37 cross section of a tree trunk diagram
Browse 2,352 tree trunk cross section stock photos and images available, or search for tree rings or water to find more great stock photos and pictures. tree rings texture background - tree trunk cross section stock pictures, royalty-free photos & images. wood crossection - tree trunk cross section stock pictures, royalty-free photos & images. Cross section of a tree trunk and stump: trunk: part of the tree, between the roots and the branches, consisting of wood on the interior and bark on the exterior.Stump: the remainder of the turnk including the roots after the tree is felled. Stump: the remainder of the turnk including the roots after the tree is felled.
Cross-section of a pine log. The three main sections of a pine log are an outer layer of bark, a circle of sapwood and a core of heartwood. Bark consists of outer layers of dead cells and an inner layer of live, dividing cells. Bark has a protective function, helping prevent attack by insect and fungal pests, and stopping the interior of the ...
Cross section of a tree trunk diagram
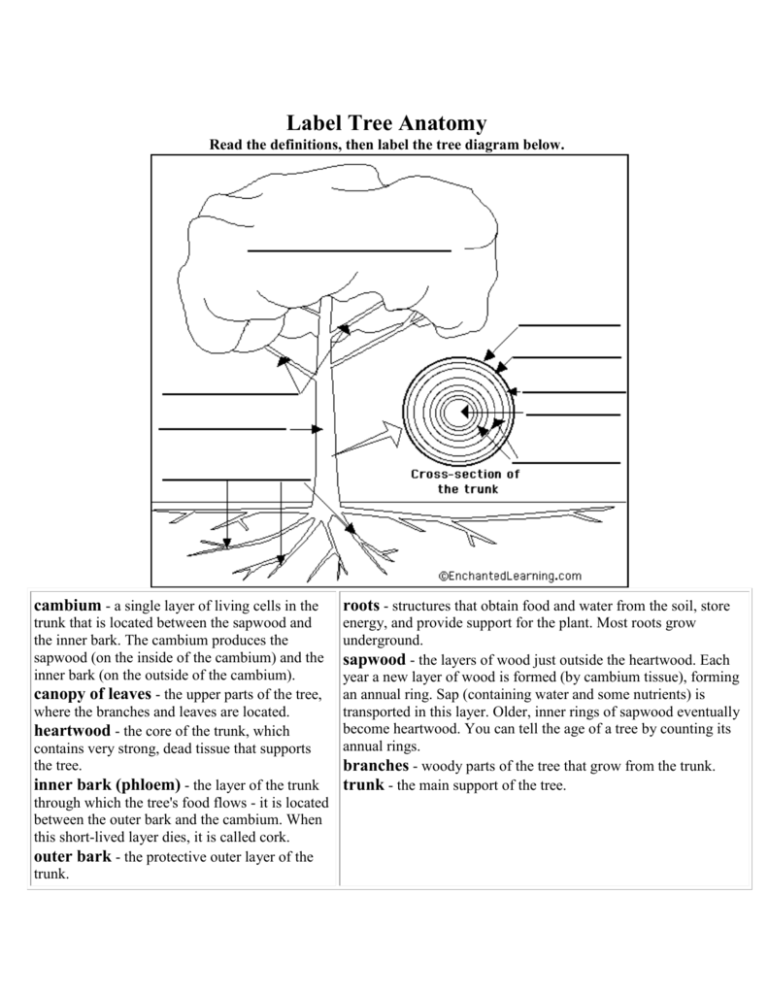
cross section of the trunk. Look at the diagram to see the five main layers and what each layer does. a) Bark: The outer layer of the trunk (and branches) is called the outer bark or just the bark. Its texture, thickness, and flexibility depend on the type of tree. Although bark looks different from tree to tree, it serves the same purpose—to protect the tree from injury and A cross-section of an adult tree trunk. The outer layer interacts with the environment. The second layer is labeled C. The next layer is labeled B, and the layer after this is labeled A. cork cambium secondary xylem lateral meristem vascular cambium apical meristem For example, if a tree is measured as 10" DBH, the radius is 5". Multiplying 5 by 5 equals 25, which when multiplied by 3.14 equals 78.5. Thus, the cross-sectional area of a 10" DBH tree is 78.5. This chart shows the cross-sectional area for trees from 2" to 50" DBH.
