38 fatty acid structure diagram
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids (With Diagram) In mammals, the major pathway of the biosynthesis of fatty acids is an extra-mitochondrial process (cytosolic and/or microsomal). To produce fatty acids from the precursor which is acetyl-coA, the cells must be able to reduce the ketone groups: this will be achieved thanks to NADPH; they must also be able to form C— C bonds in order to condense acetyl radicals: although the methyl group of ... Structure of unsaturated fatty acids in 2D system The behaviour of Langmuir monolayers corresponding to unsaturated fatty acids belonging to the omega-9 (oleic acid), omega-3 (α-linolenic and stearidonic acids) and omega-6 (linoleic, γ-linolenic and eicosadienoic acids) series was studied in order to get insight into the influence of various factors (such as subphase temperature, length, degree of unsaturation and position of the double ...
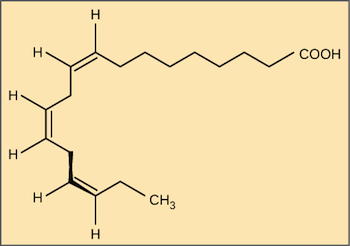
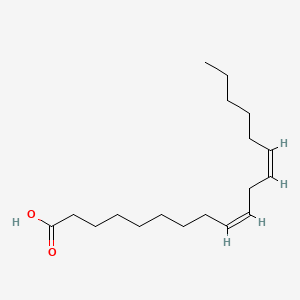
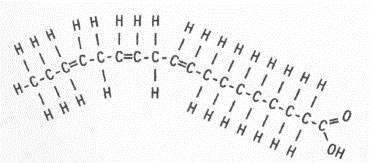
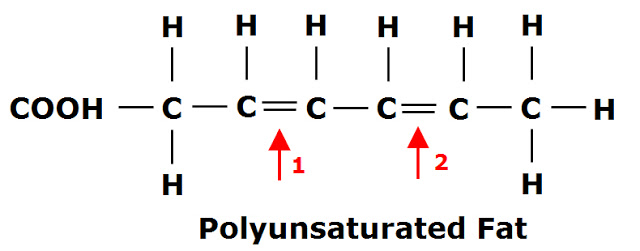
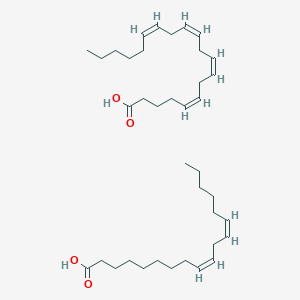
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid - an overview | ScienceDirect ... 5.2.1 PUFA structure Polyunsaturated fatty acids are hydrocarbon chains containing two or more double bonds. The characterisation of PUFAs as either an n-3 PUFA or n-6 PUFA refers to the position of the first double bond relative to the methyl end of the fatty acid. In nature, double bonds are usually in the cis (bent) format.
