38 energy diagram for hydrogen
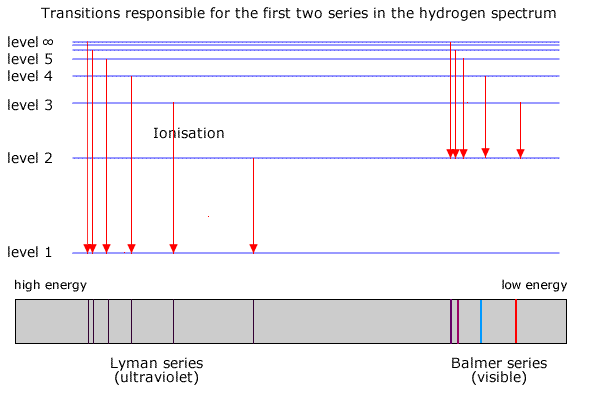
The energy levels agree with the earlier Bohr model, and agree with experiment within a small fraction of an electron volt. If you look at the hydrogen energy levels at extremely high resolution, you do find evidence of some other small effects on the energy. The 2p level is split into a pair of lines by the spin-orbit effect. Hydrogen spectrum wavelength. When a hydrogen atom absorbs a photon, it causes the electron to experience a transition to a higher energy level, for example, n = 1, n = 2. When a photon is emitted through a hydrogen atom, the electron undergoes a transition from a higher energy level to a lower, for example, n = 3, n = 2.
The hydrogen atom is the simplest in the universe that consists of only a proton and an electron. The electron is at the ground state, which is the nearest ...
Energy diagram for hydrogen
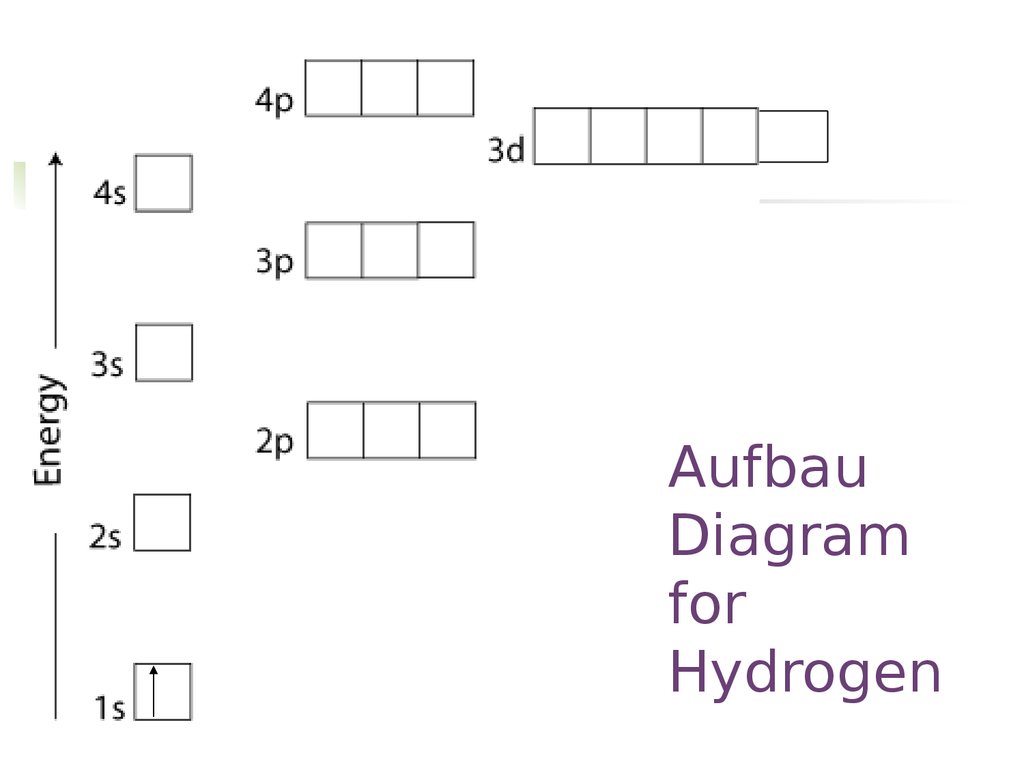
Let's look at the simplest atom, a neutral hydrogen atom. Its energy levels are given in the diagram below. The x-axis shows the allowed energy levels of electrons in a hydrogen atom, numbered from 1 to 5. The y-axis shows each level's energy in electron volts (eV). A Hydrogen atom has only one single electron revolving around the nucleus at the lowest energy level. When we heat a hydrogen atom, the electron gains energy ... Molecular orbital energy level diagrams -Hydrogen, Hypothetical, Nitrogen, Oxygen. The filling of molecular orbitals is governed by the following principles. (i)Aufbau principle (ii)Pauli's exclusion principle and (iii)Hund's rule of maximum multiplicity. Now, let us consider some examples of homo nuclear diatomic molecules.
