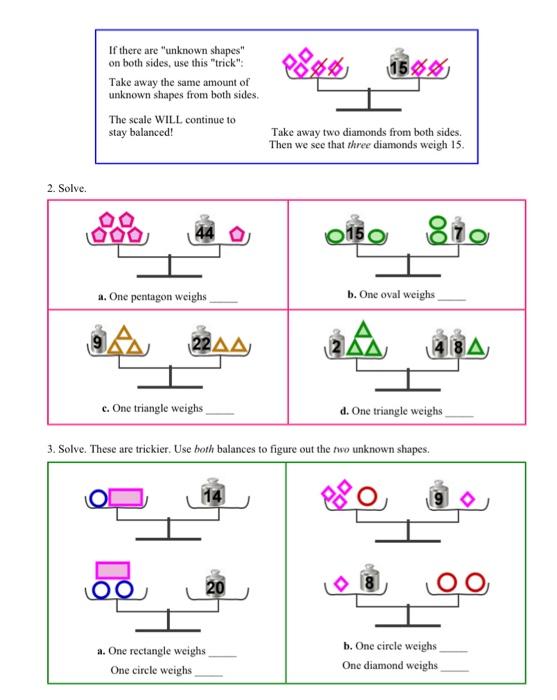
39 the diagram represents a pan balance each of the blocks marked x has the same value
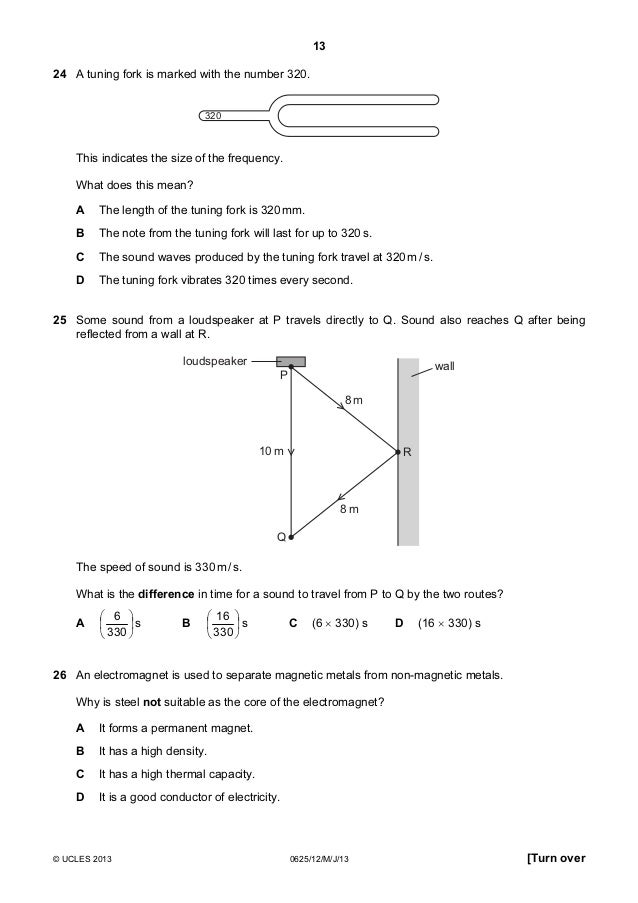
from each other are always equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. FBC FCB (5.6) = − QUESTIONS Q2. Two horizontal forces F 1, F 2 pull a banana split across a frictionless counter. Without using a calculator, determine which of the vectors in the free body diagram below best represent: a) F 1, b)F 2. What is the net force component ... bag of fertilizer at the same time as the first one. Determine the maximum allowable horizontal distance from the axle A of the wheelbarrow to the center of gravity of the second bag if she can hold only 75 N with each arm. PROBLEM 4.2 A gardener uses a 60-N wheelbarrow to transport
should fill the value in on their data table. c. Students complete the same procedure to determine the rate of movement since the formation of Oahu and the formation of Kauai. 7. After students have found the rates of movement since the formation of the three islands, they should average the numbers (add them and divide by three) to find the
The diagram represents a pan balance each of the blocks marked x has the same value
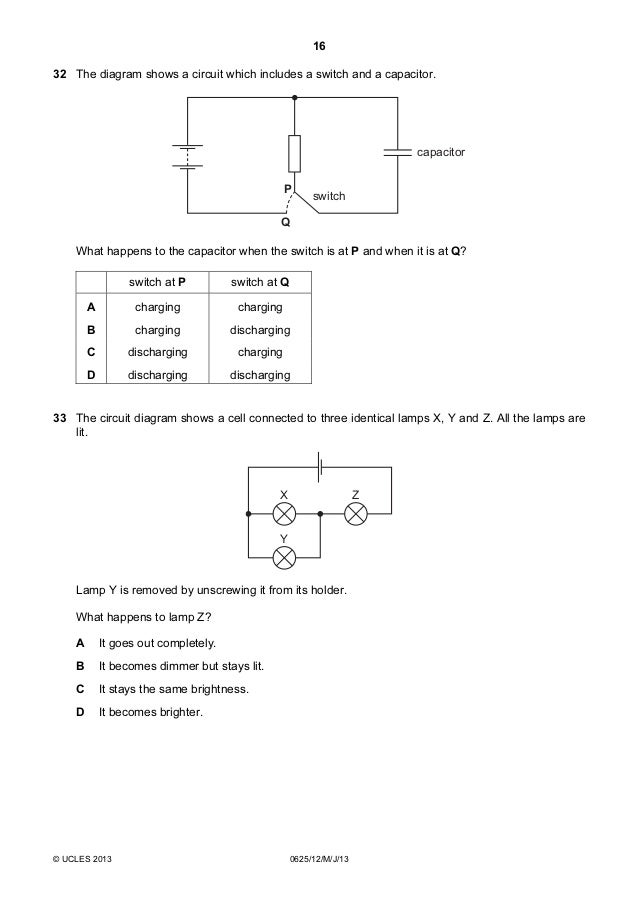
Block diagrams consist of a single block or a combination of blocks. These are used to represent the control systems in pictorial form. Basic Elements of Block Diagram. The basic elements of a block diagram are a block, the summing point and the take-off point. 14 The diagram represents a pan balance. Each of the blocks marked x has the same value. The small blocks have a value of 1. What is the value of x if each side of the balance has the same weight? O 4 O 10 O 14 navigation 16 12/21 A FONT O Type here to search. 4 The diagram shows a uniform beam being used as a balance. The beam is pivoted at its centre. A 1.0 N weight is attached to one end of the beam. An empty pan weighing 0.2 N is attached to the other end of the beam. 1.0 N beam pivot pan (0.2 N) How many 0.1 N weights must be placed on the pan in order to balance the beam? A 5 B 8 C 10 D 12
