36 hr diagram horizontal branch
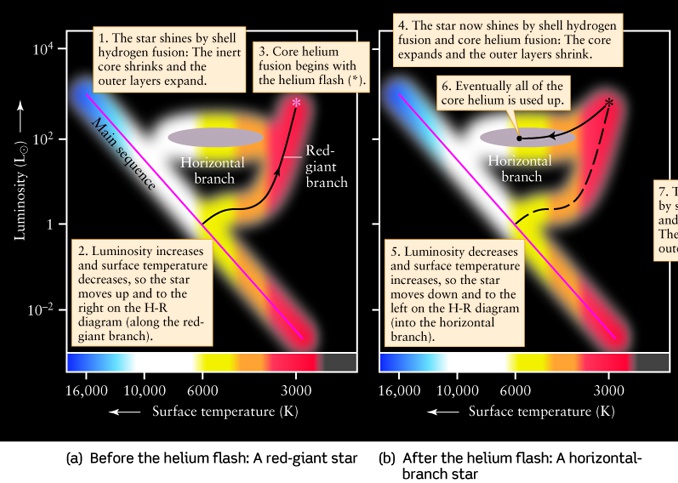
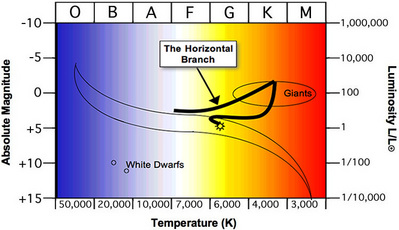
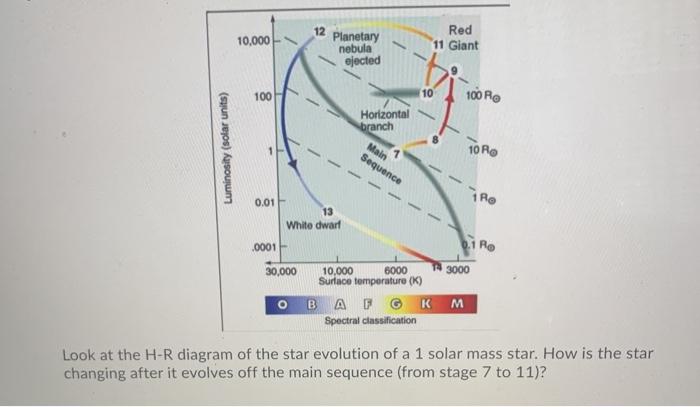
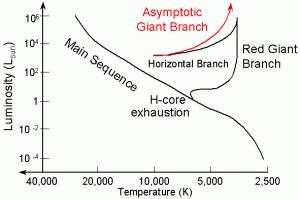
This ignition of the core causes the star to move rapidly down the H-R diagram to the Horizontal Branch region. Horizontal Branch - the HB is the region inhabited by stars which are burning Helium in their cores, converting it into Carbon. A strong feature of the HB in this particular globular cluster, M5, is a Gap in the HB. The horizontal branch is the part of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram of occupied by the stars in a typical globular cluster. It contains stars with masses of 0.6 to 0.8 solar masses that are hotter and fainter than those on the giant branch. A star appears on the horizontal branch after it has undergone its helium flash and begun to burn helium ...
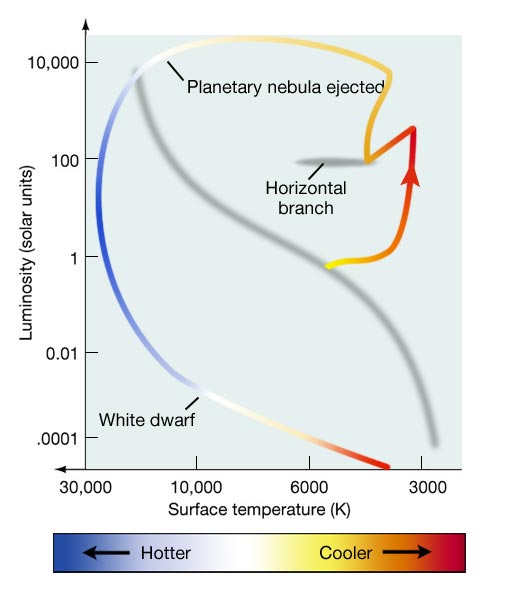
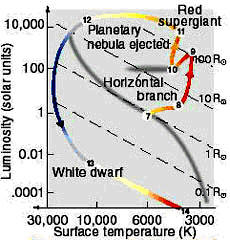
HR diagram of post‐horizontal branch evolution; b) Cross‐sectional model of post‐horizontal branch star configuration. (Not drawn to scale.) Planetary nebulae. Within a few million years, the greater part of the stellar mass is now converted to carbon and oxygen. The hydrogen‐ and helium‐burning shells have now moved so far out into ...