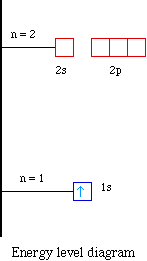
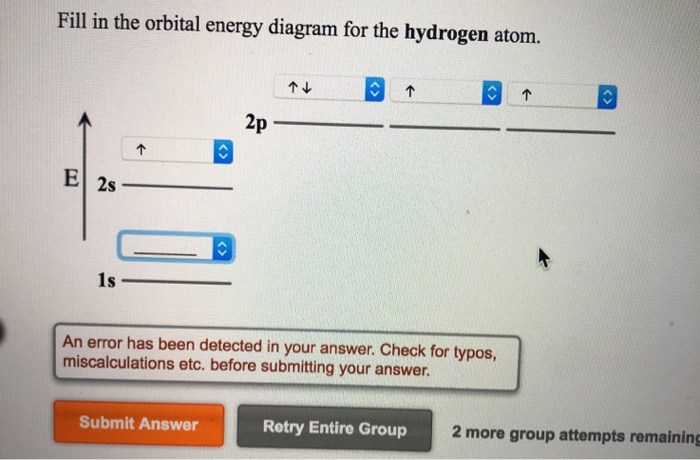
Energy diagram for hydrogen. Given figure shows energy level diagram for Hydrogen atom. Video Explanation. Was this answer helpful? 0. 0. Similar questions. When an electron in hydrogen atom jumps from the excited state to the ground state, how would the de-Broglie wavelength associate with the electron change? Justify your answer Below is a blank energy level diagram which helps you depict electrons for any specific atom. At energy level 2, there are both s and p orbitals. The 2s has lower energy when compared to 2p. The three dashes in 2p subshells represent the same energy. 4s has lower energy when compared to 3d. Therefore, the order of energy level is as follows: s ... Energy level diagrams can be useful for visualizing the complex level structure of multi-electron atoms. Forms of such diagrams are called Grotrian diagrams or term diagrams in various parts of the literature. While the energy level diagram of hydrogen with its single electron is straightforward, ... See below. Orbital diagrams are useful to show the number of electrons, number of electron shells, number of electron pairs, and electron spin directions in a particular atom/ion. Arrows represent electrons, and their spin is represented by which way they point (up or down). Two electrons can be paired into one shell (one little box) as one orbital. Groups of boxes right next to each other ...
Transcribed image text: Refer to the energy level diagram for the transitions of the hydrogen atom to answer the following: What is the energy of the principal quantum number 1, in units of reciprocal centimetres, cm-l? Number cm-1 What principal quantum number has an energy of -6855 cm-? Number Referring to the two values above, what amount of energy is given off when an atom transitions from ... The electron energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. He found that the four visible spectral lines corresponded to transitions from ... Energy-level diagram for the hydrogen atom ... Here you will find curriculum-based, online educational resources for Chemistry for all grades. This chemistry video tutorial focuses on the bohr model of the hydrogen atom. It explains how to calculate the amount of electron transition energy that is...
