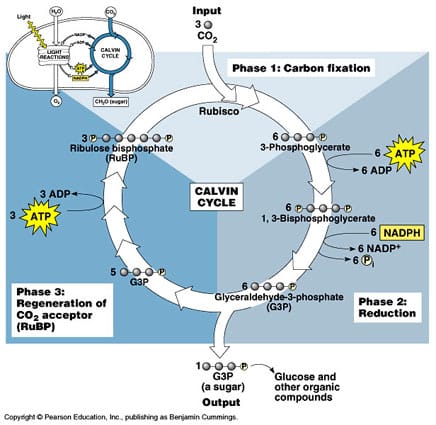
35 the calvin cycle diagram
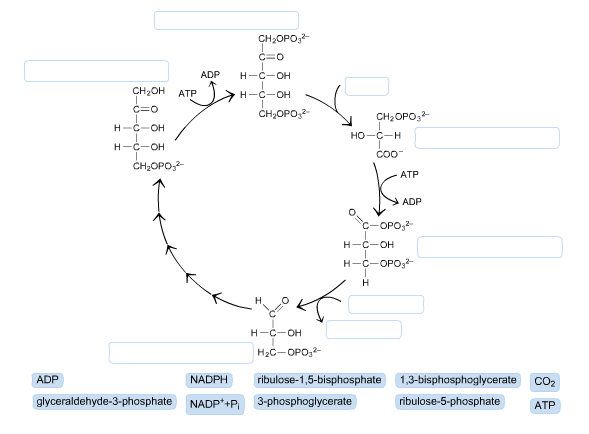
On diagram 5, fill in the labels with the following descriptions to show the connections between the light reactions and the Calvin cycle. Left side, Top to bottom: ATP, NADPH, O2, Right side, top to bottom: CO2, G3P In the Calvin cycle, carbon dioxide molecules (CO2) are combined with each other and with the electrons and H's from NADPH to form glucose (C6H12O6). How can cells store the sugar that is produced in photosynthesis? It is stored as starch. Label the diagram below to summarize the two stages of photosynthesis. Use the word bank below the ...
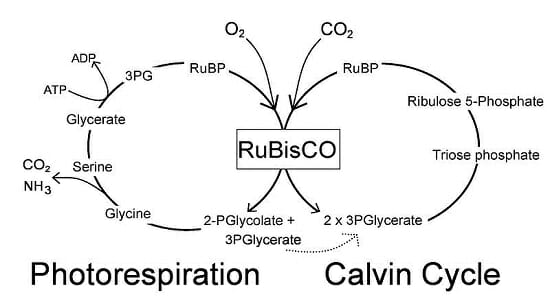
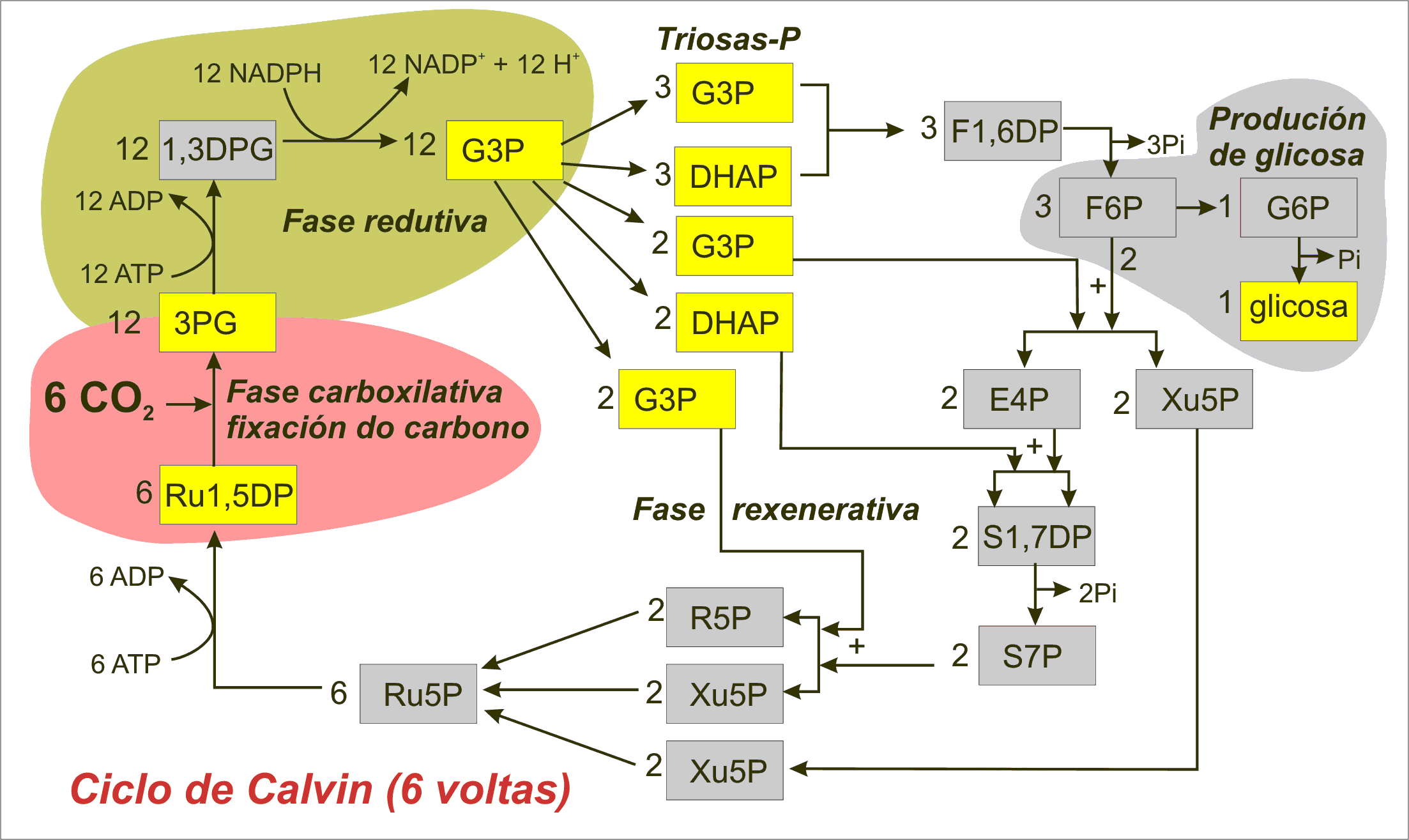
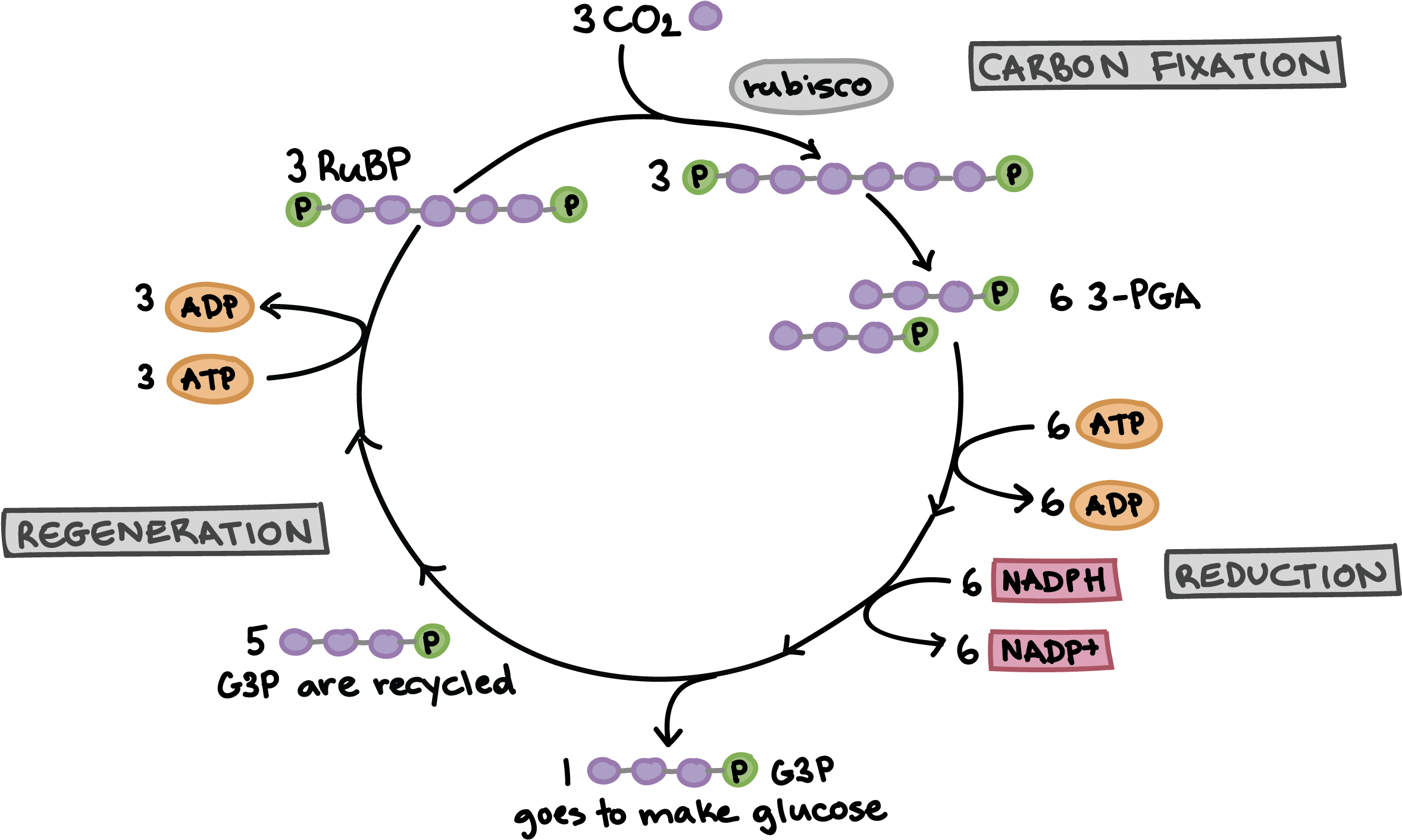
Mechanism of Calvin Cycle. Carbon dioxide bio fixation is done in Calvin Cycle in 13 reactions catalyzed by 11 enzymes in stroma. The cycle has 3 phases where the carbon dioxide is reduced and Ribulose - 1, 5 - Bisphosphate is regenerated. Ribulose - 1, 5 - Bisphosphate acts as a primary skeleton to carry CO2 and produce starch.
The calvin cycle diagram
The Calvin cycle is a set of light independent redox reactions that occur during photosynthesis and carbon fixation to convert carbon dioxide into the sugar glucose. These reactions occur in the stroma of the chloroplast, which is the