36 sliding filament theory diagram
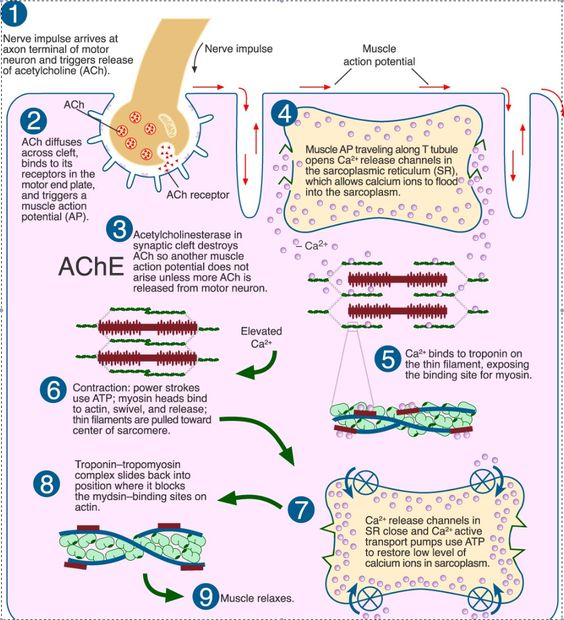
The Sliding Filament Theory ... In 1954, scientists published two groundbreaking papers describing the molecular basis of muscle contraction. These papers ... The sliding filament theory describes the force production and changing in length when a muscle fiber contracts. It takes into account the binding, movement, and releasing of proteins; actin and myosin, within the muscle cell to do contraction. This theory uses a series of steps to illustrate how the interaction of proteins (i.e. filaments ...
The theory states that the sliding of actin past myosin generates muscle tension. As actin is tethered to structures located at the lateral ends of each ...What is the Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction?What is the Part of ATP Molecules in Sliding Filament Theory in Muscle Contraction?

Sliding filament theory diagram
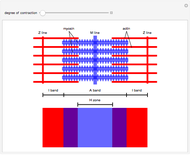
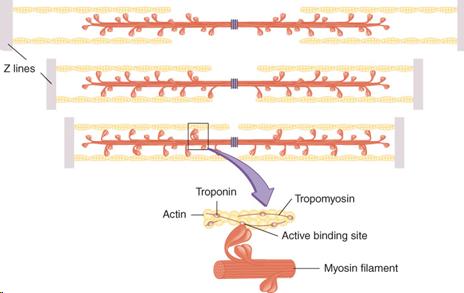
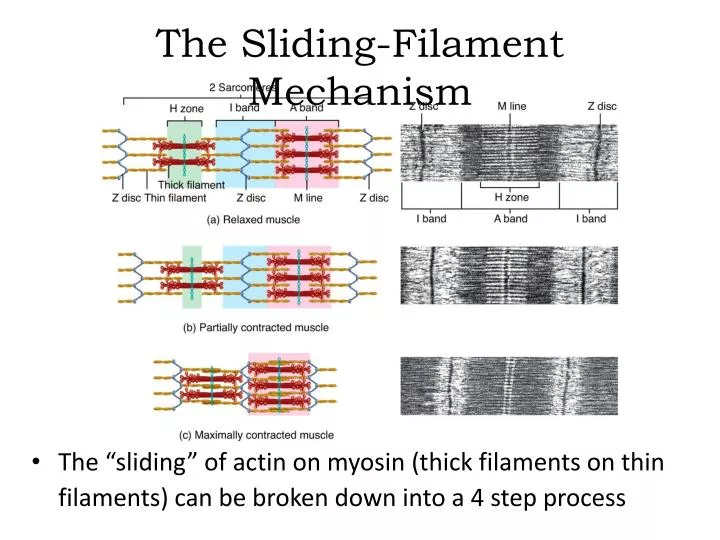
Diagram 1. Whilst the sliding filament model answered many questions relating to muscle contraction (prior to that there were some strange theories relating to balloons and animal spirits!), it also left some unresolved- for example the reasons why force increases as the muscle stretches/decreases in force as the muscle shortens, and the low cost of force production during active stretch. Introduction to sarcomere dynamics and sliding filaments. Look at any school biology textbook and the muscle chapter will show a muscle sarcomere, the building block of striated muscles, containing overlapping arrays of myosin and actin filaments (Figures 1 and 2(f)).The idea of muscle filament sliding is now a fundamental concept in biology, but it was not always so. These filaments slide in and out between each other to form a muscle contraction hence called the sliding filament theory! The diagram above shows part a myofibril called a sarcomere. This is the smallest unit of skeletal muscle that can contract. Sarcomeres repeat themselves over and over along the length of the myofibril.
