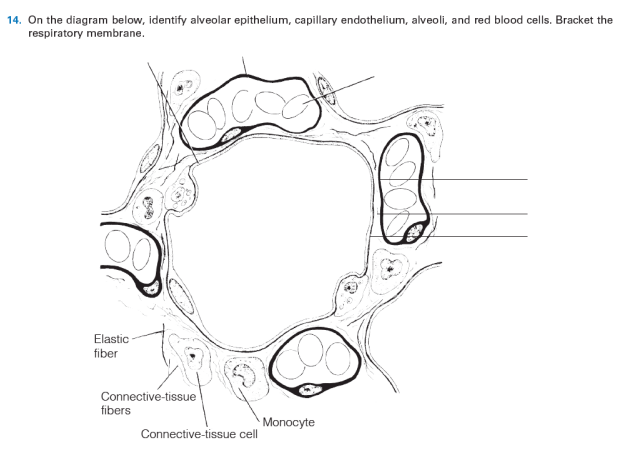
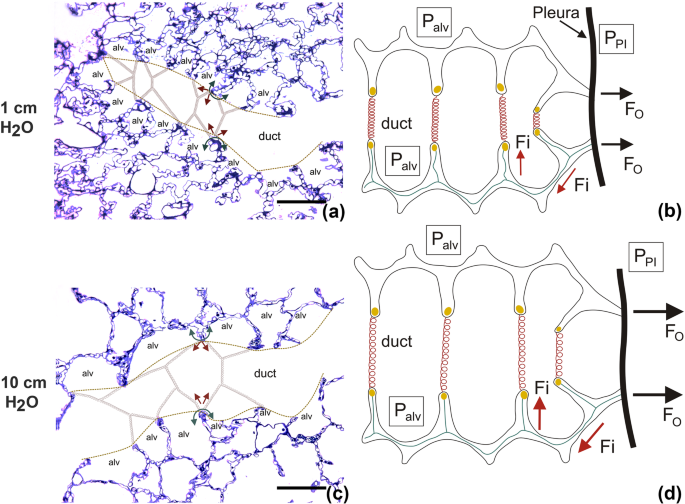
35 on the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium
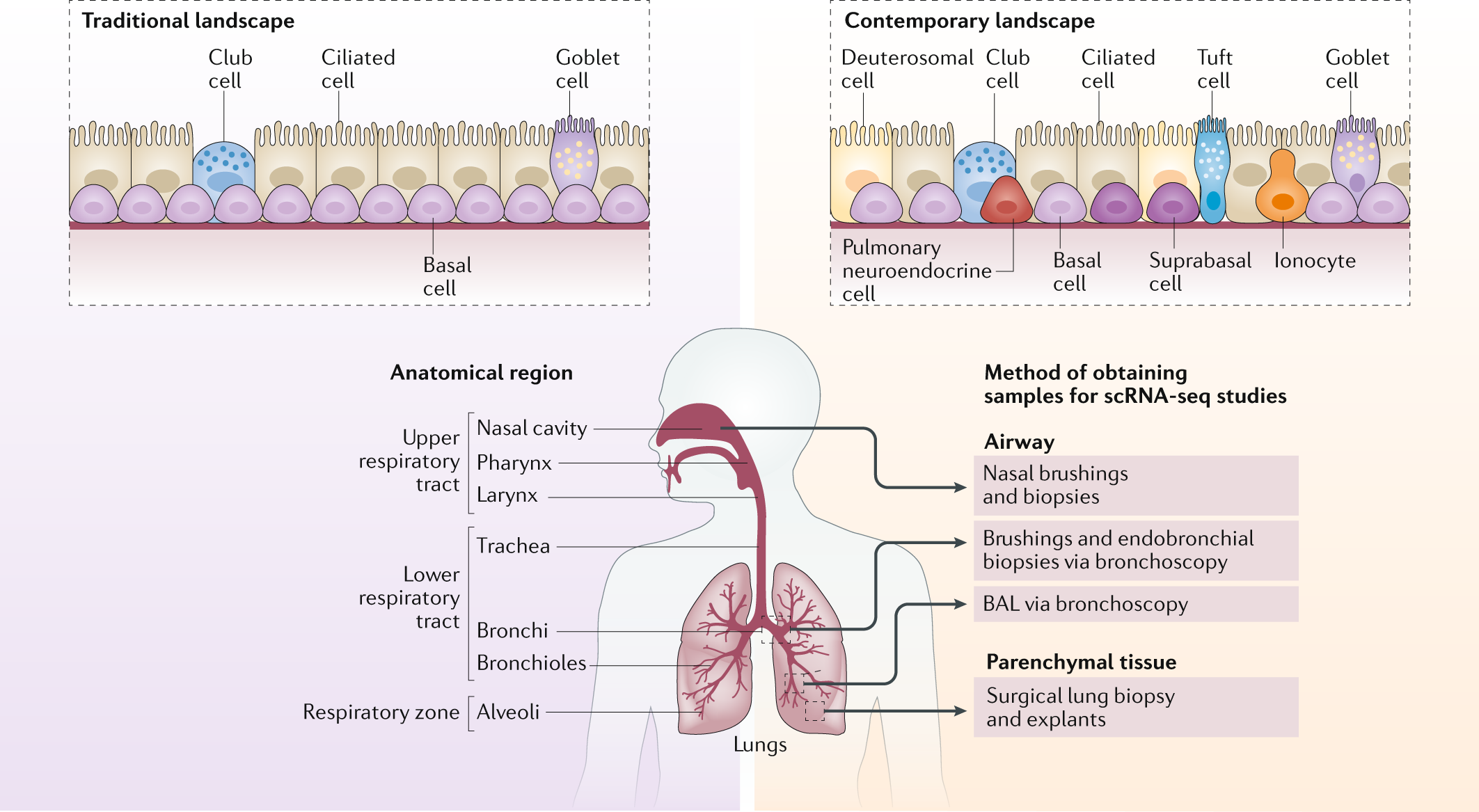
T The nasal cavity is lined by ciliated epithelium and mucous glands. The mucous glands secrete mucous. The ciliated epithelium is present on the entire lining of larynx, trachea, bronchi and bronchioles. The constant motion of cilia and mucous trap dust, micro-organisms, pollen and other minute particles present in the air. villi structure diagram. by. May 30, 2021. The normal structure of the inner surface of the small intestine lining is composed of undulating wavy projections called villi that help increase the surface area of the intestine for effective absorption of nutrients. The purpose of both structures is to increase the small intestine's surface area ...
Writing a BAL Report. Updated: Oct 31. For this piece, I thought I would chat about one of the very first cyto's I completed - a BAL prep. Bronchioalveolar lavage fluids are a great place to start as a clin path newbie. In short, we are looking for inflammation and bugs; far less often do we see neoplastic cells.

On the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium
The human body is made in different tissues and cells which are tasked with performing various functions. Do you think you know enough about where these tissues are found within the body when asked about them in a diagram? One of the ways that you can test yourself is by taking this histology lab exam toughest trivia quiz and see well you do—all the best as you tackle it. The bronchioles are lined by simple columnar to the cuboidal epithelium, and the alveoli possess a lining of thin squamous epithelium that allows for gas exchange. Structure There are four main histological layers within the respiratory system: respiratory mucosa, which includes epithelium and