38 converging lens ray diagram
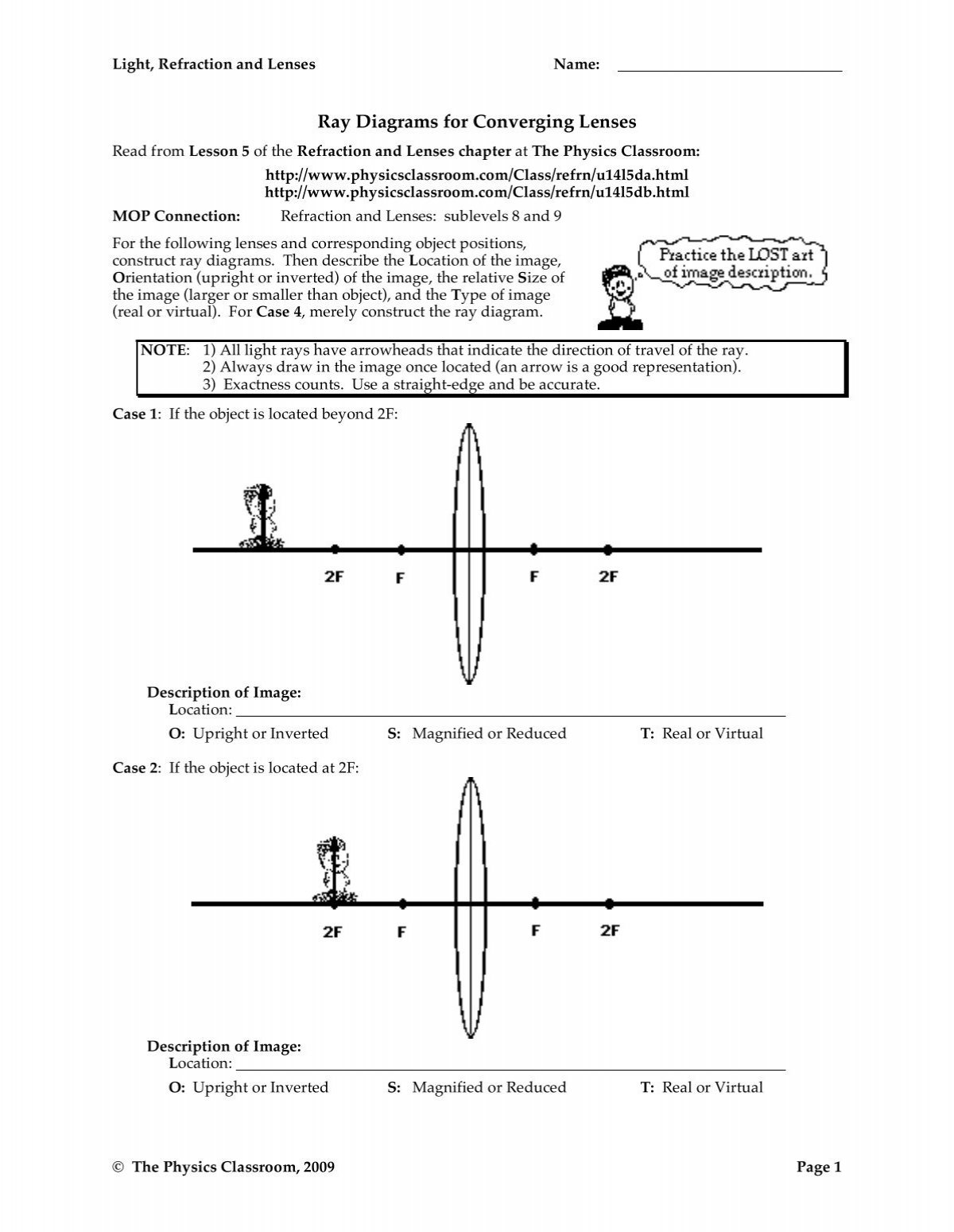
Ray Diagrams By constructing a ray diagram, we can determine where the image is located, and what it will look like. A ray diagram is a diagram showing rays that can be drawn to determine the size and location of an image formed by a mirror or lens. 21.09.2021 · Option C) shows the correct ray diagram.. But why?. First of all, we know that convex lenses are converging lenses. Now, the parallel rays of light originating from the object will undergo refraction from the convex lens and pàss through the focus.; Hence, focal length has been marked. Similarly, the the light rays originating from the object will pàss through the optical centre of the lens ...
