35 orbital diagram of copper
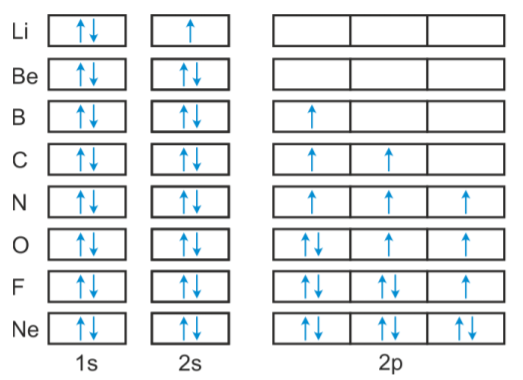
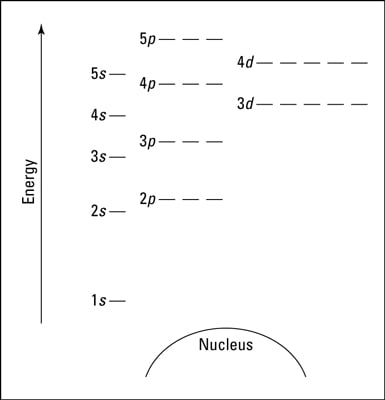
The electron configuration and the orbital diagram are: Following hydrogen is the noble gas helium, which has an atomic number of 2. The helium atom contains two protons and two electrons. The first electron has the same four quantum numbers as the hydrogen atom electron ( n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +1 2 m s = + 1 2 ). The 1s orbital at the bottom of the diagram is the orbital with electrons of lowest energy. The energy increases as we move up to the 2 s and then 2 p , 3 s , and 3 p orbitals, showing that the increasing n value has more influence on energy than the increasing l value for small atoms.
Chemistry questions and answers. a) Write the full electron configuration for Copper. b) Write the full orbital diagram for Copper. c) Write the abbreviated electron configuration for Copper. d) How many valence electrons does Copper have? Question: a) Write the full electron configuration for Copper. b) Write the full orbital diagram for Copper.

Orbital diagram of copper
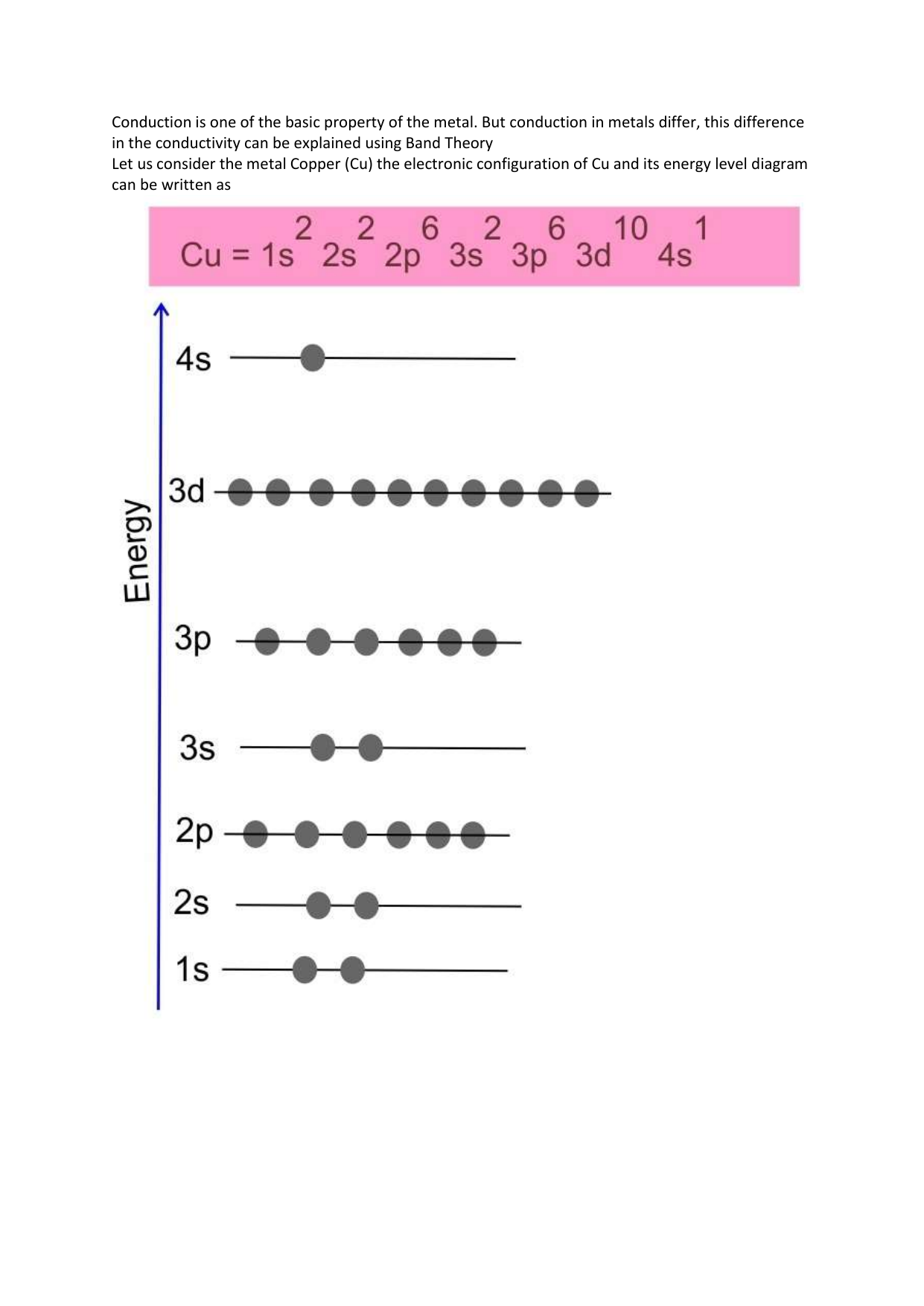
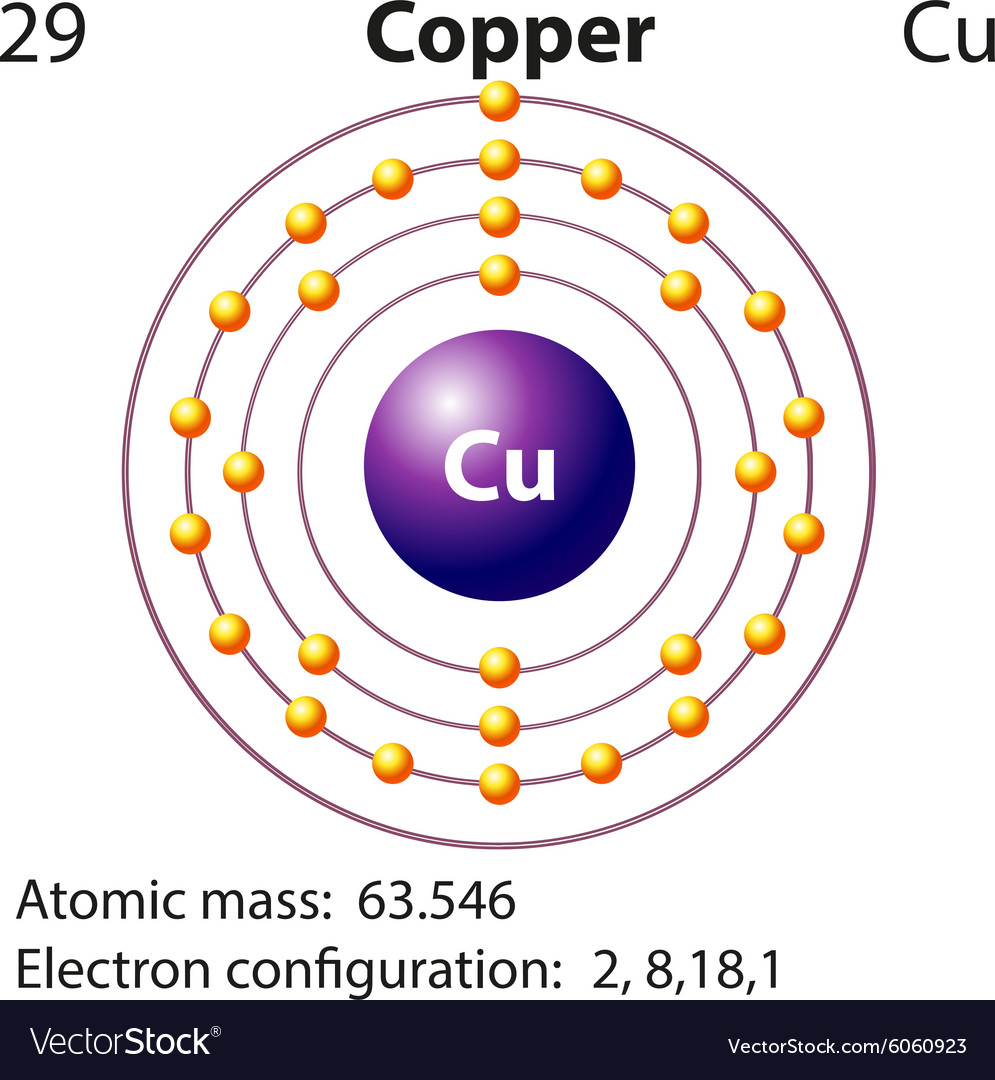
Cu (Copper) is an element with position number 29 in the periodic table. Located in the IV period. Melting point: 1083.5 ℃. Density: 8.92 g/cm 3 . The order of filling the orbitals with electrons in the Cu atom is an exception to the rule. Expected electronic configuration. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9. But in reality, one electron moves from ... What is Copper Orbital Diagram. The final ring or shell of electrons contains the typical. The molecular nature matter in change 2016. so first 2 electrons go in 1s sigma bond. An orbital is a space where a specific pair of electrons can be found. 1 Answer BRIAN M. Jan 25, 2014 Copper is in the ninth column of the transition metals in the d block of the fourth energy level of the periodic table. This would make the electron configuration for copper, 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d9 or in noble gas configuration [Ar] 4s23d9.
Orbital diagram of copper. Figure 2.2.14 Orbital diagrams of Copper (Cu) Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table Figure 2.2.15 The block structure of the Periodic Table * The ns and np sub-levels are filled for elements in Period n. * The (n-1)d sub-level is filled for elements in Period n. 9 Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11: Orbital diagram of Sodium (Na) 12: Orbital diagram of Magnesium (Mg) 13 ... The overall molecular orbital energy level diagram for σ-bonding in octahedral complexes can be shown as: Figure 10. The formation of σ-molecular orbitals (bonding, antibonding and non-bonding) in octahedral complexes of transition metals. Buy the complete book with TOC navigation, orbitals have one electron. Then additional electrons enter each orbital until 2 . electrons are in each orbital. Once all orbitals in a sublevel are filled (each with 2 . electrons), the next electron enters the next higher energy sublevel. The Aufbau diagram below illustrates the order of filling orbitals and sublevels.
