38 laws of reflection diagram
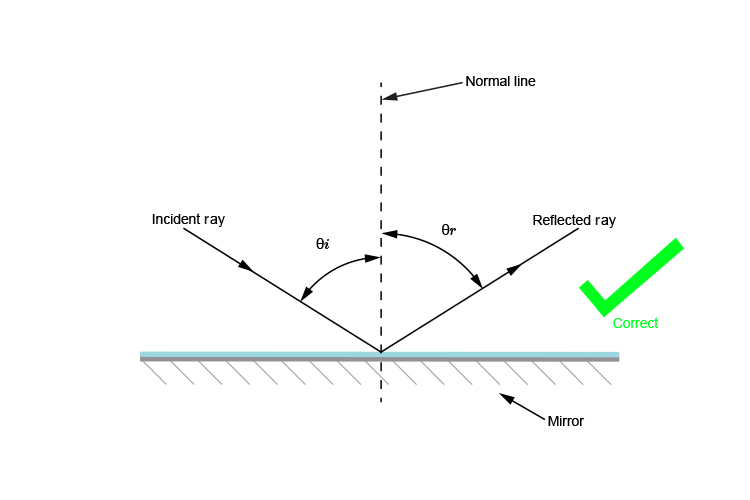
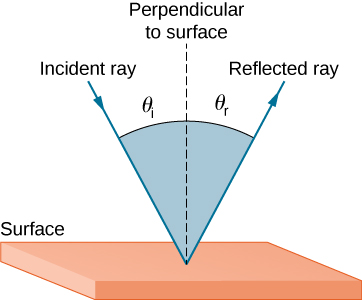
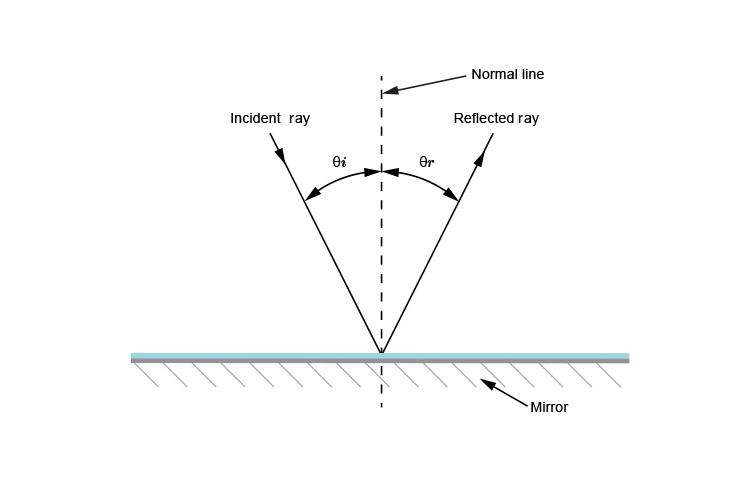
Physics Tutorial: The Law of Reflection The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). The ray of light that leaves the mirror is known as the reflected ray (labeled R in the diagram). Law of Reflection diagram Diagram - Quizlet Start studying Law of Reflection diagram. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
PhysicsLAB: Video: Law of Reflection Sample Diagram PhysicsLAB: Video: Law of Reflection Sample Diagram. The Law of Reflection states that when waves are reflected from an interface, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. The purpose of this lab is to experimentally verify this outcome. Given below are a sample screen capture and an accompanying image showing an example of the ...
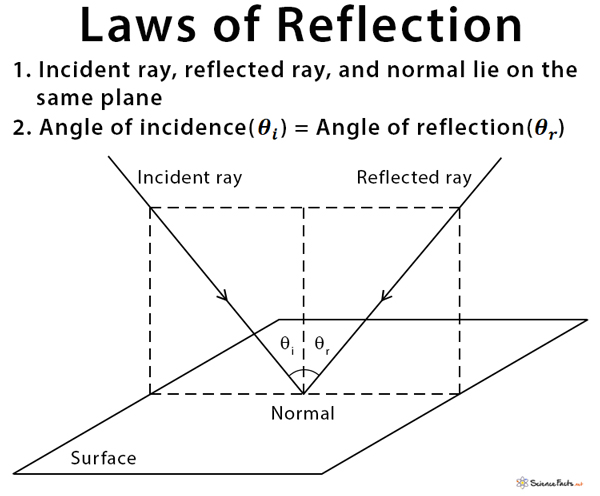
Laws of reflection diagram
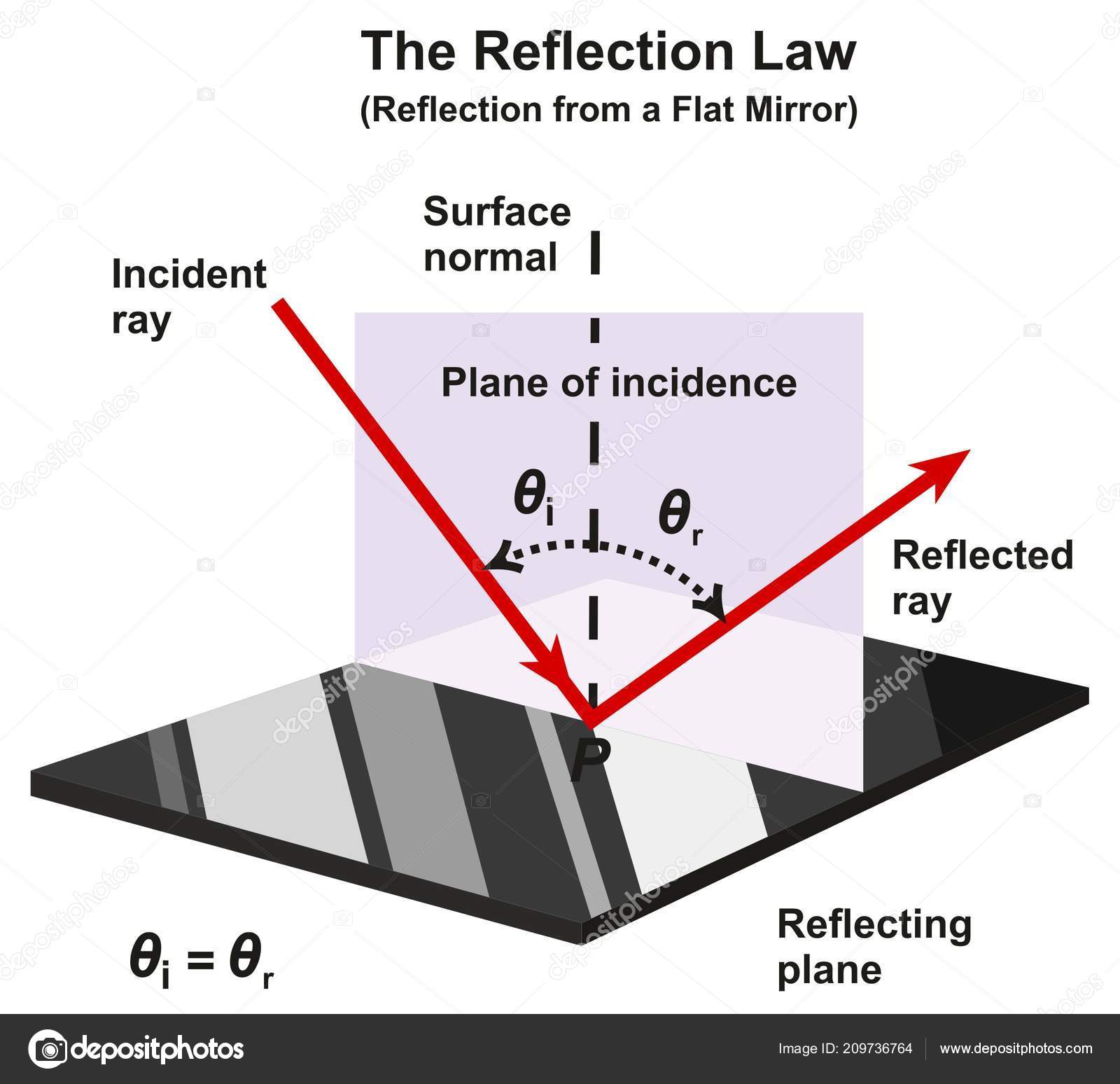
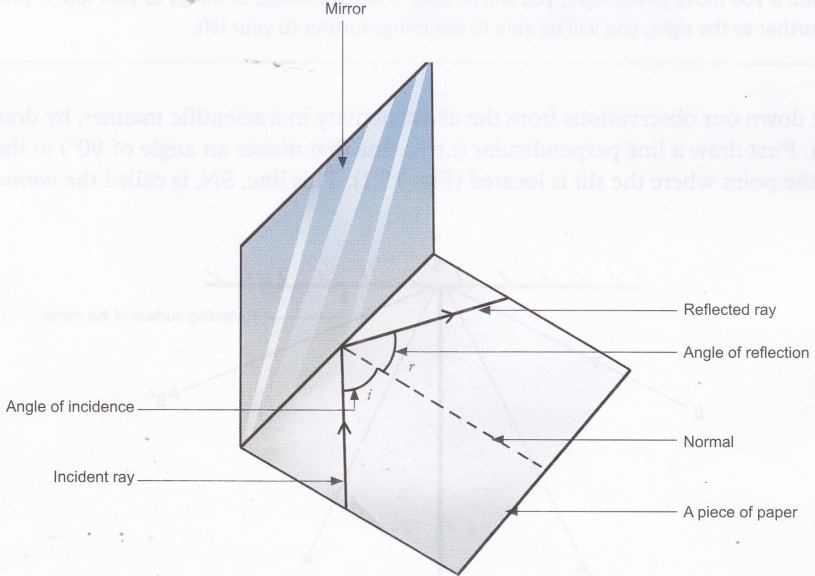
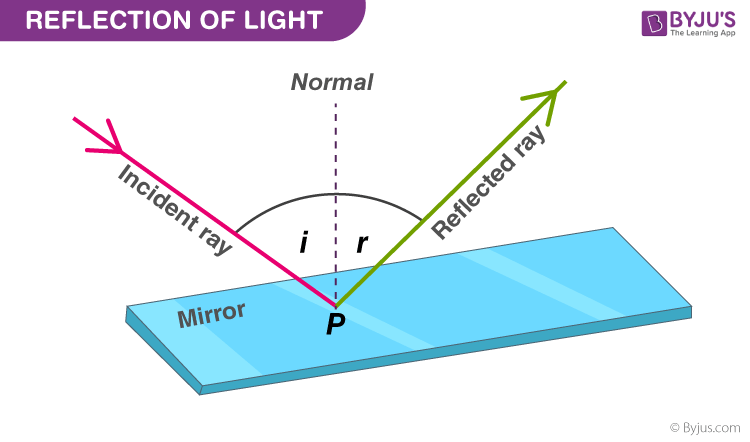
Laws of Reflection | Definition, Examples, Diagrams 1) Take a drawing board and fix a white paper on it with the help of clamps. 2) Draw a straight line AB at the centre of the paper and also a normal (ON) to AB at point 'O'. 