Fe/FeO Equilibrium Diagram. X. X. 1325 • Low temperatures CO more effective at reducing FeO • High temperatures H 2 more effective at reducing FeO CO 2 /CO. H. 2. O/H. 2. 13. THE USE OF HYDROGEN IN THE IRON AND STEEL INDUSTRY. DRI Operational. Range. Flash Iron Operational Range. reduce all FeO requires . 2X excess H 2. 1.7 GJ/t . to heat ... Bohr's model of hydrogen is based on the nonclassical assumption that electrons travel in specific shells, or orbits, around the nucleus. Bohr's model calculated the following energies for an electron in the shell, : Bohr explained the hydrogen spectrum in terms of electrons absorbing and emitting photons to change energy levels, where the ... Hydrogen is an energy carrier that can be used to store, move, and deliver energy produced from other sources. Today, hydrogen fuel can be produced through several methods. The most common methods today are natural gas reforming (a thermal process), and electrolysis. Other methods include solar-driven and biological processes. hydrogen atom, (4) to study and develop the Bohr theory of the hydrogen atom, (5) to measure the wavelengths of the Balmer series of visible emission lines from hydrogen, and (6) to learn to analyze the wavelength data to determine the Rydberg constant using
3. Energy Needs of a Hydrogen Economy Hydrogen is a synthetic energy carrier. It carries energy generated by some other processes. Electrical energy is transferred to hydrogen by electrolysis of water. But high-grade electrical energy is used not only to produce hydrogen, but also to compress, liquefy, transport, transfer or store the medium.
Hydrogen sulfide is used in the manufacture of chemicals, in metallurgy, and as an analytical reagent. The phase diagram of hydrogen sulfide is shown below the table. Chemical, physical and thermal properties of hydrogen sulfide: Values are given for gas phase at 25 o C /77 o F / 298 K and 1 bara, if not other phase, temperature or pressure given.
Hydrogen is an energy carrier, not an energy source, so the energy it delivers would ultimately have to be provided by a conventional power plant. This page considers some of the issues. ... The following diagram shows the key system components for providing AC or DC power.
MIT 8.04 Quantum Physics I, Spring 2016View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/8-04S16Instructor: Barton ZwiebachLicense: Creative ...
Energy level diagrams and the hydrogen atom. It's often helpful to draw a diagram showing the energy levels for the particular element you're interested in. The diagram for hydrogen is shown above. The n = 1 state is known as the ground state, while higher n states are known as excited states. If the electron in the atom makes a transition from ...
The energy content of hydrogen is given as either lower heating value (LHV) of 242 1 The electronegativity is a measure for the attraction of electrons to the nucleus and its difference to the partner's electronegativity defines the character of the bond: nonpolar-covalent (difference = 0), polar-covalent,
Il n'y a pas de texte répondant à ce style dans ce document.-6: Flammability Diagram for Hydrogen/Air/Nitrogen at 400°C and 1 bar For hydrogen, the minimum ignition energy is low at 0.017 mJ for mixtures with air (ISO, 2004), and even lower at 0.0012 mJ for mixtures with oxygen (Kuchta, 1986). Hydrogen has a such a low
The Figure Shows Energy Level Diagram Of Hydrogen Atom I Find Out The Transition Which Results In The Emission Of A Photon Of Wavelength 496 Nm Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Energy levels in hydrogen. This can be done electrically by heat by collision with another atom by radiation or by a free electron hitting the atom. 2 Partial Energy Level Diagram For Hydrogen Warning Because Of The Draw a partial energy level diagram for hydrogen. Partial energy level diagram for hydrogen. 41126 43477 48710 65842.
