38 plant cell cytoskeleton diagram
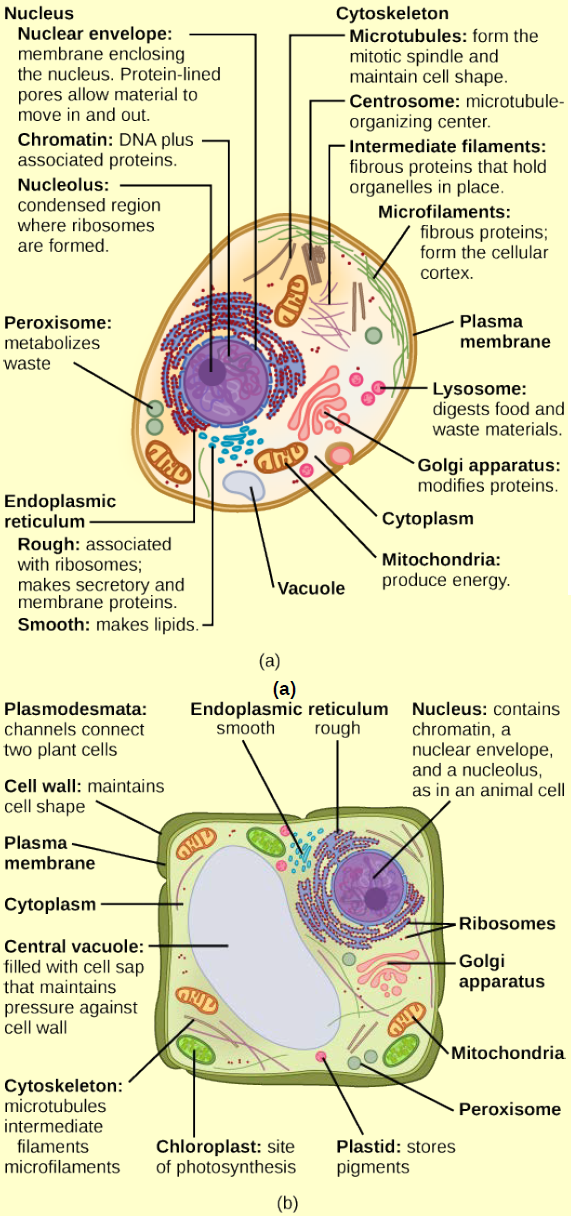
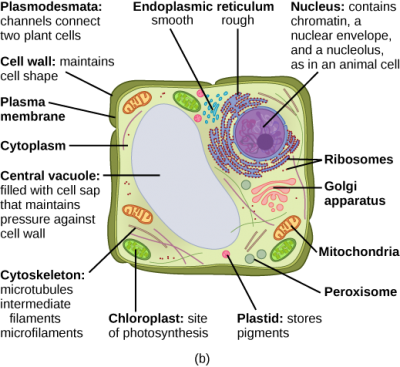
The cytoskeleton extends throughout the cell's cytoplasmand directs a number of important functions. 1. It helps the cell maintain its shape and gives support to the cell. 2. A variety of cellular organellesare held in place by the cytoskeleton. 3. It assists in the formation of vacuoles. 4. The cytoskeleton is not a static structure but is able to disassemble and reassemble its parts in order to enable internal and overall cell mobility. Types of intracellular movement supported by the cytoskeleton include transportation of vesicles into and out of a cell, chromosome manipulation during mitosis and meiosis, and organelle migration. 5. The cytoskeleton makes cell migration possible as cell motility is needed for tissue construction and repair, cytokinesis (the division of the cytoplasm) in the formation of daughter cells, and in immune cell responses to germs. 6. The cytoskeleton assists in the transportation of communication signals between cells. 7. It forms cellular appendage-lik... by D Takemoto · 2004 · Cited by 203 — A, Accumulation of cytoplasm in an Arabidopsis epidermal cell around the ... Diagrammatic representation of the organization of the plant cytoskeleton ...
The cytoskeleton organizes other constituents of the cell, maintains the ... In plant cells, much of the cell wall material passes through the Golgi as well ...