The diagram represents a pan balance each of the blocks marked x has the same value. 17. An object placed on an equal-arm balance requires 12 kg to balance it. When placed on a spring scale, the scale reads 12 kg. Everything (balance, scale, set of weights and object) is now transported to the Moon where the free-fall acceleration is one-sixth that on Earth. The new readings of the balance and spring scale (respectively) are: When the object is at x = A/2, U = ½ k(A/2) 2 = E. tot /4. Since the mechanical energy is conserved, the kinetic energy at x = A/2 is given by, K = E. tot -U = 3E. tot /4. Motion Graphs. If we graph position, velocity, and acceleration of the object on the spring, as a function of time, we get the plots shown at right. The example used here ... The diagram represents a pan balance each of the blocks marked x has the same value. The small blocks have a value of 1. What is the value of x if each side of the balance is the same x= 0; T BC- 300(0.25) - 300(0.25) = 0 T BC= 150 N # m ©M x= 0; T AB- 300(0.25) = 0 T AB= 75 N # m 5-19. Two wrenches are used to tighten the pipe. If P = 300 N is applied to each wrench, determine the maximum torsional shear stress developed within regions AB and BC. The pipe has an outer diameter of 25 mm and inner
Measure the height X of the spring and record it in your data sheet. 6. Increase the mass by 10 g increments, making sure to measure and record the height at each step, until you reach 220 g. 7. Calculate m = m mH, X = X X0,and(X X0)=2X0 for each trial. 8. Calculate the force of gravity pulling on the spring, FS = mg, for each trial. 20 is the same system drawn in an isometric view with the use of fitting symbols. Symbols are used in Fig. 2-20 which represent the pumps, valves and fittings. From observation it be- comes obvious that the use of symbols require far less effort than drawing each item in the three views of the pneumatic water booster system shown in Figs. 2-17,2- The diagram represents a pan balance each of the blocks marked x has t... What is the inverse of h? Consider 8x2 - 48x = -104. Write the equation so that a = 1; which function grows at fastest rate for increasing