Some ray diagrams may also show a third ray. Convex lenses The type of image formed by a convex lens depends on the lens used and the distance from the object to the lens.
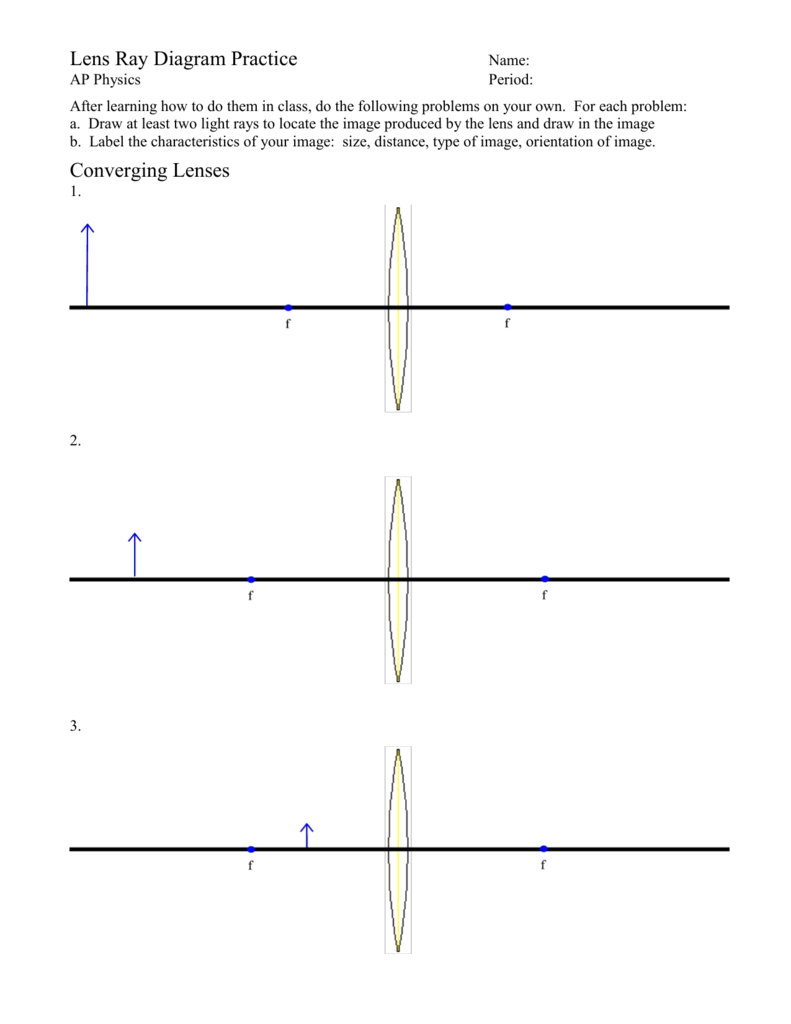
Converging lens ray diagram
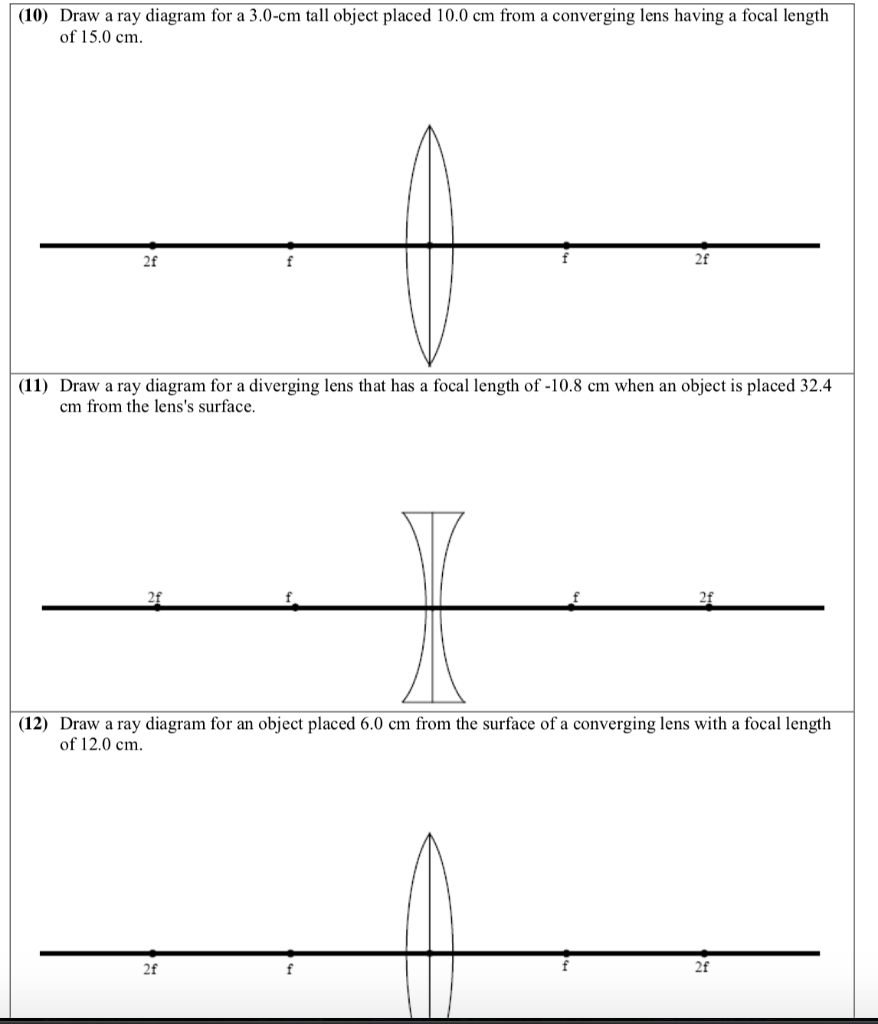
Converging Lens. Diverging Lens. F. Ray 1. F Ray 1. Ray 2. Ray 2. Ray 3 Ray 3. Images’ ’ Tracing Points Draw an arrow to represent the location of an object, then draw any two of the rays from the tip of the arrow. The image is where lines cross. Draw an arrow to represent the location of an Ray diagram for converging lenses. Converging and diverging lenses ray diagrams. There is one ray of light passing through the center of the lens. A virtual image is formed if the object is located less than one focal length from the converging lens. 10 draw a ray diagram for a 30 cm tall object placed 100 cm from a converging lens having a ... Two Converging Lens Ray Diagram. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the The third ray is not really needed, since the first two locate the image. In this section of Lesson 5, we will investigate the method for drawing ray diagrams for objects placed at various locations in front of a double convex lens.
Converging lens ray diagram. The Physics Classroom » Curriculum Corner » Refraction and Lenses » Ray Diagrams for Converging Lenses. The document shown below can be downloaded and printed. Teachers are granted permission to use them freely with their students and to use it as part of their curriculum. Visit the Usage Policy page for additional information. Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are: Here you have the ray diagrams used to find the image position for a converging lens. You can also illustrate the magnification of a lens and the difference between real and virtual images. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. A light ray that enters the lens is an incident ray. Description of how to draw ray diagrams for converging lenses for grade 10 science.