fluid-filled region between the thylakoid membrane and inner membrane of the organelle. Here is a look at the redox reactions that occur during the Calvin cycle. Calvin cycle, also known as the light independent reaction, is the second stage of photosynthesis which is a very important stage. In this stage the carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere is taken in by the plant and is converted into carbon in the form of sugar, lipids and protein, in the form of glucose. That harvest is indicated in the lower left side of the Calvin Cycle diagram. Phase III: Regeneration of RuBP Ribulose-5-phosphate. Removing a G3P from the cycle leaves us with 15 carbon atoms: there were 18 carbons immediately following the carbon fixation phase, and we just removed three carbons in G3P. To prepare to run the cycle again, the ...
The calvin cycle diagram. Which substance from the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis is a source of energy for the Calvin Cycle? Calvin Cycle DRAFT. 10th - 11th grade. 444 times. Biology. 78% average accuracy. 3 years ago. arreis018. 1. Save. Edit. Edit. Calvin Cycle DRAFT. 3 years ago. by arreis018. Played 444 times. 1. 10th - 11th grade . Biology. 78% ... reactant in the Calvin cycle from the atmosphere; combines with RuBP in carbon fixation via the catalyst rubisco NADPH electron carrier that provides high-energy electrons for photosynthesis; reduced form of NADP+; product of the light dependent reaction that goes to the Calvin cycle to aid in the reduction of a large six carbon molecule to PGAL. The Calvin cycle, or the light-independent (dark) reactions of photosythesis. Created by Sal Khan. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Email. The Calvin cycle. Photosynthesis: Calvin cycle. This is the currently selected item. The Calvin cycle. Practice: The Calvin cycle. The Calvin cycle is the cycle of chemical reactions performed by plants to “fix” carbon from CO2into three-carbon sugars. Later, plants and animals can turn these three-carbon compounds into amino acids, nucleotides, and more complex sugars such as starches. This process of “carbon fixation” is how most new organic matter is created. The sugars created in the Calvin cycle are also used by plants for long-term energy storage, unlike ATP which is used up quickly after it is created. These plantsugars can also become a source of energy for animals who eat the plants, and predators who eat those herbivores. The Calvin cycle is also sometimes referred to as the “light independent” reactions of photosynthesis, since it is not powered directly by photons from the Sun. Instead, the Calvin cycle is powered by ATP and NADPH, which are created by harnessing the energy from photons in the light-dependent reactions.