Sliding filament theory diagram. Sliding Filament Theory how muscles produce force or shorten the thick and thin filaments in a sarcomere slide past each other, shortening the length of the sarcomere. to slide past each other, the myosin heads interact with actin filaments and using ATP bend to pull past the actin The sliding filament theory explains the mechanism of muscle contraction based on muscle proteins that slide past each other to generate movement. According to the sliding filament theory, the myosin (thick) filaments of muscle fibers slide past the actin (thin) filaments during muscle contraction, while the two groups of filaments remain at relatively constant length. Sliding filament theory is a model used to explain how skeletal muscles contract. Under sliding filament theory, myosin filaments are alternated with actin filaments in horizontal lines, much like the red and white stripes on the American flag. The myosin proteins slide along the actin, releasing calcium ions that allow the head of each myosin ... Start studying Sliding filament theory (muscle contraction) 6 steps D:. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
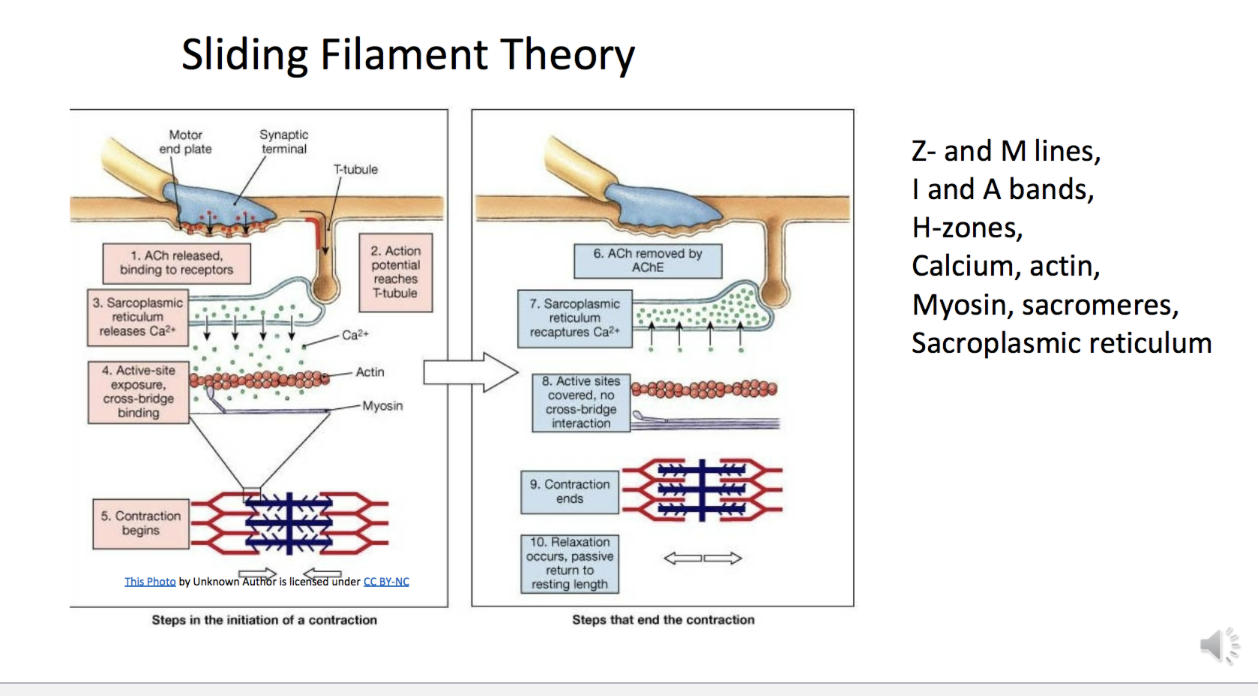
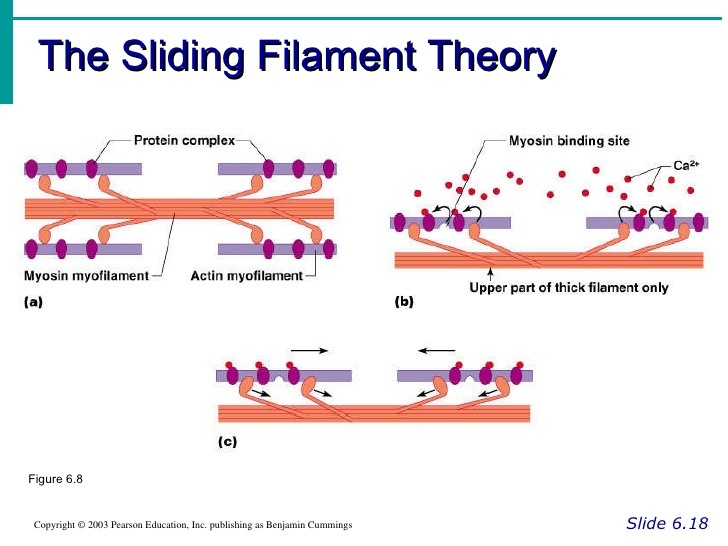
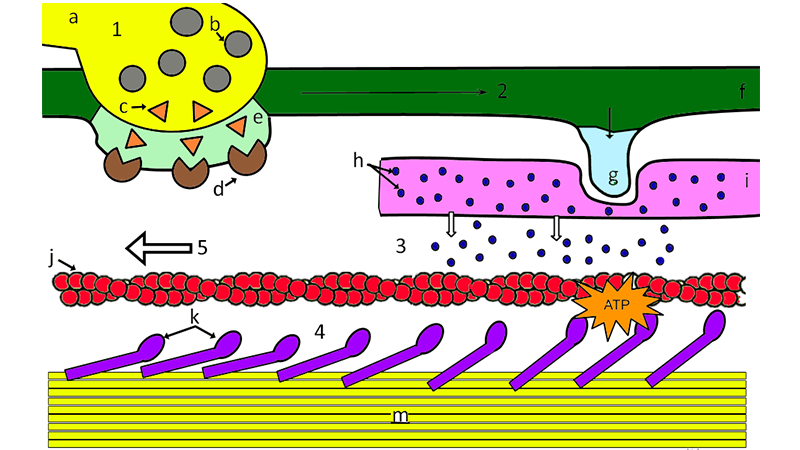
Sliding filament theory in its simplest form states that muscle fibres shorten when actin filaments slide inward on myosin filaments - pulling the z-lines closer together. If that's all Greek to you then have a quick look at the article on muscle anatomy which outlines the different components of a muscle. Have a look at the diagram below: In this video I break down the Sliding Filament Theory into steps to help you with studying and understanding the concepts. I hope you enjoy.As always, leave... The sliding filament theory of muscle contraction was developed to fit the differences observed in the named bands on the sarcomere at different degrees of ... The sliding filament theory begins with the release of calcium ions from a specialized organelle in the muscle fiber called the sarcoplasmic reticulum, as described in statement (3). Calcium ions bind to tropomyosin, causing it to pull away from and expose these myosin binding sites on the actin filament, as described in statement (2).