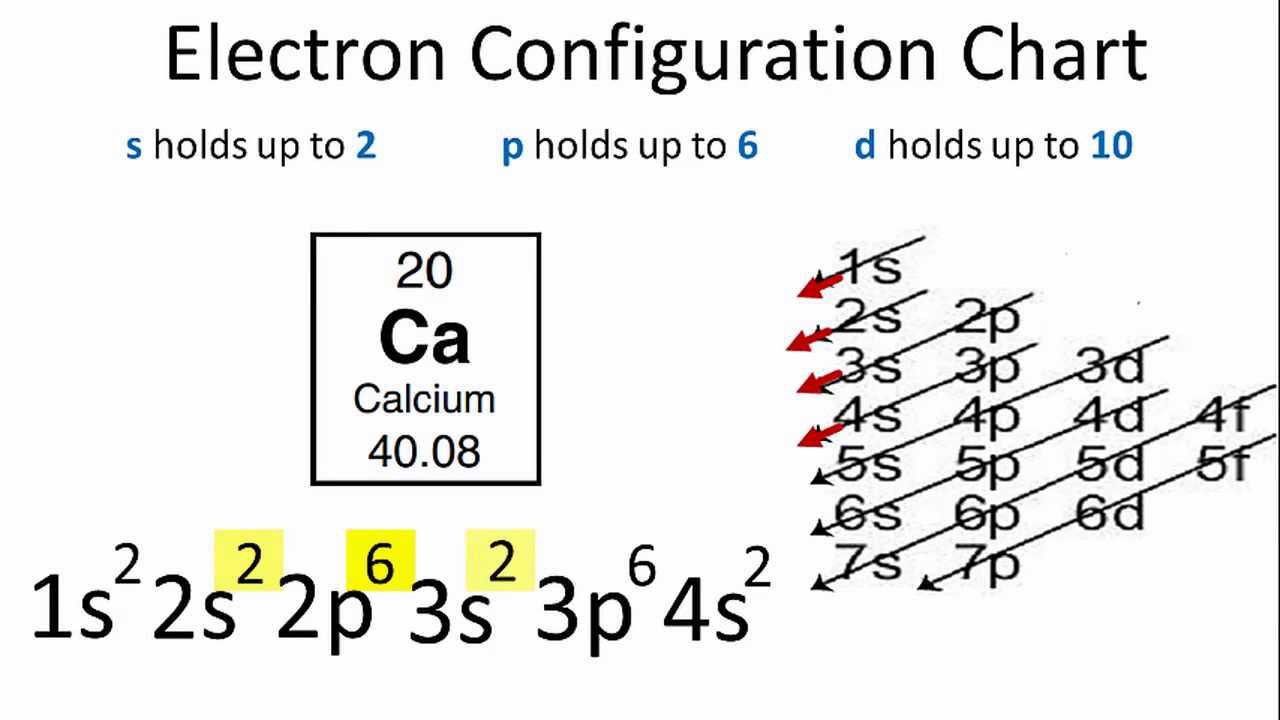
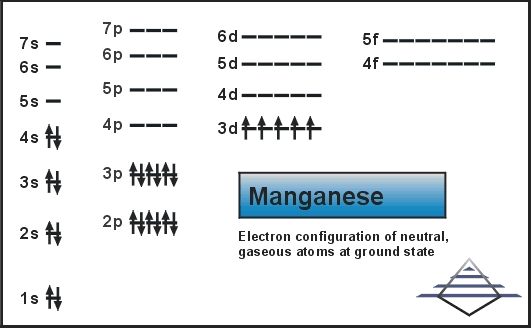
The ratio of the average mass per atom of an isotope to 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom. Relative atomic mass is also known as atomic weight (symbol: A r ). Notes (Cu) m: Standard Atomic Weight. Cu: 63.546 (3) Isotopic Composition 63 69.15% 63 69.15% 65 30.85% 65 30.85%. Orbital Diagrams An orbital diagram is a sketch which shows electron population in atomic orbitals with the electron's spin indicated by up and down arrows. Copper atoms have 29 electrons and the shell structure is 2. 41,038 results Gen Chemistry. Orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. Three rules are useful in forming orbital diagrams. According to the Auf Bau Principle, each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital. You jump up a little bit in energy and we get the 2s orbital that make it the 2p sublevel. Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal -each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for "build up" •Electrons are notated with an arrow -Up arrow goes first then, down arrow -Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom
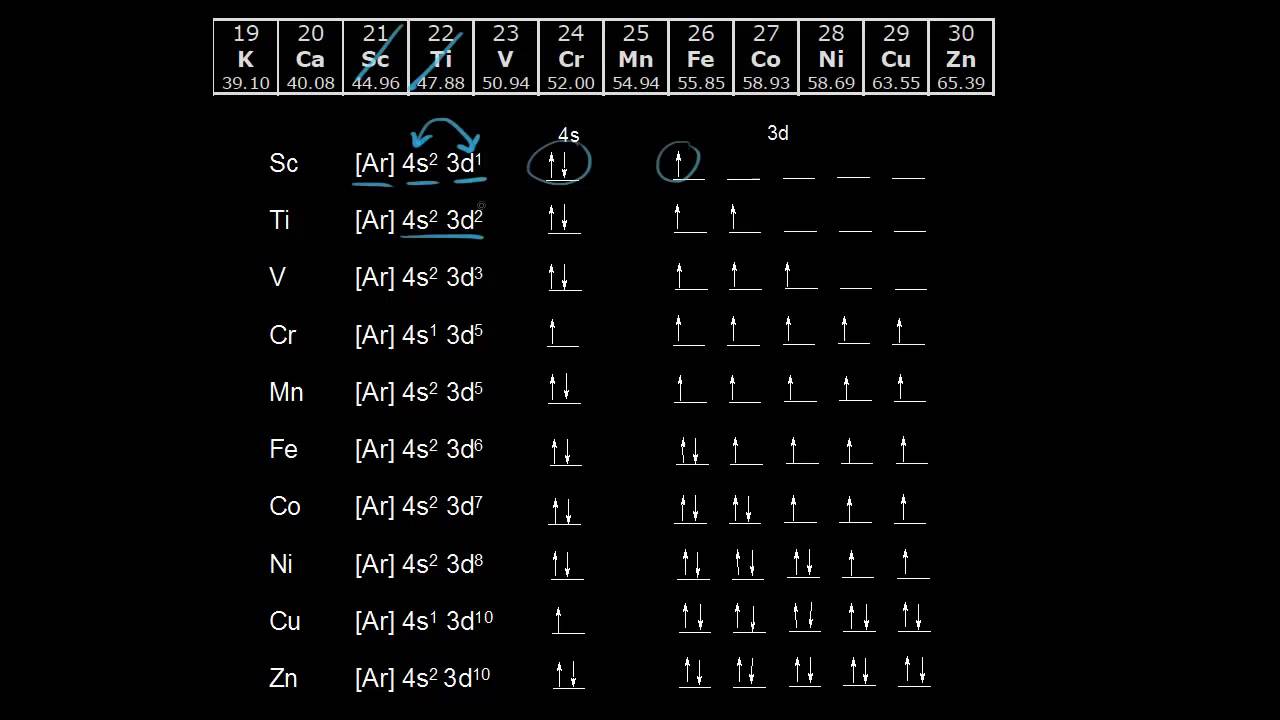
Re: Why are Copper and Chromium exceptions? When doing the electron configurations for these elements, they are exceptions to the general rule because a completely full or half full d sub-level is more stable than a partially filled d sub-level, so an electron from the 4s orbital is excited and rises to a 3d orbital. Atomic