Plant cell cytoskeleton diagram
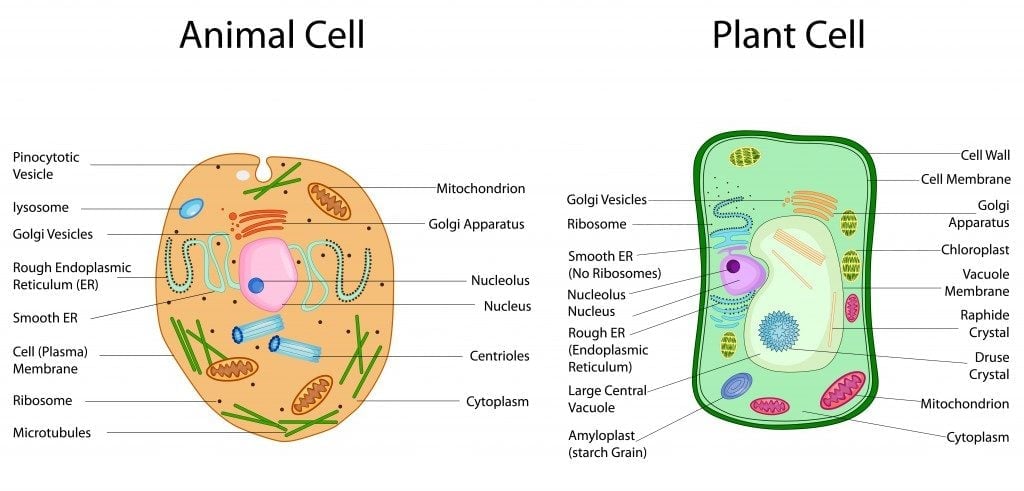
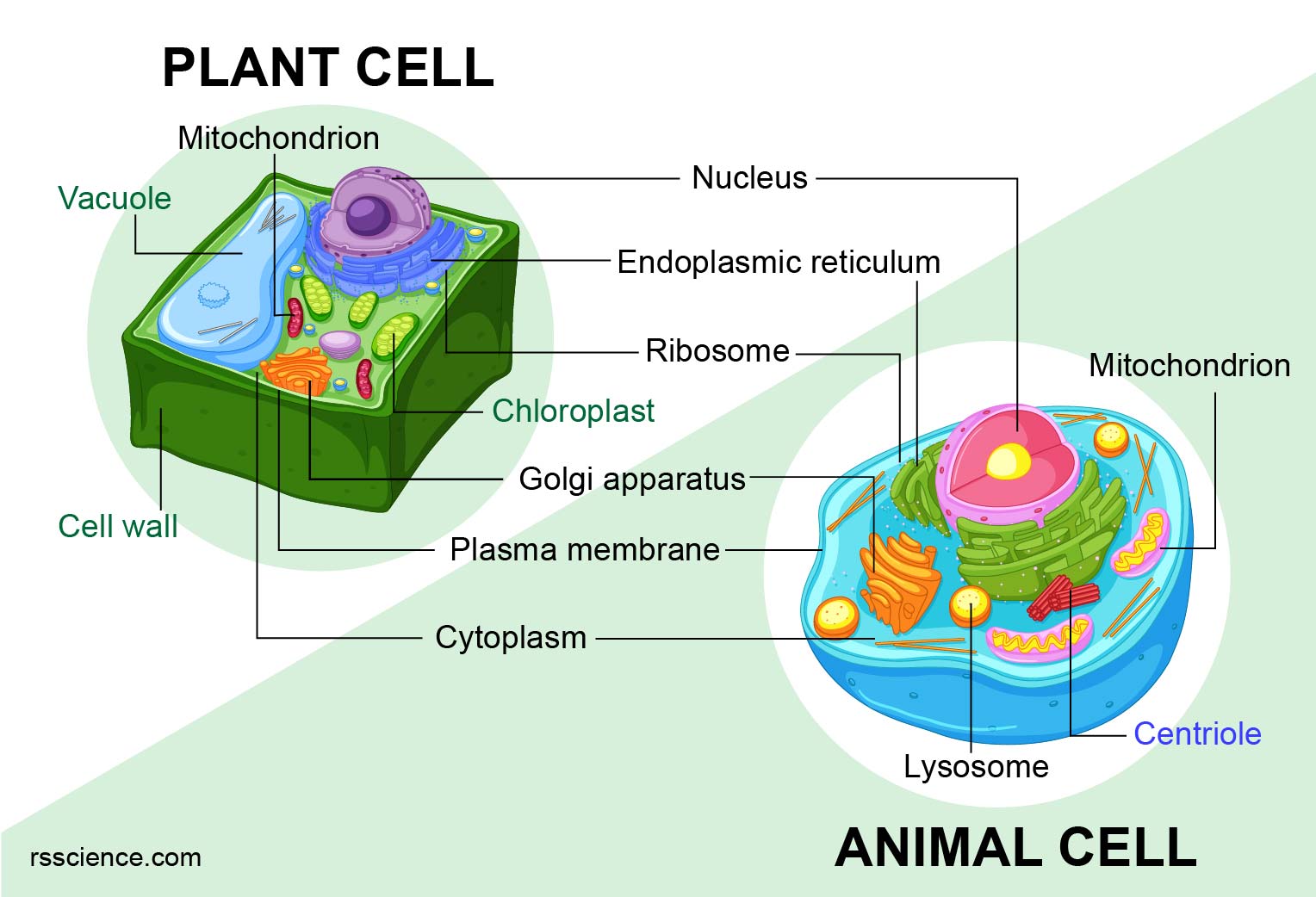
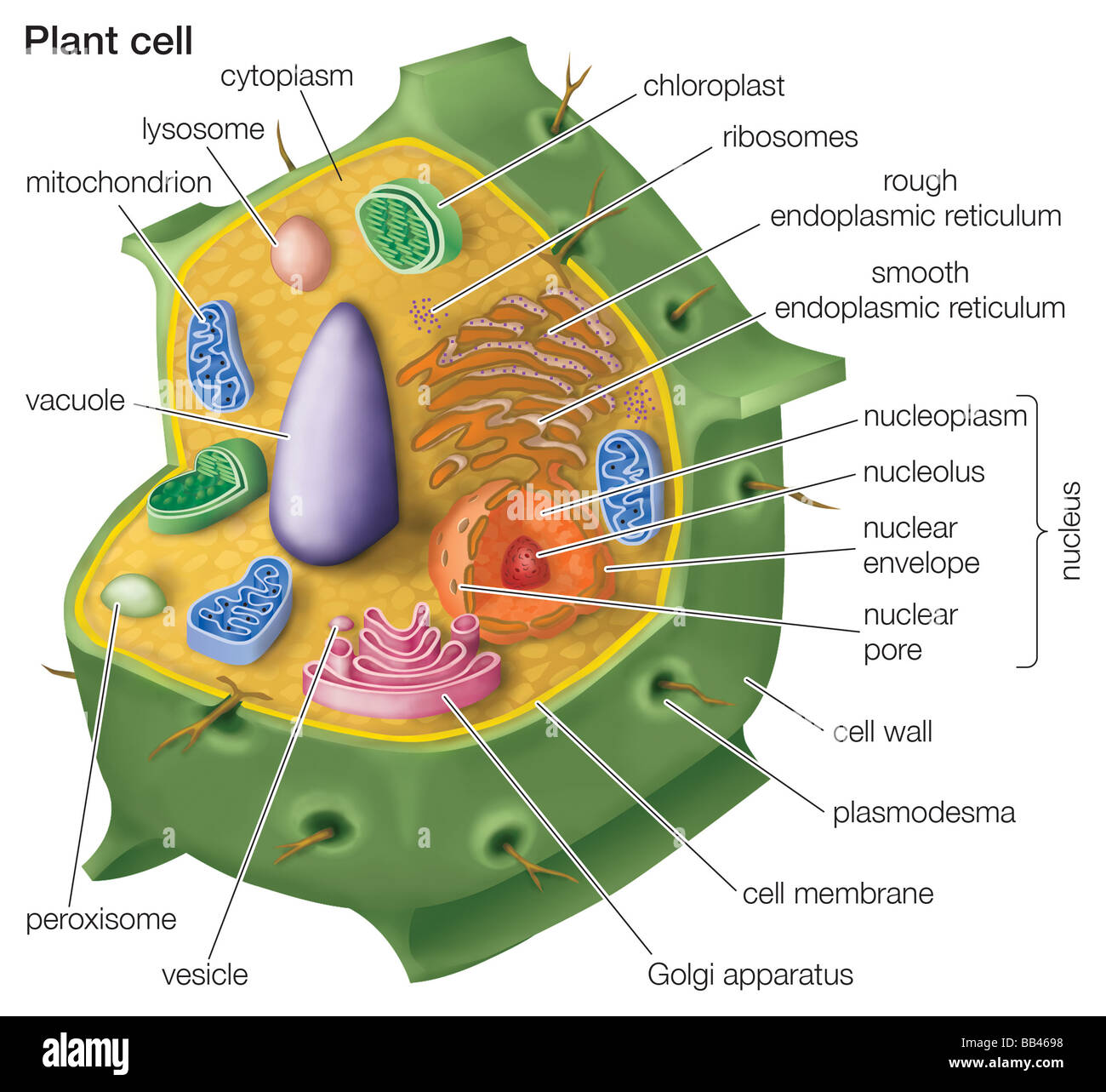
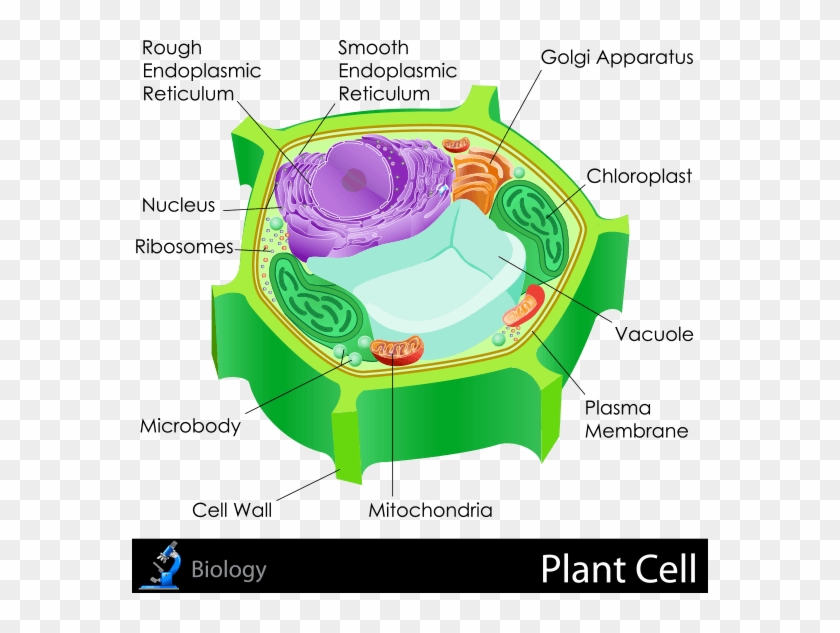