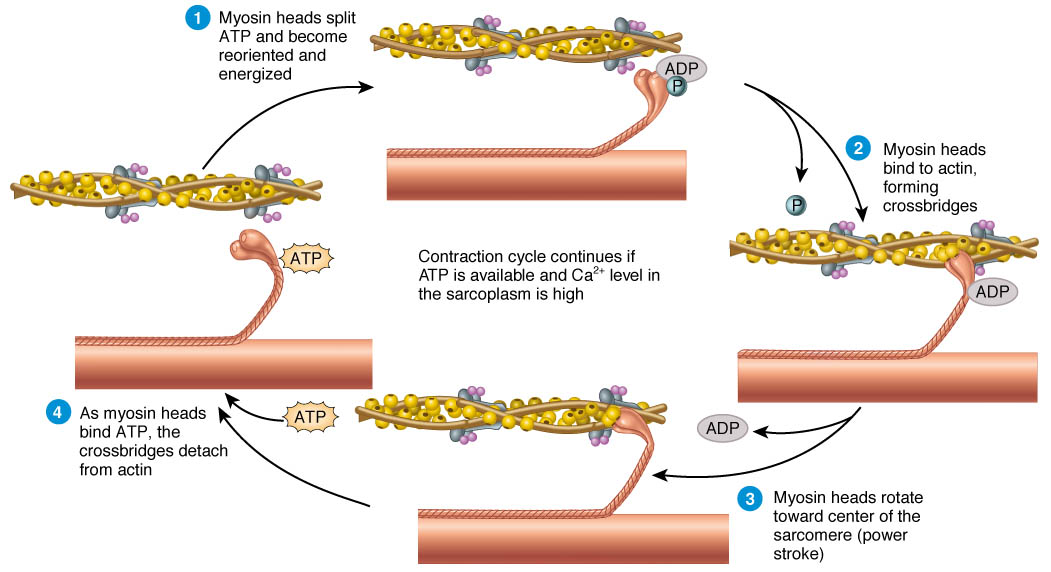
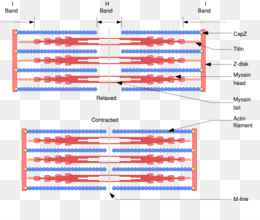
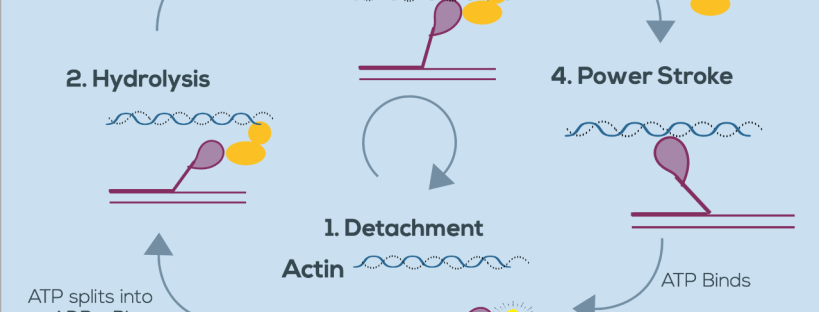
The Sliding Filament Theory of Muscles. Sliding filament theory explains how the actin and myosin (protein filaments) create a muscle contraction. The sliding filament theory is fantastic for explaining what happens to muscles during and after exercise and how muscle contractions work, and it is usually illustrated by various diagrams which for ... SLIDING FILAMENT THEORY It has the following steps: 1. Before contraction begins, an ATP molecule binds to the myosin head of the cross-bridges. 2. The ATPase activity of the myosin head immediately cleaves the ATP molecule but the products (ADP+P) remains bound to the head. Now the myosin head is in a high energy state and ready to bind to the ... Sliding Filament Theory of Muscle Contraction. The mechanism of muscle contraction is explained by sliding filament model. This theory was proposed by H.E Huxley and J. Hanson, and A. F. Huxley and R. Niedergerke in 1954. The arrangement of actin and myosin myofilament within a sarcomere is crucial in the mechanism of muscle contraction. The diagram above shows part a myofibril called a sarcomere. ... Sarcomere.Muscles How muscles contract - The Sliding Filament Theory A muscle contains many muscle fibers A muscle fiber is a series of fused cells Each fiber contains a bundle of myofibrils. band, and a sarcomere.