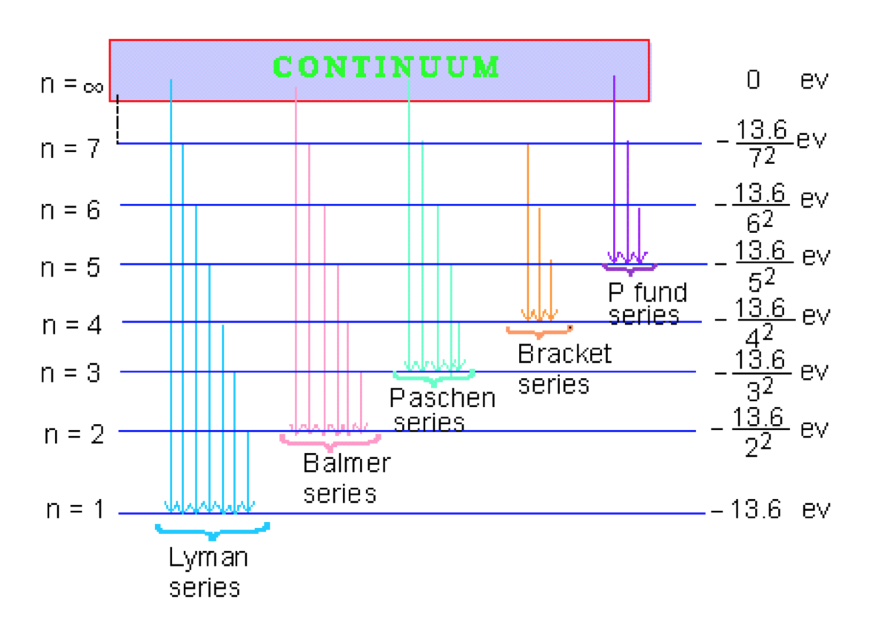
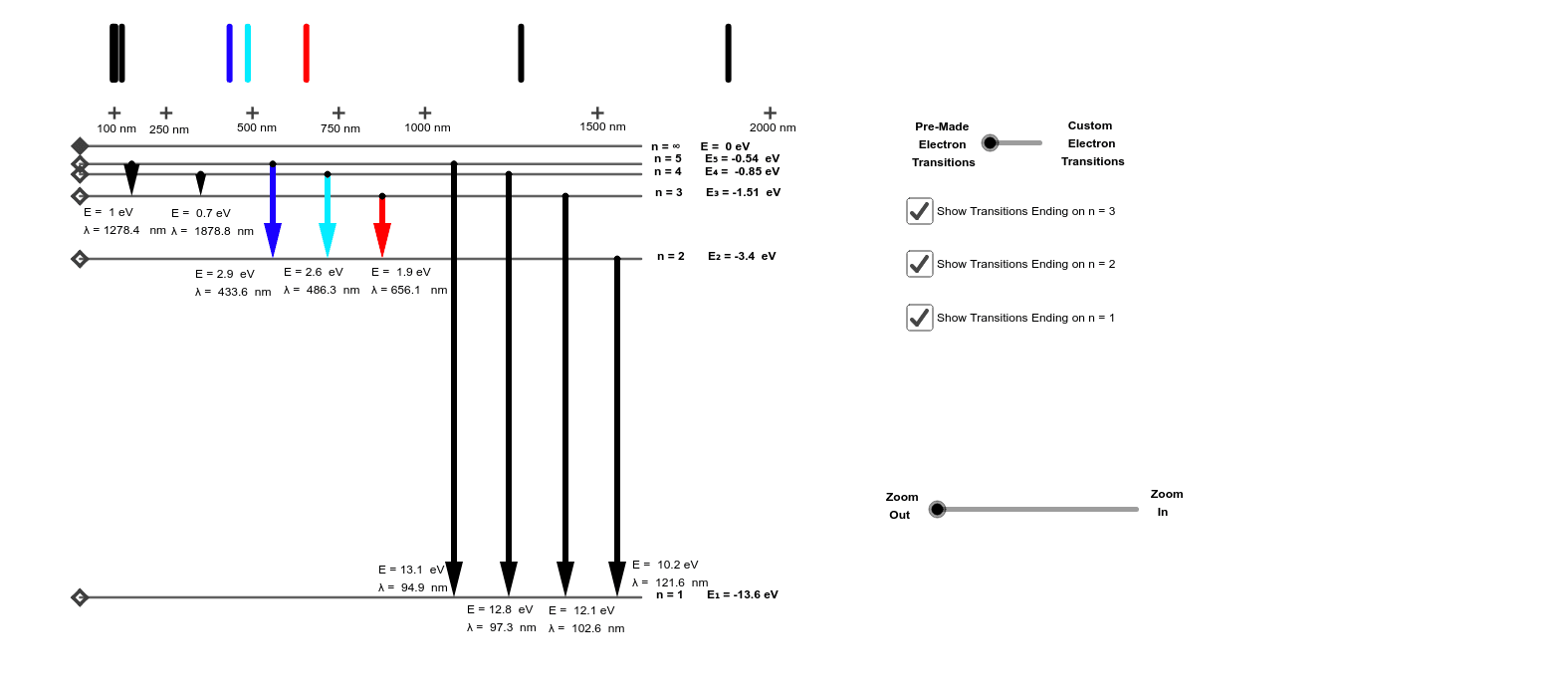
The ionization energy of an atom is the energy required to remove the electron completely from the atom. (transition from ground state n = 0 to infinity n = ∞ ). For hydrogen, the ionization energy = 13.6eV. When an excited electron returns to a lower level, it loses an exact amount of energy by emitting a photon.