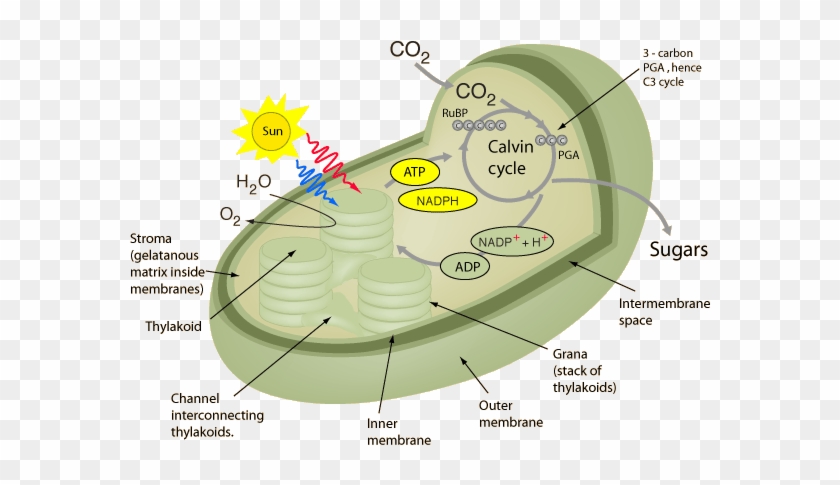
Schematic diagram of light reaction and Calvin cycle C4 cycle or Hatch and Slack pathway It is the alternate pathway of C3 cycle to fix CO 2. In this cycle, the first formed stable compound is a 4 carbon compound viz., oxaloacetic acid. Hence it is called C4 cycle. The In the Calvin cycle, carbon atoms from are fixed (incorporated into organic molecules) and used to build three-carbon sugars. This process is fueled by, and dependent on, ATP and NADPH from the light reactions. Unlike the light reactions, which take place in the thylakoid membrane, the reactions of the Calvin cycle take place in the stroma (the ... Calvin Cycle Diagram. angelo. November 8, 2021. An Overview Of Photosynthesis Cooperation Of The Light Reactions And The Calvin Cycle Photosynthesis Biology Classroom Study Chemistry. Simple Diagram Of The Calvin Cycle The Light Independent Reaction Of Photosynthesis Biology Lessons Biochemistry Notes Biology Classroom. Calvin cycle also referred to as dark reaction of photosynthesis is a light independent reaction. They take place in the stroma of the chloroplast. Accordingly, the formation of sugar compounds with carbon-dioxide as the starting compound drives Calvin cycle. However, there is no activation of electrons in the Calvin cycle.
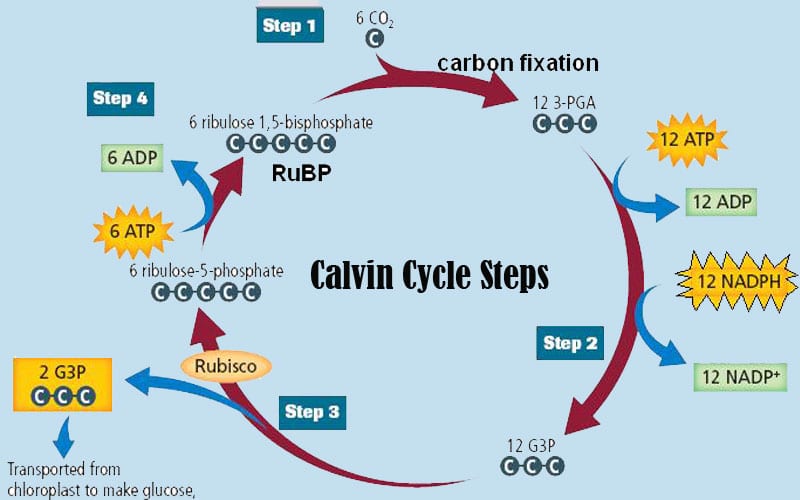
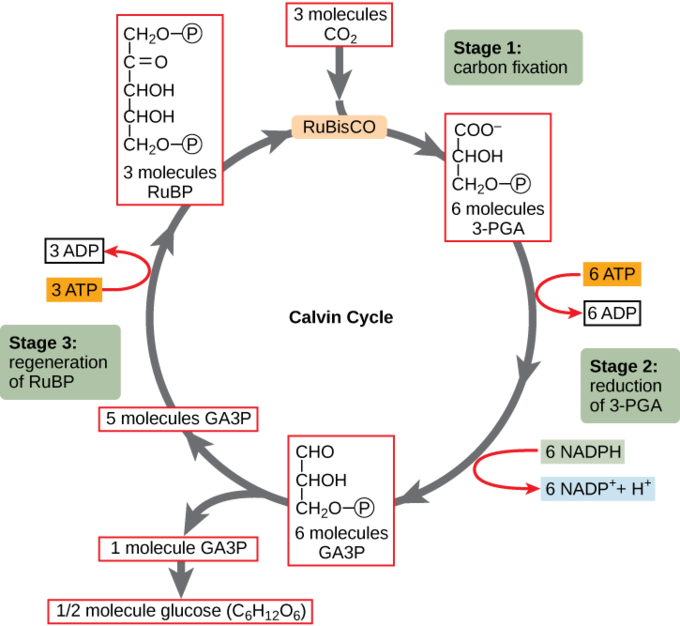
The Calvin cycle reactions (Figure 5.15) can be organized into three basic stages: fixation, reduction, and regeneration. In the stroma, in addition to CO 2, two other chemicals are present to initiate the Calvin cycle: an enzyme abbreviated RuBisCO, and the molecule ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). RuBP has five atoms of carbon and a phosphate ... The Calvin cycle is a process that plants and algae use to turn carbon dioxide from the air into sugar, the food autotrophs need to grow. Every living thing on Earth depends on the Calvin cycle. Plants depend on the Calvin cycle for energy and food.Other organisms, including herbivores, also depend on it indirectly because they depend on plants for food. The Calvin Cycle LSM 3.3-3 The molecule released from the Calvin cycle is used to form. This can be stored as molecules. is reduced using to form . One molecule of leaves the cycle as a final product, while the other five molecules continue through the Calvin cycle. The five molecules go through a series of reactions The Calvin cycle occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast. It uses ATP and NADPH, produced during the light reactions, to synthesise sugars by fixing CO 2. The Calvin cycle has three main stages: Carboxylation: It is the first phase of the Calvin cycle. It involves the carboxylation of ribulose bisphosphate by using CO 2. The reaction is ...