Hr diagram horizontal branch
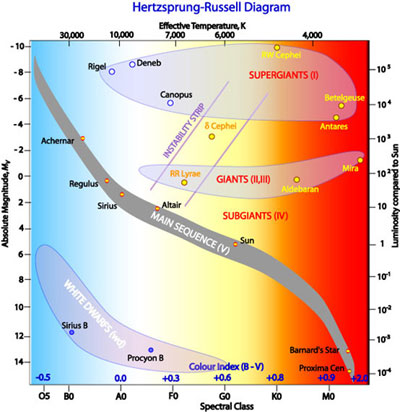
Definition. The horizontal-branch (HB) is the region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram occupied by evolved stars – after the red giant stage – of low mass and low metallicity (abundance of elements heavier than He less than 0.1 that of the Sun), during their central He-burning (He-fusion) phase. The HB is observed in globular clusters, whereas in open clusters (having approximately solar metallicity ), stars are confined to the bottom of the red giant branch during core He-burning. Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (rus -ĕl) (H-R diagram) A two-dimensional graph that demonstrates the correlation between spectral type (and hence temperature) and luminosity of stars, discovered independently by the Danish astronomer E. Hertzsprung in 1911 and the American astronomer H.N. Russell in 1913.Instead of a uniform distribution, any large sample of stars is found to form well-defined ... A star is on the horizontal branch of the HR diagram. Which of the following describes nuclear fusion within the star? helium to carbon in the core; hydrogen to helium in the first shell Explanation: Horizontal branch stars are evolved stars and are not on the main sequence. Their cores have become hot enough that they can fuse helium to carbon.
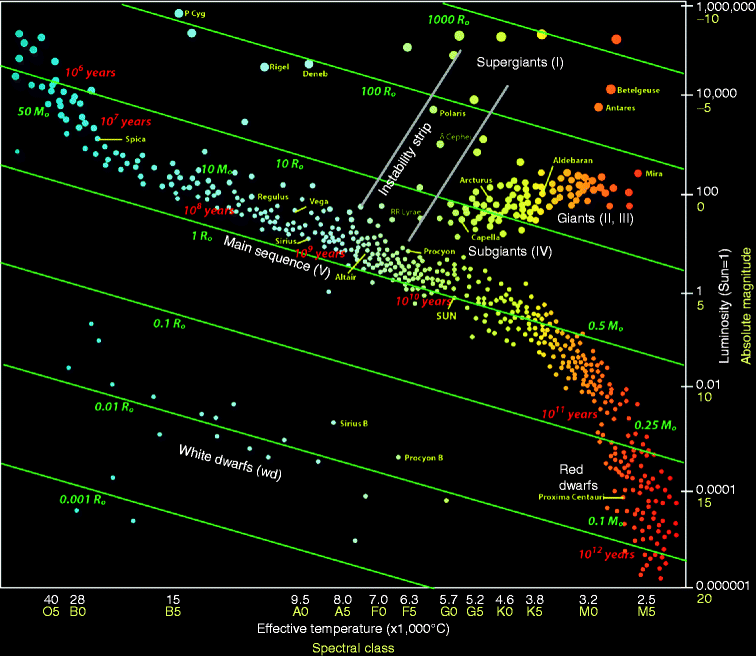
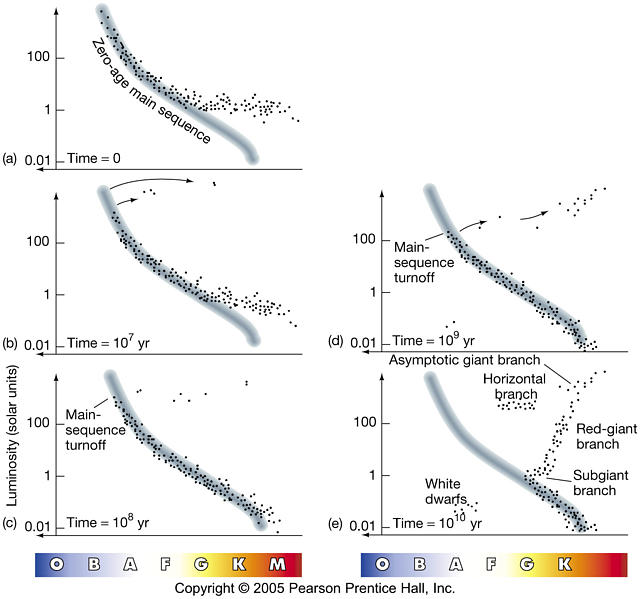
Hr diagram horizontal branch. Horizontal Branch Distribution The distribution of stars horizontally on the HB branch of a cluster HR diagram is because of differences in detailed structure, in particular the mass of the envelope. The left end of the branch corresponds to stars with lower mass envelopes and the right end to stars with higher mass envelopes. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, abbreviated as H-R diagram, HR diagram or HRD, is a scatter plot of stars showing the relationship between the stars' absolute magnitudes or luminosities versus their stellar classifications or effective temperatures.The diagram was created independently in 1911 by Ejnar Hertzsprung and by Henry Norris Russell in 1913, and represented a major step towards ... They form a horizontal branch in the HR diagram. The core-helium fusing lifetime is shorter than the main-sequence (core-hydrogen fusing) lifetime because the star is more luminous and because helium fusion is less efficient than hydrogen fusion. 11.7 SUMMARY. Figure 2: A Color-Magnitude Diagram (CMD). Each dot corresponds to one star. Shown are the main sequence (MS), location of white dwarfs (WD), the Horizontal Branch (HB), and the Giant Branch (GB). With time, stars evolve o the main sequence, go up into the giant branch, back down into the horizontal branch, and eventually become white dwarfs.