supporting lamina propria, submucosa, cartilage and ... Identify the components of head and neck structures on a diagram. Chapter 14: Periodontium: Cementum, Alveolar Process, and the Periodontal Ligament. Define and pronounce the key terms in this chapter. Give an overview of periodontium properties, including its components. Identify each individual component of the periodontium on a diagram.
On the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium. Using co-localization tools, the number of apoptotic epithelial-positive cells (Caspase-3 + NucView405 +) that are also PBMC cell tracker negative (GFP −) was quantified and setting different object sizes for alveolar epithelial cells (~900-3000 pixels) and PBMCs (~200-600 pixels) in the ICY image analysis software. This image analysis ... Simple epithelium can be divided into 4 major classes, depending on the shapes of constituent cells. The cells found in this epithelium type are flat and thin, making simple squamous epithelium ideal for lining areas where passive diffusion of gases occur.Areas where it can be found include: skin, capillary walls, glomeruli, pericardial lining, pleural lining, peritoneal cavity lining, and ... Epithelium is one of only 4 types of human body tissues.Like all types, it is formed by cells within an extracellular matrix (ECM). The cells in this tissue are tightly packed within a thin ECM. Forming sheets that cover the internal and external body surfaces (surface epithelium) and secreting organs (glandular epithelium). Functions of epithelial tissue are secretion, protection, absorption ... Pleural effusion pathophysiology diagram. 08-10-2014 · Nursing Care Plan for Premature Babies - These days we want to discuss the article with the title health Nursing Care Plan for Premature Babies we hope you get what you're looking for. We are here trying to make the best possible to provide information on this blog.