The Calvin cycle has three stages. In stage 1, the enzyme RuBisCO incorporates carbon dioxide into an organic molecule. In stage 2, the organic molecule is reduced. In stage 3, RuBP, the molecule that starts the cycle, is regenerated so that the cycle can continue. In summary, it takes six turns of the Calvin cycle to fix six carbon atoms from ...

Photosynthesis The Calvin Cycle Full Step By Step Explanation Science Biology Final Exam Review Instant Download Science Notes Science Biology Biology College
The Calvin cycle reactions (Figure 5.15) can be organized into three basic stages: fixation, reduction, and regeneration.In the stroma, in addition to CO 2, two other chemicals are present to initiate the Calvin cycle: an enzyme abbreviated RuBisCO, and the molecule ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP).RuBP has five atoms of carbon and a phosphate group on each end.
This video is the second of two parts. Part A examined the light reactions. This part provides, in music and rhyme, a detailed explanation of the Calvin Cycl...
The carbon skeletons of five molecules of G3P are rearranged by the last steps of the Calvin cycle into 3 molecules of RuBP - to accomplish this, the cycle spends 3 more molecules of ATP - RuBP is now prepared to receive CO2 and restart the cycle again...
The Calvin cycle (C 3-cycle) or PCR-cycle can be divided into three stages: (a) Car-boxylation, during which atmospheric CO 2 combines with 5-C acceptor molecule ribulose 1, 5-bisphosphate (RuBP) and converts it into 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3-PGA); (b) Reduction, which consumes ATP + NADPH (produced during primary photochemical reaction) and converts 3-PGA into 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde ...

Photorespiration Vector Illustration Labeled Photosynthesis Education Scheme Diagram With Oxidative Photosynthetic Carbon Cycle Rubisco Photorespiration And Calvin Cycle Explanation Infographic Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock
The Calvin cycle diagram below shows the different stages of Calvin Cycle or C3 cycle that include carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration. Stages of C3 Cycle. Calvin cycle or C3 cycle can be divided into three main stages: Carbon fixation.