3) Draw a straight line PQ making certain angle (Angle i) with ON. 4) Fix two pins at the points P and Q on the paper vertically. Laws of Reflection - Explanation and Experiment - Teachoo Laws of Reflection There are 2 laws of Reflection The Incident ray, Reflected ray and the Normal, all lie in the same plane The Angle of Incidence is always equal to Angle of Reflection So, in our figure above, Incident ray OP, reflected ray OQ and Normal ray ON all lie on the same plane And, Angle of incidence = Angle of Reflection What is reflection? Write the laws of reflection. Reflection: The process of sending back the light rays which fall on polished surface is called reflection of light. Laws of reflection: (i) The angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of incidence. (ii) The incident rays, reflected rays and the normal, all lie in the same plane.
Laws of reflection diagram. CBSE NCERT Notes Class 8 Physics Light - ExamFear Law 1 : The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane. Law 2 : Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Law 3 or Law of Lateral Inversion: In a image formed by a mirror, the left of the object appears to be the right and the right of the object appears to be the right. › reflection-of-lightSELINA Solutions for Class 9 Physics Chapter 7 - Reflection ... Reflection involves a change in direction of the light ray. The angle of incidence is the angle between this normal line and the incident ray. The angle of reflection is the angle between this normal line and the reflected ray. According to the law of reflection, • the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Explain the laws of reflection with the help of a diagram ... According to Law of Reflection, 1- The angle of the incident light ray is equal to the angle of the reflected light ray:- When a ray of light strikes on the smooth surface it gets reflected. We draw a perpendicular line at the point of incidence, this line is called normal ray. Using the law of reflection - Ray diagram rules Using the law of reflection - Ray diagram rules. When we observe an object in a convex mirror there are three ways to try to work out how the light rays from an object focus into the eye of an observer. Use the ray diagram flat/plane mirror rules. Use the laws of reflection. Use new ray diagram rules and create a virtual image.
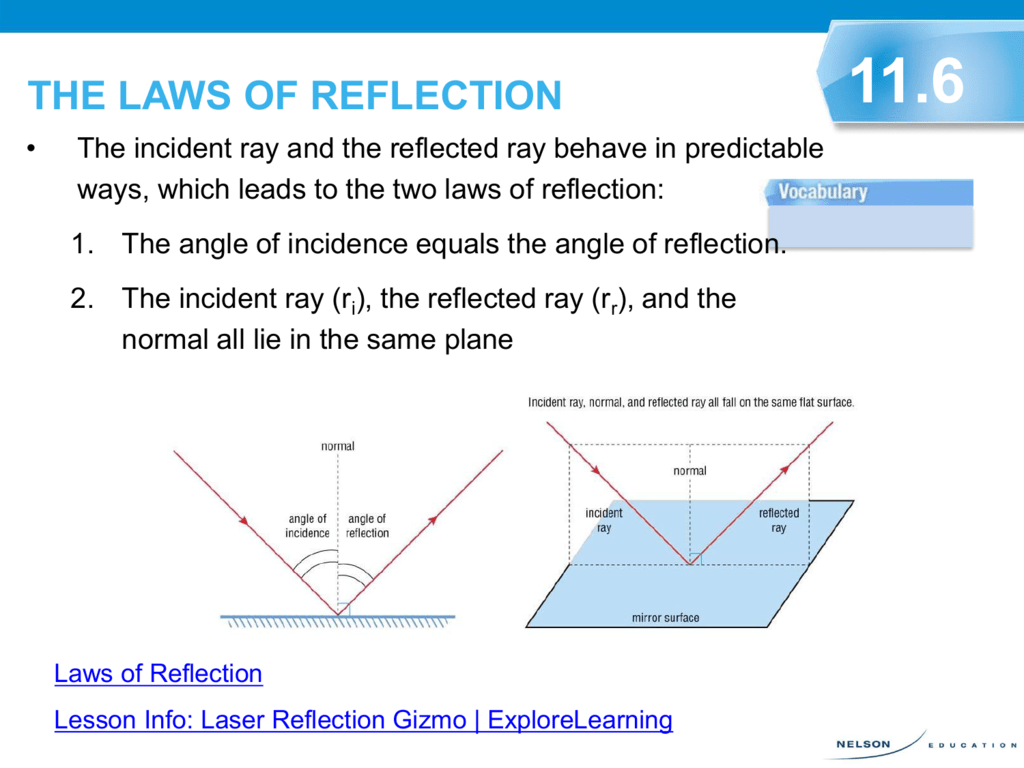