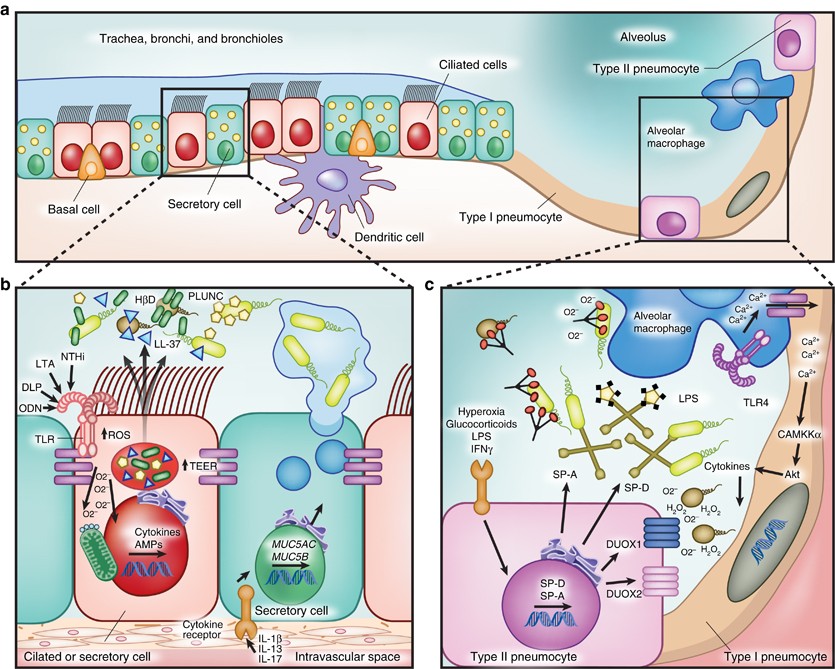
Here are wiring diagram s for Ford Escort, F-series, Fiesta, Focus, Mustang, Ranger, Kuga and Many other's. Download. Ford F-250 2002 Electrical Wiring Diagram s PDF.pdf. 5.8Mb. The left rear brake line on 4x4 4w-disc has blown a pinhole due to corrosion. The hard line ties into a splitter fitting on the rear axle. The external nose is visible and is pyramidal in shape, with the root located in the upper region and the base located in the lower region. The variance in shape depends on the shape of the ethmoid bone which is an anterior cranial bone located between the eyes. The internal nose is divided into the left and right nasal cavities by the nasal ... This is the term used to describe the tree-like structure of passageways that brings air into the lungs. The walls of the alveoli are very thin. This lets oxygen and CO2 pass easily between the alveoli and capillaries, which are very small blood vessels. One cubic millimeter of