34 centripetal force free body diagram
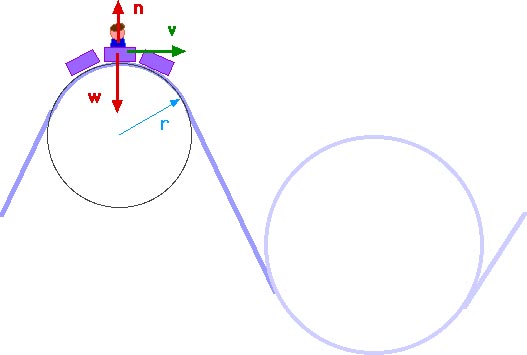
A free-body diagram for the car is shown at left. Both the normal force, N (blue components) and the friction force, f (red components) have been resolved into horizontal and vertical components. Notice that the friction force acts up the incline, to keep the car from sliding toward the center of the turn.
Learn why a centripetal force exists, three important things to remember about centripetal force, and drawing free body diagrams for objects moving in circles. This is an AP Physics 1 topic. Content Times: 0:01 Newton's Second Law for Centripetal Force. 1:10 Three things to remember about Centripetal Force. 2:41 Drawing a free body diagram.
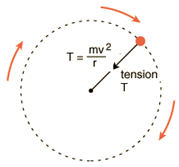
When a free body diagram of a ball being swung in a circle is drawn ( example ), only tension and weight are drawn on it. I understand that the centripetal force equals tension plus weight at the top of the circle, and tension minus weight at the bottom of it, but there must also always be an equal centrifugal force because of Newton's 3rd Law.
Centripetal force free body diagram
Figure 3 shows a free body diagram for a car on a frictionless banked curve. If the angle[latex]\boldsymbol{\theta}[/latex]is ideal for the speed and radius, then the net external force will equal the necessary centripetal force. The only two external forces acting on the car are its weight[latex]\textbf{w}[/latex]and the normal force of the road[latex]\textbf{N}.[/latex](A …
This test covers Newton's Laws of Motion, forces, coefficients of friction, free-body diagrams, and centripetal force. Part I. Multiple Choice 1. A locomotive engine of unknown mass pulls a series of railroad cars of varying mass: the first car has mass m, the second car has mass 2m, and the last car has mass 3m.
Free Body Diagram Centripetal Force This is sometimes referred to as the centripetal force requirement. However, your body, being in motion, tends to continue in motion while the car is skidding to a stop. . ice slides out of the freezer and a mechanical arm exerts a force to accelerate it across the icy, friction free surface.
Centripetal force free body diagram.
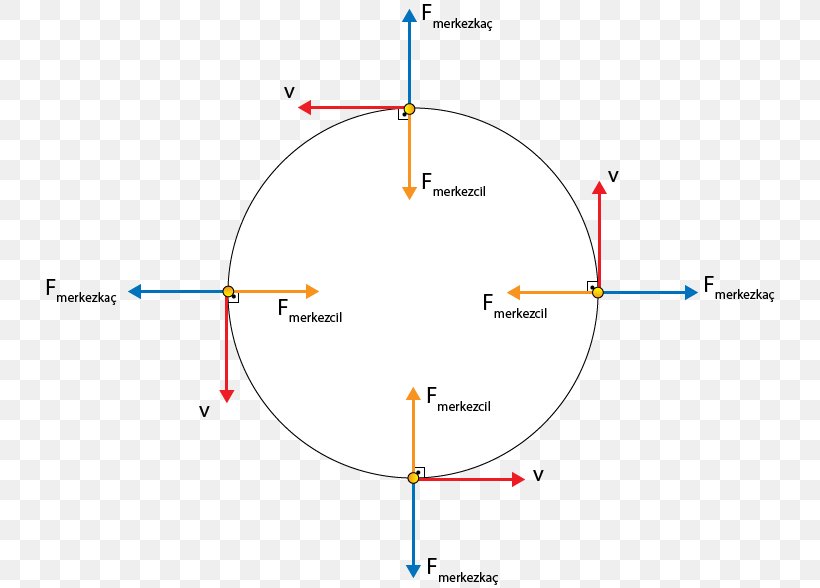
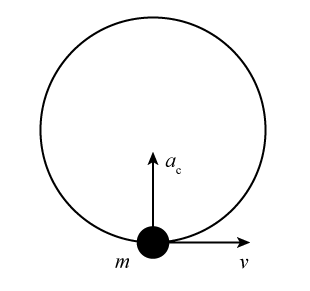
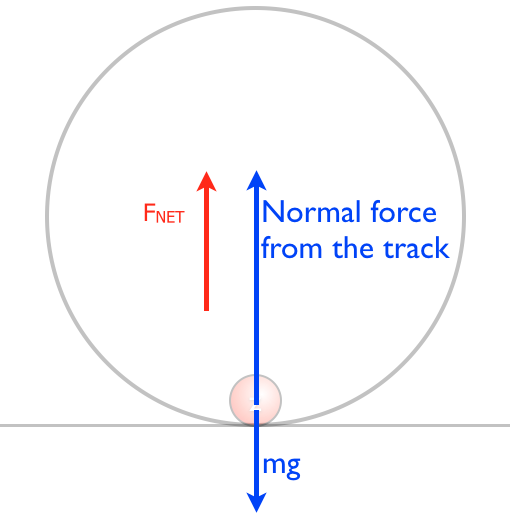
You do NOT put a centripetal force on a free-body diagram for the same reason that ma does not appear on a free body diagram; F = ma is the net force, and the net force happens to have the special form when we're dealing with uniform circular motion.