Fatty acid structure diagram
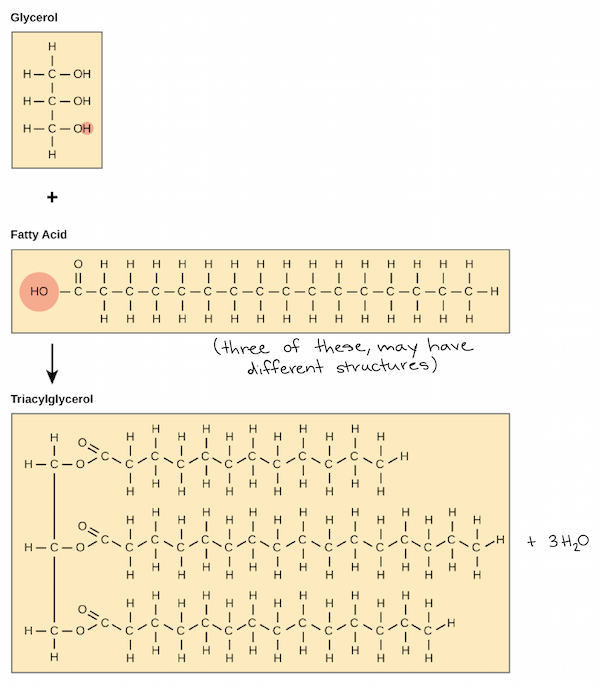
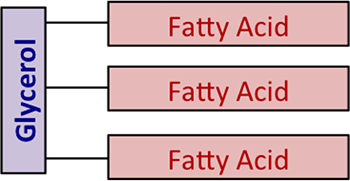
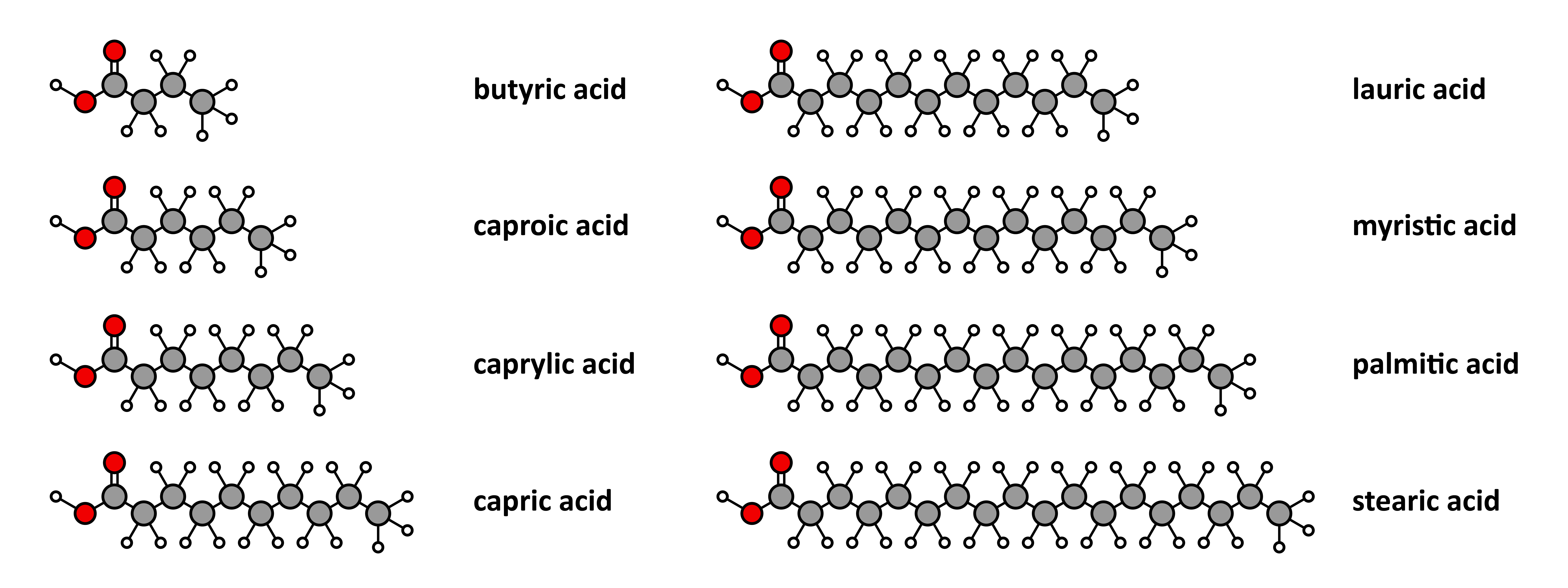
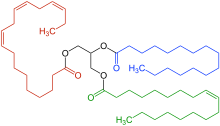
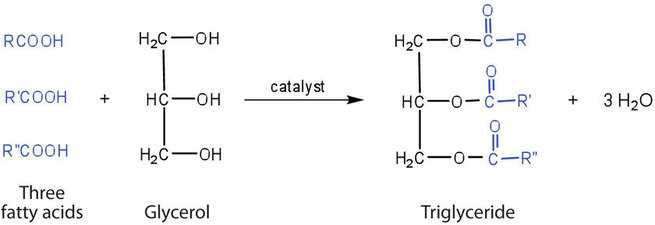
Fatty acid - Wikipedia Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 6 to 12 carbons, which can form medium-chain triglycerides. Long-chain fatty acids (LCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 13 to 21 carbons. Very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 22 or more carbons. Saturated fatty acids Solved Human Digestive System 10. Which structure | Chegg.com Which structure represented in the diagram below absorbs most of the fatty acids and glycerol from the small intestines 12. Base your answer to the following question the diagram below. For each statement select the organ that is most closely associated with the statement below. A number may be used more than once not at all.] 0. Structure of a Triglyceride Molecule | Healthfully Structure. The main molecule that starts the structure of a triglyceride is glycerol. Glycerol is a three-carbon molecule with three hydroxyl groups on them. These hydroxyl groups are the site of an ester reaction with three fatty acid molecules. The fatty acids can be different types, and the fatty acid structure defines the type of triglyceride.