LAWS OF REFLECTION | Physics Quiz - Quizizz 26 Questions Show answers. Question 1. SURVEY. 30 seconds. Report an issue. Q. Section B1a. Given that the angle of incidence = 30 degrees. a. Draw a ray diagram, labelling clearly the normal, incident ray, angle of incidence, reflected ray and angle of reflection accurately. Law of reflection - Reflection and refraction of light ... the angle of reflection, r, is the angle between the normal and reflected ray. The law of reflection states that: angle of incidence i = angle of reflection r. For example, if a light ray hits a... › 10838 › 3118Convex Lens - Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table - Teachoo Nov 18, 2021 · For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positionsHence, we take different casesCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray parallel to principal axis passes through t State The Laws Of Reflection Of Light - BYJUS Laws of reflection The laws of reflection determine the reflection of incident light rays on reflecting surfaces, like mirrors, smooth metal surfaces, and clear water. Following are the laws of reflection: The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the surface of the mirror all lie in the same plane.
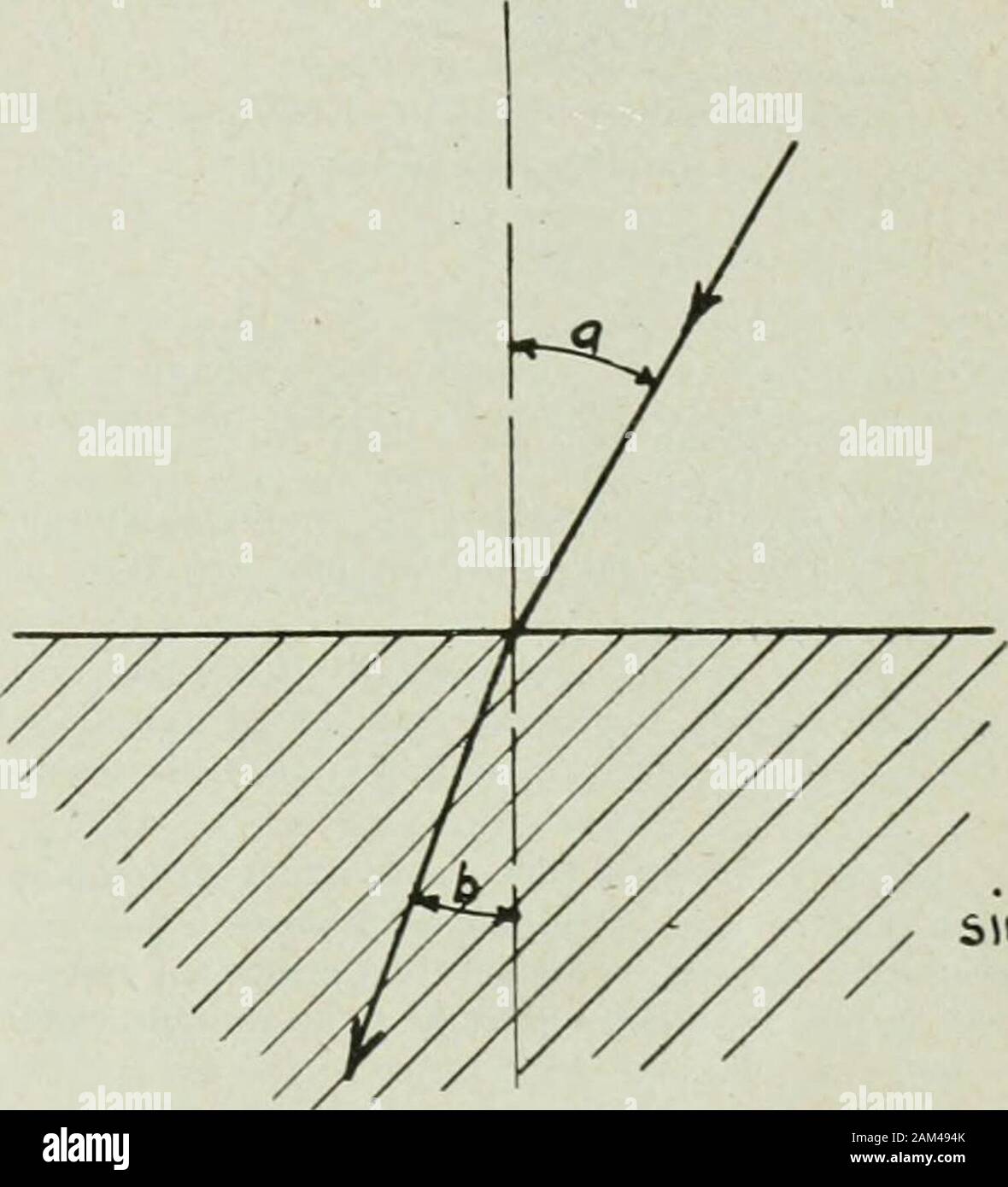
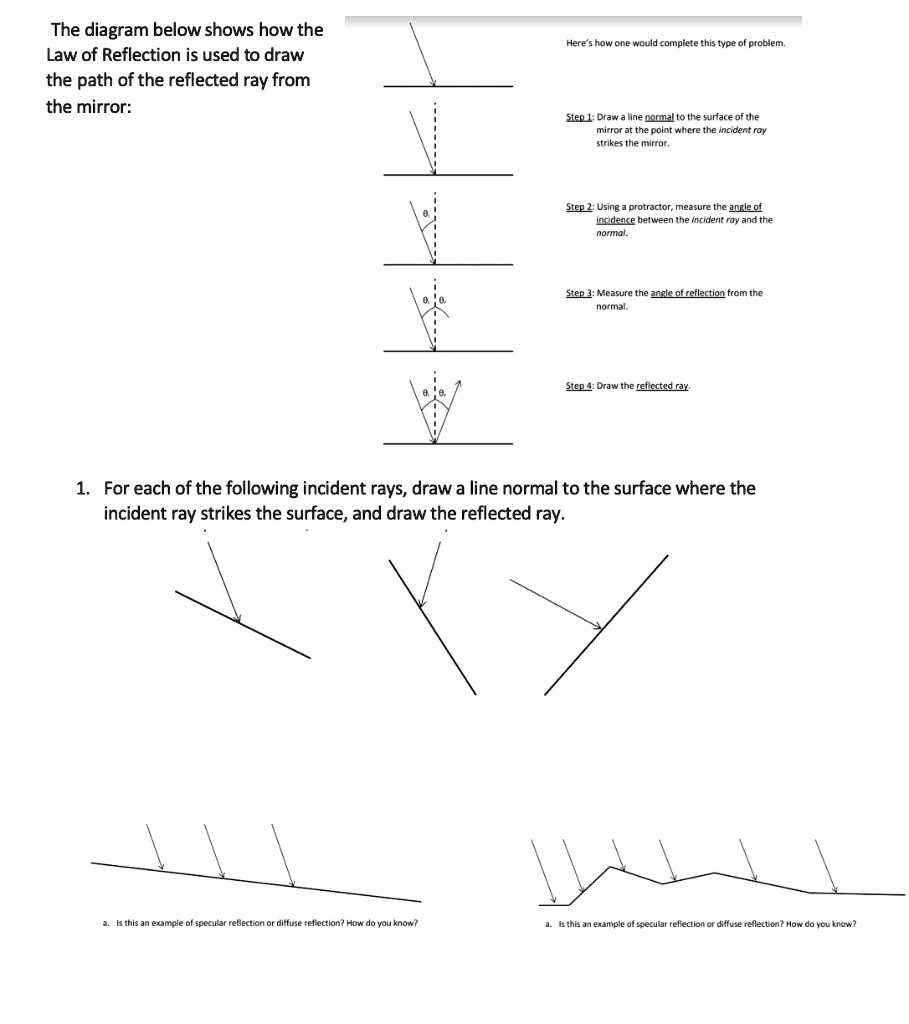
State the laws of reflection of light The second law of reflection states that t he angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. Both angles are measured with respect to the normal to the mirror. See the diagram below for reference. To know more about laws of reflection of light, read the detailed article on reflection of light. Read Less. NCERT Book Solutions. › Concept-BuildersBalanced vs. Unbalanced Forces Interactive Each interactive concept-builder presents learners with carefully crafted questions that target various aspects of a discrete concept. There are typically multiple levels of difficulty and an effort to track learner progress at each level. › reviews › Newtons-LawsNewton's Laws Review - with Answers #4 - Physics Classroom In the free-body diagram, these two forces are represented by the F frict arrow. The value of this resistive force is given as 2.43x10 5 N. This is the net force since there are no other horizontal forces; it is the force which causes the acceleration of the train. The Laws of Reflection and Refraction The law of reflection tells us that ? 2 = ? 3; on the basis of this and our conclusion about the relationship of ? 1 and ? 3, we can express ? 2 in terms of ? 1 as follows. Practice Problem : Complete the diagram to show (approximately) the path of the ray upon reflection by the mirror shown below.