lung tissue contains around 170 alveoli. Here, we identify a regulatory pathway that controls alveolar progenitor differentiation and lactation by governing Notch activation in mouse. Loss of Robo1 in the mammary gland epithelium activates Notch signaling, which expands the alveolar progenitor cell population at the expense of alveolar differentiation, resulting in compromised lactation.
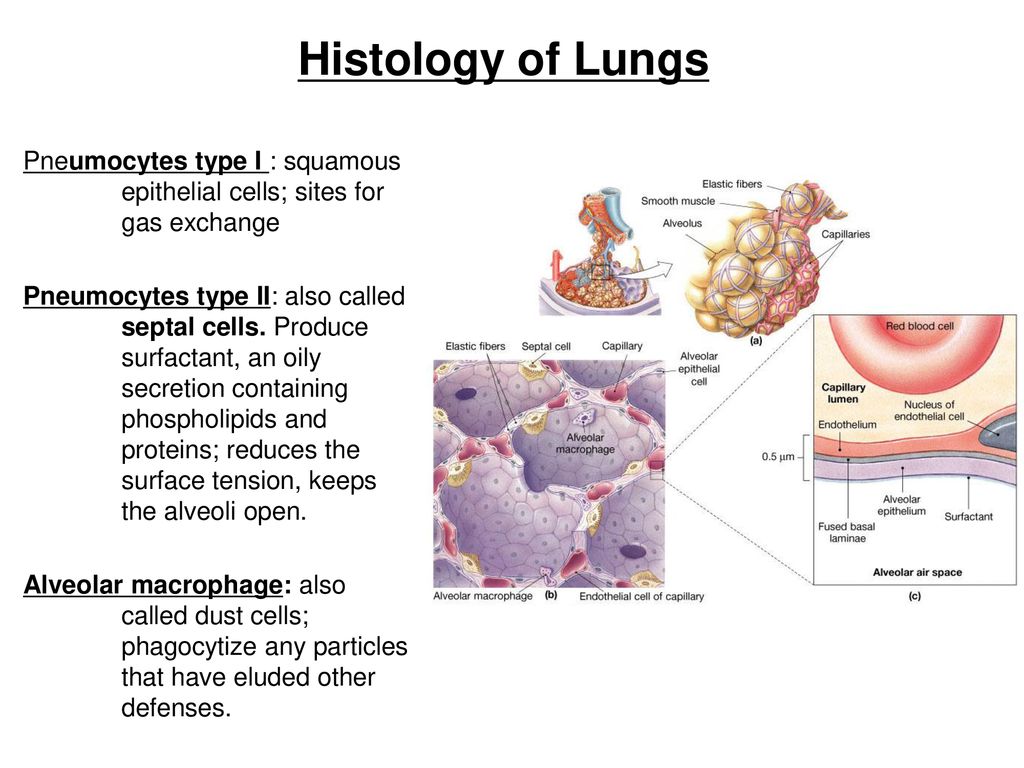
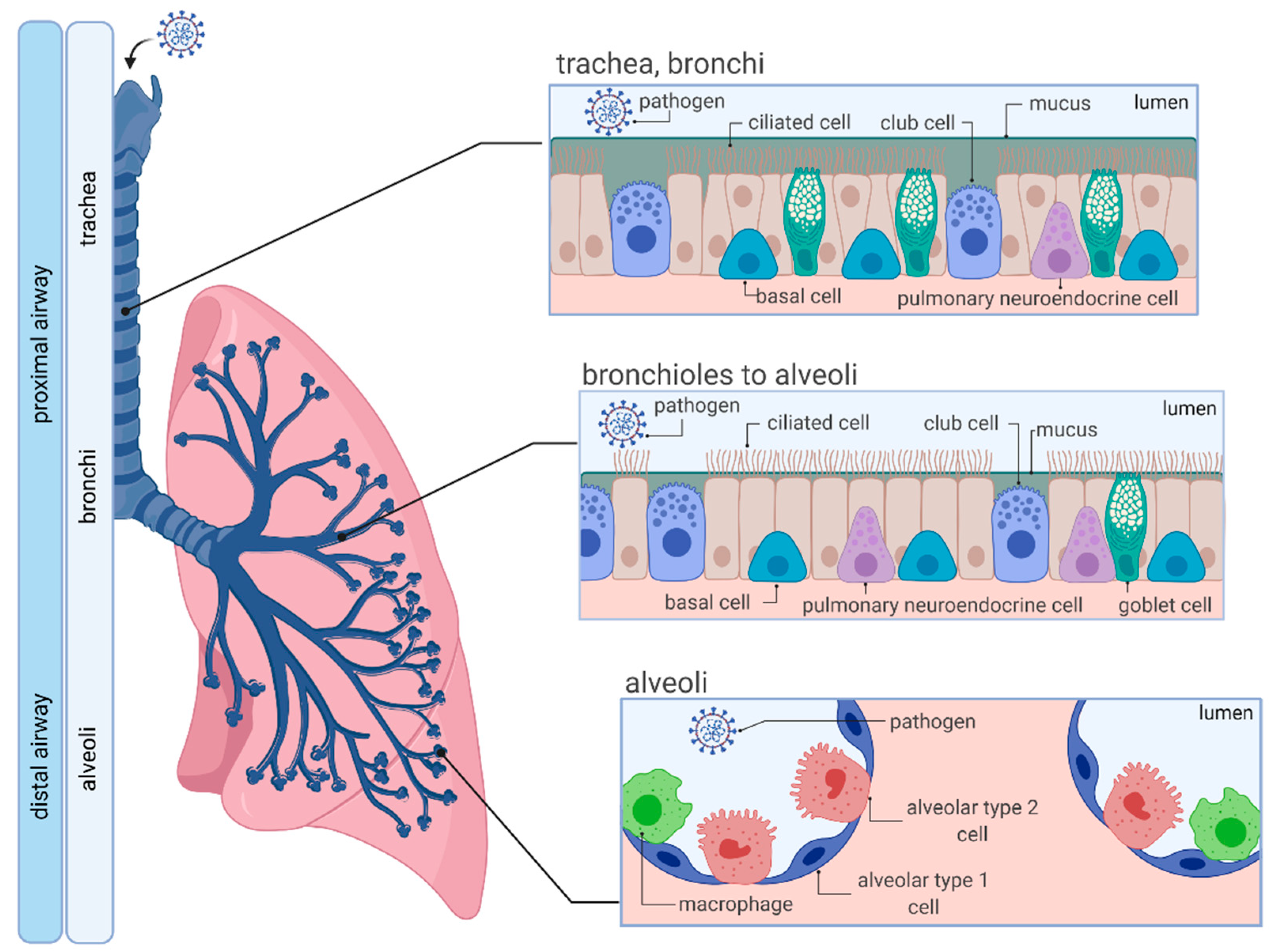
The intraalveolar septa are the partition of two adjacent alveoli. They consists of two thin squamous epithelium layer. Mucosa layer of alveoli. Alveolar duct and alveolar sac lined by the patches of simple cuboidal epithelium. But alveolus is lined by simple squamous epithelium. These simple epithelium of alveoli contain the three major cells ... Anatomy. A bronchus, which is also known as a main or primary bronchus, represents the airway in the respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs.Bronchi