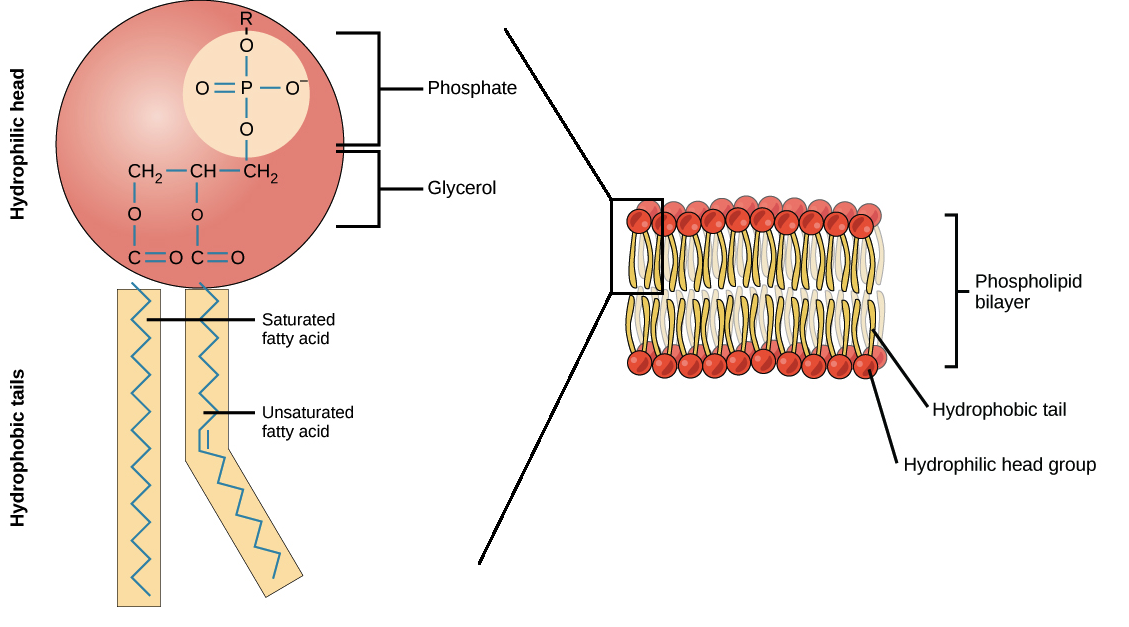
Fatty acid structure diagram. Chemical structure of trans fatty acids (trans fats ... Download scientific diagram | Chemical structure of trans fatty acids (trans fats) from publication: Trans fats in New Zealand: Time for labelling regulations? | Trans fats (trans fatty acids) are ... Fatty Acid Structure | Saturated Fatty Acid Structure ... The fatty acids structure are chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms that are linked together. They are linear chains of carbon and hydrogen atoms. There is a carboxyl group at the end of the fatty... FATTY ACIDS | Biology - Quizizz The diagram shows the structure of palmitic acid. What type of fatty acid is palmitic acid? (apply knowledge using the picture) answer choices saturated trans fat cis fat (monounsaturated) polyunsaturated Question 11 30 seconds Q. What type of molecule is shown in this diagram? answer choices trans unsaturated fatty acid cis unsaturated fatty acid Structure of Fatty Acids | Download Scientific Diagram The structures of a few of these compounds are shown in Figure 1. In this note, all compounds will be referred to as fatty acids, even though the actual compounds may be aldehydes, hydro- carbons,...