Laws of Reflection - First and Secons Law with Examples Law 1 - The primary law of reflection expresses that the reflection point is dependably comparable to the point of incidence. If the episode beam falls on the plane mirror along with the typical, for example, 90°, the reflected beam will go along a similar way.
byjus.com › physics › concave-convex-mirrorsConcave Mirrors And Convex Mirrors - Image Formation, Ray Diagram A ray passing through the center of curvature of the spherical mirror will retrace its path after reflection. Image Formation By Concave Mirror By changing the position of the object from the concave mirror, different types of images can be formed.
what are the laws of reflection? explain with diagram ... The reflection of light takes place from a reflecting Surface according to definite laws. These are known as Laws of Reflection. 1. The incident ray, the reflected ray and normal at the point of incidence, lie in the same plane. 2. The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection (∠i = ∠r).
electron6.phys.utk.edu › optics421 › modulesReflection and Refraction - University of Tennessee Reflection. Reflection is the abrupt change in the direction of propagation of a wave that strikes the boundary between two different media. At least some part of the incoming wave remains in the same medium. Assume the incoming light ray makes an angle θ i with the normal of a plane tangent to the boundary.
Sample Problems for The Law of Reflection When light is reflected from a surface, the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection, where both angles are measured from the path of the light to the normal to the surface at the point at which light strikes the surface. This equality is known as the law of reflection. Sample Problem 1:
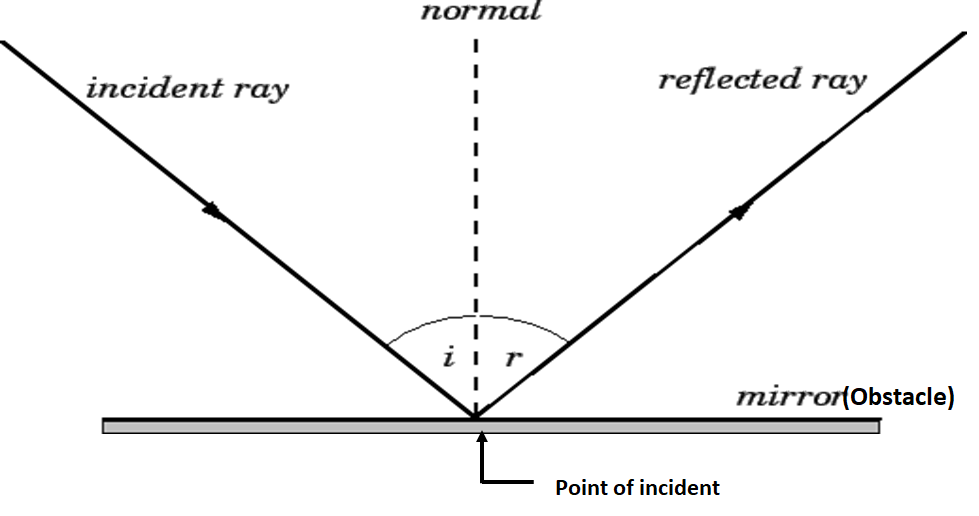
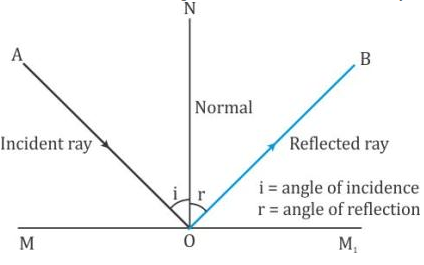
State the laws of Reflection along with a suitable diagram. State the laws of Reflection along with a suitable diagram. Easy Solution Verified by Toppr I = Incident ray R = Reflected ray N = Normal ∠ i = angle of incidence ∠ r = angle of reflection There are two basic laws of reflection of light - (i) The incident ray the reflected ray and the normal to the reflecting
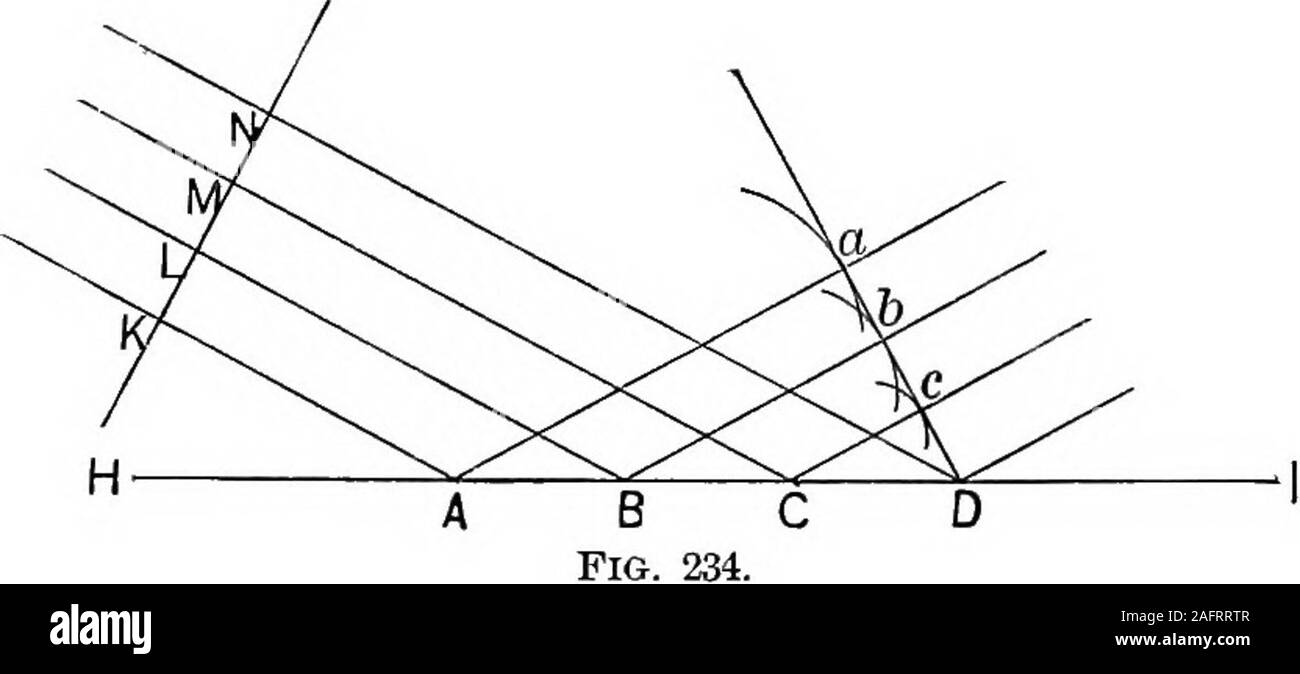
Huygens' Principle: Proving the Law of Reflection | Study.com In our diagram, we now label the reflected angle, along with triangles ABD and ACD, that we will use to prove the law of reflection. Using this diagram, we can form two triangles labelled ABD and ACD.
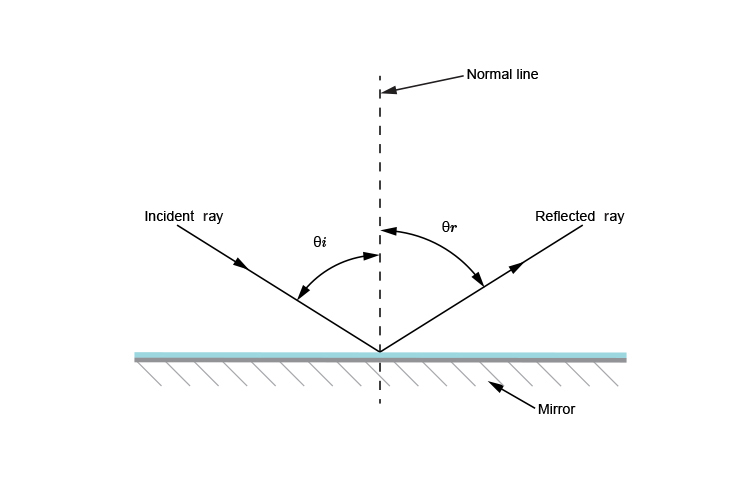
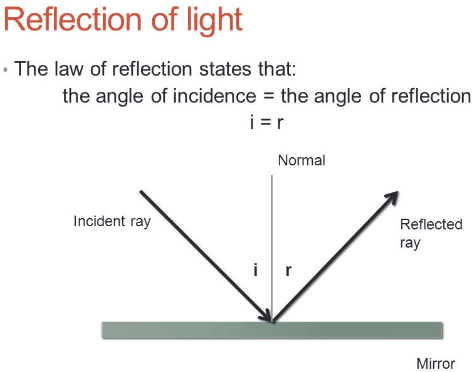
Reflection - Light waves - KS3 Physics Revision - BBC Bitesize The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, i = r. It works for any angle. For example: the angle of reflection is 30° if the angle of incidence is 30 ...
Class 8 Light - Laws of Reflection - Toppr Draw a ray diagram showing the formation of Image of a point object by a plane mirror. What is reflection? Write the laws of reflection. A small hole P is made in a piece of cardboard. The hole is illuminated by a torch as shown in Fig. 16.3. The pencil of light coming out of the hole falls on a mirror. At which point should the eye be placed ...
What is refraction of light? Draw the diagram of ... Laws of refraction state that: The incident ray refracted ray, and the normal to the interface of two media at the point of incidence all lie on the same plane. The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant. This is also known as Snell's law of refraction. sin i/sin r = constant. μ 1 sin i ...