values of x? h(x)... Match the mathematicians to their descriptions. Tiles regarded as the... What is this tool used for ? C) Dawn has agreed to mow 2/3 of the lawn at camp. She has done 3/4 of her job. What portion of the lawn has Dawn done? Step 1: THE LAWN AT CAMP Dawn's part of the job In this diagram the lawn has been divided into three equal parts. Each represents 1/3 of the lawn. Two of the parts represent Dawn's part of the job—which is 2/3 of the lawn.
will maintain the speed at (or near) the desired value despite these external conditions. Example 3 (Inverted Pendulum). Suppose we try to balance a stick vertically in the palm of our hand. The sensor, controller and actuator in this example are our eyes, our brain, and our hand, respectively. This is an example of a feedback control system. each object, and particles with a larger size have a larger mass.] Explain your reasoning. 40 4. In Figure 4 below, a graph shows the relationship between mass and volume for two substances, A and B. Use the graph to answer questions about these two substances. Two Pan Balance a) You have built a simple two-pan balance shown above to compare the The Peak value represents the distance to the top of the waveform measured from a zero reference. For discussion purposes we'll assign a Peak value of 1.0. The Peak-to-Peakvalue is the amplitude measured from the top most part of the waveform to the bottom most part of the waveform. The Average value is the average amplitude value for the ... Finally, sketch a line through the points and label it “Demand for X.” (Assume that the demand curve for X is a straight line.) d) For extra practice, try assuming that the price of Y changes instead of the price of X. Suppose the new situation has price levels Px = $5 and Py = $5 (this is our “situation 3”).
k( x)2 mgh k = h d k( x)2 2mgd = 3 6 2200 0:22 2 10 9:81 6 = 0:425 0.7 A block of mass m 1 = 18:0 kg is connected to a block of mass m 2 = 32.0 kg by a massless string that passes over a light, frictionless pulley. The 32.0-kg block is connected to a spring that has negligible mass and a force constant of k = 220 N/m as shown in the gure below.