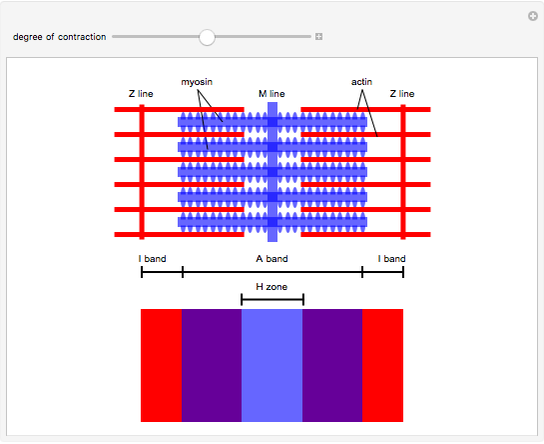
Sliding filament theory : • During muscle contraction, thin filaments show sliding inward towards the H-zone. • Sarcomere shortens, without changing the length of thin and thick myofilaments. • The cross bridge of the thick myofilaments connects with the portions of actin of the thin myofilaments. These cross bridge move on the surface of ...
The sliding filament model, proposed to explain muscle contraction in 1954, has proven to be very robust. Muscle contraction as well as much of the motility of nonmuscle cells has now been shown to be produced by the relative motion of actin filaments and myosin filaments or myosins attached to cargoes.
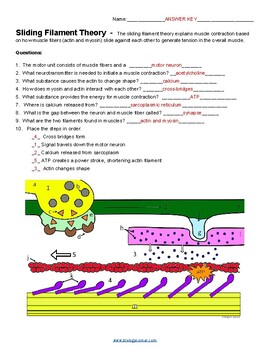
Instructions: Label the following diagram using the numbers for the thirteen steps to the sliding filament theory. You may need to illustrate some details e.g. ca2+, ATP binding to myosin, hydrolysis of ATP, etc.
Sliding filament theory . In 1954, two researchers, Jean Hanson and Hugh Huxley from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, made a model for muscle tissue contraction which is known as the sliding filament theory.This theory describes the way a muscle cell contracts or shortens as a whole by the sliding of thin filaments over thick filaments and pulling the Z discs behind them closer.
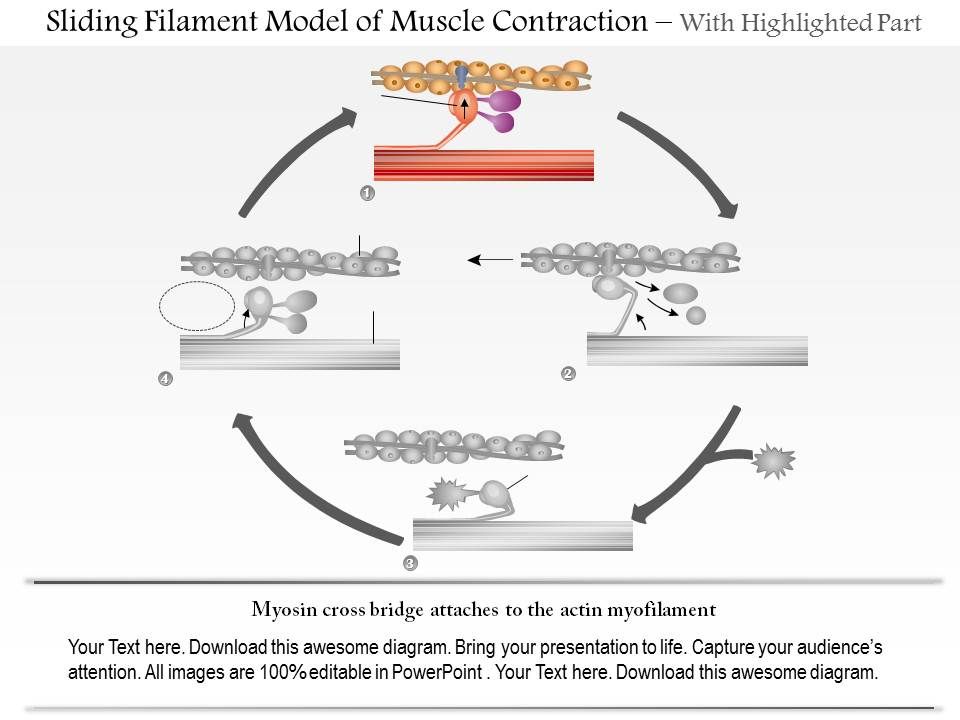
Download scientific diagram | A textbook diagram of the sliding filament model of muscle contraction and a Dynamic compositional model.