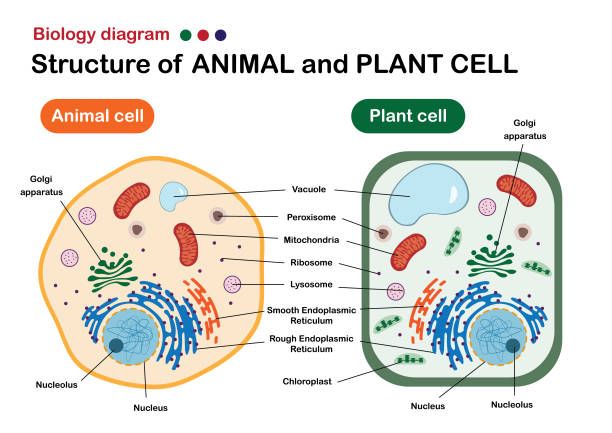
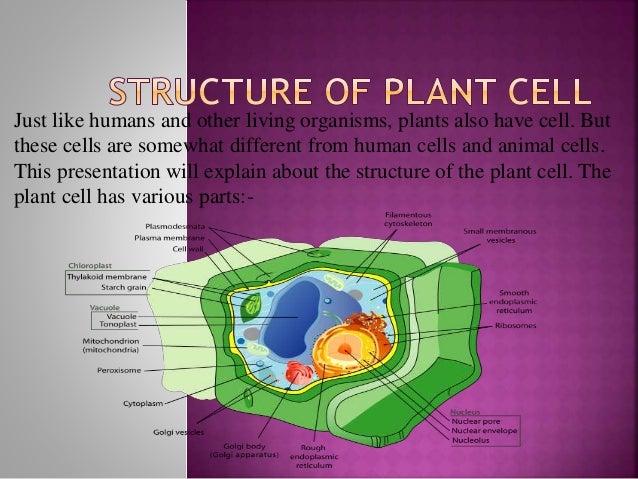
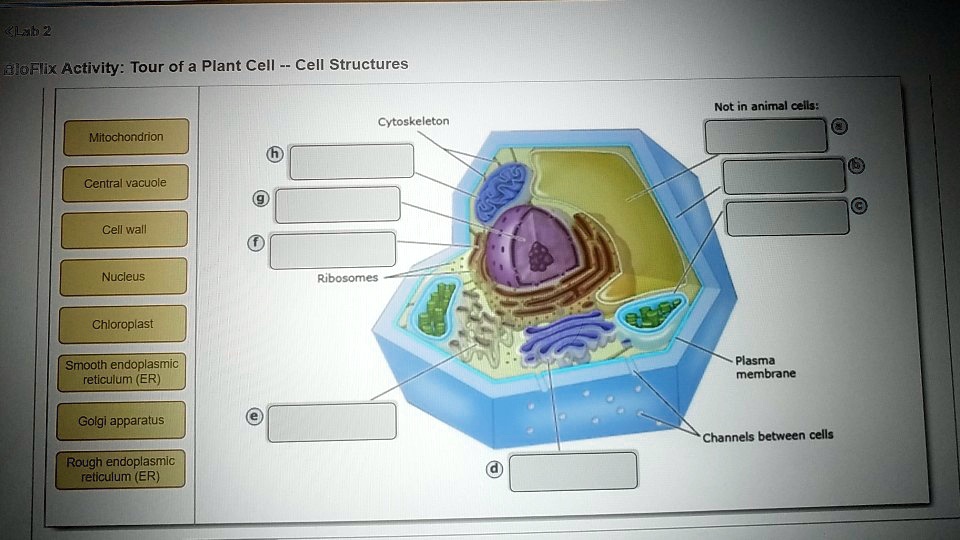
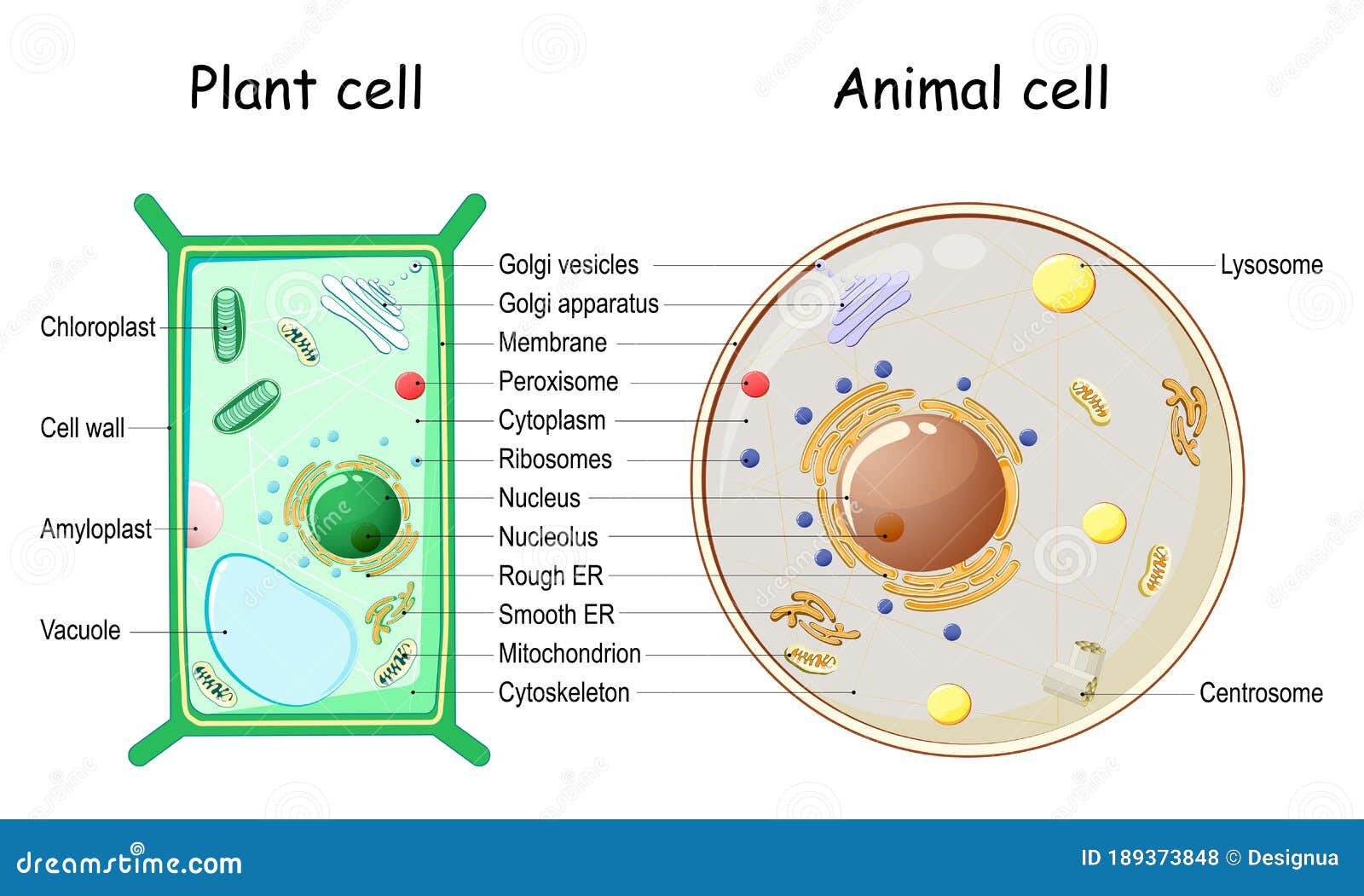
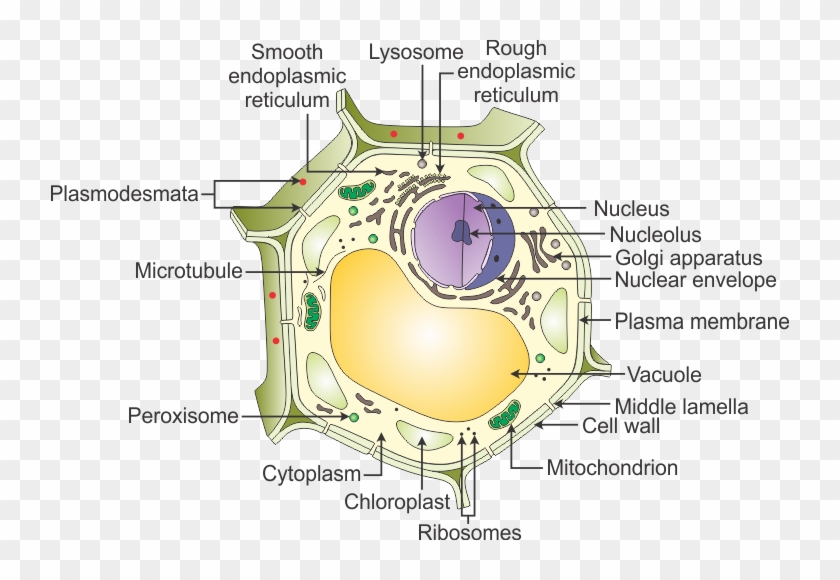
24 Aug 2020 — In these diagrams, the g–tubulin-containing nucleation complex is shown as a purple ... Actin dynamics in the cortical array of plant cells. cytoplasm cytoskeleton Parts of a plant cell: cell wall – provides rigid structure and protection; made of cellulose (dark green) cell membrane – surrounds the internal cell parts; controls passage of materials in and out of the cell cytoplasm – everything inside of the cell membrane except for the nucleus (light green) Microtubules, microfilaments (actin filaments), and intermediate filaments. ... Cells with their centrosome removed can still divide, and plant cells, ...