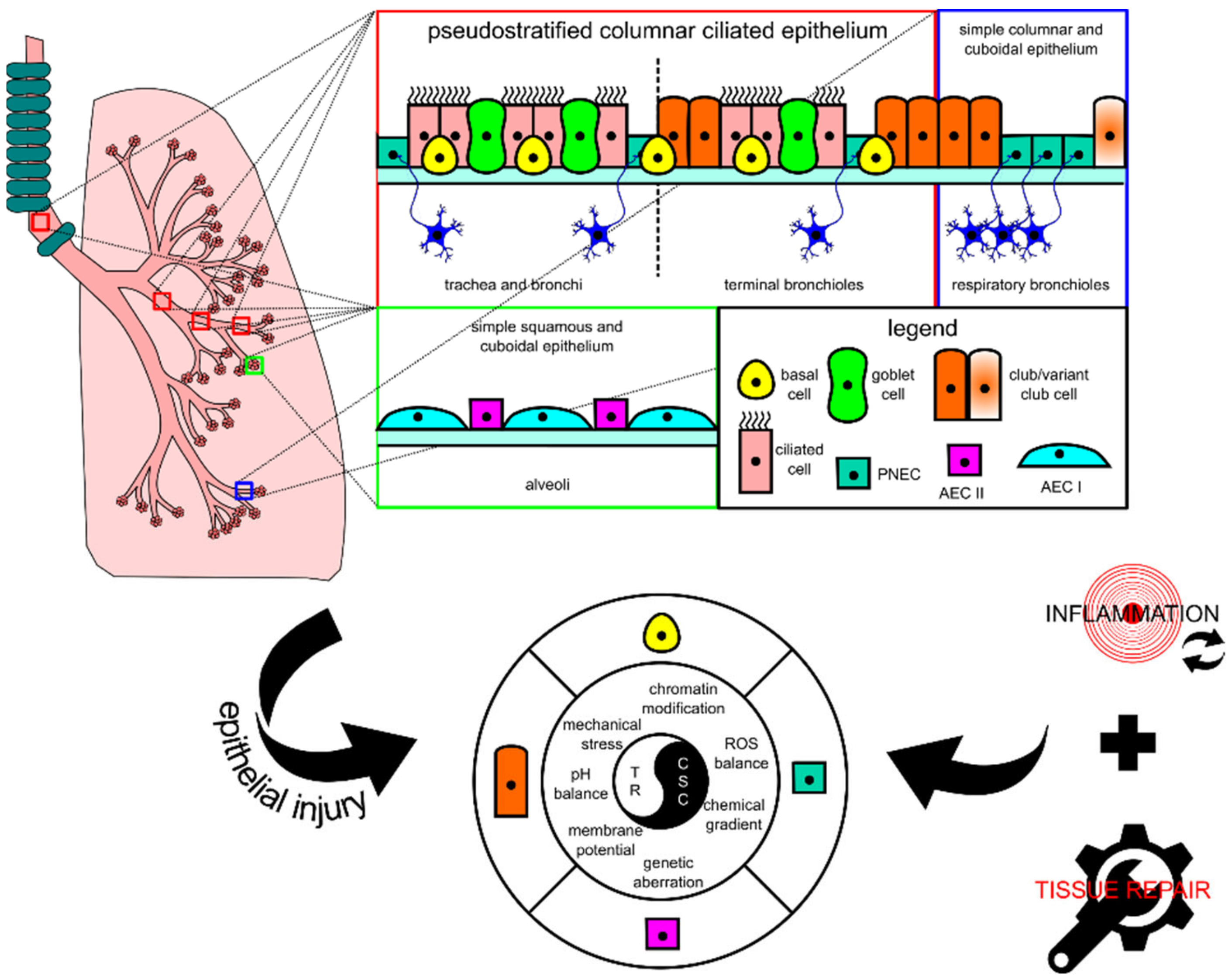
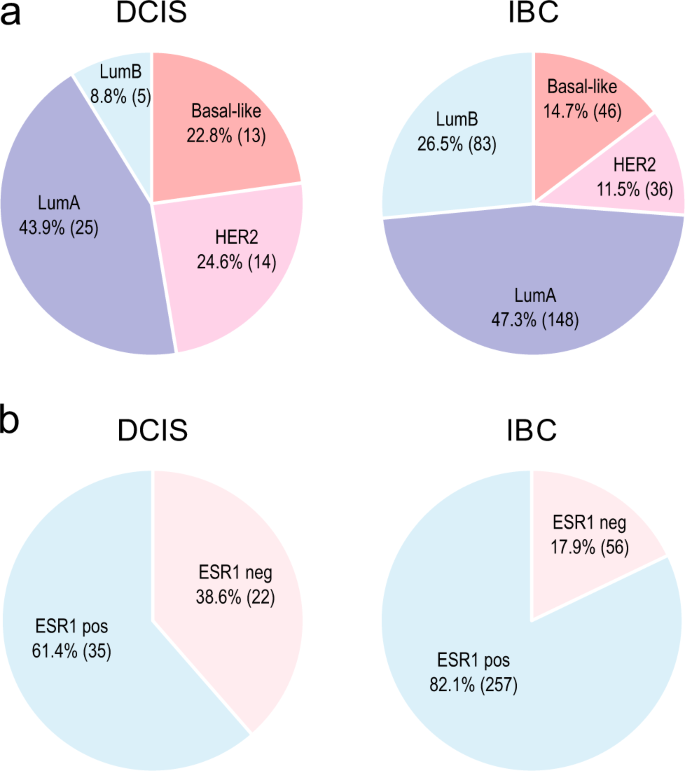
Ijms Free Full Text Understanding Lung Carcinogenesis From A Morphostatic Perspective Prevention And Therapeutic Potential Of Phytochemicals For Targeting Cancer Stem Cells Html
For numbers 2a–2b, select Yes or No to indicate whether the value of the equation is correct. 2a. 55 − (12 + 2), value: 41 Yes No 2b. 25 + (14 − 4) ÷ 5, value: 27 Yes No 3. Carmine buys 8 plates for $1 each. He also buys 4 bowls. Each bowl costs twice as much as each plate. The store is having a sale that gives Carmine $3 off the bowls.
AREN 2110 SOLUTIONS FALL 2006 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS 6, 7 and 8 SOLUTIONS: HOMEWORK #6 Chapter 5 Problems 5-45 A number of brass balls are to be quenched in a water bath at a specified rate. The rate at which heat needs to be removed from the water in order to keep its temperature constant is to be determined.
Measuring Mass with a Triple-Beam Balance A triple-beam balance has a pan and three beams with sliding masses called riders. At one end of the beams is a pointer that indicates whether the mass on the pan is equal to the masses shown on the beam. To use: 1. Make sure the balance is zeroed before measuring the mass of an object.