filament would slide back on the thick filament. ** Note: Many myosins (about 200) make up each thick filament - so there are many myosin heads (cross bridges) available to bind the thin filament. In this animation you see only four of these cross bridges, but keep in mind there are many more on each thick filament. Page 28. Multiple Myofilaments
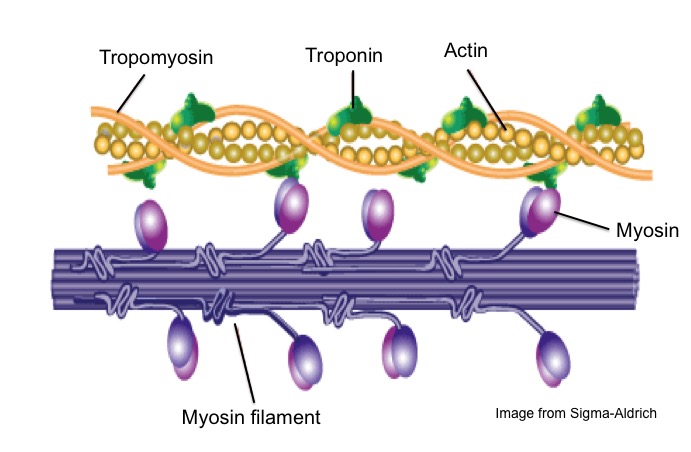
sliding filament theory A proposed mechanism of muscle contraction in which the actin and myosin filaments of striated muscle slide over each other to shorten the length of the muscle fibres (see sarcomere).Myosin-binding sites on the actin filaments are exposed when calcium ions bind to troponin molecules in these filaments. This allows bridges to form between actin and myosin, which requires ...
Sliding filament theory STEP 1: At first the muscle is relaxed. To get the muscle to contract the actin has to be brought close together. To get the actin together the myosin has cross bridges which pull them near each other but the actin has proteins tropmyosin and troponin which stop the cross bridges from pulling them together.
Sliding Filament theory Diagram. muscle contraction & sliding filament theory teachpe at a very basic level each muscle fibre is made up of smaller fibres called myofibrils these contain even smaller structures called actin and myosin filaments these filaments slide in and out between each other to form a muscle contractions hence called the sliding filament theory the diagram above shows part ...
The sliding filament theory is the explanation for how muscles contract to produce force. As we have mentioned on previous pages, the actin and myosin filaments within the sarcomeres of muscle fibres bind to create cross-bridges and slide past one another, creating a contraction. The sliding filament theory explains how these cross-bridges are ...