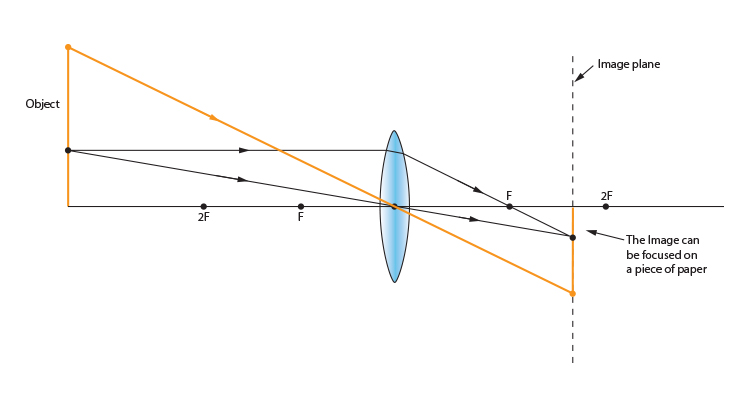
A ray diagram using this virtual object shows the location of the final image (bottom part of Figure O). Numerically, we can verify the accuracy of the ray diagram with: An arrow is placed 50 cm away from a converging lens (f= 25cm). On the other side of this first lens is a second converging lens (f. Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed ... oPhysics: Interactive Physics Simulations. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex lenses. Move the tip of the "Object" arrow to move the object. Move the point named " Focus' " to change the focal length. Move the point named " Focus' " to the right side of the lens to change to a concave lens. The behavior of this third incident ray is depicted in the diagram below. Now we have three incident rays whose refractive behavior is easily predicted. These three rays lead to our three rules of refraction for converging and diverging lenses. These three rules are summarized below. Refraction Rules for a Converging Lens. Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a ... Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from converging lens of focal length 10 cm . Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and nature of the image formed.
A virtual image is formed if the object is located less than one focal length from the converging lens. To see why this is so, a ray diagram can be used. A ray diagram for the case in which the object is located in front of the focal point is shown in the diagram at the right. Observe that in this case the light rays diverge after refracting through the lens. This interactive tutorial utilizes ray traces to explore how images are formed by the three primary types of converging lenses, and the relationship between the object and the image formed by the lens as a function of distance between the object and the focal points. A converging lens that is curved on both sides (there are two types of converging lens- concave and convex.) A converging lens causes the light rays that are travelling parallel to its principal axis to