Answer (1 of 3): Hydrogen has only one electron, so the only relevant force (in a classical approximation) is between the one negatively charged electron and the positively charged nucleus. In a multi-electron atom, the negatively charged electrons repel each other. We call this effect "electron...
Quantum mechanically the energy of a single photon is related to its wavelength as E γ = hc/λ Therefore, the wavelength of the emitted photon is: This perfectly describes the spectrum of the hydrogen atom! PHYS 1493/1494/2699: Exp. 7 - Spectrum of the Hydrogen Atom
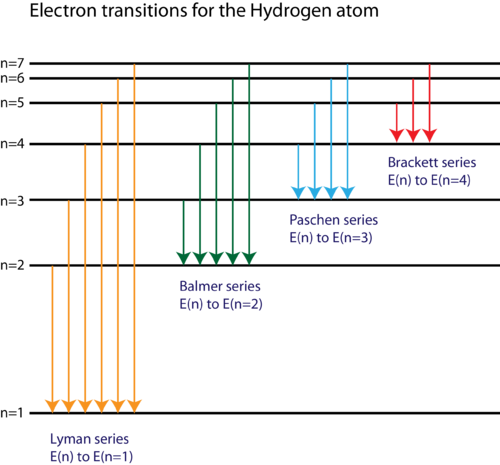
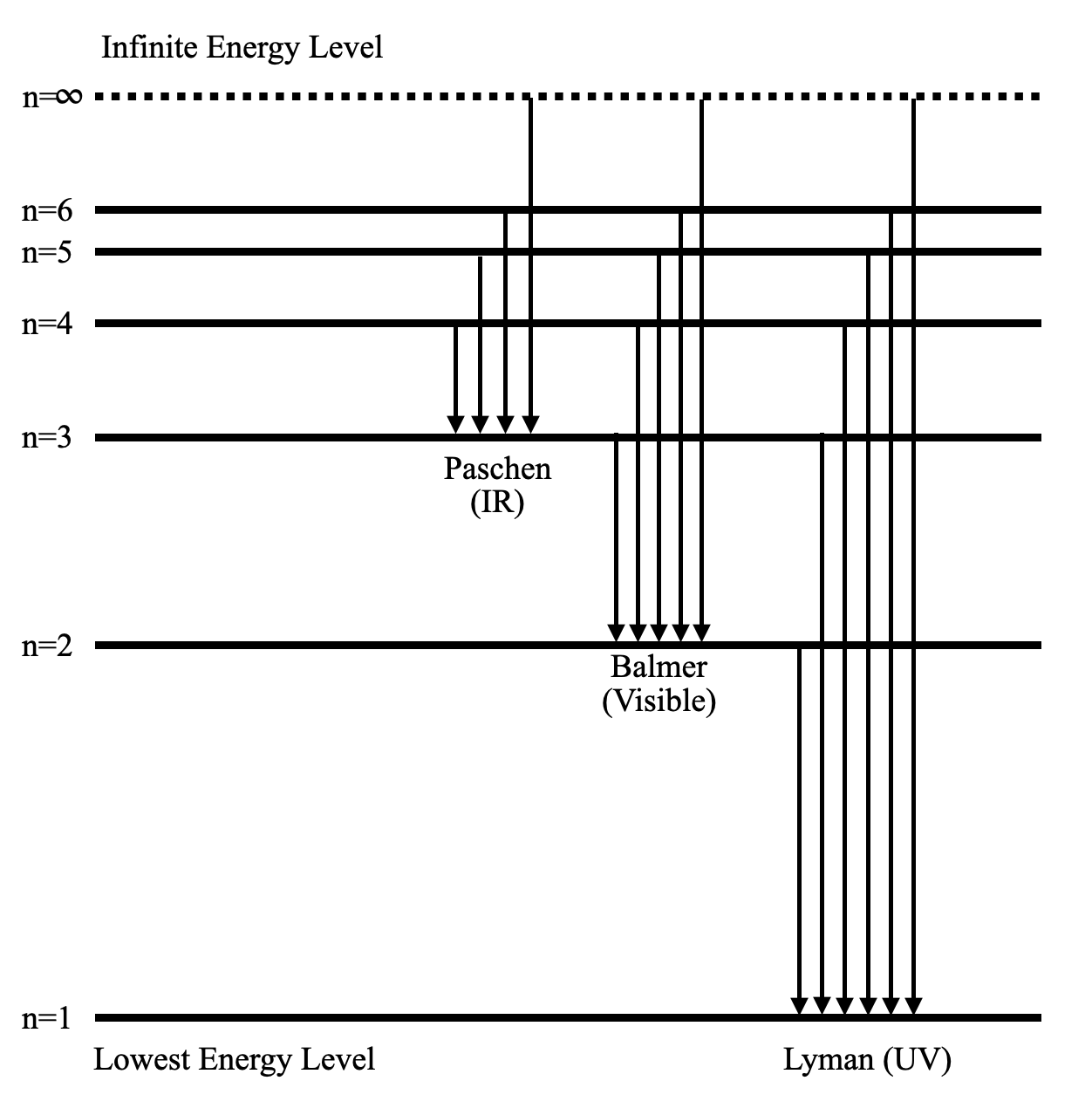
Energy Level Diagram for Hydrogen Atom: Energy level diagrams indicate us the different series of lines observed in a spectrum of the hydrogen atom. The horizontal lines of the diagram indicate different energy levels. The vertical lines indicate the transition of an electron from a higher energy level to a lower energy level.