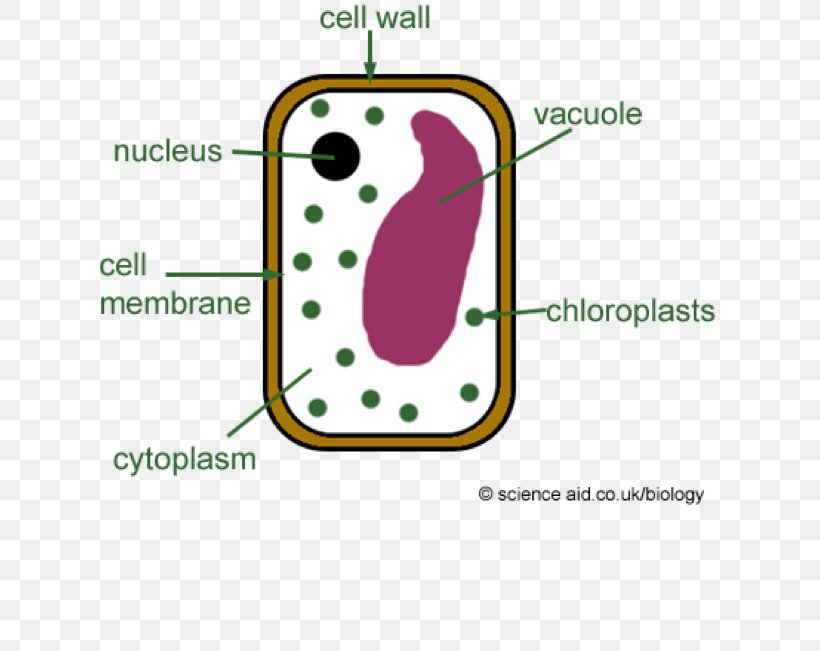
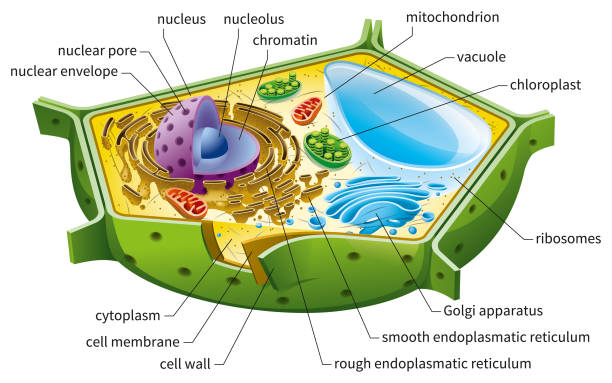
Plant cell cytoskeleton diagram. synthesis of the cell wall in plants. In addition to the roles described above, Stuart Hameroff and Roger Penrose have proposed that microtubules function in ...Prokaryotic cytoskeleton · Microfilament · Intermediate filament · Microtubule 28 Apr 2017 — Plants, animals, fungi, and protists have eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are less complex, with no true nucleus or organelles except ... In Figure 3.8 b, the diagram of a plant cell, you see a structure external to the plasma membrane called the cell wall. The cell wall is a rigid covering ... ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about Cytoskeleton:- 1. Meaning of Cytoskeleton 2. Components of Cytoskeleton. Meaning of Cytoskeleton: Earlier idea of cell was that it was a collection of some cell organelles suspended in cell sap. But with the advancement of microscopic techniques and the discovery of electron microscopy the idea of cell […]
Plant cytoskeleton — This strength is entrenched within the highly concentrated matrix of water and glycoproteins. Plant cytoskeleton. Cytoskeleton Diagram.Plant cytoskeleton · Mitochondria of the plant cell · Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of... Jan 13, 2021 · Plant Cell Diagram Cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton gives cells structure and shape and allows them to move around. It's also important for intracellular transport.. A bacteria diagram in actual fact helps us to learn more approximately this single cell organisms that have neither membrane-bounded nucleolus or organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts. Actin filaments are also involved in cytokinesis and cell movement (Figure 3). A four-part schematic shows cell structures that are supported by actin filaments ... Cytoskeleton Diagram. This diagram of the cytoskeleton of a cell is a simple representation of the way the microtubules and microfilaments of the cytoskeleton form a three-dimensional network that extends throughout the cytoplasm within the cell membrane.
The cytoskeleton is a complex network of fibers that supports the interior of a cell. Cross-linked by molecular connectors into systems that support cellular membranes, it holds internal structures, such as the nucleus, in place and controls various kinds of cell movement. Virtually all eukaryotic cells, including plant cells, have a cytoskeleton. Cytoskeletal systems extend internally from the membrane covering the cell surface to the surface of the membrane system surrounding the cell’s ... Microtubules, microfilaments (actin filaments), and intermediate filaments. ... Cells with their centrosome removed can still divide, and plant cells, ... cytoplasm cytoskeleton Parts of a plant cell: cell wall – provides rigid structure and protection; made of cellulose (dark green) cell membrane – surrounds the internal cell parts; controls passage of materials in and out of the cell cytoplasm – everything inside of the cell membrane except for the nucleus (light green) 24 Aug 2020 — In these diagrams, the g–tubulin-containing nucleation complex is shown as a purple ... Actin dynamics in the cortical array of plant cells.
/animal-cells-vs-plant-cells-373375_final-5b462d7fc9e77c00375014f1.png)














0 Response to "38 plant cell cytoskeleton diagram"
Post a Comment