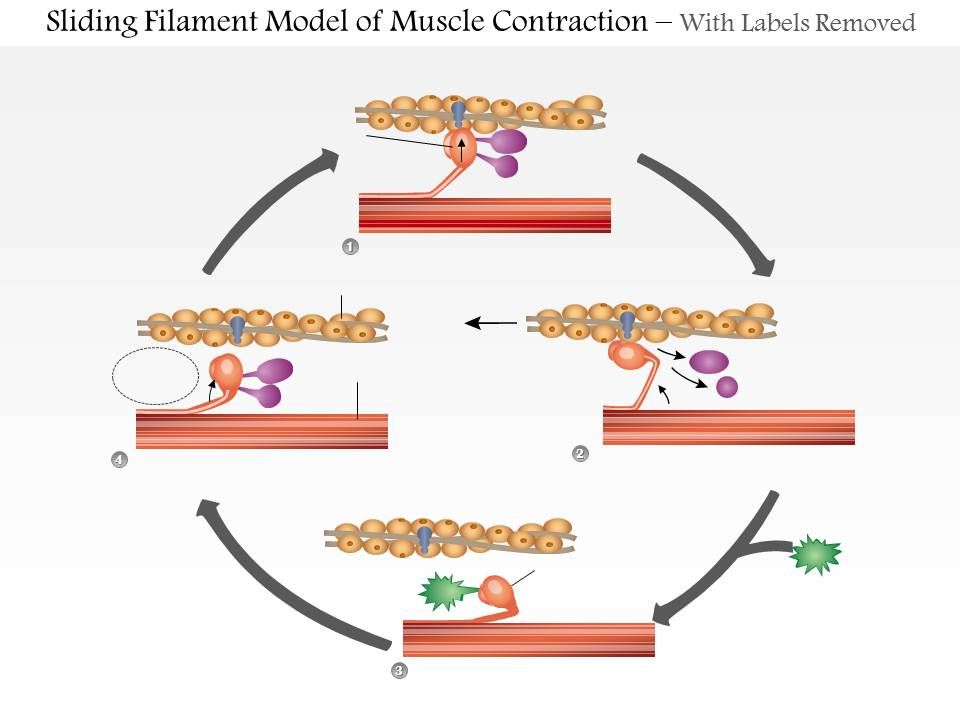
0614 Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction Medical Images For Powerpoint Powerpoint Design Template Sample Presentation Ppt Presentation Background Images
Start studying Sliding Filament Theory (6 Steps). Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
The sliding filament theory describes how muscles are supposed to contract at the cellular level. Hugh Huxley and Jean Hanson proposed the sliding filament model of muscle contraction in 1954. When studying how sliding filament theory works, it is helpful to have a thorough grasp of skeletal muscle anatomy.
0614 Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction Medical Images For Powerpoint Powerpoint Design Template Sample Presentation Ppt Presentation Background Images
The sliding filament theory is a suggested mechanism of contraction of striated muscles, actin and myosin filaments to be precise, which overlap each other resulting in the shortening of the muscle fibre length. Actin (thin) filaments combined with myosin (thick filaments) conduct cellular movements. Myosin is a protein that converts ATP ...
The Steps of Muscle Contraction: The Sliding Filament Theory Key events that must take place before the contraction of a muscle fiber begins: SR releases calcium ions into the cytosol The calcium ions will bind to troponin which causes the troponin-tropomyosin complexes to move away from the myosin binding sites on actin.
These filaments slide in and out between each other to form a muscle contraction hence called the sliding filament theory! The diagram above shows part a myofibril called a sarcomere. This is the smallest unit of skeletal muscle that can contract. Sarcomeres repeat themselves over and over along the length of the myofibril.
Introduction to sarcomere dynamics and sliding filaments. Look at any school biology textbook and the muscle chapter will show a muscle sarcomere, the building block of striated muscles, containing overlapping arrays of myosin and actin filaments (Figures 1 and 2(f)).The idea of muscle filament sliding is now a fundamental concept in biology, but it was not always so.
Diagram 1. Whilst the sliding filament model answered many questions relating to muscle contraction (prior to that there were some strange theories relating to balloons and animal spirits!), it also left some unresolved- for example the reasons why force increases as the muscle stretches/decreases in force as the muscle shortens, and the low cost of force production during active stretch.