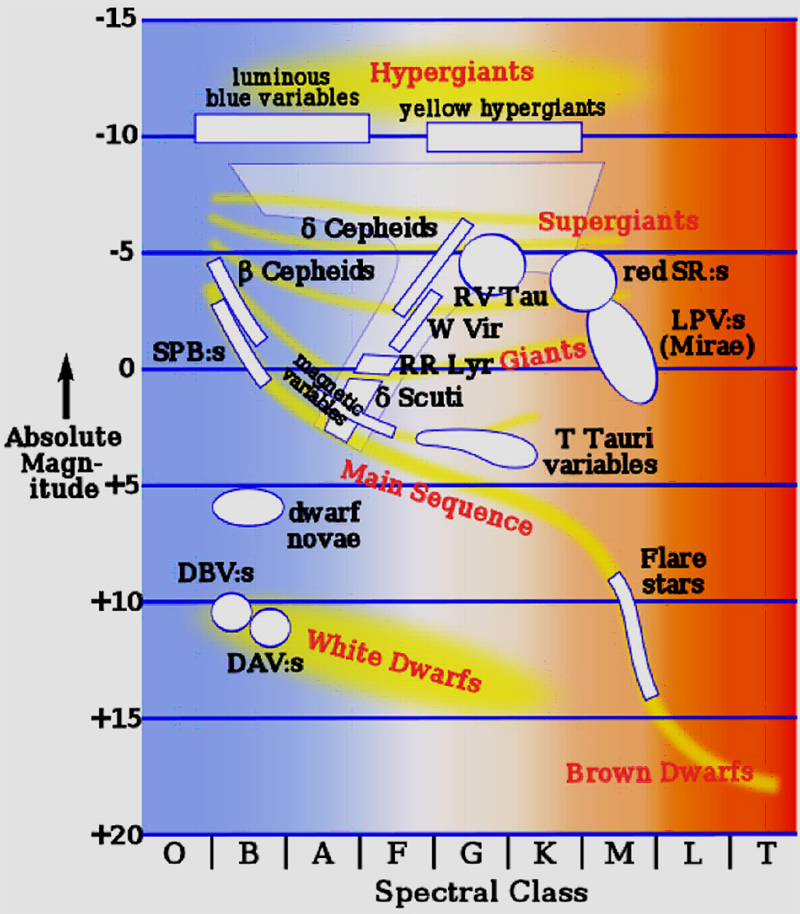
The post red-giant branch loops go through the instabilitystrip. Stars in the strip pulsate with periods of days or weeks (depend-ing on their luminosity). These are Cepheid variables. Stars with M > 10 M⊙ ignite helium before reaching the Hayashi line. Their evolution in the HR diagram is qualitatively 水平分枝 (すいへいぶんし 、horizontal branch )は、ヘルツシュプルング・ラッセル図(HR図)上に現れる星の系列の一つで、質量が2 M ☉ (太陽質量)未満の恒星が赤色巨星分枝の後に経る進化の段階である。 HR図上でおよそ水平な系列を示すため「水平分枝」と呼ばれる The horizontal-branch (HB) is the region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram occupied by evolved stars – after the red giant stage – of low mass and low metallicity (abundance of elements heavier than He less than 0.1 that of the Sun), during their central He-burning (He-fusion) phase. Posted on. January 22, 2022 by quizs. A star is on the horizontal branch of the H- R diagram. Which statement is true? A star is on the horizontal branch of the H- R diagram. Which statement is true? A) It is about to experience the helium flash. B) It is burning both hydrogen and helium. C) It is burning only helium.