If there is a centripetal force causing centripetal acceleration, it must point to the center. The normal force is the only force in this case that points to the center. Normal force doesn't always point to the center; there are always exceptions! Solve each problem case by case - use your free-body diagrams!
Redbelly98 said: Centripetal force is a net force on the car, it is caused by one or more of the other forces that have been mentioned. but i thought the sum of all the forces has to equal the net force (ie, centripetal force) - how come on my diagram those force vectors dont add up to the centripetal force vector? Share: Share.
The forces at the bottom are shown here in a free-body diagram. The two forces at the bottom are co-linear, with the upward tension force T being larger than the downward weight, mg, by the required centripetal force. In your experiment, you will compare the measured tension force with one calculated based on the motion. Figure 1.
Explain. large tires because they provide more friction to prevent you from sliding off. As a skater forms a circle, what force is responsible for making her turn? Use a free body diagram in your answer. Centripetal force/acceleration because it is what keeps her in the circular path. Do you feel yourself thrown to either side when you ...
A free-body diagram for the ball at an instant in time is shown in Figure 2. The magnitude of the tension force is also indicated in Figure 2. Which of the following equations represents the centripetal acceleration of the ball if its tangential speed is increased to 2v0?
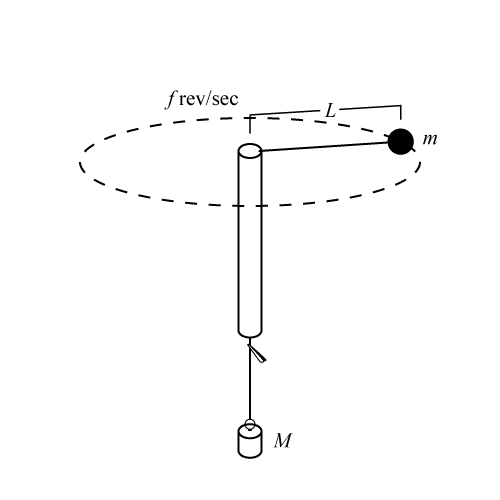
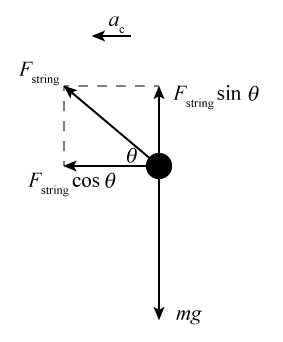
Now draw below a free body diagram of the revolving rubber stopper. From Newton's second law and the free body diagram of the revolving rubber stopper, the horizontal component of the string's tension on the revolving rubber stopper must be ms a = FT cos θ (4) Substitute equation (2) for centripetal acceleration into (4). ms(4π2r/T2)= FT ...
One method to determine the centripetal force acting on a mass is to utilize free body diagrams and force summation equations. Let us consider a mass traveling in a vertical circle attached to a string. Drawing a free body diagram of this mass when it's at the lowest point of its circular path gives us the following.