Fatty Acids -- Overview - University of Utah The elements of fatty acid structure are quite simple. There are two essential features: The chain length ranges from 4 to 30 carbons; 12-24 is most common. The chain is typically linear, and usually contains an even number of carbons. The many fatty acids which occur naturally arise primarily through variation of chain length and degree of ... Trans fatty acids: definition, structure, health effects ... Unsaturated fatty acids most commonly have their double bonds in cis configuration; the other, less common configuration is trans. Cis bond causes a bend in the fatty acid chain, whereas the geometry of trans bond straightens the fatty acid chain, imparting a structure more similar to that of saturated fatty acids. CONTENTS Fatty acids: definition, structure, and classification Fatty acids (FAs) are a class of lipids consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, arranged as a linear carbon chain skeleton of variable length, generally with an even number of atoms, with a carboxyl group at one end. Fatty acids from 2 to 30 carbons or more occur, but the most common and important ones contain between 12 and 22 carbon atoms and are found in many different animal and plant ... Fat and Cholesterol Metabolism Notes: Diagrams ... Fatty acid synthesis Fatty acid oxidation Ketone body metabolism Osmosis High-Yield Notes This Osmosis High-Yield Note provides an overview of Fat and Cholesterol Metabolism essentials. All Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently.
Fatty acid molecule with micelle and side view structure ... You can use this royalty-free vector image "Fatty acid molecule with micelle and side view structure outline diagram" for personal and commercial purposes according to the Standard or Extended License. The Standard License covers most use cases, including advertising, UI designs, and product packaging, and allows up to 500,000 print copies. structure fatty acid Flashcards and Study Sets | Quizlet fatty acid structure. saturated fatty acid have. all the available bonds in a saturated…. unsaturated fatty acids have. the double bonds makes the. a single bond between carbons in the hydrocarbon chain. are saturated with hydrogen. double bonds between carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain. molecule bends which means they cannot pack ... Fatty Acid Structure | Examples | Types | Physical ... Fatty acids are composed of long hydrocarbon chains terminated by carboxylic acid groups. Fatty acids are basically the primary derivative of lipids. Chain length from 4 to usually 24C atoms. They contain even number of C atoms majority of fatty acids are those containing 16 and 18 C atoms. Fatty Acid Structure Described Below. Fatty Acids: Definition, Structure, Function & Types ... Fatty Acid Structure Fatty acids are composed of carbon chains containing a methyl group at one end and a carboxyl group at the other.
IB HL 2.1.S1 - mysciencesquad.weebly.com Draw the molecular diagram of a saturated fatty acid. Identify the carboxyl and methyl groups on a fatty acid. Draw the generalized structure of an amino acid. Label the amine group, carboxyl group, alpha carbon and R group on an amino acid. Complex macromolecules may commonly be comprised of smaller, recurring subunits called monomers
PDF Fatty Acids: Structures and Introductory article Properties The influence of a fatty acid's structure on its melting point is such that branched chains and cis double bonds will lower the melting point compared with that of equiv-alent saturated chains. In addition, the melting point of a fatty acid depends on whether the chain is even- or odd-numbered; the latter have higher melting points.