will branch into smaller tubes that become bronchioles.. The trachea (windpipe) is found inferior to the thyroid cartilage and superior to division into the left and right main bronchus. The trachea divides into the left and right main ... The respiratory tract has two major divisions: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract. The organs in each division are shown in Figure 16.2. 2. In addition to these organs, certain muscles of the thorax (the body cavity that fills the chest) are also involved in respiration by enabling breathing. The alveolar wall or septum is made up of three tissue components: surface epithelium, supporting tissue, and an extensive network of continuous capillaries. Centrally it has capillaries surrounded by a vibrant network of elastin, reticular, and collagen fibers with a layer of squamous epithelial of two adjacent alveoli on either side.
Checks and balances diagram. 27 Feb 2015 — Each branch has powers that it can use to check and balance the ... Be prepared to present your graphic organizer and explain your diagram. 6 Jan 2021 — Checks and Balance chart is a type of diagram used for showing the domestic political system of a nation. The type of chart has been used ...
39 White Rodgers Type 91 Relay Wiring Diagram; 35 On The Diagram Below Identify Alveolar Epithelium; 39 Baseball Field Diagram Fillable; 37 Polaris Predator 500 Carburetor Diagram; 35 Airxcel Thermostat Wiring Diagram; 40 Light Reactions Of Photosynthesis Diagram; 38 Ruger Sr22 Parts Diagram; 39 Eukaryotes Vs Prokaryotes Venn Diagram
Primary human alveolar epithelial cells (hAECs) were populated on the surfaces of the sacs to form the monolayer epithelium. The alveolar lung model was further subjected to cyclic inhalation/exhalation movements, as well as used to investigate the effects of cigarette smoke and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2 ...