Why Do The Size Of Gaps Energy Between Different Energy Levels Of Mercury Hg Vary As It Goes Further Away From The Mercury Atom Physics Stack Exchange
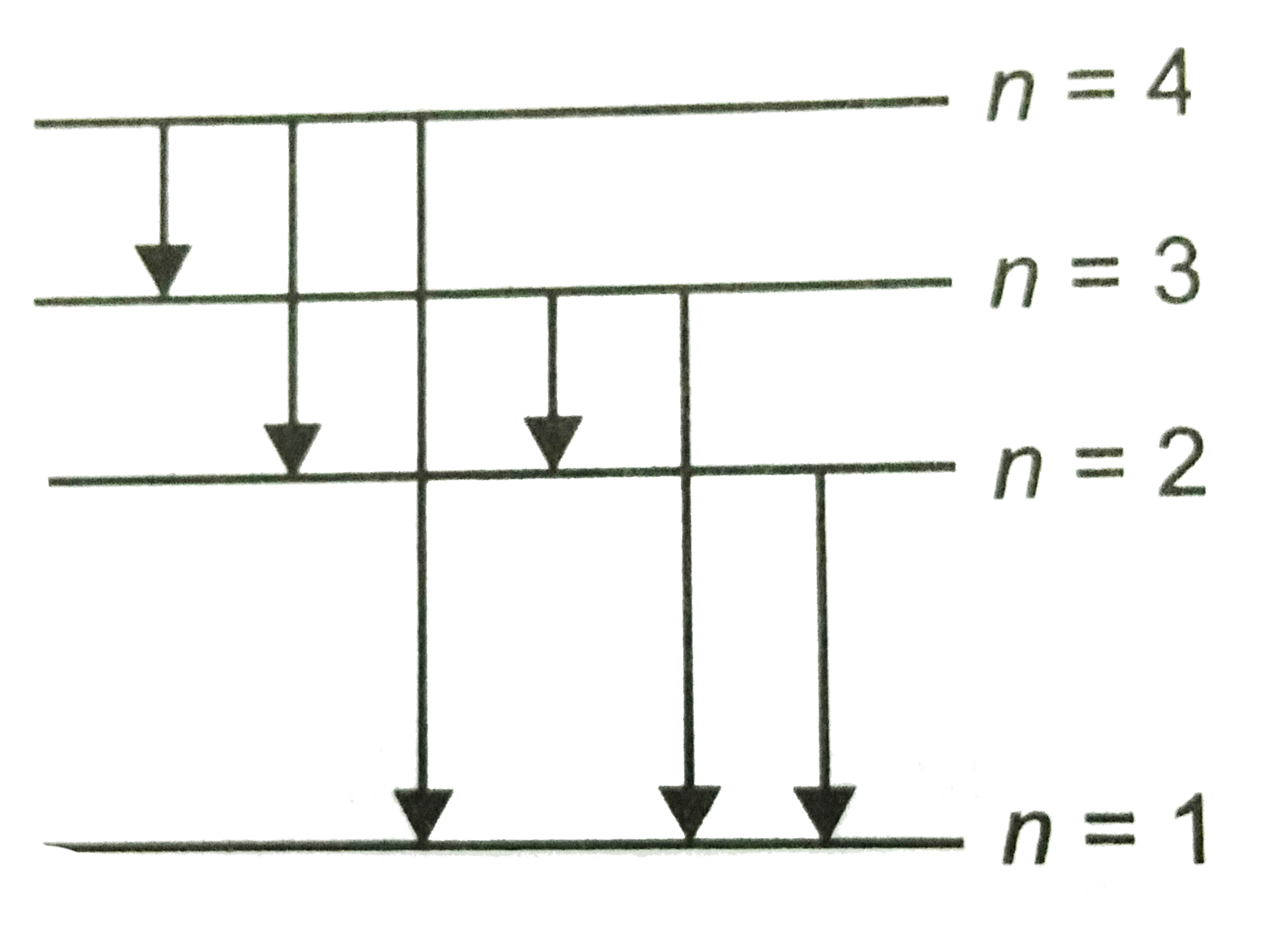
The following is a diagram of energy states and transitions in the hydrogen atom. Match each arrow with the correct response below. a) The emission line with the longest wavelength. b) The absorption line with the shortest wavelength. c) The emission line with the lowest energy. d) The absorption line with the highest energy. e) The emission line with the highest frequency.
When there is no additional energy supplied to it, hydrogen's electron is found at the 1-level. This is known as its ground state. If you supply enough energy to move the electron up to the infinity level, you have ionised the hydrogen. The ionisation energy per electron is therefore a measure of the distance between the 1-level and the ...
The energy level diagram of the hydrogen atom is given below: The transition of electrons from a higher energy level (n>1) to the ground level (n=1) gives rise to the Lyman series in hydrogen spectra.

Draw To Scale An Energy Level Diagram For Hydrogen For Levels With N 1 2 3 4 5 6 Show Label The Following Transitions On The Diagram And Calculate The Wavelengths A The Transition Associated Wit Study Com
Another question that though the internuclear distance at a particular point is constant yet potential energy keeps on increasing. I think the point where potential energy become zero we can say that attractive forces between electron and nucleus of bonding hydrogen atoms just equals the repulsive force between bonding hydrogen electrons.