Block 1 and block 2 have the same mass, m, and are released from the top of two inclined planes of the same height making 30° and 60° angles with the horizontal direction, respectively. If the coefficient of friction is the same in both cases, which of the blocks is going faster when it reaches the bottom of its respective incline?
2 1 A student measures the length of a rod XY by holding it next to a metre rule. X Y 99 98 97 96 95 94 cm The student writes down the length as 94.8 cm. Which statement is correct? A The value is correct. B The value is incorrect because it should be 95.2 cm. C The value is incorrect because it should be in millimetres.
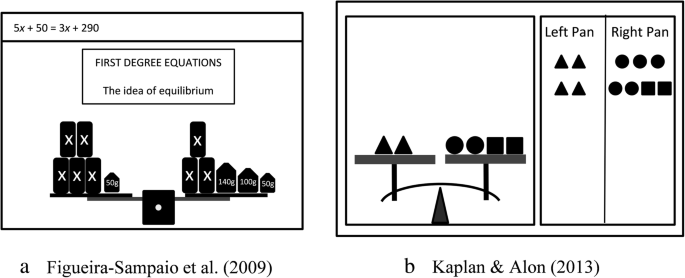
The Balance Model For Teaching Linear Equations A Systematic Literature Review International Journal Of Stem Education Full Text
Name and label each contact force acting on the object. There is at least one force at each point of contact; there may be more than one. When necessary, use subscripts to distinguish forces of the same type. Name and label each long-range force acting on the object. For now, the only long-range force is weight.