Review Sheet 23 Anatomy Respiratory Review Sheet 23 On the diagram below, identify alveolar epithelium, capillary endo the lium, alveoli, and red blood cells. Bracket the respiratory membrane. VÉeu É Elastic fiber O st W C on nective-tissue fibers I M on ocyte C on nective-tissue cell Why does oxygen move from the.
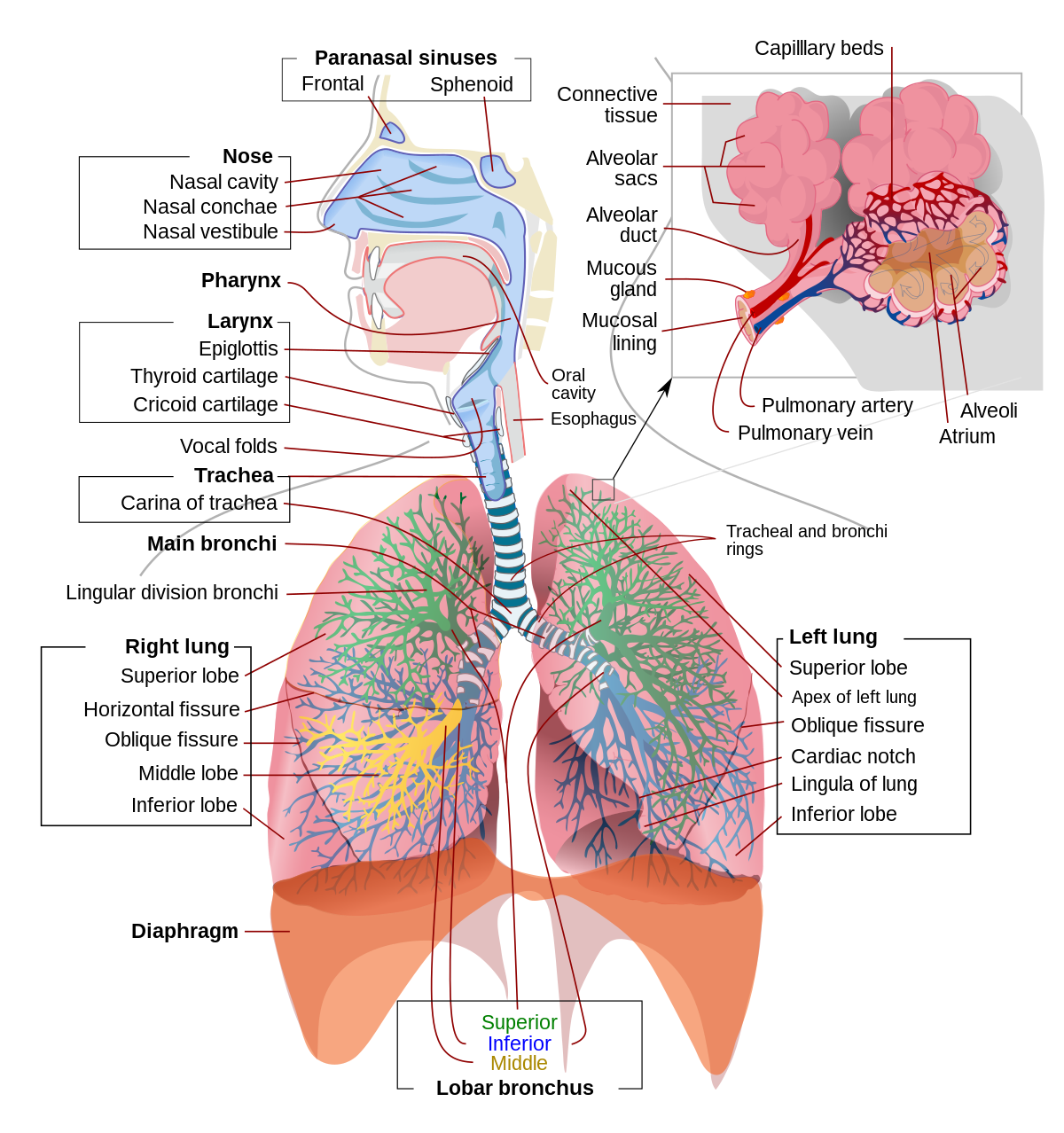
Respiratory system (Systema respiratorum) The respiratory system, also called the pulmonary system, consists of several organs that function as a whole to oxygenate the body through the process of respiration (breathing).This process involves inhaling air and conducting it to the lungs where gas exchange occurs, in which oxygen is extracted from the air, and carbon dioxide expelled from the body.
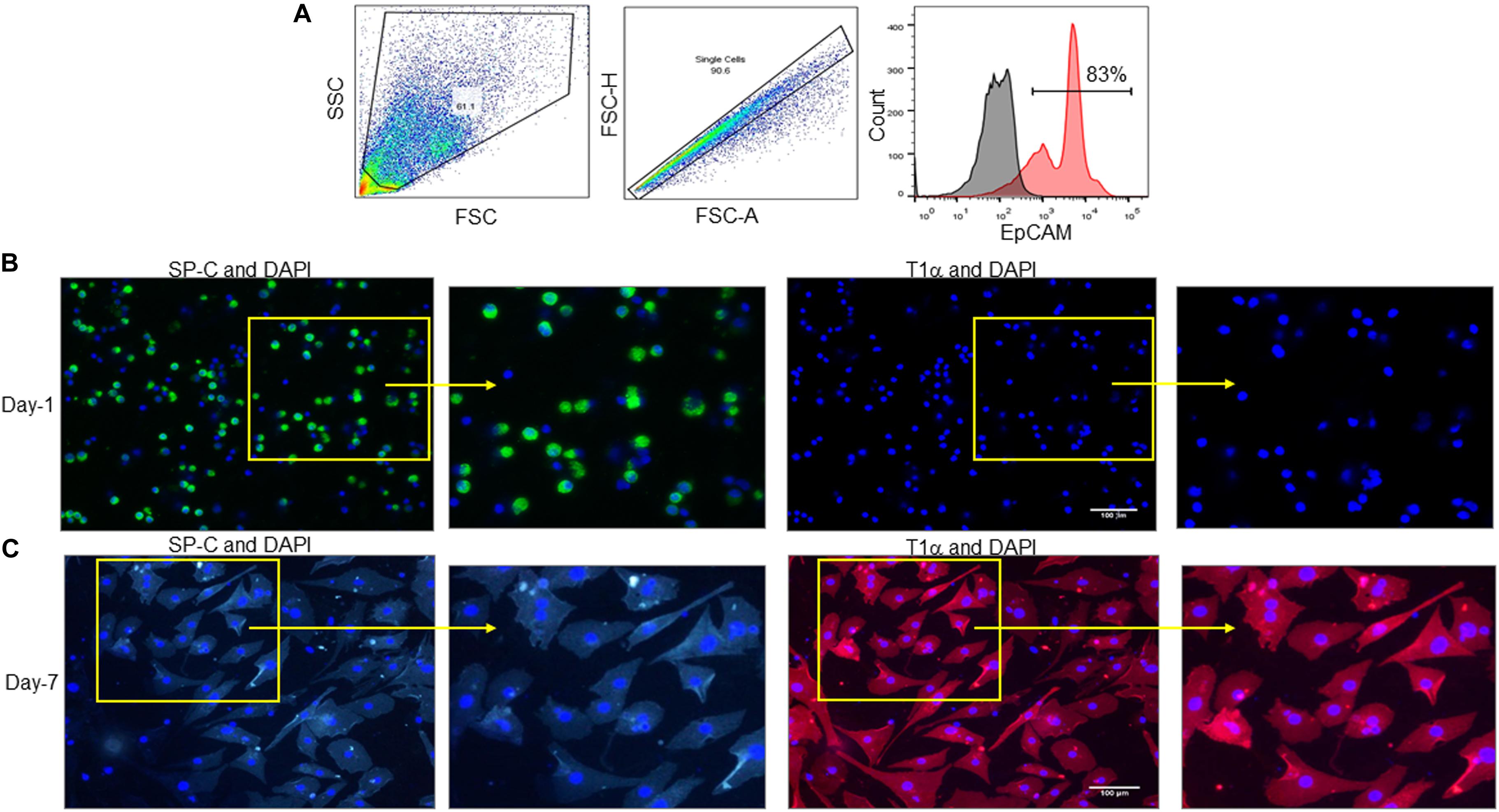
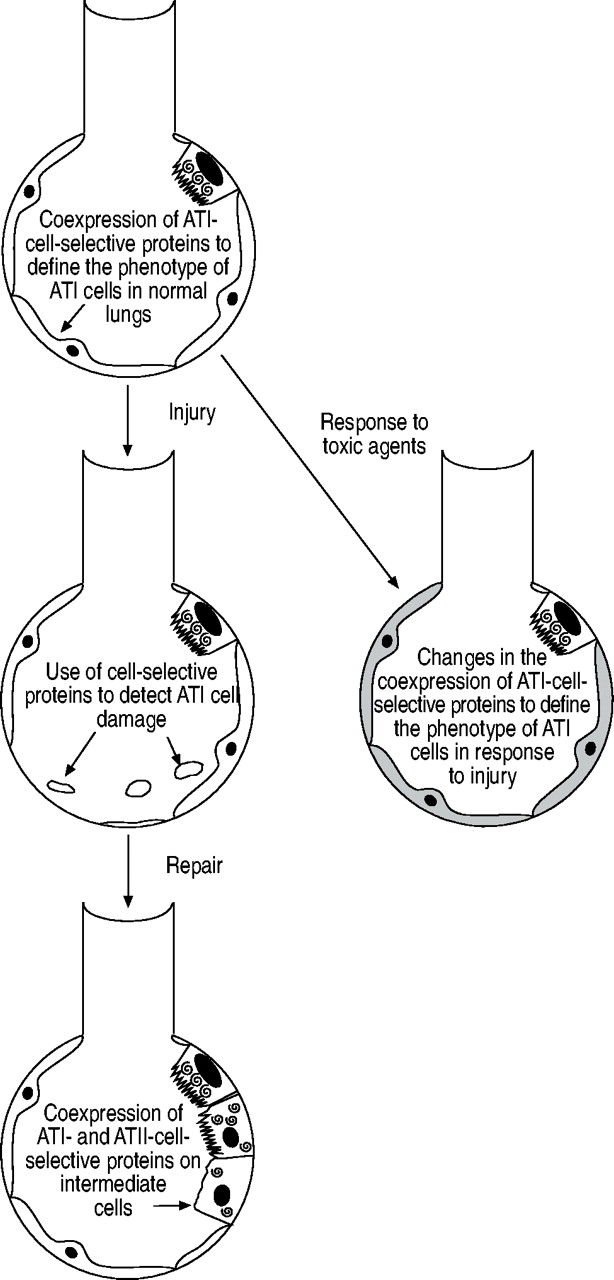
Alveolar type I (ATI) 5 lung epithelial cells (Aqp5 +, RAGE +), ... The boxed area was magnified below. Arrows indicate a positive elastin signal. ... Our results identify a typical transcription ...