hhh Flashcards | Quizlet the molecule shown in the diagram is a _____ fatty acid. polyunsaturated O> OH. which of the following options correctly relate the melting points of fatty acids to their molecular structure? Increasing the number of C atoms in the hydrocarbon chain raises the melting point
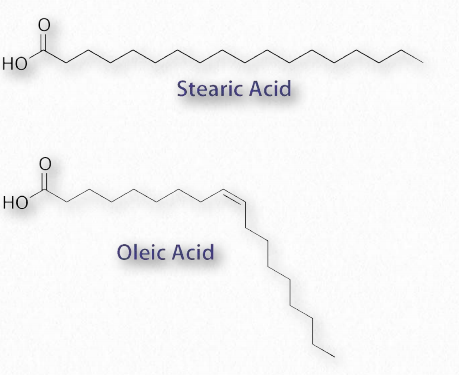
Notes on Fatty Acids (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion In unsaturated fatty acids, at least two but usually no more than six of the carbon atoms of the hydrocarbon chain are linked together by double bonds. The two most common unsaturated fatty acids are oleic acid and linoleic acid, depicted in Figure 6-1 along with the saturated fatty acid stearic acid.
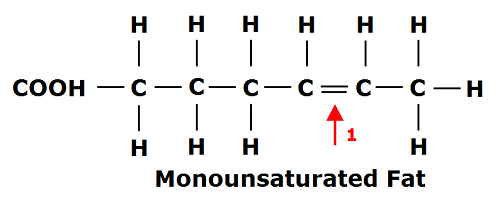
The Benefits of Monounsaturated Fatty Acids To illustrate this, the diagram below shows the chemical structure of a monounsaturated fatty acid; The chemical structure of a monounsaturated fatty acid, showing the double carbon bond. As you can see, there is a double bond between two carbon (C) atoms instead of those carbon atoms being bound to hydrogen (H).
Fatty Acid Molecule Vector & Photo (Free Trial) | Bigstock Fatty acid molecule with micelle and side view structure outline diagram. Labeled educational chain with hydrophobic nonpolar tail and hydrophilic polar head vector illustration. Isolated closeup.
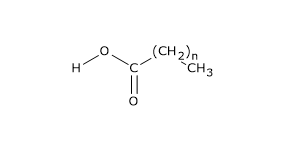
Saturated Fatty Acid: Structure, Formula & Example - Video ... Lauric Acid Saturated fatty acids are composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. The general formula is shown in the following illustration. Here, the number of hydrogen (H) atoms (2n) is twice...
Structure of the human fatty acid synthase KS-MAT didomain ... We describe the high-resolution crystal structure of a large part of human FAS that encompasses the tandem domain of beta-ketoacyl synthase (KS) connected by a linker domain to the malonyltransferase (MAT) domain. Hinge regions that allow for substantial flexibility of the subdomains are defined.
Fatty Acids - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Fatty acids consist of a long hydrocarbon chain (-CH 2 -CH 2 -) with a carboxyl group, typically at the terminus of the molecule. The hydrocarbon chain can be saturated or unsaturated (containing double bonds) depending on the origin of the fatty acid.
Structure of a Triglyceride Molecule | Healthfully Structure. The main molecule that starts the structure of a triglyceride is glycerol. Glycerol is a three-carbon molecule with three hydroxyl groups on them. These hydroxyl groups are the site of an ester reaction with three fatty acid molecules. The fatty acids can be different types, and the fatty acid structure defines the type of triglyceride.
Solved Human Digestive System 10. Which structure | Chegg.com Which structure represented in the diagram below absorbs most of the fatty acids and glycerol from the small intestines 12. Base your answer to the following question the diagram below. For each statement select the organ that is most closely associated with the statement below. A number may be used more than once not at all.] 0.
Fatty acid - Wikipedia Medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 6 to 12 carbons, which can form medium-chain triglycerides. Long-chain fatty acids (LCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 13 to 21 carbons. Very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA) are fatty acids with aliphatic tails of 22 or more carbons. Saturated fatty acids























0 Response to "38 fatty acid structure diagram"
Post a Comment