refract and cross the principal axis at a fixed point called the focal point. (This is explained in more detail below). (A ray diagram is given ... Virtual image formed by a converging lens When the object O is placed near to the lens such that the object distance u is less that the focal length f, then a virtual image is formed. A virtual image cannot be captured on screen. Virtual image is formed when u < f Ray Diagram for Lenses
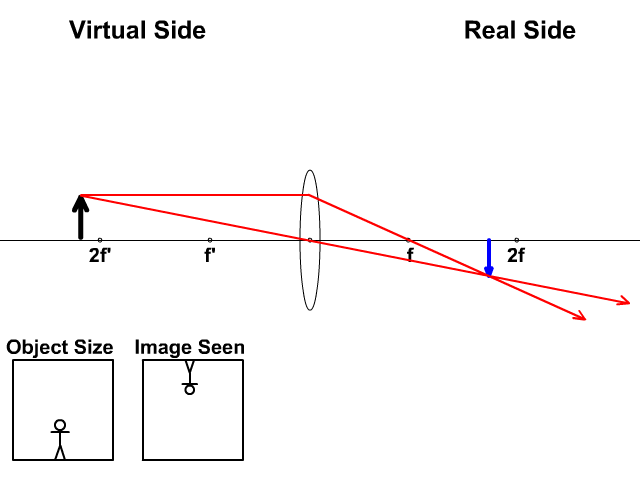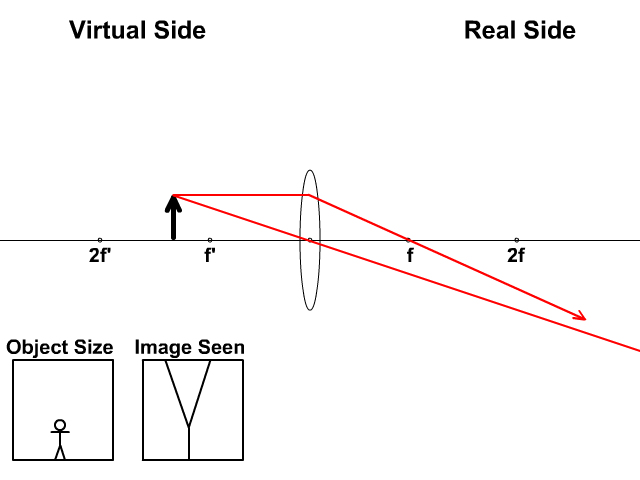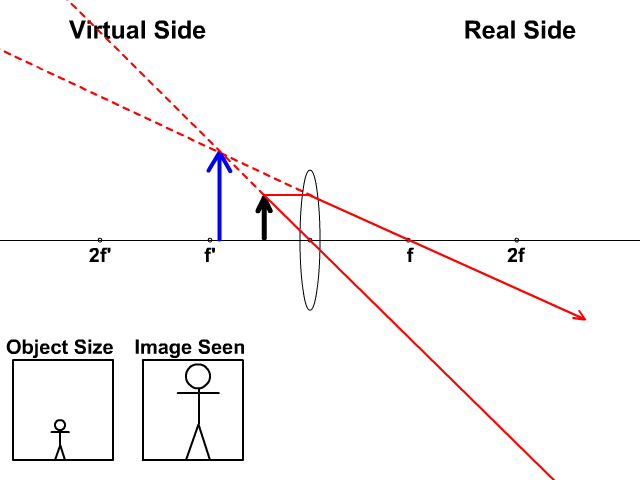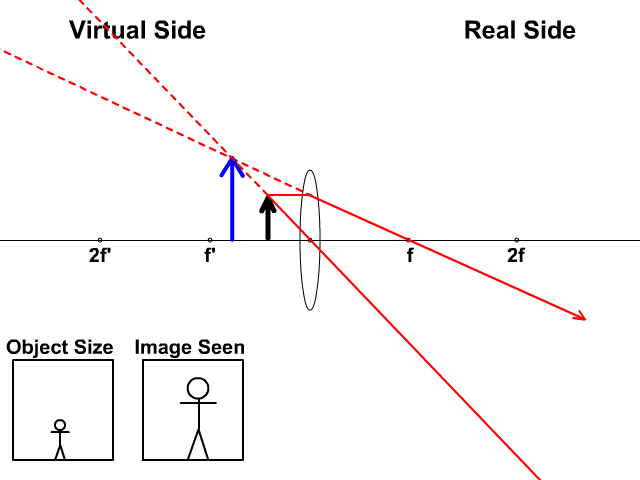
Previously in Lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the general location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by double convex lenses.Perhaps you noticed that there is a definite relationship between the image characteristics and the location where an object placed in front of a double convex lens.
A converging lens is an optical lens that converges all rays of light passing through it. The primary purpose of a converging lens is to focus the incoming rays from an object and converge them to form an image. The image can be magnified, diminished, or remain the same depending on the distance of the object from the lens.
This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. The rays parallel to the principal axis and the ray through the center of the lens are drawn.Locators allow you to drag both the object and the lens. You can change the focal length using a slider.
For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray pa
A convex lens is thicker in the middle than it is at the edges. Parallel light rays that enter the lens converge. They come together at a point called the principal focus. In a ray diagram, a ...
Application of converging lens. Trick to drawing ray diagrams for converging lens: There is one ray of light passing through the center of the lens. Always. 2 rays are enough to determine the position of image/object. The other ray of light ALWAYS passes through the focal point of the lens. Either the first focal point of the second focal point.