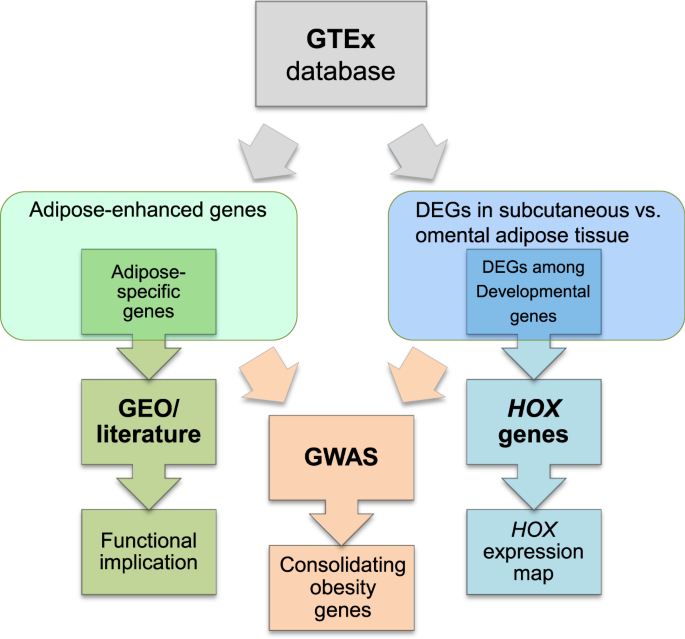
Integrative Analysis Revealing Human Adipose Specific Genes And Consolidating Obesity Loci Scientific Reports
4 The diagram shows a uniform beam being used as a balance. The beam is pivoted at its centre. A 1.0 N weight is attached to one end of the beam. An empty pan weighing 0.2 N is attached to the other end of the beam. 1.0 N beam pivot pan (0.2 N) How many 0.1 N weights must be placed on the pan in order to balance the beam? A 5 B 8 C 10 D 12
1. Every body continues in its state of rest, or of uniform motion in a right line, unless it is compelled to change that state by forces impressed on it. 2. The (rate of) change of motion is proportional to the motive force impressed: and is made in the direction of the right line in which that force is impressed.
blocks. The brake blocks have a total mass of 0.12 kg and the material from which they are made has a -specific heat capacity of 1200 J kg 1 K-. (i) Calculate the maximum rise in temperature of the brake blocks. 60% of the KE = 0.60 x 3040 = 1824 (J) (1 mark) Q = mc 1824 = 0.12 x 1200 x (1 mark) = 13 K (1 mark) (12.7 K)

2021 Guideline For The Prevention Of Stroke In Patients With Stroke And Transient Ischemic Attack A Guideline From The American Heart Association American Stroke Association Stroke
Display the diagrams and explain that each square labeled with a 1 weighs 1 unit, and each shape labeled with a letter has an unknown weight. Arrange students in groups of 2. Give 5-10 minutes of quiet work time and time to share their responses with a partner, followed by a whole-class discussion.
That portion of the Pb-Sn phase diagram (Figure 9.8) that pertains to this problem is shown below; the point labeled "H" represents the 85.1 wt% Sn-14.9 wt% Pb composition at 200°C. As may be noted, point H lies within the β + L phase field. A tie line has been constructed at 200°C; its intersection

The Diagram Represents A Pan Balance Each Of The Blocks Marked X Has The Same Value The Small Blocks Brainly Com
Since in a balanced situation the two sides of the balance hold equal weight, we can model simple equations with a balance. In the pictures below, each circle represents one and the block represents the unknown x. To find out what the block weighs, you can. add the same amount (circles or blocks) to BOTH sides; take away the same amount from ...
The diagram below shows a resultant vec-tor, R. Which diagram best represents a pair of com-ponent vectors, A and B, that would combine to form resultant vector R? ANSWER: (1) 5. A vector makes an angle, h, with the horizon-tal. The horizontal and vertical components of the vector will be equal in magnitude if the angle is ANSWER: (2) 45° PART ...
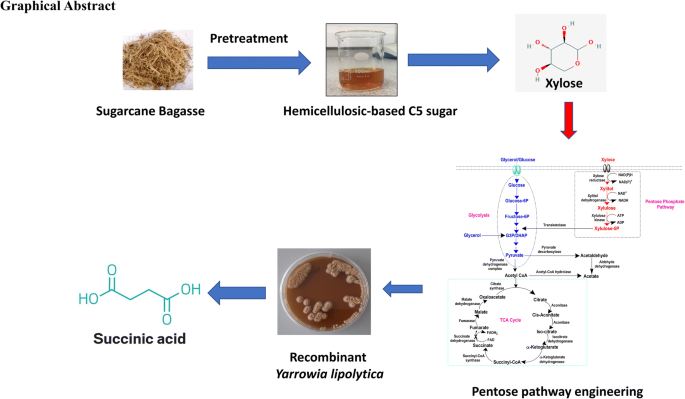
Bioproduction Of Succinic Acid From Xylose By Engineered Yarrowia Lipolytica Without Ph Control Biotechnology For Biofuels Full Text
Physics 1011/2111 Labs ~ General Guidelines The Physics 1011 and 2111 labs will be divided into small groups (so you will either be working with one lab partner, or, for the larger classes, in a small group).
4 The diagram shows a uniform beam being used as a balance. The beam is pivoted at its centre. A 1.0 N weight is attached to one end of the beam. An empty pan weighing 0.2 N is attached to the other end of the beam. 1.0 N beam pivot pan (0.2 N) How many 0.1 N weights must be placed on the pan in order to balance the beam? A 5 B 8 C 10 D 12
14 The diagram represents a pan balance. Each of the blocks marked x has the same value. The small blocks have a value of 1. What is the value of x if each side of the balance has the same weight? O 4 O 10 O 14 navigation 16 12/21 A FONT O Type here to search.