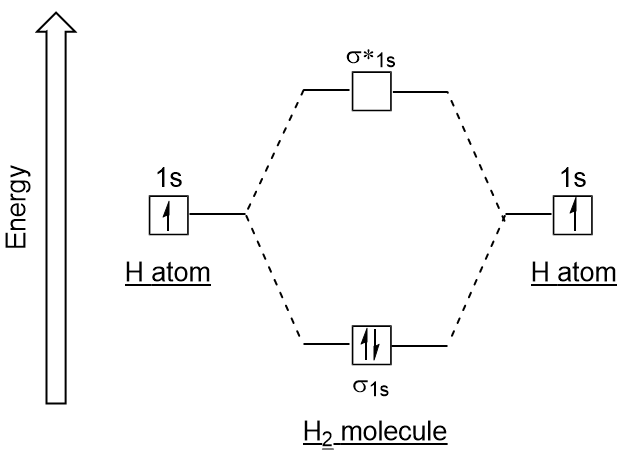
Molecular orbital energy level diagrams -Hydrogen, Hypothetical, Nitrogen, Oxygen. The filling of molecular orbitals is governed by the following principles. (i)Aufbau principle (ii)Pauli's exclusion principle and (iii)Hund's rule of maximum multiplicity. Now, let us consider some examples of homo nuclear diatomic molecules.
A Hydrogen atom has only one single electron revolving around the nucleus at the lowest energy level. When we heat a hydrogen atom, the electron gains energy ...
Let's look at the simplest atom, a neutral hydrogen atom. Its energy levels are given in the diagram below. The x-axis shows the allowed energy levels of electrons in a hydrogen atom, numbered from 1 to 5. The y-axis shows each level's energy in electron volts (eV).

The Figure Shows An Energy Level Diagram For The Hydrogen Atom Several Transitions Are Marked As I Ii Iii The Diagram Is Only Indicative And Not Be Scale Img Src Https D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images

The Energy Diagram Below Shows The Absorption Emission Spectrum For Hydrogen What Is The Smallest Energy Possible Of An Absorbed Photon A 0 66 Ev B 0 85 Ev C 3 4 Ev D 10 2 Ev
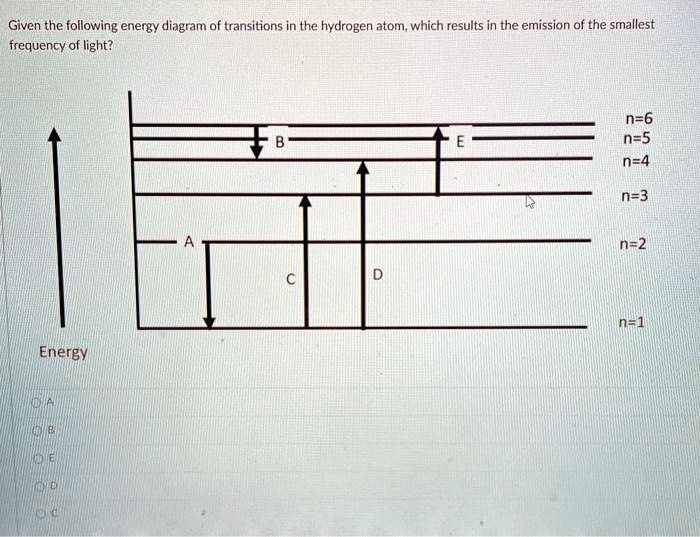
Solved Given The Following Energy Diagram Of Transitions In The Hydrogen Atom Which Results In The Emission Of The Smallest Frequency Of Light N 6 N 5 N 4 N 3 Nz2 Energy

Draw The Energy Level Diagram Of Hydrogen Showing All The Types Of Possible Transitions That Can Occur Show The Ir Uv Vl Study Com
A Rigorous Quantum Mechanical Calculation Shows That In A Hydrogen Atom A Transition Between Two Sublevels Of The Fundamental State See The Previous Problem Results In The Emission Or Absorption Of Photons Corresponding

















0 Response to "38 energy diagram for hydrogen"
Post a Comment