History of Calvin Cycle: The cycle was discovered by Calvin, Benson and their colleagues in California, U.S.A. They fed Chlorella and Scenedesmus with radioactive 14 C in carbon dioxide. Radioactive carbon, 14 C has a half life of 5568 years. Therefore, the path of CO 2 fixation can be easily traced with its help.
Diagram of the Calvin cycle. The correct answer is A. The Calvin cycle uses ATP to make glucose. The Calvin cycle and Krebs cycle both require energy molecules in order to complete their reactions. However, the Calvin cycle uses some ATP to make glucose, while the Kreb's cycle produces some ATP in the process of glucose modifications.
Calvin Cycle Diagram. The Calvin cycle occurs in the chloroplast stroma, the region between the thylakoid membrane and the organelle’s inner membrane just after completing the light reaction of photosynthesis. The light reaction helps the Calvin cycle by providing ATP which is its energy source, and NADPH for reducing ability.

In The Given Representation Of Calvin Cycle Identify A B And C And Slect The Correct Option Img Src Https D10lpgp6xz60nq Cloudfront Net Physics Images Ncert Fing Bio Obj Xi Php C13 E01 060 Q01 Png Width 80
What makes the Calvin cycle a cycle? 13. Complete the diagram of the Calvin cycle by filling in the missing labels. The Calvin cycle uses carbon dioxide molecules as well as ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions to make sugars. The reactions of the Calvin cycle use ATP and NADPH as energy sources. They do not directly require light.
The Calvin cycle, Calvin-Benson-Bassham (CBB) cycle, reductive pentose phosphate cycle (RPP cycle) or C3 cycle is a series of biochemical redox reactions that take place in the stroma of chloroplast in photosynthetic organisms.The cycle was discovered in 1950 by Melvin Calvin, James Bassham, and Andrew Benson at the University of California, Berkeley by using the radioactive isotope carbon-14.

Bogobiology The Calvin Cycle One Of My Favorite Diagrams Photosynthesis Calvincycle Apbio Lightindependentreactions Studying Science Diagram Facebook
The Calvin cycle, which is also called the reductive pentose phosphate cycle, is the most widespread CO 2 biofixation pathway among autotrophs. It exists in plants and microalgae, as well as photoautotrophic and chemoautotrophic bacteria. As shown in Fig. 15.1, the key step of the Calvin cycle is catalyzed by the enzyme ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase, which fixes a CO 2 molecule onto a ...
That harvest is indicated in the lower left side of the Calvin Cycle diagram. Phase III: Regeneration of RuBP Ribulose-5-phosphate. Removing a G3P from the cycle leaves us with 15 carbon atoms: there were 18 carbons immediately following the carbon fixation phase, and we just removed three carbons in G3P. To prepare to run the cycle again, the ...
Calvin cycle, also known as the light independent reaction, is the second stage of photosynthesis which is a very important stage. In this stage the carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere is taken in by the plant and is converted into carbon in the form of sugar, lipids and protein, in the form of glucose.
The Calvin cycle is a set of light independent redox reactions that occur during photosynthesis and carbon fixation to convert carbon dioxide into the sugar glucose. These reactions occur in the stroma of the chloroplast, which is the fluid-filled region between the thylakoid membrane and inner membrane of the organelle. Here is a look at the redox reactions that occur during the Calvin cycle.
Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Essay Diamond Calvin Cycle 3d Model Free Transparent Png Clipart Images Download

0614 Calvin Cycle Medical Images For Powerpoint Powerpoint Shapes Powerpoint Slide Deck Template Presentation Visual Aids Slide Ppt

Simple Diagram Of The Calvin Cycle The Light Independent Reaction Of Photosynthesis Biology Lessons Biology College Biology Notes

Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle In Chloroplast Calvin Cycle Makes Sugar From Carbon Dioxide This Diagram Shows Simplified






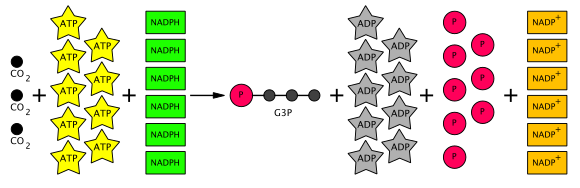


/2000px-Calvin-cycle4.svg-58a397c25f9b58819c5ba0d6.png)






0 Response to "35 the calvin cycle diagram"
Post a Comment