Block diagrams consist of a single block or a combination of blocks. These are used to represent the control systems in pictorial form. Basic Elements of Block Diagram. The basic elements of a block diagram are a block, the summing point and the take-off point.
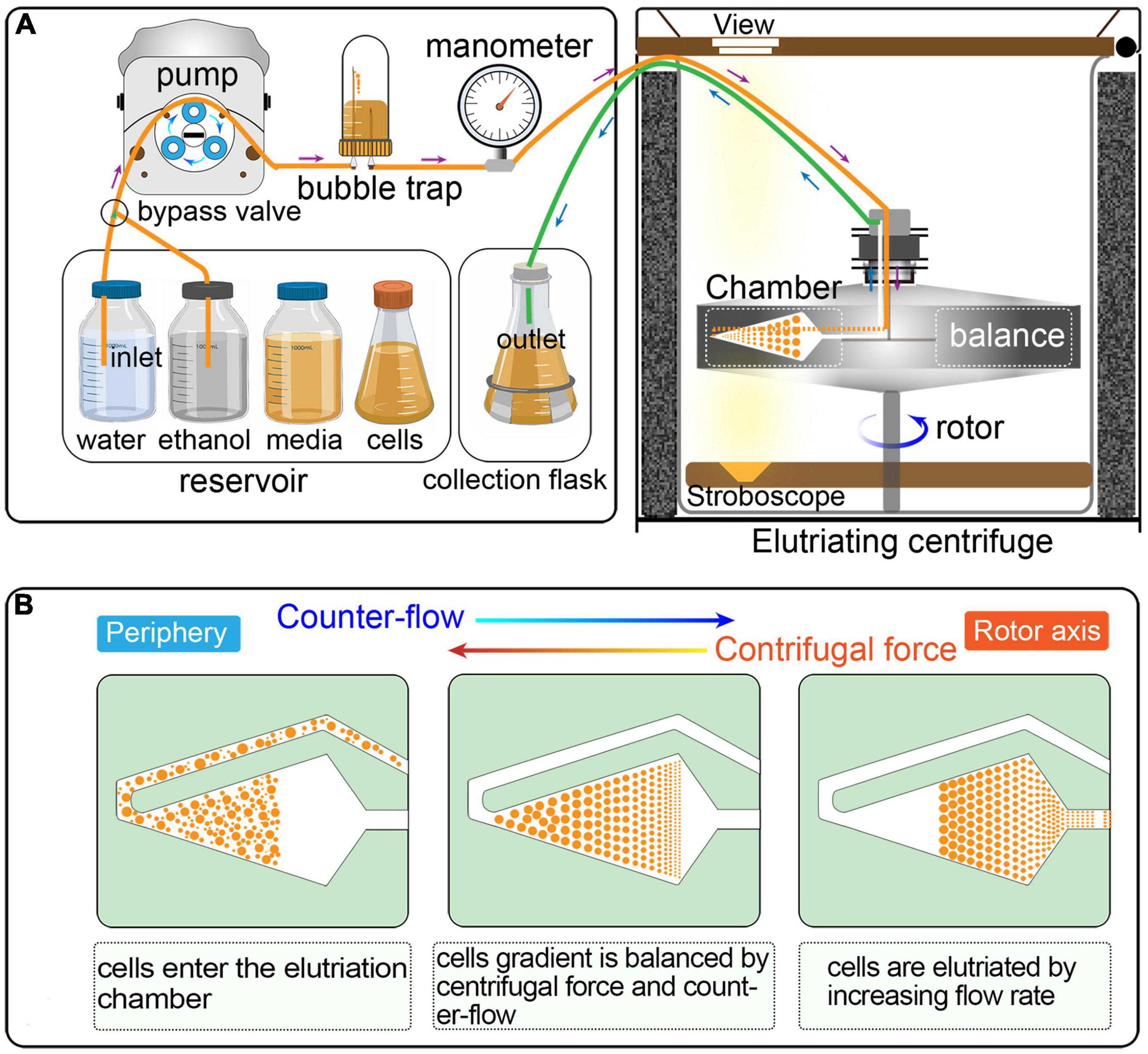
Frontiers An Optimized And Versatile Counter Flow Centrifugal Elutriation Workflow To Obtain Synchronized Eukaryotic Cells Cell And Developmental Biology

Kdigo 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline For Diabetes Management In Chronic Kidney Disease Kidney International

Kdigo 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline For Diabetes Management In Chronic Kidney Disease Kidney International

A Method Of Optimizing Network Topology Structure Combining Viterbi Algorithm And Bayesian Algorithm

The Diagram Represents A Pan Balance Each Of The Blocks Marked X Has The Same Value The Small Blocks Brainly Com

Gray Level Co Occurrence Matrix Glcm Texture Based Crop Classification Using Low Altitude Remote Sensing Platforms Peerj






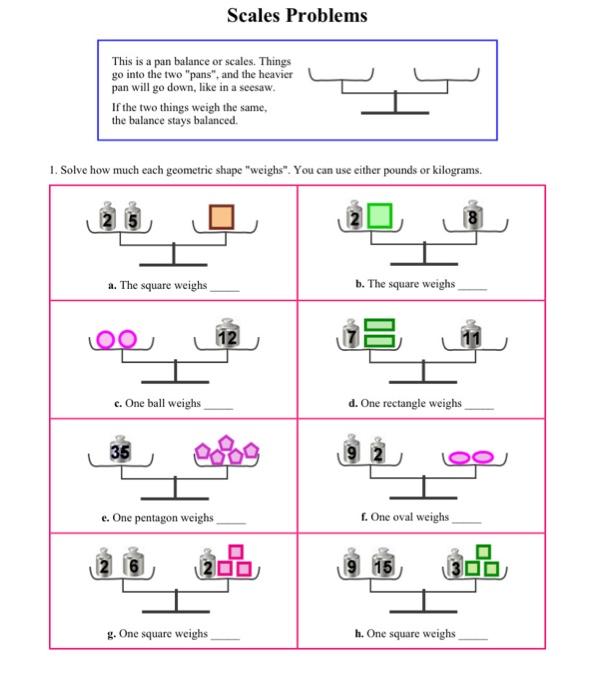


0 Response to "39 the diagram represents a pan balance each of the blocks marked x has the same value"
Post a Comment