Centripetal Force Questions and Answers. Get help with your Centripetal force homework. Access the answers to hundreds of Centripetal force questions that are explained in a …
Which free-body diagram in Figure 5.11 correctly shows the force(s) acting on the Earth (E) as it orbits the Sun, when the Earth is at the position shown, to the right of the Sun? is the gravitational force exerted on the Earth by the Sun, while stands for centripetal force. The correct free-body diagram is diagram 3, which
Once more the F norm must provide sufficient force to produce the required inward or centripetal net force. Earlier in Lesson 2, the use of Newton's second law and free-body diagrams to solve circular motion diagrams was illustrated. It was emphasized at that time that any given physical situation could be analyzed in terms of the individual ...
Figure 3 shows a free body diagram for a car on a frictionless banked curve. So too is the force. Solving for centripetal force using a free body diagram a 70 kg student is riding a roller coaster and is at the top of the vertical loop. As always the place to start is with a free body diagram which just has two forces the tension and the weight.
http://www.physicseh.com/Free simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website.
The centripetal force for a conventional simple pendulum is provided by the tension in the cable/string. The free body diagram for the pendulum bob is tension in the direction of the cable/string toward the pivot point, which is at the center of rotation of the pendulum bob, and gravitational force which is constant and straight down.
A centripetal force (from Latin centrum, "center" and petere, "to seek") is a force that makes a body follow a curved path.Its direction is always orthogonal to the motion of the body and towards the fixed point of the instantaneous center of curvature of the path. Isaac Newton described it as "a force by which bodies are drawn or impelled, or in any way tend, towards a …
The correct free-body diagram is diagram 3, which shows only the force of gravity applied by the Sun on the Earth. The word "centripetal" means "directed toward the center." When an object experiences uniform circular motion, the object has a centripetal acceleration directed toward the center of the circle.
Answer (1 of 10): Friction. Let's just assume you are on bench seat in a carraige or something and not gripping a horse (or reindeer?) with your thighs. You are "trying" to go straight ahead, tangentially to the circular path. If the seat were frictionless, that's what you would do and would be f...
05.08.2021 · The book definition of centripetal force tells us that it's the force that acts on any object that moves along a curved path.The direction of the force is always parallel to the curvature's radius r.. Usually, we deal with centripetal force examples when talking about a circular motion.It's the simplest type of nonlinear movement.
26.11.2021 · Centripetal Force Formula. If we know the acceleration of the body, Then by Newton’s law, we can write, Net force, \(F=ma,\) This force is the centripetal force that is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by the centripetal acceleration\((a_c).\) i.e \(F = \frac{{m{v^2}}}{r}\) and \(F = mr{\omega ^2}\) Examples of Centripetal Force in ...
Draw the free body diagram for the mass at the bottom of the loop, and the write the force summation equation from it. Then use it to calculate the centripetal force of the mass at the bottom of the loop. (15 points) 2. Calculate the centripetal force for the mass at the bottom of the loop using the formula mvb/R (10 points) 3.
Including a centrifugal force in a free-body diagram is considered a mistake in elementary mechanics, although as Peter Shor points out, it is not a mistake at all if you are working in a non-inertial frame (which is consistent, just considered slightly more advanced).
Free-body diagrams can be used as a convenient way to keep track of ... and the Feynman diagram represents any force arising from an interaction as occurring at the vertex with an associated instantaneous change in the direction of the particle world lines. Gauge bosons are emitted away from the vertex as wavy lines and, in the case of virtual particle exchange, are …
As the centripetal force acts upon an object moving in a circle at constant speed, the force always acts inward as the velocity of the object is directed tangent to the circle. This would mean that the force is always directed perpendicular to the direction that the object is being displaced. The angle Theta in the above equation is 90 degrees and the cosine of 90 degrees is 0. Thus, …
Solving for Centripetal Force using a Free Body Diagram A 70 kg student is riding a roller coaster and is at the top of the vertical loop. The loop has a radius of 16 m, and the car's velocity at the top is 12 m/s.
Free Body Diagram Centripetal force. physics help centripetal force free body diagrams part 7 free simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website centripetal force and free body diagram 1 the problem statement all variables and given known data a draw a free body diagram for mass mb while in motion fig 2a identify the centripetal
There is no such thing, and, in my opinion, you should never put a centripetal force on a free-body diagram. When an object is experiencing uniform circular motion there is definitely a net force directed toward the center of the circle, but this force comes from one or more of the standard forces we've discussed already.
Draw a free body diagram of the forces to see what the angle ... centripetal force: any net force causing uniform circular motion. ideal banking: the sloping of a curve in a road, where the angle of the slope allows the vehicle to negotiate the curve at a certain speed without the aid of friction between the tires and the road; the net external force on the vehicle equals the horizontal ...