Some stars will continue from the red giant branch onto the "horizontal branch," which reaches back toward the bluer and dimmer portion of the diagram. A labelled HR diagram. Click to see original size. The horizontal branch is so named because in low-metallicity star collections like globular clusters, HB stars lie along a roughly horizontal line in a Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. Because the stars of one globular cluster are all at essentially the same distance from us, their apparent magnitudes all have the same relationship to their absolute magnitudes, and thus absolute-magnitude-related properties are plainly visible on an H-R diagram confined to stars of that cluster, undiffused by ... As you can see in the HR diagram below (Fig. 6.4), the evolutionary track of a Sun-like star now moves the star back towards the Main Sequence. This region of the HR diagram is called the horizontal branch , because stars in this phase of their evolution populate a narrow, almost horizontal box that extends to hotter temperatures from the red ... Red Giant Branch on H-R Diagram ... As it does so, it moves onto the Horizontal Branch. He Flash to Horizontal Branch on the H-R Diagram ...
Horizontal Branch stars. This is a phase of stellar evolution undergone by intermediate- mass stars, i.e. those with masses 0.8 M⊙ < < 8 M⊙, a range which encompasses the majority of stars in the Galaxy, including our Sun. After departing the Main Sequence, these stars spend time on the Red Giant Branch, a phase characterised by hydrogen burning in a shell around the stellar core which causes their atmospheres to expand.
Horizontal Branch: In the horizonal branch, the star produces its energy by the helium fusion at the core. During this period, the star's total energy output (luminosity) will remain constant and hence the star will move horizontally along the HR diagram. Asymptotic Giant Branch:
This means the star moves to the left horizontally on the H-R diagram on something appropriately called the horizontal branch. Thus, such a star is known as a horizontal branch star, a star that is...
The star contracts and its surface temperature increases. So it moves to the left on the HR diagram. The name horizontal branch is given because of the presence of stars with the same luminosity (brightness, on the y-axis) across a horizontal branch of stars of different spectral types (surface temp, on the x axis).
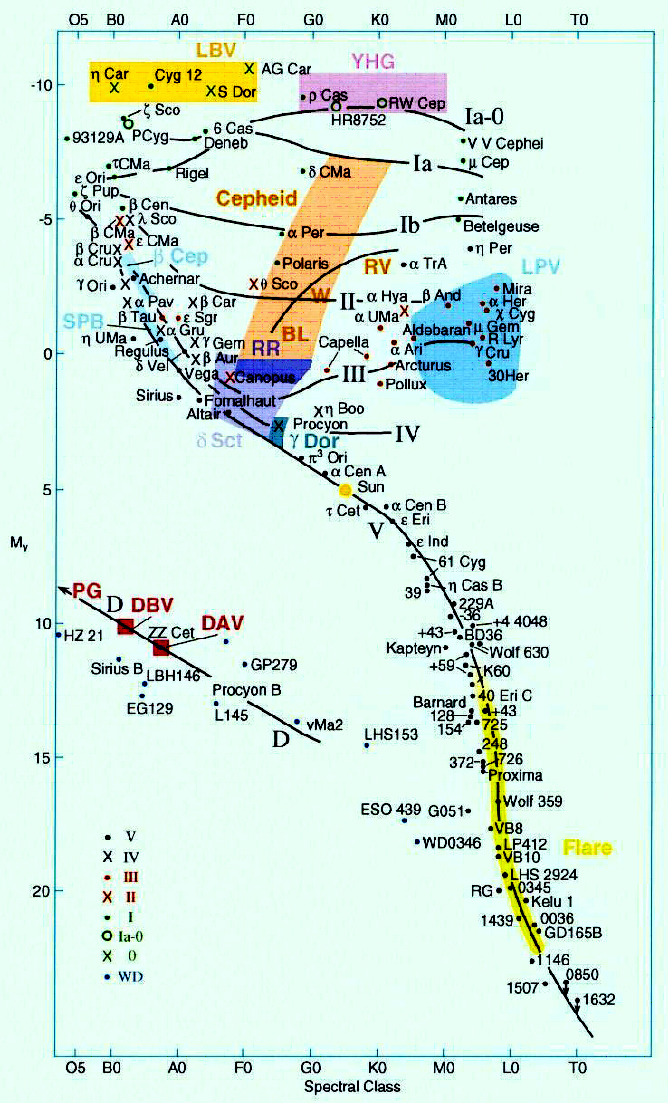
H-R Diagram of Globular Clusters differs from even old open cluster like NGC 188 long horizontal branch (with RR Lyrae stars): consequence of low heavy-element abundance "turn-off point of MS also low: even low mass stars (~0.8 solar mass) have evolved ---> GC stars are old! ~12-13 billion years
A detailed study of the structure of zero-age horizontal-branch (ZAHB) models is studied in order to show how the hydrostatic structure of these models changes with the input parameters and determines the H-R diagram location of a given model. The properties of composite polytropes on the homology-invariant (U,V)-plane are demonstrated. A variety of test models and sequences were constructed ...