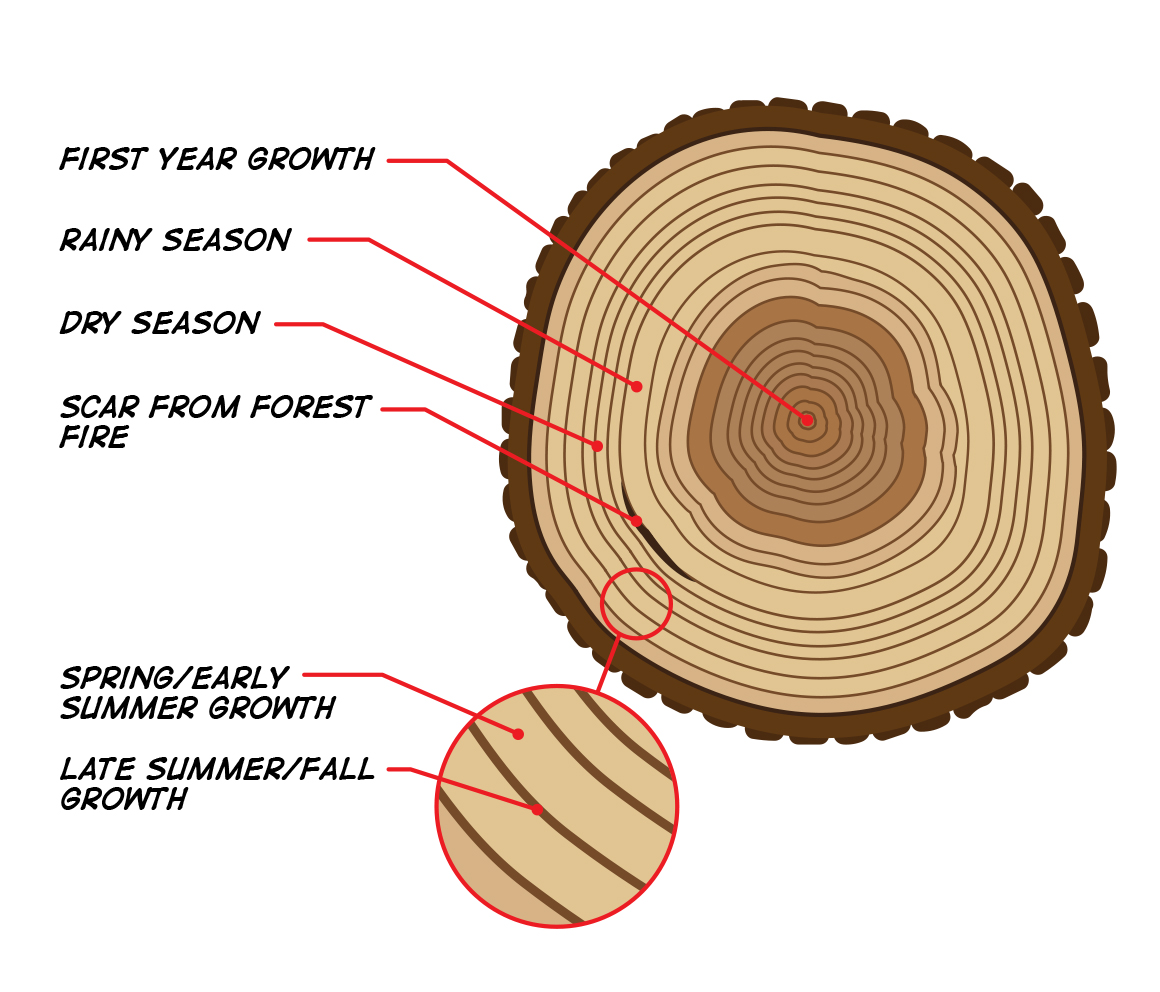
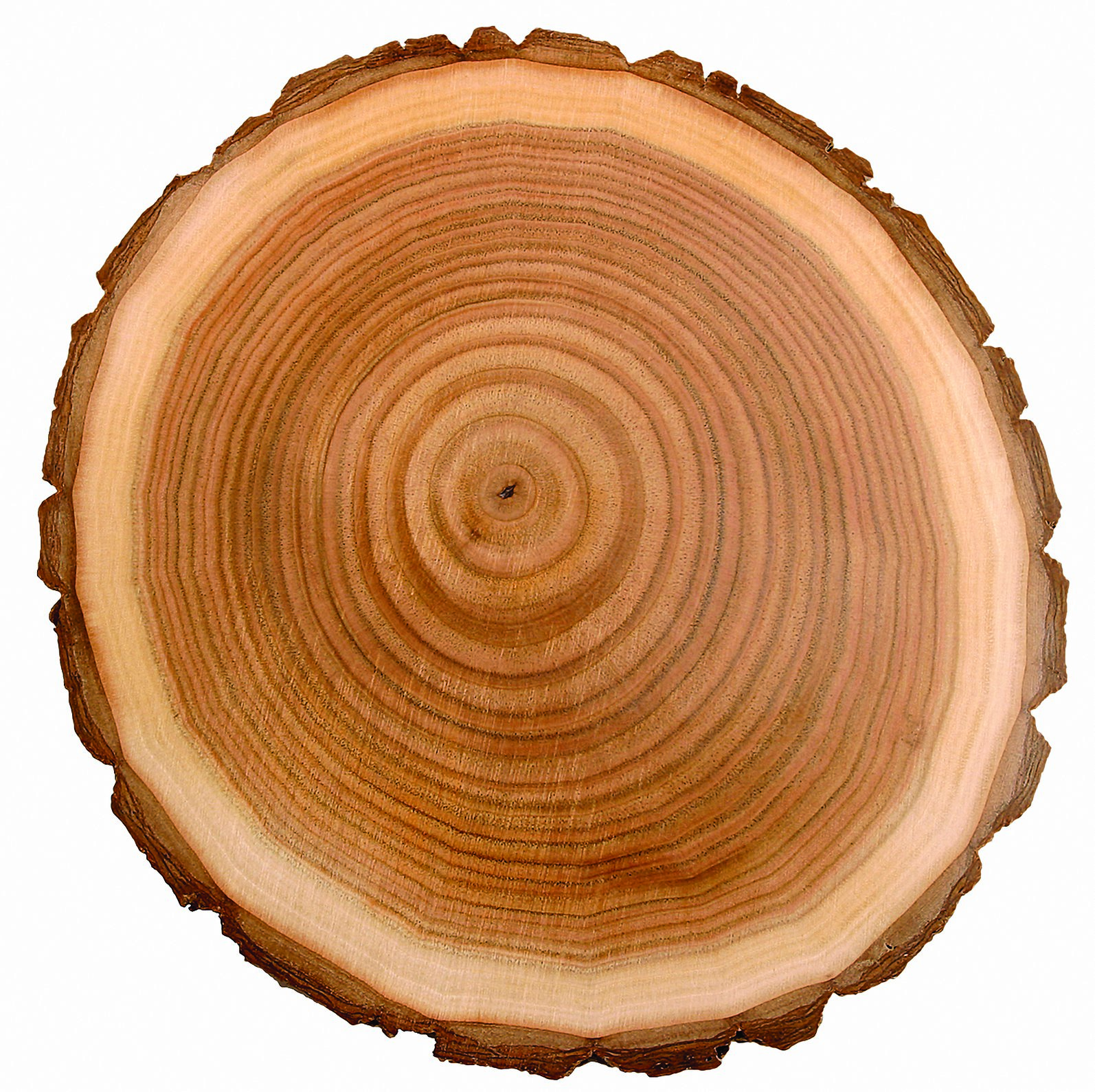
Cross section of a tree trunk diagram. For those of you who don't know what a tree "cookie" is, a tree cookie is a sliced portion of a tree trunk or limb that can show each and every annual ring on a viewable plane. A tree cross-section disk or cookie can be one of the best botanical teaching aids to kids and adults on things happening in a tree and environmental effects on trees. Cracked tree trunk cross section with annual rings close-up isolated on white background. Annual tree growth rings of the cross-section of a tree trunk isolated on white. Overhead view. Wood texture of cut tree trunk, close-up. Cross section of tree trunk showing growth rings. Abstract texture of tree stump, crack wood ancient. Anatomy of a Tree The Inside Story. The outer bark is the tree's protection from the outside world. Continually renewed from within, it helps keep out moisture in the rain, and prevents the tree from losing moisture when the air is dry. It insulates against cold and heat and wards off insect enemies. Right: Cross section of the trunk of a California fan palm (Washingtonia filifera) showing scattered vascular bundles that appear like dark brown dots. The dot pattern also shows up in the petrified Washingtonia palm (left). The pores in the petrified palm wood are the remains of vessels.
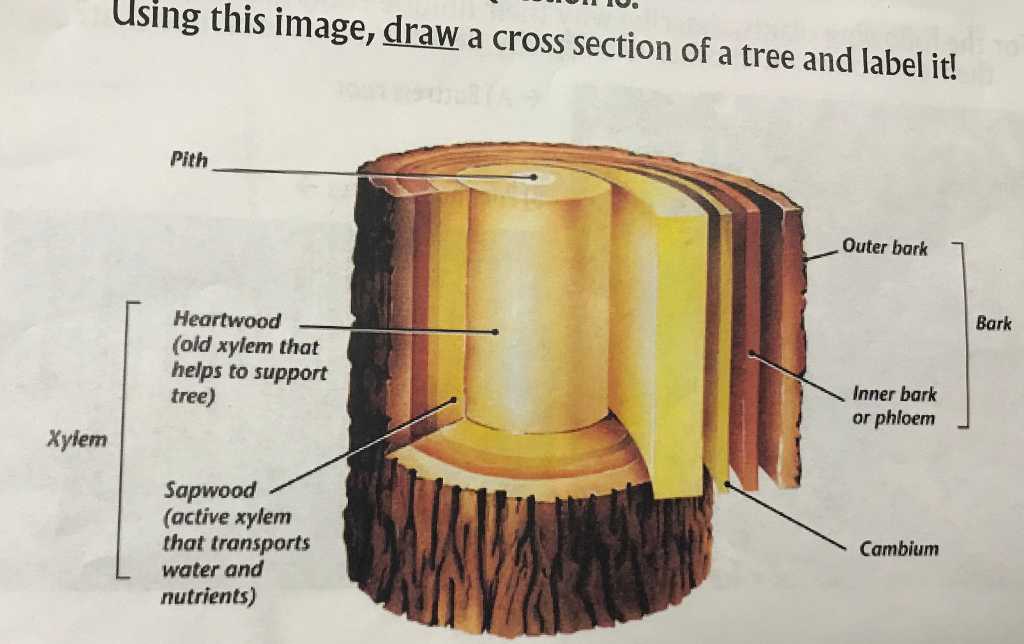
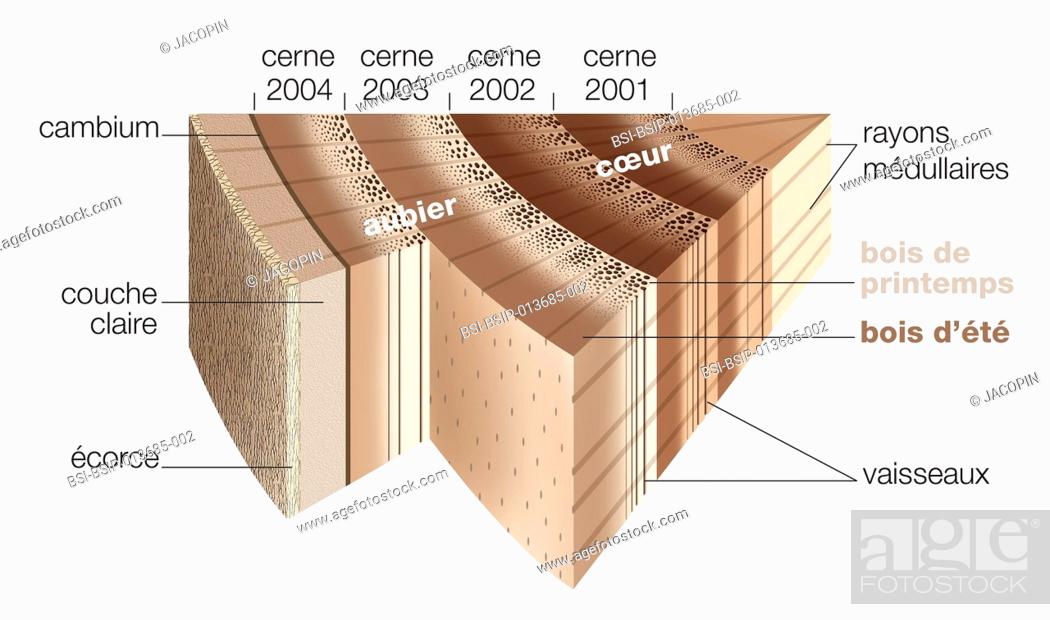
Cross-section of a Tree Trunk. Cross-section of a tree trunk. Format. Diagram . Credit. Image courtesy of MIT OpenCourseWare.. MIT OpenCourseWare Course of Origin. 4.401 Introduction to Building Technology Spring 2006 Macro Cross-section Characteristics By cutting a tree and exposing the cross section, you can observe the bark, phloem (bark-producing layer), cambium (a thin layer inside the bark where cell division takes place) and xylem (sapwood and heartwood) (Figure 2). The heart-wood is the darker-colored material that is formed in the center of the tree. Label the following diagram of a plant, the cross section of its stem, and the longitudinal section of its root. ... Predict what the cross section of a four-year-old tree trunk would look like if there were drought conditions for the first two years of the tree's life and wet conditions for the most recent two years. Cross section diagram of a tree trunk. The amount of photosynthesis that can occur in the leaves is directly related to the amount of water that the roots can absorb. A small root system can only support the photosynthesis of a small canopy, and roots can only grow larger if they have enough energy (sugar) provided by the leaves.
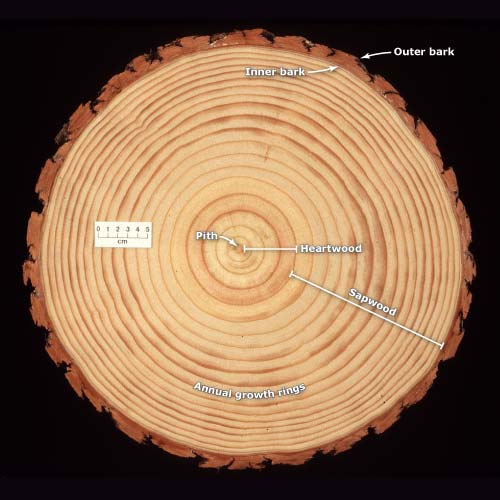
In cross-section, 98% of the massive lycopsid trunk was periderm, making the term "bark stem" appropriate for these trees (Selmeier, 1996, p. 139). Not only was the structure of these trees very different from modern trees their growth was as well. Parts of a Tree Diagram A mature tree has three basic parts: 1) roots, 2) crown, and 3) trunk or bole. Although the structure of these parts may vary based on the altitude and geographical position of the tree, each of them performs distinct functions. This basswood (Tilia americana) trunk cross section has 24 distinct annual rings.The central core of wood (#1 in close-up photo) counts as the first year of growth since the pith is no longer present. The smaller series of concentric rings (knot) at the bottom of the photo is a lateral branch embedded in the main trunk. The annual rings of a tree are made each year when a new layer of wood is added to the trunk and branches of the tree. New wood grows from the cambium layer between the old wood and the bark. The annual growth of a tree can be measured by the distance between the growth rings shown in the illustration below. As the growth rate slows down in the ...
Feb 9, 2015 - Cross-section of a tree trunk. Format Diagram Credit Image courtesy of MIT OpenCourseWare. MIT OpenCourseWare Course of Origin 4.401 Introduction to Building Technology Spring 2006 MIT Course Instructor An…
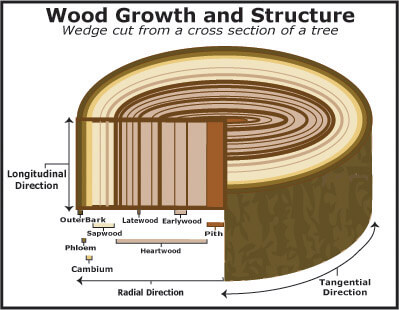
The main function of hardwood fibers is mechanical support, which is mainly based on the thick second layer (S 2 layer), which is thicker than the first layer (S 1 layer) and the third layer (S 3 ...
In a cross section, the pith may be rounded, triangular or star shaped. Tree Rings . In woody dicot plants, the rings grow to make a complete ring around the stem. Xylem growth makes the "annual rings" used to tell a tree's age. In woody dicot plants, water and mineral movement occurs in the more recent years of xylem rings.
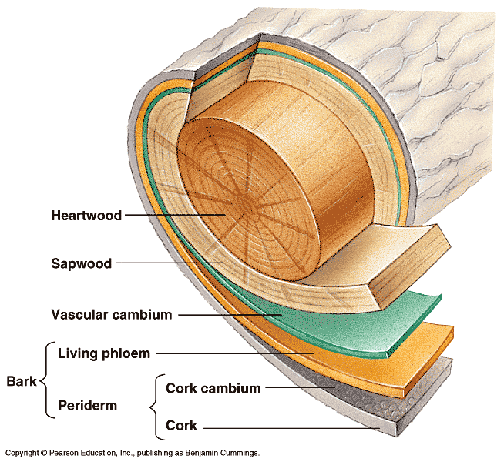
Examination of the cross sectional surface of a tree trunk reveals three distinct zones (Fig. 3): the bark, the light coloured outer region (the sapwood) and the dark coloured region (the heartwood). These sapwood and heartwood zones serve distinct functions in the living tree and have very different characteristics that influence the behavior ...
Trunk (Stem)—supports the leaves and the branches of the tree and also contains the xylem, the cambium, the phloem, and the heartwood. ∗. Heartwood—inner core of dead wood that supports the tree. As a tree grows, older xylem cells in the center of the tree become inactive and die, forming the heartwood. ∗
The diagram shows a pile of 10 tree trunks. Each tree trunk has a circular cross-section of radius 31 cm and length 15 m. A plastic sheet is wrapped around the pile. C is the centre of one of the circles. CE and CD are perpendicular to the straight edges, as shown.
cross section of a trunk Moving from the center to the periphery there are six parts: the pith, the heartwood, the sapwood, the cambium, the phloem and the bark. previous next heartwood Hard dark-colored wood layer made of dead sapwood; it encircles the pith and supports the trunk and branches. pith
cross section of the trunk. Look at the diagram to see the five main layers and what each layer does. a) Bark: The outer layer of the trunk (and branches) is called the outer bark or just the bark. Its texture, thickness, and flexibility depend on the type of tree. Although bark looks different from tree to tree, it serves the same purpose—to ...
Feb 9, 2015 - Cross-section of a tree trunk. Format Diagram Credit Image courtesy of MIT OpenCourseWare. MIT OpenCourseWare Course of Origin 4.401 Introduction to Building Technology Spring 2006 MIT Course Instructor An…
The xylem tissue appears as a dark ring in the cross section of a tree trunk. The age of the tree can be determined by counting the number of rings from the inside of the tree trunk to the outside. The broader the springwood layers the more favourable the climatic conditions of that season.
Education Chart of Biology for Cross Section of Leaf Diagram. Although a leaf looks thin, its is made up of several layers of cells. You can see these if you. ... Structure of the slice of the tree layers in cross section. Tree trunk different layers scheme. Cross section of.
Tree Anatomy THE ANATOMY OF A TREE The major parts of a tree are leaves, flowers and fruit, trunk and branches, and roots. LEAVES Leaves are basically sheets (or sticks) of spongy living cells connected by tubular conducting cells to the "plumbing system" of the tree. They are connected to the air around them by openings called stomates,
Anatomy of a tree. This information is courtesy the Arbor Day Foundation. A: The outer bark is the tree's protection from the outside world. Continually renewed from within, it helps keep out moisture in the rain, and prevents the tree from losing moisture when the air is dry. It insulates against cold and heat and wards off insect enemies.
Stem Anatomy Vascular Cambium: Area of cell division that is responsible for secondary growth. Creates and separates the xylem and phloem. Xylem: Grows to the inside of the vascular cambium to transport water and nutrients from roots to leaves. Prominent cells are vessels, tracheids, fibers (Angiosperm)
For example, if a tree is measured as 10" DBH, the radius is 5". Multiplying 5 by 5 equals 25, which when multiplied by 3.14 equals 78.5. Thus, the cross-sectional area of a 10" DBH tree is 78.5. This chart shows the cross-sectional area for trees from 2" to 50" DBH.
A cross-section of an adult tree trunk. The outer layer interacts with the environment. The second layer is labeled C. The next layer is labeled B, and the layer after this is labeled A. cork cambium secondary xylem lateral meristem vascular cambium apical meristem
cross section of the trunk. Look at the diagram to see the five main layers and what each layer does. a) Bark: The outer layer of the trunk (and branches) is called the outer bark or just the bark. Its texture, thickness, and flexibility depend on the type of tree. Although bark looks different from tree to tree, it serves the same purpose—to protect the tree from injury and











/Abies_grandis_cross_section_cropped-58dbfd383df78c5162683700.jpg)









0 Response to "37 cross section of a tree trunk diagram"
Post a Comment