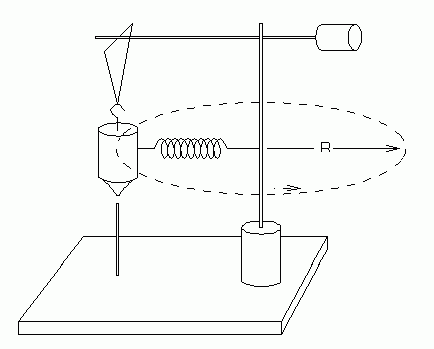
26.08.2018 · Quantitative centripetal force apparatus-free body diagram. Last Post; Nov 11, 2011; Replies 1 Views 4K. E. Free Body Diagram. Last Post; Mar 7, 2009; Replies 1 Views 2K. K. Situation diagram and free body diagram. Last Post; May 2, 2011; Replies 1 Views 7K. S. Representing Free body diagrams. Last Post; Oct 23, 2015; Replies 9 Views 1K. Free Body …
free body diagram shows that the gravity force W W is balanced by the normal force N N from the road. If we now increase the bank angle θ θ below, then we see that a friction force F F tangential to the road is needed to keep the bus from sliding. In practice, this force will be limited by F ≤μN F ≤ μ N, where μ μ is the coefficient of friction.
http://www.physicshelp.caGO AHEAD and click on this site...it wont hurt.Free simple easy to follow videos all organized on our website
Figure 3a shows the free body diagram for the rotating bob in uniform circular motion. The weight of the mass is balanced by the tension in the suspending string. The centripetal force is provided by the tension in the spring attaching the bob to the shaft. We can measure the tension in the spring in a static state, i.e., without rotation as shown in the Figure 3b. When the bob is …
(Figure) shows a free-body diagram for a car on a frictionless banked curve. If the angle is ideal for the speed and radius, then the net external force equals the necessary centripetal force. The only two external forces acting on the car are its weight and the normal force of the road













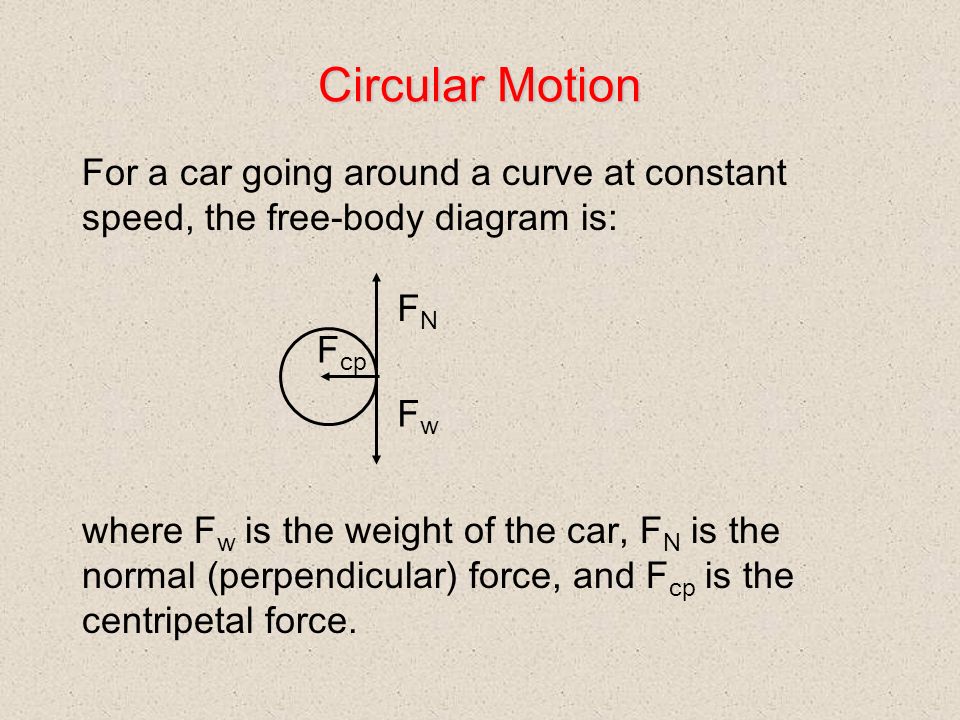


0 Response to "34 centripetal force free body diagram"
Post a Comment