0614 Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction Medical Images For Powerpoint Powerpoint Design Template Sample Presentation Ppt Presentation Background Images
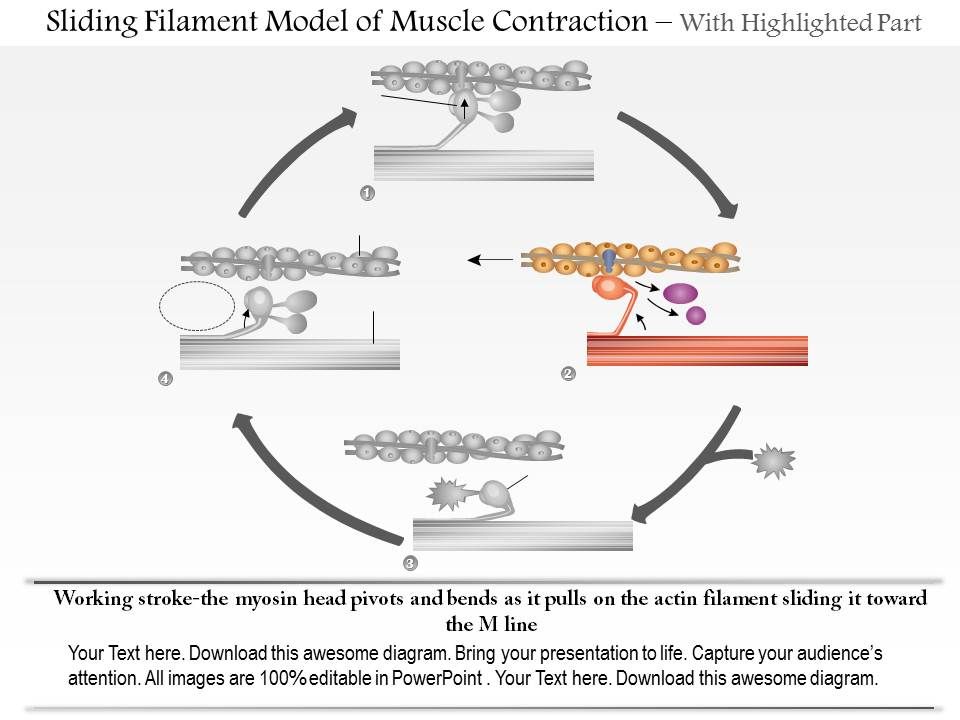
0614 Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction Medical Images For Powerpoint Powerpoint Design Template Sample Presentation Ppt Presentation Background Images
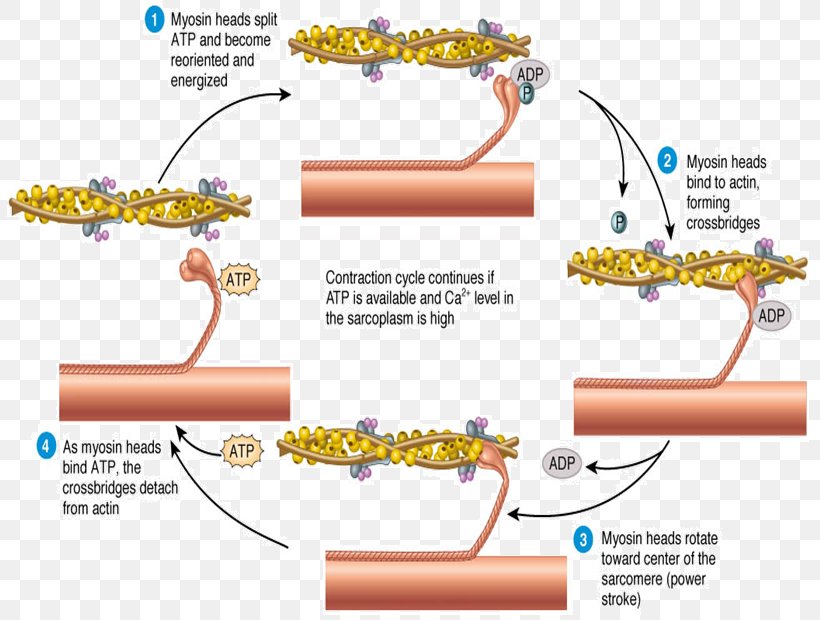
Skeletal Muscle Muscle Contraction Sliding Filament Theory Sarcomere Png 817x620px Skeletal Muscle Actin Action Potential Animal












0 Response to "36 sliding filament theory diagram"
Post a Comment