Explain With The Help Of A Diagram Why The Convex Lens Is Also Called Converging Lens Physics Topperlearning Com Rv8ec6gpp
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction.A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually arranged along a common axis.Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape.
Ray diagram for converging lens. Ray 1 is parallel to the axis and refracts as if from F. Ray 2 heads towards F' before refracting parallel to the axis. Ray 3 passes straight through the center of the lens. image is always virtual, upright and reduced O F I F' Ray diagram for diverging lens
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. Three principal rays can be used to locate and size the image formed by a single lens, with examples for converging and diverging lenses. The three principal rays are:. A ray from the top of the object proceeding parallel to the centerline perpendicular to the lens, passing through the principal focal point beyond the lens.
Explain With The Help Of A Diagram Why The Convex Lens Is Also Called A Converging Lens Studyrankersonline
Diverging Lenses As such, the rules for how light behaves when going through a diverging lens is a little bit different. You will be expected to be able to draw a Ray Diagram of a converging and diverging lens on our upcoming test without the rules.
The top diagram shows the formation of the virtual object where converging rays are prevented from meeting by the diverging lens. enter image. Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the focal point (i.e., in a direction such.Ray Diagrams for Lenses.
Ray diagram for a converging or diverging lens; Nice variation of the previous simulation by John Welch, showing the lens changing shape; Test yourself - what's behind the curtain? (Lenses) Puzzle - find the focal length of the lens (I) Puzzle - find the focal length of the lens (II) By converting our sims to HTML5, we make them seamlessly available across platforms and devices. The distortion ...
Shows how to draw ray diagrams to locate the image formed by a convex lens. You can see a listing of all my videos at my website, http://www.stepbystepscienc...
An object is located 4 cmcm from a converging lens. Use the ray diagram in the figure to determine the image distance s′s′ and the focal length ff of the lens. Make sure to express your answers using the sign conventions described above.(Figure 5) a.) s′=12cm and f=6cm b.) s′=12cm and f=−6cm c.) s′=−12cm and f=6cm d.) s′=−12cm
Draw a ray diagram to show how a converging lens is used as a magnifying glass to observe a small object. Mark on your diagram the foci of the lens and the position of the eye. Solution: The object is placed between the focal point F 1 and convex lens and its image is formed at the same side of the lens which is enlarged. Hence, this lens can be used as a magnifying lens. Question: 18. Draw a ...
To explain how to draw the diagrams, there are two key things to remember. 1 A converging lens refracts the light so that any ray of light parallel to the principal axis (the thick horizontal line) is turned to pass through the focal point. Rays of light parallel to the principal axis are all refracted through the focal point.
Convex Lens Ray Diagrams For lenses, the following three rays are typically used in ray diagrams. Keep in mind that an inflnite number of rays actually form the image. Ray # 1 For a lens, the flrst ray starts from the top of the object and extends parallel to the optical axis to the center of the lens. This ray, for a converging (convex) lens,
A ray entering a converging lens through its focal point exits parallel to its axis. ... The ray diagram in Figure 13 shows that the image is on the same side of the lens as the object and, hence, cannot be projected—it is a virtual image. Note that the image is closer to the lens than the object.
Convex (converging) and concave (diverging) lenses are drawn as, V W To understand image formation we use ray diagrams. Here is an example for aconvex lens: F The image of the top of the object is formed where the light rays cross. In a perfect lens all the rays from a point on the object will meet at one other point - so we only need to draw two rays! Section 1: Introduction (Refraction and ...
For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes through t

Draw Neat And Well Labelled Ray Diagrams For Image Formation By A Convex Lens When An Object Is At 2f 1
Two Converging Lens Ray Diagram. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the The third ray is not really needed, since the first two locate the image. In this section of Lesson 5, we will investigate the method for drawing ray diagrams for objects placed at various locations in front of a double convex lens.