What are the laws of reflection? - Quora Following laws of reflection are valid for smooth surfaces like mirror,still water surface etc. (1)the incident ray, Normal and reflected ray all lie in same plane. (2)incident ray and reflected ray always lie in opposite to the Normal (3) angle of incidence is always equal to angle of angle of reflection. 11K views View upvotes
Law of Reflection (Diagram) Diagram | Quizlet Angle of Reflection The angle measured between the reflected ray and the normal. Mirror Smooth, shiny surfaces make the best mirrors. The flat side on the diagram is the shiny side. Law of Reflection (plane mirror) Angle of incidence = Angle of Reflection Sets with similar terms Light and wave terms 13 terms Caleb_Sowah
Reflection: Definition, Laws of Reflection and Multiple ... Reflection: Definition, Laws of Reflection and Multiple Reflections (explained with diagram)! When light falls on an object, some of it bounces off the object. The bouncing off of light at a surface is called reflection. All surfaces reflect light. How well a surface reflects light depends upon the nature of the surface.
The three laws of reflection - Mammoth Memory The three laws of reflection Any mirror obeys the three laws of reflection, flat, curved, convex or concave. The three laws of reflection are 1. The angle between the incident ray and the normal is equal to the angle between the reflected ray and the normal 2. The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray are all in the same plane 3.
What is the Law of Reflection: Definition and A Simple ... Here's a diagram to help you visualize the law of reflection a bit better: Angle of incidence and angle of reflection In the diagram above, the light ray approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray, while the one that bounces off the mirror is called the reflected ray.
Laws Of Reflection: Definition, Types, Diagrams ... According to the Law of Reflection, θ = θ r Hence, Angle of Reflection = 60° Q2: A light ray strikes a reflective plane surface at an angle of 54° with the surface. (i) Calculate the angle of incidence. (ii) Calculate the angle of reflection. (iii) Calculate the angle made by the reflected ray and the surface.
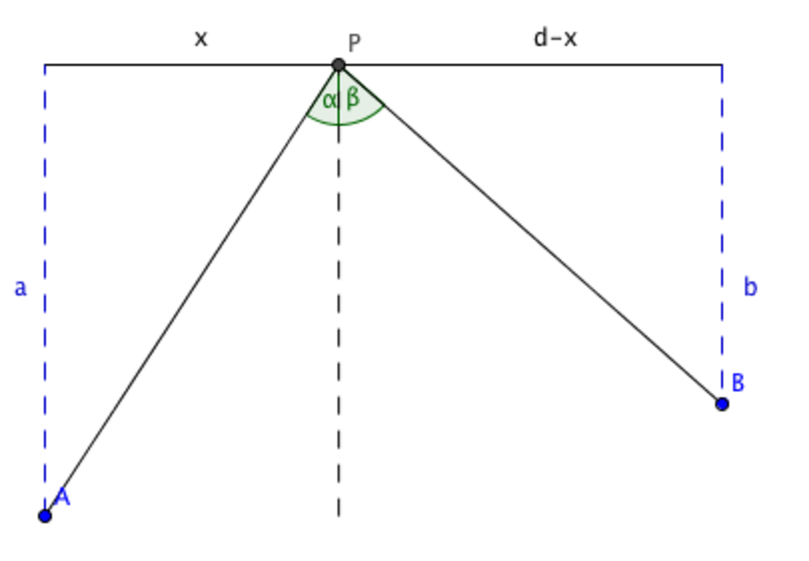
› optics › reflectionReflection of Light Rays, Examples and Solutions Solution: We first complete the given diagram with the angles of incidence and reflection as shown below and also labeling the incident and reflected rays. For the incident ray at A and the reflected ray at B to be parallel, angles i + r and i' + r' have to be supplementary.(geometry: parallel lines cut by a transversal).
What is reflection? Write the laws of reflection. Reflection: The process of sending back the light rays which fall on polished surface is called reflection of light. Laws of reflection: (i) The angle of reflection is always equal to the angle of incidence. (ii) The incident rays, reflected rays and the normal, all lie in the same plane.
Laws of Reflection - Explanation and Experiment - Teachoo Laws of Reflection There are 2 laws of Reflection The Incident ray, Reflected ray and the Normal, all lie in the same plane The Angle of Incidence is always equal to Angle of Reflection So, in our figure above, Incident ray OP, reflected ray OQ and Normal ray ON all lie on the same plane And, Angle of incidence = Angle of Reflection
Laws of Reflection | Definition, Examples, Diagrams 1) Take a drawing board and fix a white paper on it with the help of clamps. 2) Draw a straight line AB at the centre of the paper and also a normal (ON) to AB at point 'O'. 3) Draw a straight line PQ making certain angle (Angle i) with ON. 4) Fix two pins at the points P and Q on the paper vertically.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ReflectionLaw-5946c6dd5f9b58d58a2f2efc.png)

















0 Response to "38 laws of reflection diagram"
Post a Comment