What is the horizontal branch for stars in a cluster plotted on an HR diagram? What happens to a low-mass star after helium fusion ends? Why can't it fuse carbon into heavier elements? How do red giants manufacture carbon-rich dust grains? Why are these important for life? What is a planetary nebula?
a) Draw the H-R diagram, making sure to indicate the axes and the location of the Main Sequence stars [3pt] b) Roughly indicate where is the location of the Sun [1pt] c) Indicate where the hot blue stars are [1 pt] d) Indicate where the cold red stars are [1pt] e) Indicate where on the diagram you would put a protostar [2pt] f) Indicate where ...
Question: Which type of stars spend part of their lives on the "horizontal branch" of the HR diagram? a. super-massive stars b. red dwarf stars c. stars with about 20 times the Sun's mass d. "mid-sized" stars similar to our Sun. e.
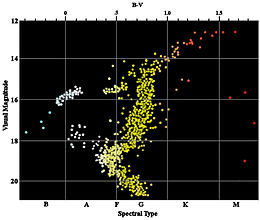
Overview - By selecting stars with a range of colours and brightnesses off this true colour image of a small region in the globular cluster NGC104 (47 Tuc) you can investigate the structure of the cluster's Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram resulting from stellar evolution. The image is a composite made up of three separate images taken in the ultraviolet (3800Å, U), blue (4500Å, B) and ...
The HR Diagram for a Specific Case. figure 3 HR Diagram for Globular Cluster M5. In figure 3 above, we see an HR plot of the stars in globular cluster M5 (I shamelessly confess that I took this diagram from that page). The X-axis plots "B-V", which is the color index, and "B-V" means "B minus V", where B and V are the relative brightness of the B and V colors, in the system of magnitudes ...
h r diagram wikibooks, what is plotted on the horizontal axis of an h r diagram, hr diagram and stellar evolution tim thompson, an airplane is flying in a horizontal circle at a speed of, plotting variable stars on the h r diagram activity, horizontal branch wikipedia, hertzsprung russell diagram national schools observatory, the hertzsprung
Core temperature about 100 million K. Helium main sequence (also known as "red clump" if it hugs the giant branch, or "horizontal branch" if it spreads out to hotter temperatures). 2nd-longest phase. Roughly 0.4 billion yr. Fuel: Core He fusion. Star is a stable red giant. Asymptotic giant branch. Fuel: H and He fusion in shells.
As you can see in the HR diagram below (Fig. 6.4), the evolutionary track of a Sun-like star now moves the star back towards the Main Sequence. This region of the HR diagram is called the horizontal branch , because stars in this phase of their evolution populate a narrow, almost horizontal box that extends to hotter temperatures from the red ...
Astronomy Chapter 20. A. as a red giant or supergiant. B. as a protostar. C. as a planetary nebula. D. as a main sequence star. E. as a T Tauri variable star. D. as a main sequence star. A star is on the horizontal branch of the H-R diagram.
A star is on the horizontal branch of the HR diagram. Which of the following describes nuclear fusion within the star? helium to carbon in the core; hydrogen to helium in the first shell Explanation: Horizontal branch stars are evolved stars and are not on the main sequence. Their cores have become hot enough that they can fuse helium to carbon.
Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (rus -ĕl) (H-R diagram) A two-dimensional graph that demonstrates the correlation between spectral type (and hence temperature) and luminosity of stars, discovered independently by the Danish astronomer E. Hertzsprung in 1911 and the American astronomer H.N. Russell in 1913.Instead of a uniform distribution, any large sample of stars is found to form well-defined ...
Definition. The horizontal-branch (HB) is the region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram occupied by evolved stars – after the red giant stage – of low mass and low metallicity (abundance of elements heavier than He less than 0.1 that of the Sun), during their central He-burning (He-fusion) phase. The HB is observed in globular clusters, whereas in open clusters (having approximately solar metallicity ), stars are confined to the bottom of the red giant branch during core He-burning.










0 Response to "36 hr diagram horizontal branch"
Post a Comment