The airway, or respiratory tract, describes the organs of the respiratory tract that allow airflow during ventilation. [1][2][3]They reach from the nares and buccal opening to the blind end of the alveolar sacs. They are subdivided into different regions with various organs and tissues to perform specific functions. The airway can be subdivided into the upper and lower airway, each of which ...
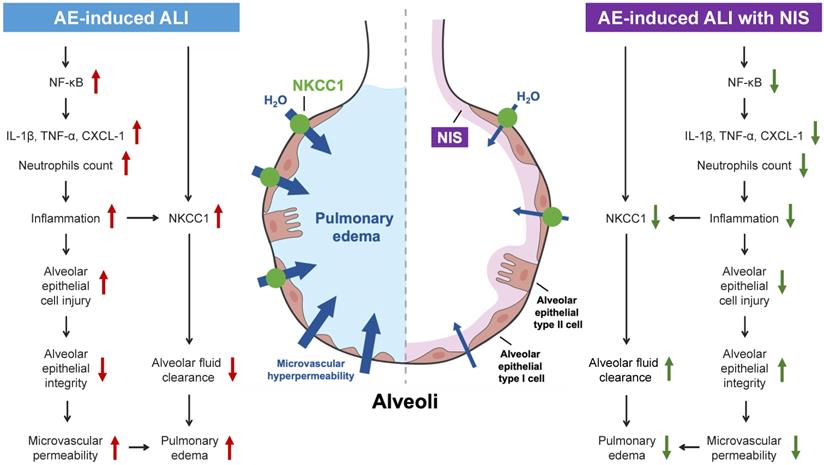
Alveolar epithelial injury is one of the important pathological changes in idiopathic pulmonary interstitial fibrosis (IPF), but the regulatory mechanism remains unclear. Here, we reported that ...
The nasal cavity is a roughly cylindrical, midline airway passage that extends from the nasal ala anteriorly to the choana posteriorly.[1] It is divided in the midline by the nasal septum. On each side, it is flanked by the maxillary sinuses and roofed by the frontal, ethmoid, and sphenoid sinuses in an anterior to posterior fashion.[1] While seemingly simple, sinonasal anatomy is composed of ...
Gas exchange is the process by which oxygen and carbon dioxide move between the bloodstream and the lungs. This is the primary function of the respiratory system and is essential for ensuring a constant supply of oxygen to tissues. This article will discuss the principles of gas exchange, factors affecting the rate of exchange and relevant clinical conditions.
The type II alveolar cells (also known as type II pneumocytes) have two functions: (1) to repair the alveolar epithelium when squamous cells are damaged, and (2) to secrete pulmonary surfactant. Surfactant is composed of phospholipids and protein, and coats the alveoli and smallest bronchioles, which prevents the pressure buildup from ...
Identify the components of head and neck structures on a diagram. Chapter 14: Periodontium: Cementum, Alveolar Process, and the Periodontal Ligament. Define and pronounce the key terms in this chapter. Give an overview of periodontium properties, including its components. Identify each individual component of the periodontium on a diagram.
The bronchioles are lined by simple columnar to the cuboidal epithelium, and the alveoli possess a lining of thin squamous epithelium that allows for gas exchange. Structure There are four main histological layers within the respiratory system: respiratory mucosa, which includes epithelium and supporting lamina propria, submucosa, cartilage and ...
The human body is made in different tissues and cells which are tasked with performing various functions. Do you think you know enough about where these tissues are found within the body when asked about them in a diagram? One of the ways that you can test yourself is by taking this histology lab exam toughest trivia quiz and see well you do—all the best as you tackle it.













:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/alveolar-sac/j761cjMMZrj6LkMNQf1srw_Alveolar_sac.png)


0 Response to "35 on the diagram below identify alveolar epithelium"
Post a Comment