" is defined to be motion along a circle with constant speed. This may be a good time to review Section 4.4 for the kinematics of motion along a circle. ... A free-body diagram for the forces on the car is shown in Figure 6.3.9, along with the acceleration (which is in the radial direction, ...
Uniform Circular Motion (Cont.) The question of an outward . outward force can be resolved by asking what happens when the string breaks! When central force is removed, ball continues in straight line. v. Ball moves tangent to ... Free-body Diagram n mg ...
Forces and Free-Body Diagrams in Circular Motion. The Forces in Circles Concept Builder provides learners with the challenge of identifying the free-body diagrams for situations involving the motion of objects in circles. Learners are presented with a short verbal description of an object's motion. They toggle through a set of free-body ...
Imagine the colored rectangles above depict a roller coaster at different points during a loop, red being the top, orange the right, green the left, and yellow the bottom. Let's practice with free-body diagrams for uniform circular motion by drawing one for each position of the roller coaster.













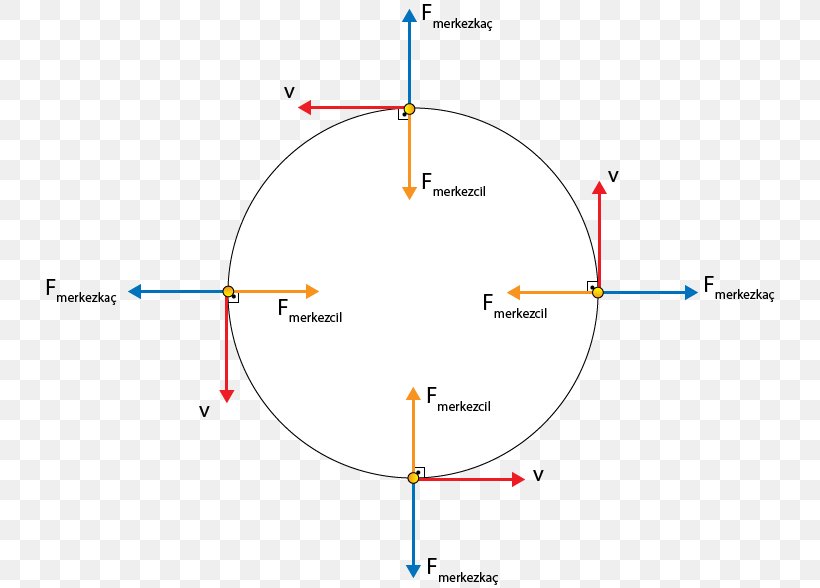

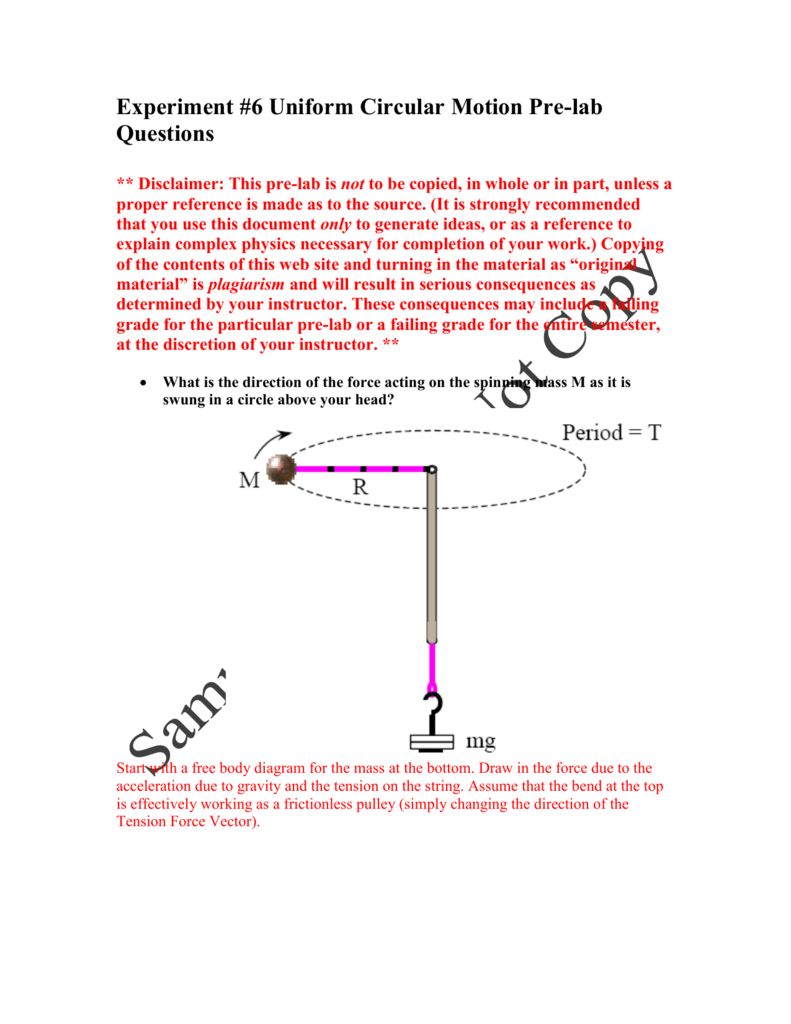
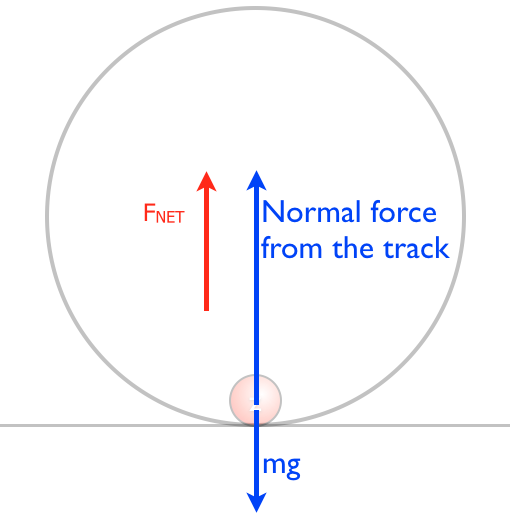




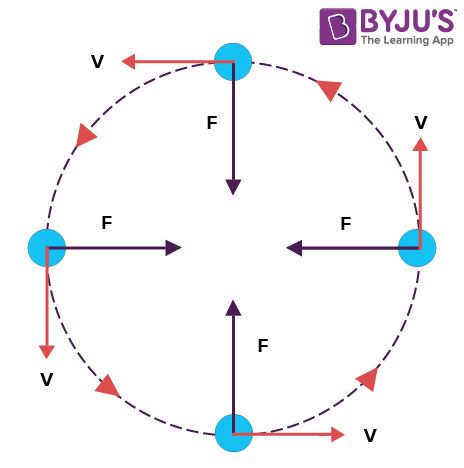

0 Response to "38 uniform circular motion free body diagram"
Post a Comment