Orbital Diagram for Copper (Cu) Copper ion(Cu +,Cu 2+) electron configuration. Ground state electron configuration of copper(Cu) is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 1. The electron configuration shows that the last shell of copper has an electron and the d-orbital has a total of ten electrons. In this case, the valence electrons of copper are one. There are two types of copper ions. In writing the electron configuration for Copper the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for Copper go in the 2s orbital. The next six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. The electron configuration of copper and the orbital diagram is the main topic in this article…. Read More Copper(Cu) electron configuration and orbital diagram. Silicon(Si) electron configuration and orbital diagram. Silicon(Si) is the 14th element in the periodic table and its symbol is 'Si'. Silicon is a semiconductor material.
Start by drawing its orbital notation for the outermost, valence electrons. [Ne] ↑↓ ↑↓ ↑ ↑ 3s 3p Sulfur is a nonmetal and tends to gain electrons, creating the -2 charge. Gaining two electrons gives it an octet of 3s23p6. • Copper has two common oxidation states, +1 and +2.
Answer to: Draw and explain the orbital diagram for copper (Z = 29). By signing up, you'll get thousands of step-by-step solutions to your homework...
An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration. (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) 1s. →. 2s.
Jun 14, 2012 · The electron configuration of copper is 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s1.
Download scientific diagram | Schematic molecular orbital diagram for Cu( II / I ) complexes showing the orbital degeneracy in the reduced state. Orbitals with similar from publication: Probing ...
The orbital diagram, the electron configuration and the energy diagram. All three ways are useful. The next atom is helium with 2 electrons. So the second electron could go into the 1s orbital with the opposite spin of the first electron or it could go into the next orbital in the n = 2 level.
1 Answer BRIAN M. Jan 25, 2014 Copper is in the ninth column of the transition metals in the d block of the fourth energy level of the periodic table. This would make the electron configuration for copper, 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d9 or in noble gas configuration [Ar] 4s23d9.
What is Copper Orbital Diagram. The final ring or shell of electrons contains the typical. The molecular nature matter in change 2016. so first 2 electrons go in 1s sigma bond. An orbital is a space where a specific pair of electrons can be found.
Cu (Copper) is an element with position number 29 in the periodic table. Located in the IV period. Melting point: 1083.5 ℃. Density: 8.92 g/cm 3 . The order of filling the orbitals with electrons in the Cu atom is an exception to the rule. Expected electronic configuration. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9. But in reality, one electron moves from ...












/aufbauexample-56a129555f9b58b7d0bc9f48.jpg)





0 Response to "35 orbital diagram of copper"
Post a Comment