Ray diagram for converging lenses. Converging and diverging lenses ray diagrams. There is one ray of light passing through the center of the lens. A virtual image is formed if the object is located less than one focal length from the converging lens. 10 draw a ray diagram for a 30 cm tall object placed 100 cm from a converging lens having a ...

Convex Lens Concave Lens How To Determine Focal Length Ray Diagrams Image Properties Real Virtual Inverted Size Correction Of Eye Defects Causes Of Long Sight Short Sight Igcse Gcse 9 1 Physics Revision Notes
Converging Lens. Diverging Lens. F. Ray 1. F Ray 1. Ray 2. Ray 2. Ray 3 Ray 3. Images’ ’ Tracing Points Draw an arrow to represent the location of an object, then draw any two of the rays from the tip of the arrow. The image is where lines cross. Draw an arrow to represent the location of an
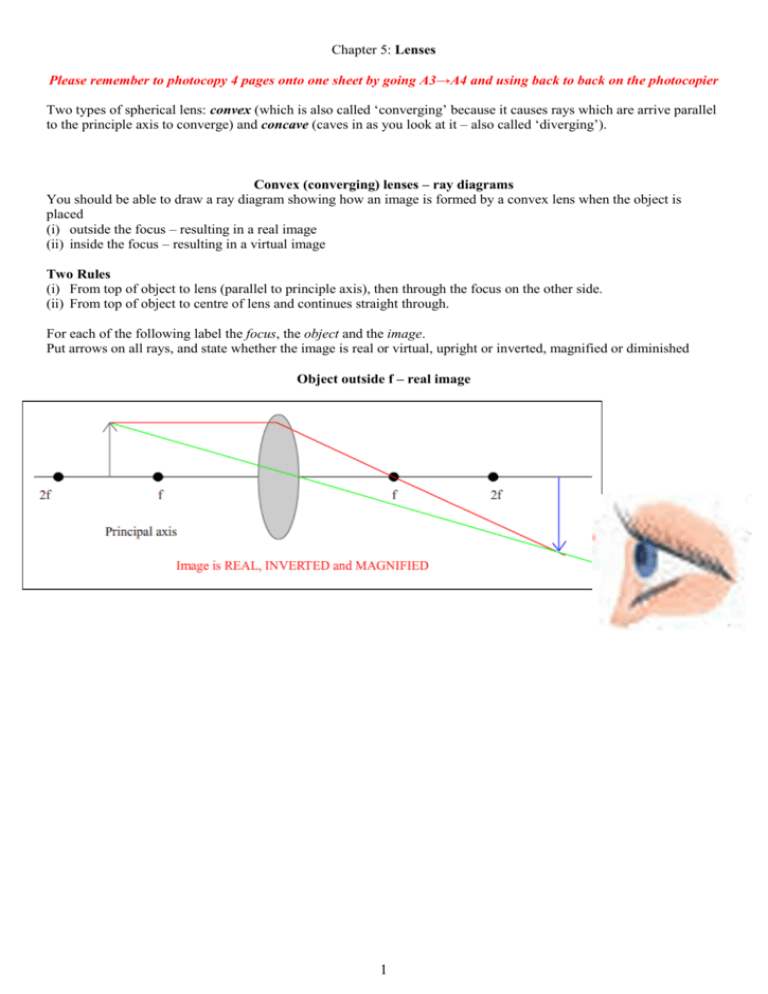








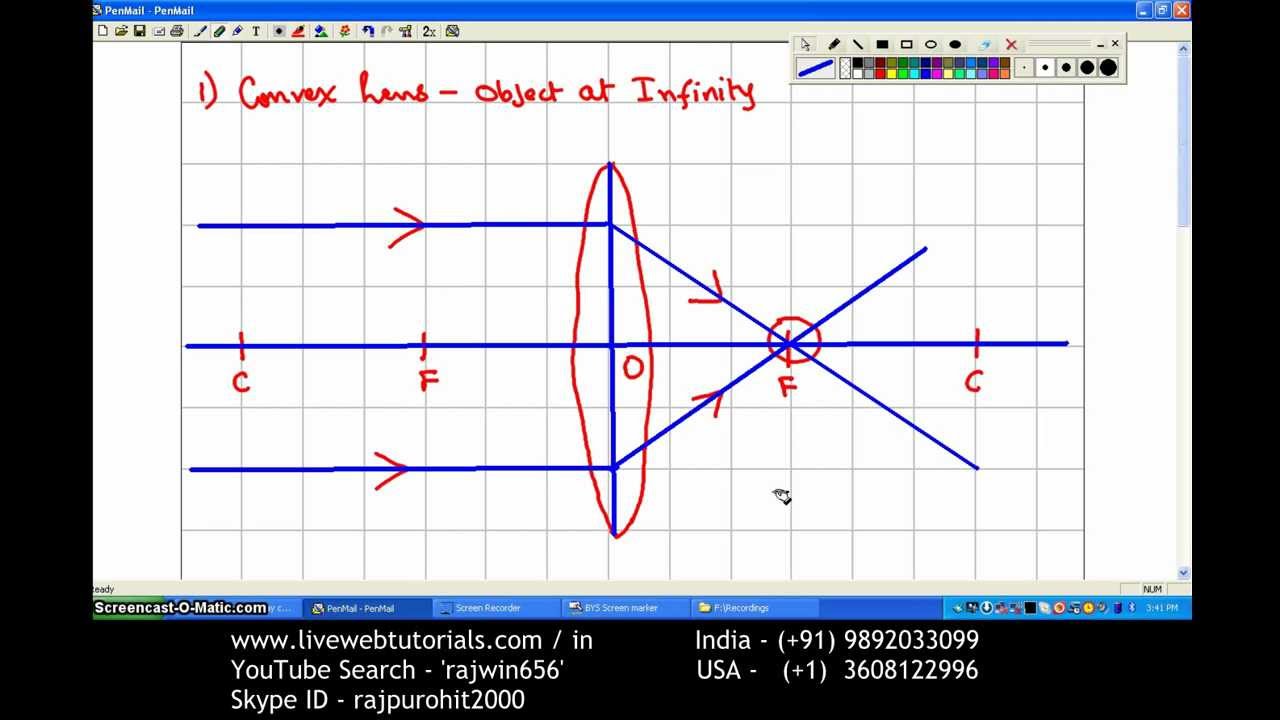


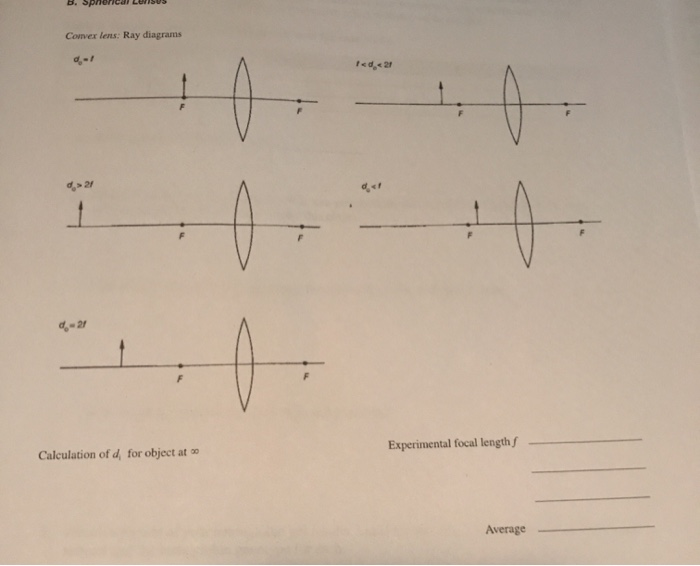








0 Response to "38 converging lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment